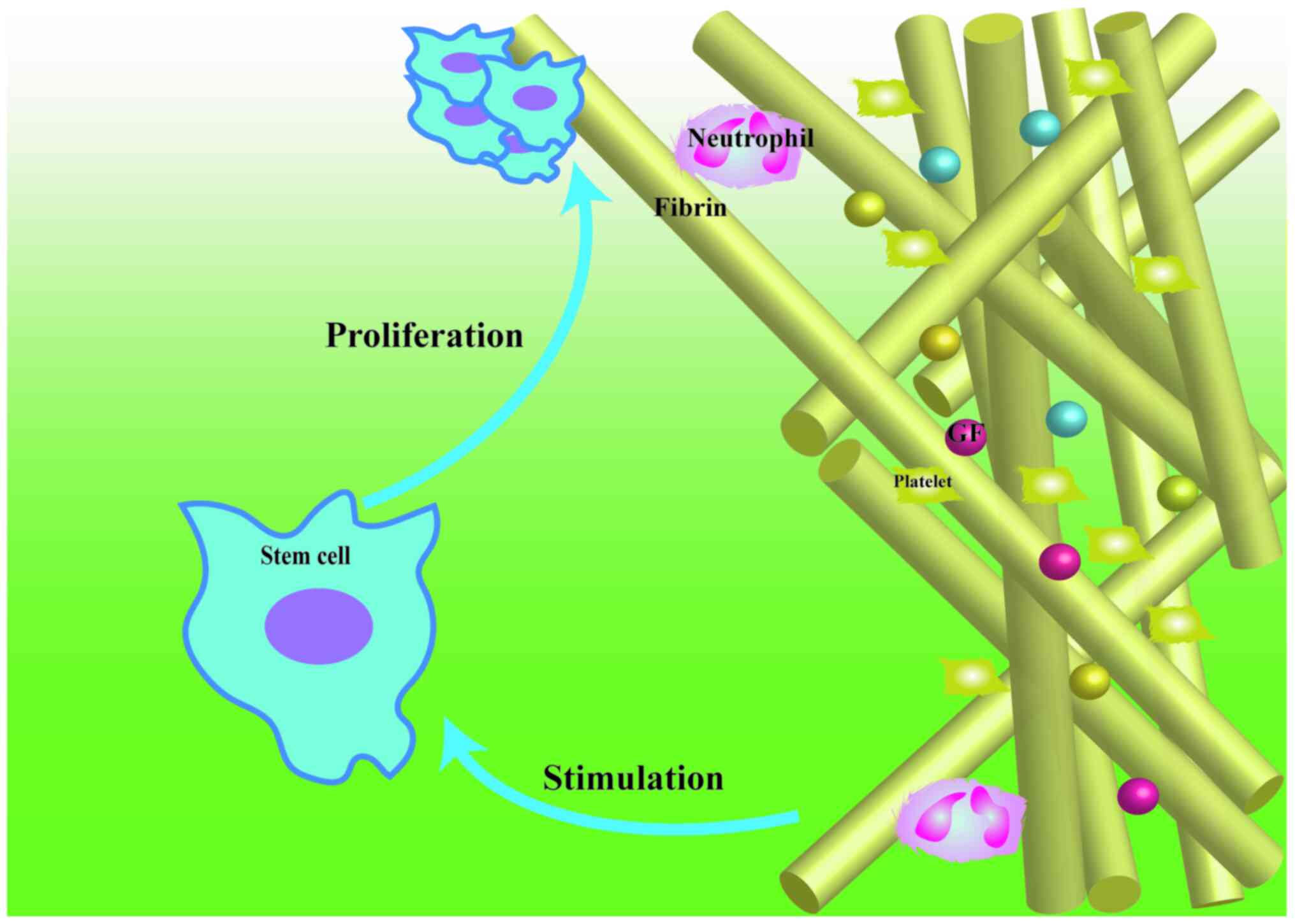
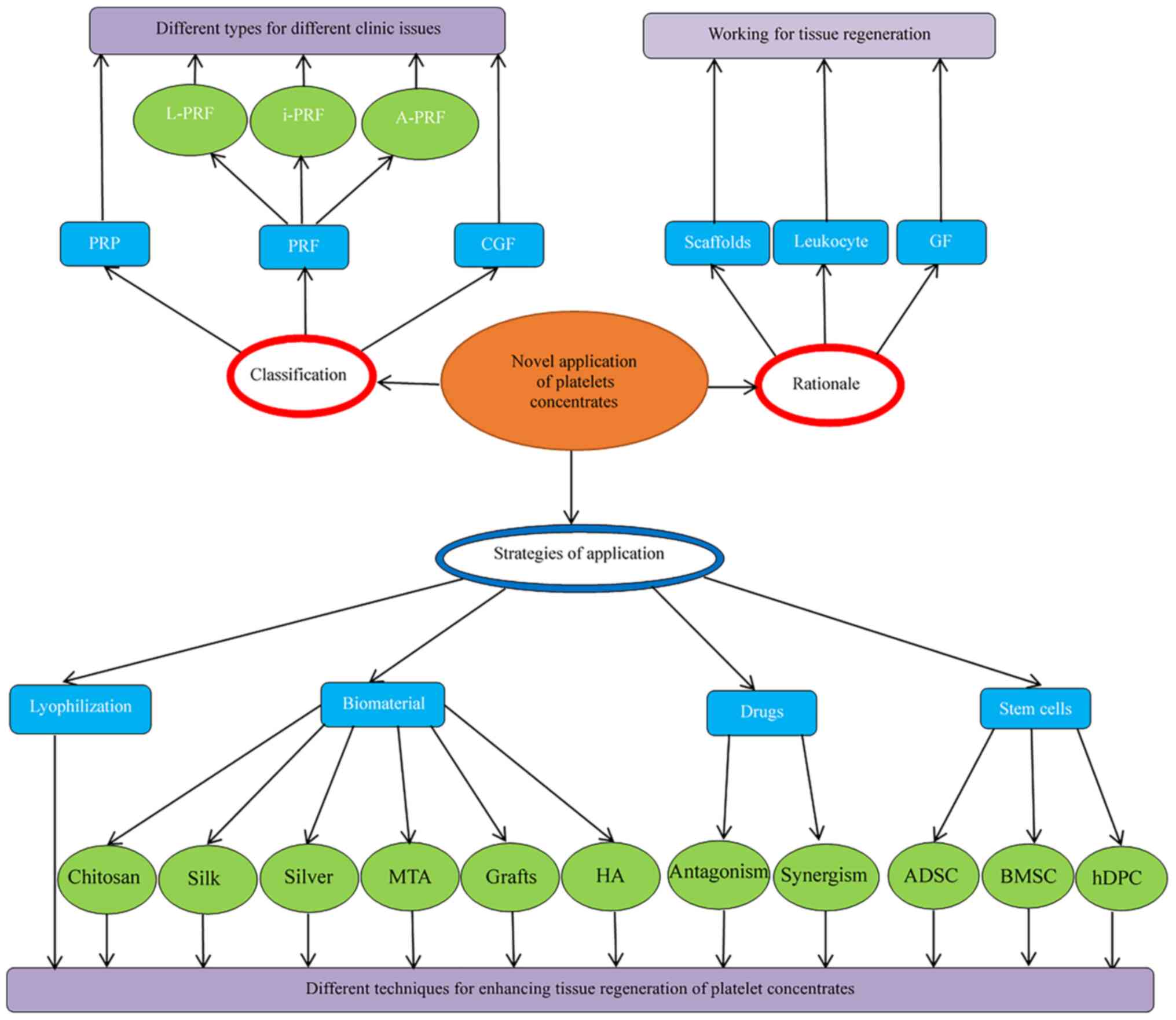
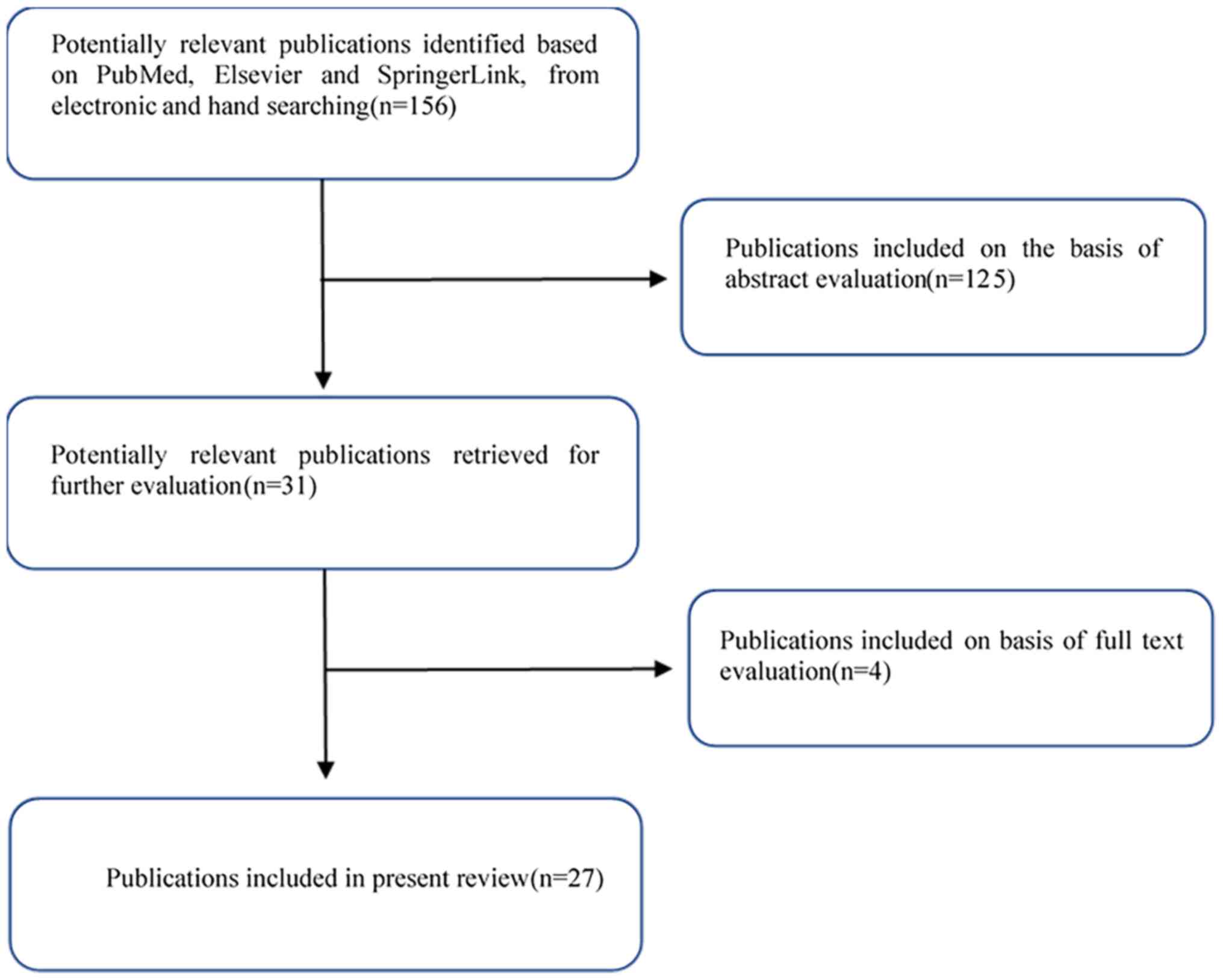
|
1
|
Bishop CJ, Kim J and Green JJ: Biomolecule
delivery to engineer the cellular microenvironment for regenerative
medicine. Ann Biomed Eng. 42:1557–1572. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Abou Neel EA, Chrzanowski W, Salih VM, Kim
HW and Knowles JC: Tissue engineering in dentistry. J Dent.
