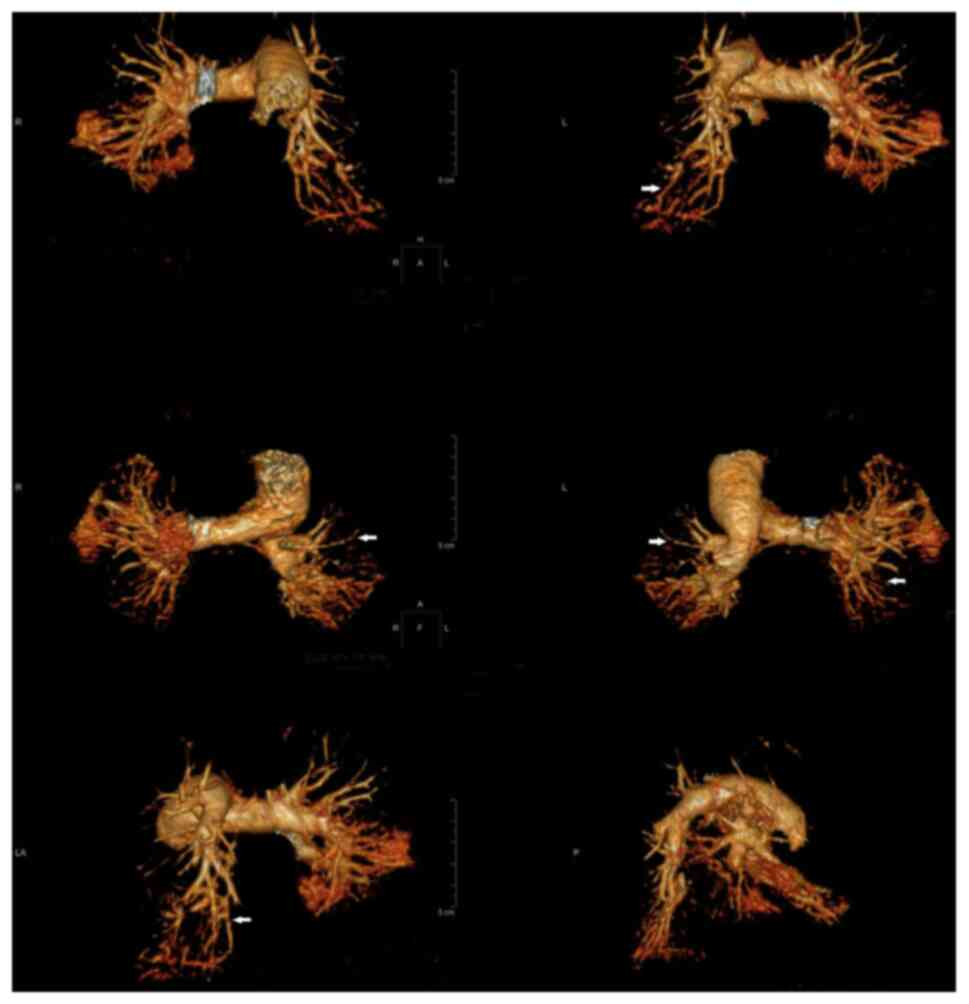
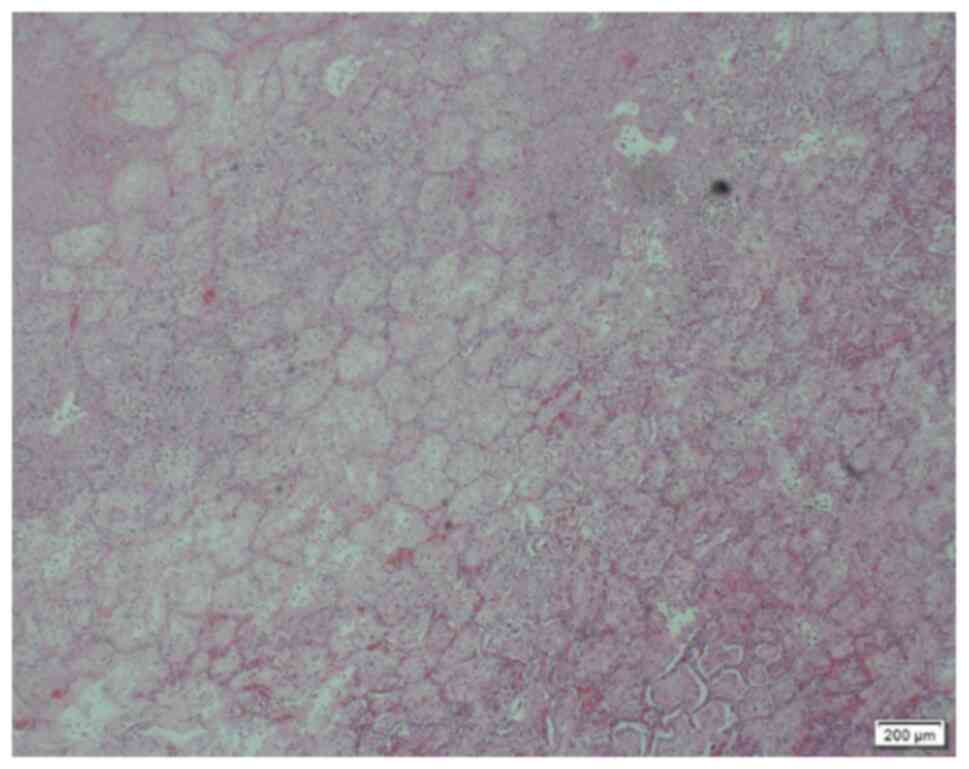
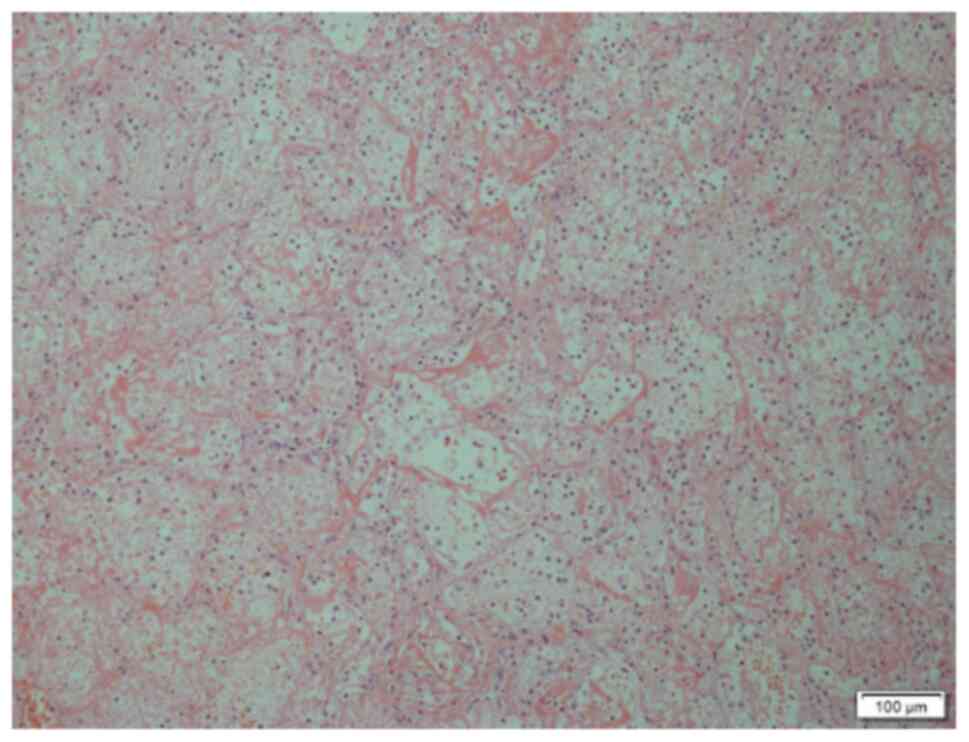
|
1
|
Jain S, Williams DJ, Arnold SR, Ampofo K,
Bramley AM, Reed C, Stockmann C, Anderson EJ, Grijalva CG, Self WH,
et al: Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among
U.S children. N Engl J Med. 372:835–845. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tashiro M, Fushimi K, Kawano K, Takazono
T, Saijo T, Yamamoto K, Kurihara S, Imamura Y, Miyazaki T,
Yanagihara K, et al: Comparison of efficacy of antimicrobial agents
among hospitalized patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
pneumonia in Japan during large epidemics of macrolide-resistant
M. pneumoniae infections: A nationwide observational study.
Clin Infect Dis. 65:1837–1842. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Omori R, Nakata Y, Tessmer HL, Suzuki S
and Shibayama K: The determinant of periodicity in Mycoplasma
pneumoniae incidence: An insight from mathematical modelling.
Sci Rep. 5(14473)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tanaka T, Oishi T, Miyata I, Wakabayashi
S, Kono M, Ono S, Kato A, Fukuda Y, Saito A, Kondo E, et al:
Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, Japan,
2008-2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 23:1703–1706. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Huang L, Chen H and Peng S: Spontaneous
pneumomediastinum, emphysema, and pulmonary bullae associated with
refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in a child.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 52:E77–E80. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pereyre S, Goret J and Bébéar C:
Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Current knowledge on macrolide
resistance and treatment. Front Microbiol. 7(974)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Narita M: Classification of extrapulmonary
manifestations due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection on the
basis of possible pathogenesis. Front Microbiol.
7(23)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Olson D, Watkins LK, Demirjian A, Lin X,
Robinson CC, Pretty K, Benitez AJ, Winchell JM, Diaz MH, Miller LA,
et al: Outbreak of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-associated
Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Pediatrics. 136:e386–e394.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dhaliwal K and Enright K: Rare
extrapulmonary complications of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2016(bcr2015214044)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Witmer CM, Steenhoff AP, Shah SS and
Raffini LJ: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, splenic infarct, and
transient antiphospholipid antibodies: A new association?