42:915–928. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Miron RJ and Zhang Y: Autologous liquid
platelet rich fibrin: A novel drug delivery system. Acta Biomater.
75:35–51. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kobayashi E, Flückiger L,
Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Sawada K, Sculean A, Schaller B and Miron RJ:
Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and
advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 20:2353–2360. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miron RJ, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Bishara M,
Zhang Y, Hernandez M and Choukroun J: Platelet-rich fibrin and soft
tissue wound healing: A systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
23:83–99. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alsousou J, Ali A, Willett K and Harrison
P: The role of platelet-rich plasma in tissue regeneration.
Platelets. 24:173–182. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Görmeli G, Görmeli CA, Ataoglu B, Çolak C,
Aslantürk O and Ertem K: Multiple PRP injections are more effective
than single injections and hyaluronic acid in knees with early
osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 25:958–965.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang Y, Liu X, Xu X and Liu J:
Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid
or corticosteroids for knee osteoarthritis: A prospective
randomized controlled study. Orthopade. 48:239–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bhujbal R, A Malik N, Kumar N, Kv S, I
Parkar M and Mb J: Comparative evaluation of platelet rich plasma
in socket healing and bone regeneration after surgical removal of
impacted mandibular third molars. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent
Prospect. 12:153–158. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Del Fabbro M, Bucchi C, Lolato A, Corbella
S, Testori T and Taschieri S: Healing of postextraction sockets
preserved with autologous platelet concentrates. A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 75:1601–1615.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Alio JL, Rodriguez AE, De Arriba P,
Gisbert S and Abdelghany AA: Treatment with platelet-rich plasma of
surgically related dormant corneal ulcers. Eur J Ophthalmol.
28:515–520. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tambella AM, Attili AR, Dini F, Palumbo
Piccionello A, Vullo C, Serri E, Scrollavezza P and Dupré G:
Autologous platelet gel to treat chronic decubital ulcers: A
randomized, blind controlled clinical trial in dogs. Vet Surg.
43:726–733. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tambella AM, Attili AR, Dupré G,
Cantalamessa A, Martin S, Cuteri V, Marcazzan S and Del Fabbro M:
Platelet-rich plasma to treat experimentally-induced skin wounds in
animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
13(e0191093)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Burgos-Alonso N, Lobato I, Hernández I,
San Sebastian K, Rodríguez B, March AG, Perez-Salvador A, Arce V,
Garcia-Alvarez A, Gomez-Fernandez MC, et al: Autologous
platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of venous leg ulcers in
primary care: A randomised controlled, pilot study. J Wound Care.
27 (Suppl 6):S20–S24. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Martinez-Zapata MJ, Martí-Carvajal AJ,
Solà I, Expósito JA, Bolíbar I, Rodríguez L, Garcia J and Zaror C:
Autologous platelet-rich plasma for treating chronic wounds.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev: May 25, 2016. doi:
10.1002/14651858.CD006899.pub3.
|
|
16
|
Moneib HA, Youssef SS, Aly DG, Rizk MA and
Abdelhakeem YI: Autologous platelet-rich plasma versus conventional
therapy for the treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers: A
comparative study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 17:495–501. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Picard F, Hersant B, Bosc R and Meningaud
JP: The growing evidence for the use of platelet-rich plasma on
diabetic chronic wounds: A review and a proposal for a new standard
care. Wound Repair Regen. 23:638–643. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Masoudi E, Ribas J, Kaushik G, Leijten J
and Khademhosseini A: Platelet-rich blood derivatives for stem
cell-based tissue engineering and regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Rep.
2:33–42. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hatakeyama I, Marukawa E, Takahashi Y and
Omura K: Effects of platelet-poor plasma, platelet-rich plasma, and
platelet-rich fibrin on healing of extraction sockets with buccal
dehiscence in dogs. Tissue Eng Part A. 20:874–882. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Anitua E, Nurden P, Prado R, Nurden AT and
Padilla S: Autologous fibrin scaffolds: When platelet- and
plasma-derived biomolecules meet fibrin. Biomaterials. 192:440–460.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL,
Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J and Gogly B: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A
second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related
biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 101:e45–e50. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shah R, M G T, Thomas R and Mehta DS: An
Update on the protocols and biologic actions of platelet rich
fibrin in dentistry. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 25:64–72.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ghanaati S, Booms P, Orlowska A, Kubesch
A, Lorenz J, Rutkowski J, Landes C, Sader R, Kirkpatrick C and
Choukroun J: Advanced platelet-rich fibrin: A new concept for
cell-based tissue engineering by means of inflammatory cells. J
Oral Implantol. 40:679–689. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wend S, Kubesch A, Orlowska A, Al-Maawi S,
Zender N, Dias A, Miron RJ, Sader R, Booms P, Kirkpatrick CJ, et
al: Reduction of the relative centrifugal force influences cell
number and growth factor release within injectable PRF-based
matrices. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 28(188)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pitzurra L, Jansen IDC, de Vries TJ,
Hoogenkamp MA and Loos BG: Effects of L-PRF and A-PRF+
on periodontal fibroblasts in in vitro wound healing experiments. J
Periodontal Res. 55:287–295. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Miron RJ, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Hernandez
M, Kandalam U, Zhang Y, Ghanaati S and Choukroun J: Injectable
platelet rich fibrin (i-PRF): Opportunities in regenerative
dentistry? Clin Oral Investig. 21:2619–2627. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Malli Sureshbabu N, Selvarasu K, v JK,
Nandakumar M and Selvam D: Concentrated growth factors as an
ingenious biomaterial in regeneration of bony defects after
periapical surgery: A report of two cases. Case Rep Dent.
2019(7046203)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Rasmusson L and
Albrektsson T: Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure
platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin
(L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 27:158–167. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Boateng JS, Matthews KH, Stevens HN and
Eccleston GM: Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A
review. J Pharm Sci. 97:2892–2923. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Broughton G II, Janis JE and Attinger CE:
The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 117 (Suppl
7):12S–34S. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Etulain J: Platelets in wound healing and
regenerative medicine. Platelets. 29:556–568. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Walsh TG, Metharom P and Berndt MC: The
functional role of platelets in the regulation of angiogenesis.
Platelets. 26:199–211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pierce GF, Mustoe TA, Altrock BW, Deuel TF
and Thomason A: Role of platelet-derived growth factor in wound
healing. J Cell Biochem. 45:319–326. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Briquez PS, Hubbell JA and Martino MM:
Extracellular matrix-inspired growth factor delivery systems for
skin wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:479–489.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Martino MM, Brkic S, Bovo E, Burger M,
Schaefer DJ, Wolff T, Gürke L, Briquez PS, Larsson HM,
Gianni-Barrera R, et al: Extracellular matrix and growth factor
engineering for controlled angiogenesis in regenerative medicine.
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 3(45)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Janmey PA, Winer JP and Weisel JW: Fibrin
gels and their clinical and bioengineering applications. J R Soc
Interface. 6:1–10. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sánchez M, Anitua E, Delgado D, Prado R,
Sánchez P, Fiz N, Guadilla J, Azofra J, Pompei O, Orive G, et al:
Ultrasound-guided plasma rich in growth factors injections and
scaffolds hasten motor nerve functional recovery in an ovine model
of nerve crush injury. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 11:1619–1629.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Haugh MG, Murphy CM and O'Brien FJ: Novel
freeze-drying methods to produce a range of
collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds with tailored mean pore sizes.
Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 16:887–894. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Roy I and Gupta MN: Freeze-drying of
proteins: Some emerging concerns. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
39:165–177. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shi L, Li R, Wei S, Zhou M, Li L, Lin F,
Li Y, Guo Z, Zhang W, Chen M, et al: Effects of a protective agent
on freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.