Pediatrics. 119:e292–e295. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bao Y, Li X, Wang K, Zhao C, Ji X and
Jiang M: Central retinal artery occlusion and cerebral infarction
associated with Mycoplasma pneumonia infection in children. BMC
Pediatr. 16(210)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kang B, Kim DH, Hong YJ, Son BK, Lim MK,
Choe YH and Kwon YS: Complete occlusion of the right middle
cerebral artery associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
pneumonia. Korean J Pediatr. 59:149–152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Oeser C, Andreas M, Rath C, Habertheuer A
and Kocher A: Left ventricular thrombus in a patient with cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma, hypereosinophilia and Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infection-a challenging diagnosis: A case report. J Cardiothorac
Surg. 10(21)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bakshi M, Khemani C, Vishwanathan V, Anand
RK and Khubchandani RP: Mycoplasma pneumonia with antiphospholipid
antibodies and a cardiac thrombus. Lupus. 15:105–106.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jin X, Zou Y, Zhai J, Liu J and Huang B:
Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with concomitant
acute cerebral infarction in a child: A case report and literature
review. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e0103)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tincani A, Balestrieri G, Allegri F,
Cinquini M, Vianelli M, Taglietti M, Sanmarco M, Ichikawa K, Koike
T, Meroni P and Boffa MC: Overview on anticardiolipin ELISA
standardization. J Autoimmun. 15:195–197. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, Blaivas A,
Jimenez D, Bounameaux H, Huisman M, King CS, Morris TA, Sood N, et
al: Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and
expert panel report. Chest. 149:315–352. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Monagle P, Cuello CA, Augustine C, Bonduel
M, Brandão LR, Capman T, Chan AKC, Hanson S, Male C, Meerpohl J, et
al: American society of hematology 2018 Guidelines for management
of venous thromboembolism: Treatment of pediatric venous
thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2:3292–3316. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Graw-Panzer KD, Verma S, Rao S, Miller ST
and Lee H: Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in a child with
pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Natl Med Assoc.
101:956–958. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Huang P, Chen Q, Lin Z and Tian W:
Two separated thrombi in deep veins associated with pulmonary
embolism after Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: A case in
adolescent female. Transl Pediatr. 2:198–201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Brown S, Padley S, Bush A, Cummins D,
Davidson S and Buchdahl R: Mycoplasma pneumonia and pulmonary
embolism in a child due to acquired prothrombotic factors. Pediatr
Pulmonol. 43:200–202. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Su HY, Jin WJ, Zhang HL and Li CC:
Clinical analysis of pulmonary embolism in a child with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi.
50:151–154. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Wei H, Chang Y and Lu S: A case report of
pulmonary embolism associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
pneumonia. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 53:143–144. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Zhuo Z, Li F, Chen X, Jin P, Guo Q and
Wang H: Mycoplasma pneumonia combined with pulmonary infarction in
a child. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:1482–1486. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qin Y, Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang W, He L and
Liu C: Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia complicated with
pulmonary embolism in children: A case report. J Clin Pediatr.
37:765–768. 2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Liu F, Guo C, et al: A report of
2 cases of pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumonia complicated
with pulmonary embolism. Chin J Pract Pediatr. 34:1043–1045.
2019.(In Chinese). doi: 10.19538/j.ek2019120617.
|
|
27
|
Dijl FN, Curtin J, Lord D and Fitzgerald
DA: Pulmonary embolism in children. Paediatr Respir Rev.
13:112–122. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Simmons BP and Aber RC: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae pneumonia. Symptoms mimicking pulmonary embolism
with infarction. JAMA. 241:1268–1269. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li T, Yu H, Hou W, Li Z, Han C and Wang L:
Evaluation of variation in coagulation among children with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: A case-control study. J Int
Med Res. 45:2110–2118. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Narita M: Pathogenesis of neurologic
manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Pediatr
Neurol. 41:159–166. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sotgiu S, Pugliatti M, Rosati G, Deiana GA
and Sechi GP: Neurological disorders associated with Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection. Eur J Neurol. 10:165–168. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Nagashima M, Higaki T, Satoh H and Nakano
T: Cardiac thrombus associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infection. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 11:849–851.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Senda J, Ito M, Atsuta N, Watanabe H,
Hattori N, Kawai H and Sobue G: Paradoxical brain embolism induced
by Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with deep venous
thrombus. Intern Med. 49:2003–2005. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ascer E, Marques M and Gidlund M: M
pneumoniae infection, pulmonary thromboembolism and
antiphospholipid antibodies. BMJ Case Rep.
2011(bcr1220103561)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
van Es N, van der Hulle T, van Es J, den
Exter PL, Douma RA, Goekoop RJ, Mos IC, Galipienzo J, Kamphuisen
PW, Huisman MV, et al: Wells rule and d-Dimer testing to rule out
pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and individual-patient data
meta-analysis. Ann intern Med. 165:253–261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M and
Meyer G: Management of pulmonary embolism: An update. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 67:976–990. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Moore AJE, Wachsmann J, Chamarthy MR,
Panjikaran L, Tanabe Y and Rajiah P: Imaging of acute pulmonary
embolism: An update. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 8:225–243.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|