30:58–65. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang Z, Han L, Sun T, Wang W, Li X and Wu
B: Preparation and effect of lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin on
the osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in
vitro and in vivo. Heliyon. 5(e02739)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li Q, Reed DA, Min L, Gopinathan G, Li S,
Dangaria SJ, Li L, Geng Y, Galang MT, Gajendrareddy P, et al:
Lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) promotes craniofacial bone
regeneration through Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 15:8509–8525.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang J, Qi X, Luo X, Li D, Wang H and Li
T: Clinical and immunohistochemical performance of lyophilized
platelet-rich fibrin (Ly-PRF) on tissue regeneration. Clin Implant
Dent Relat Res. 19:466–477. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Z, Jin H, Xie Q, Jiang Z, Guo S, Li Y
and Zhang B: Controlled release strategies for the combination of
fresh and lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin on bone tissue
regeneration. BioMed Res Int. 2019(4923767)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sam G, Vadakkekuttical RJ and Amol NV: In
vitro evaluation of mechanical properties of platelet-rich fibrin
membrane and scanning electron microscopic examination of its
surface characteristics. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 19:32–36.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Behera SS, Das U, Kumar A, Bissoyi A and
Singh AK: Chitosan/TiO2 composite membrane improves proliferation
and survival of L929 fibroblast cells: Application in wound
dressing and skin regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 98:329–340.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Mohammadi R, Mehrtash M, Mehrtash M,
Hassani N and Hassanpour A: Effect of platelet rich plasma combined
with chitosan biodegradable film on full-thickness wound healing in
rat model. Bull Emerg Trauma. 4:29–37. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shimojo AA, Perez AG, Galdames SE, Brissac
IC and Santana MH: Stabilization of porous chitosan improves the
performance of its association with platelet-rich plasma as a
composite scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C. 60:538–546. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang L, Wan M, Li Z, Zhong N, Liang D and
Ge L: A comparative study of the effects of concentrated growth
factors in two different forms on osteogenesis in vitro. Mol Med
Rep. 20:1039–1048. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ansarizadeh M, Mashayekhan S and
Saadatmand M: Fabrication, modeling and optimization of lyophilized
advanced platelet rich fibrin in combination with collagen-chitosan
as a guided bone regeneration membrane. Int J Biol Macromol.
125:383–391. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Dal Pra I, Freddi G, Minic J, Chiarini A
and Armato U: De novo engineering of reticular connective tissue in
vivo by silk fibroin nonwoven materials. Biomaterials.
26:1987–1999. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Horan RL, Antle K, Collette AL, Wang Y,
Huang J, Moreau JE, Volloch V, Kaplan DL and Altman GH: In vitro
degradation of silk fibroin. Biomaterials. 26:3385–3393.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Franco AR, Fernandes EM, Rodrigues MT,
Rodrigues FJ, Gomes ME, Leonor IB, Kaplan DL and Reis RL:
Antimicrobial coating of spider silk to prevent bacterial
attachment on silk surgical sutures. Acta Biomater. 99:236–246.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lee EH, Kim JY, Kweon HY, Jo YY, Min SK,
Park YW, Choi JY and Kim SG: A combination graft of
low-molecular-weight silk fibroin with Choukroun platelet-rich
fibrin for rabbit calvarial defect. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol Endod. 109:e33–e38. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kuchur OA, Tsymbal SA, Shestovskaya MV,
Serov NS, Dukhinova MS and Shtil AA: Metal-derived nanoparticles in
tumor theranostics: Potential and limitations. J Inorg Biochem.
209(111117)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang J, Xu Q, Huang C, Mo A, Li J and Zuo
Y: Biological properties of an anti-bacterial membrane for guided
bone regeneration: An experimental study in rats. Clin Oral
Implants Res. 21:321–327. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Khorshidi H, Haddadi P, Raoofi S, Badiee P
and Dehghani Nazhvani A: Does adding silver nanoparticles to
leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin improve its properties? BioMed
Res Int. 2018(8515829)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Woo SM, Kim WJ, Lim HS, Choi NK, Kim SH,
Kim SM and Jung JY: Combination of mineral trioxide aggregate and
platelet-rich fibrin promotes the odontoblastic differentiation and
mineralization of human dental pulp cells via BMP/Smad signaling
pathway. J Endod. 42:82–88. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Abdullah WA: Evaluation of bone
regenerative capacity in rats claverial bone defect using platelet
rich fibrin with and without beta tri calcium phosphate bone graft
material. Saudi Dent J. 28:109–117. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Karayürek F, Kadiroğlu ET, Nergiz Y,
Coşkun Akçay N, Tunik S, Ersöz Kanay B and Uysal E: Combining
platelet rich fibrin with different bone graft materials: An
experimental study on the histopathological and immunohistochemical
aspects of bone healing. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 47:815–825.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ohba S, Wang W, Itoh S, Takagi Y, Nagai A
and Yamashita K: Acceleration of new bone formation by an
electrically polarized hydroxyapatite microgranule/platelet-rich
plasma composite. Acta Biomater. 8:2778–2787. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Sadeghinia A, Davaran S, Salehi R and
Jamalpoor Z: Nano-hydroxy apatite/chitosan/gelatin scaffolds
enriched by a combination of platelet-rich plasma and fibrin glue
enhance proliferation and differentiation of seeded human dental
pulp stem cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1924–1931.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Suga H, Glotzbach JP, Sorkin M, Longaker
MT and Gurtner GC: Paracrine mechanism of angiogenesis in
adipose-derived stem cell transplantation. Ann Plast Surg.
72:234–241. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Klar AS, Güven S, Zimoch J, Zapiórkowska
NA, Biedermann T, Böttcher-Haberzeth S, Meuli-Simmen C, Martin I,
Scherberich A, Reichmann E, et al: Characterization of vasculogenic
potential of human adipose-derived endothelial cells in a
three-dimensional vascularized skin substitute. Pediatr Surg Int.
32:17–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lee SH, Jin SY, Song JS, Seo KK and Cho
KH: Paracrine effects of adipose-derived stem cells on
keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts. Ann Dermatol. 24:136–143.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Moon KM, Park YH, Lee JS, Chae YB, Kim MM,
Kim DS, Kim BW, Nam SW and Lee JH: The effect of secretory factors
of adipose-derived stem cells on human keratinocytes. Int J Mol
Sci. 13:1239–1257. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Stessuk T, Puzzi MB, Chaim EA, Alves PC,
de Paula EV, Forte A, Izumizawa JM, Oliveira CC, Frei F and
Ribeiro-Paes JT: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells: Stimulatory effects on proliferation and
migration of fibroblasts and keratinocytes in vitro. Arch Dermatol
Res. 308:511–520. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Park CG, Joo MW, Jeong J, Kang YK and Lee
DR: Evaluation of the effects of the combination of autologous
mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on structural bone
allograft healing. Cell Tissue Bank. 18:229–238. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Mills DC, Robb IA and Roberts GC: The
release of nucleotides, 5-hydroxytryptamine and enzymes from human
blood platelets during aggregation. J Physiol. 195:715–729.
1968.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Chen Y, Niu Z, Xue Y, Yuan F, Fu Y and Bai
N: Improvement in the repair of defects in maxillofacial soft
tissue in irradiated minipigs by a mixture of adipose-derived stem
cells and platelet-rich fibrin. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
52:740–745. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Sun CK, Zhen YY, Leu S, Tsai TH, Chang LT,
Sheu JJ, Chen YL, Chua S, Chai HT, Lu HI, et al: Direct
implantation versus platelet-rich fibrin-embedded adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells in treating rat acute myocardial infarction.
Int J Cardiol. 173:410–423. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang X, Li G, Guo J, Yang L, Liu Y, Sun Q,
Li R and Yu W: Hybrid composites of mesenchymal stem cell sheets,
hydroxyapatite, and platelet-rich fibrin granules for bone
regeneration in a rabbit calvarial critical-size defect model. Exp
Ther Med. 13:1891–1899. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wang ZS, Feng ZH, Wu GF, Bai SZ, Dong Y,
Chen FM and Zhao YM: The use of platelet-rich fibrin combined with
periodontal ligament and jaw bone mesenchymal stem cell sheets for
periodontal tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 6(28126)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wu CC, Sheu SY, Hsu LH, Yang KC, Tseng CC
and Kuo TF: Intra-articular Injection of platelet-rich fibrin
releasates in combination with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in the treatment of articular cartilage defects: An in vivo
study in rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
105:1536–1543. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
He X, Chen WX, Ban G, Wei W, Zhou J, Chen
WJ and Li XY: A new method to develop human dental pulp cells and
platelet-rich fibrin complex. J Endod. 42:1633–1640.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Graves LL, Bukata SV, Aghazadehsanai N,
Chang TI, Garrett NR and Friedlander AH: Patients receiving
parenteral bisphosphonates for malignant disease and having
developed an atypical femoral fracture are at risk of concomitant
osteonecrosis of the jaw: an evidence-based review. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 74:2403–2408. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lundberg AP, Roady PJ, Somrak AJ, Howes ME
and Fan TM: Zoledronate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw in a
dog with appendicular osteosarcoma. J Vet Intern Med. 30:1235–1240.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Kharazmi M, Hallberg P, Warfvinge G and
Michaëlsson K: Risk of atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis
of the jaw associated with alendronate use compared with other oral
bisphosphonates. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:1911–1913.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Street J, Bao M, deGuzman L, Bunting S,
Peale FV Jr, Ferrara N, Steinmetz H, Hoeffel J, Cleland JL,
Daugherty A, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates
bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:9656–9661. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Krüger TB, Herlofson BB, Landin MA and
Reseland JE: Alendronate alters osteoblast activities. Acta Odontol
Scand. 74:550–557. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Steller D, Herbst N, Pries R, Juhl D and
Hakim SG: Positive impact of Platelet-rich plasma and Platelet-rich
fibrin on viability, migration and proliferation of osteoblasts and
fibroblasts treated with zoledronic acid. Sci Rep.
9(8310)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ginés C, Cuesta S, Kireev R, García C,
Rancan L, Paredes SD, Vara E and Tresguerres JAF: Protective effect
of resveratrol against inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis
in pancreas of aged SAMP8 mice. Exp Gerontol. 90:61–70.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Borsani E, Bonazza V, Buffoli B, Nocini
PF, Albanese M, Zotti F, Inchingolo F, Rezzani R and Rodella LF:
Beneficial effects of concentrated growth factors and resveratrol
on human osteoblasts in vitro treated with bisphosphonates. BioMed
Res Int. 2018(4597321)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Xu FT, Liang ZJ, Li HM, Peng QL, Huang MH,
Li Q, Liang YD, Chi GY, Li H, Yu BC, et al: Ginsenoside Rg1 and
platelet-rich fibrin enhance human breast adipose-derived stem cell
function for soft tissue regeneration. Oncotarget. 7:35390–35403.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Raafat SN, Amin RM, Elmazar MM, Khattab MM
and El-Khatib AS: The sole and combined effect of simvastatin and
platelet rich fibrin as a filling material in induced bone defect
in tibia of albino rats. Bone. 117:60–69. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Isobe K, Watanebe T, Kawabata H, et al:
Mechanical and degradation properties of advanced platelet-rich
fibrin (A-PRF), concentrated growth factors (CGF), and
platelet-poor plasma-derived fibrin (PPTF). Int J Implant Dent.
3(17)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Masuki H, Okudera T, Watanebe T, et al:
Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in
platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF),
advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth
factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent. 2:2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|