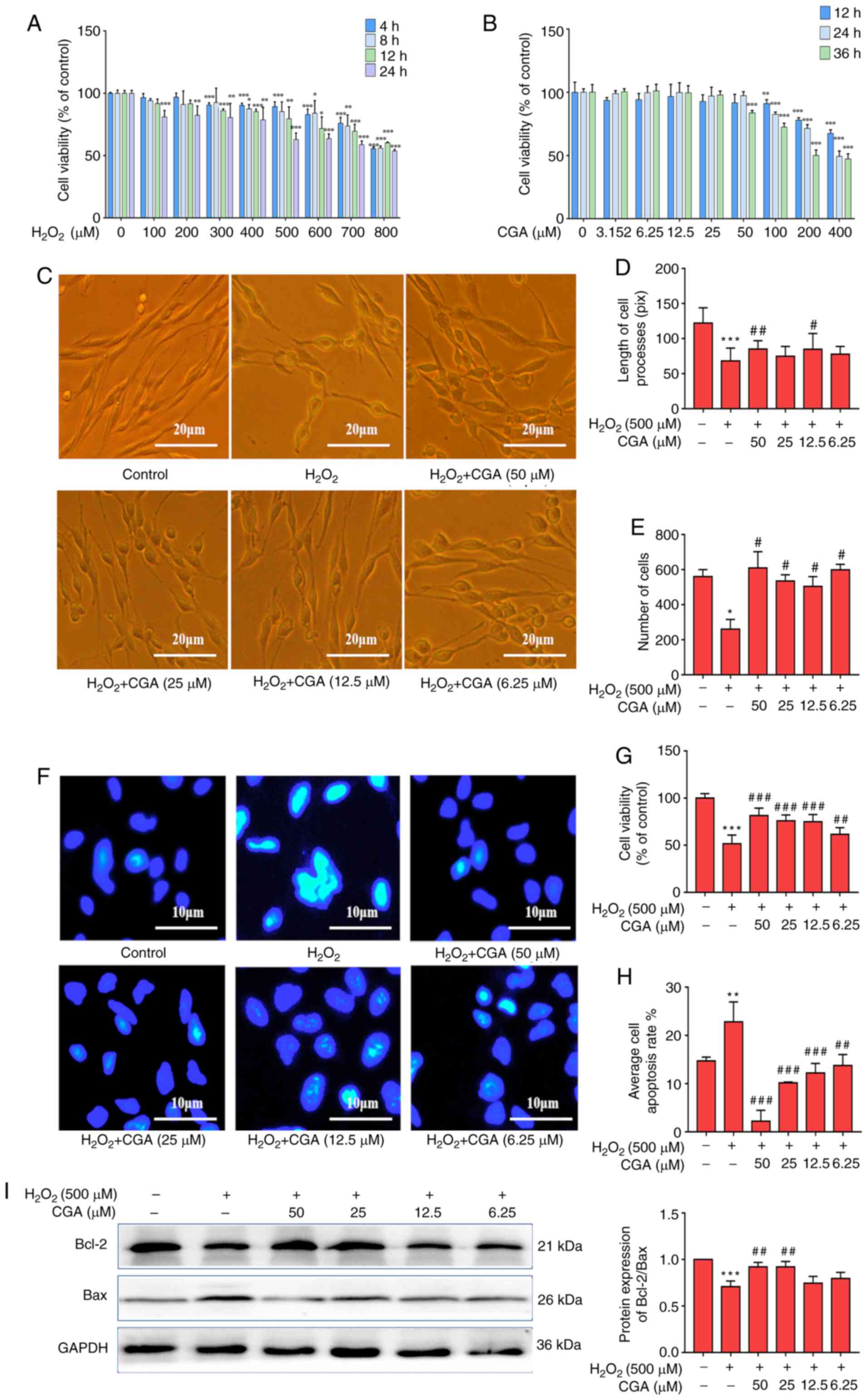
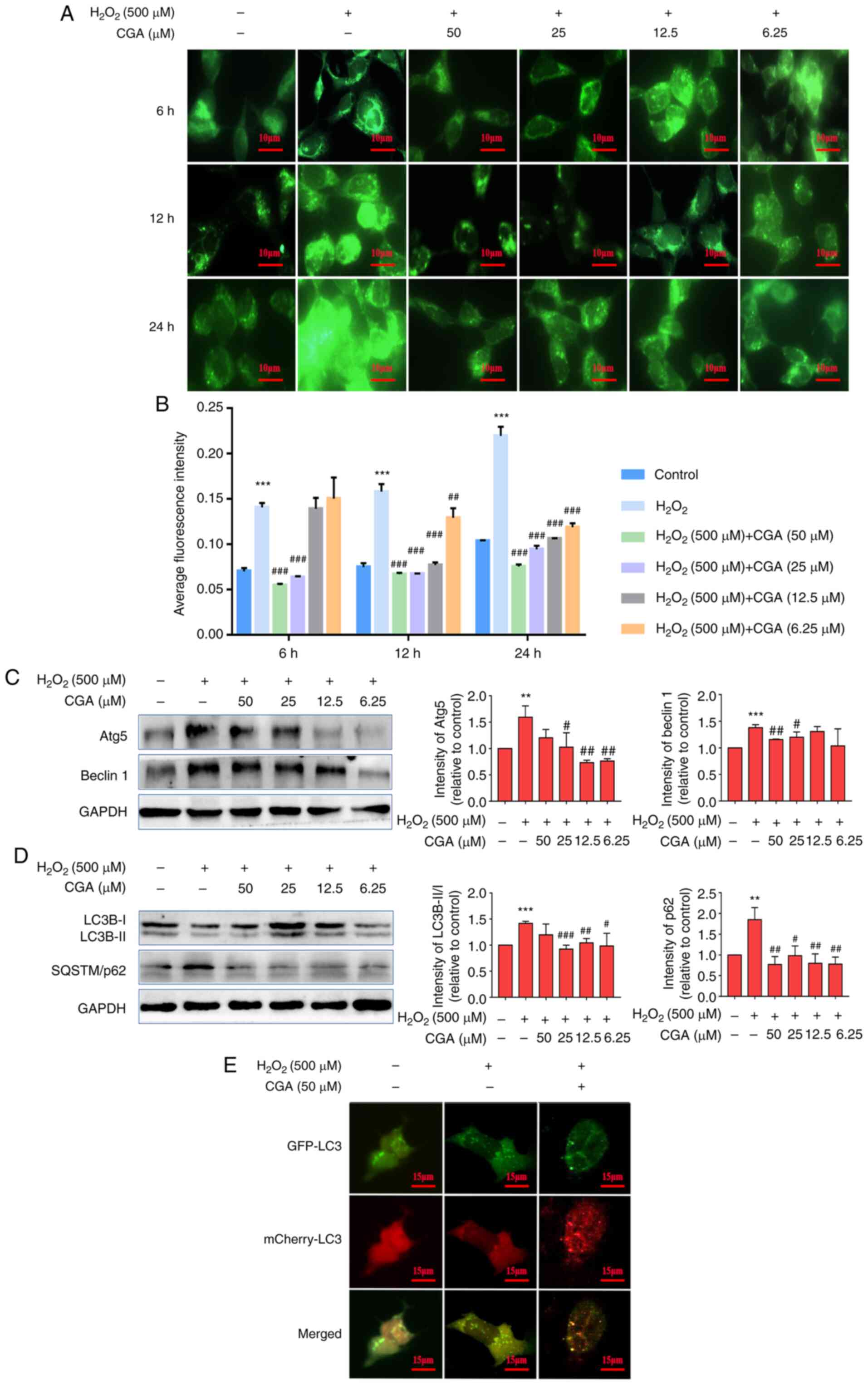
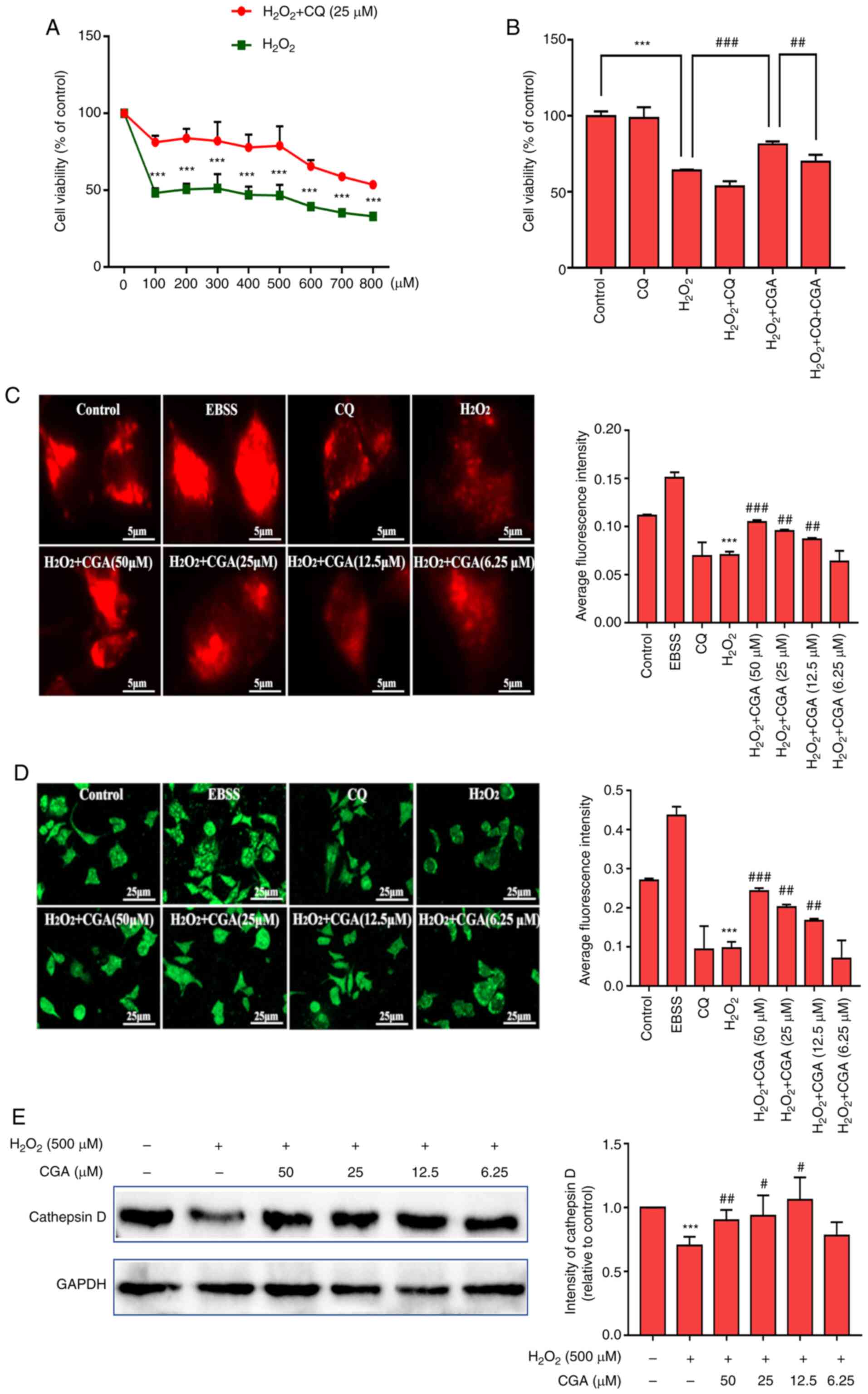
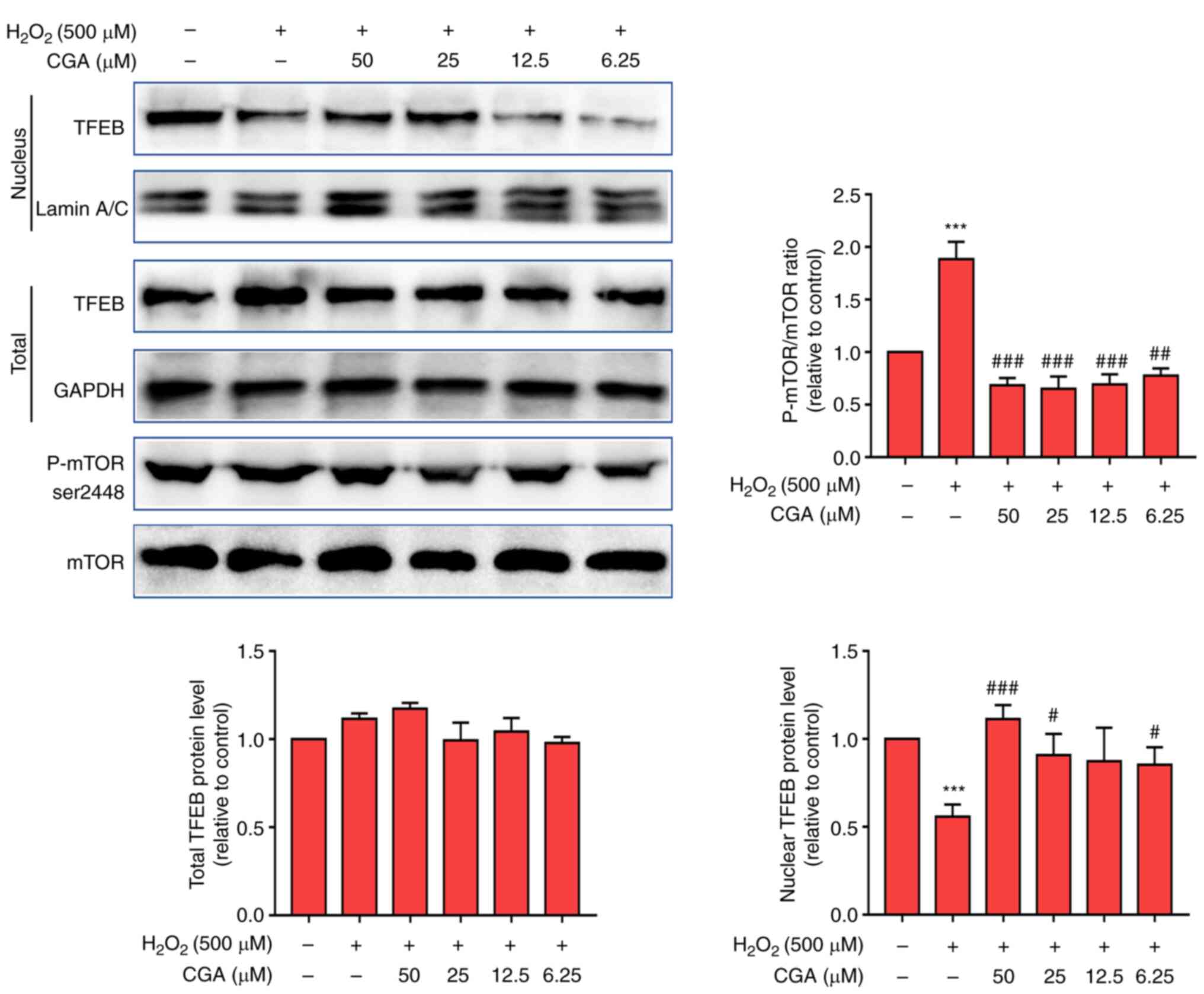
|
1
|
Pugazhenthi S: Metabolic syndrome and the
cellular phase of Alzheimer's disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
146:243–258. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ryu JC, Zimmer ER, Rosa-Neto P and Yoon
SO: Consequences of metabolic disruption in Alzheimer's disease
pathology. Neurotherapeutics. 16:600–610. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee M, McGeer E and McGeer PL: Activated
human microglia stimulate neuroblastoma cells to upregulate
production of beta amyloid protein and tau: Implications for
Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging. 36:42–52.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hampel H, Mesulam MM, Cuello AC,
Khachaturian AS, Vergallo A, Farlow MR, Snyder PJ, Giacobini E and
Khachaturian ZS: Revisiting the cholinergic hypothesis in
Alzheimer's disease: Emerging evidence from translational and
clinical research. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 6:2–15. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Manyevitch R, Protas M, Scarpiello S,
Deliso M, Bass B, Nanajian A, Chang M, Thompson SM, Khoury N,
Gonnella R, et al: Evaluation of metabolic and synaptic dysfunction
hypotheses of Alzheimer's disease (AD): A meta-analysis of CSF
markers. Curr Alzheimer Res. 15:164–181. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Haapasalo A, Pikkarainen M and Soininen H:
Alzheimer's disease: A report from the 7th Kuopio Alzheimer
symposium. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 5:379–382. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen XQ and Mobley WC: Exploring the
pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease in basal forebrain cholinergic
neurons: Converging insights from alternative hypotheses. Front
Neurosci. 13(446)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
He Z, Guo JL, McBride JD, Narasimhan S,
Kim H, Changolkar L, Zhang B, Gathagan RJ, Yue C, Dengler C, et al:
Amyloid-β plaques enhance Alzheimer's brain tau-seeded pathologies
by facilitating neuritic plaque tau aggregation. Nat Med. 24:29–38.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Swomley AM and Butterfield DA: Oxidative
stress in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: Evidence
from human data provided by redox proteomics. Arch Toxicol.
89:1669–1680. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Korovila I, Hugo M, Castro JP, Weber D,
Höhn A, Grune T and Jung T: Proteostasis, oxidative stress and
aging. Redox Biol. 13:550–567. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lévy E, El Banna N, Baïlle D,
Heneman-Masurel A, Truchet S, Rezaei H, Huang ME, Béringue V,
Martin D and Vernis L: Causative links between protein aggregation
and oxidative stress: A review. Int J Mol Sci.
20(3896)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chu Q, Zhu Y, Cao T and Zhang Y, Chang Z,
Liu Y, Lu J and Zhang Y: Studies on the neuroprotection of osthole
on glutamate-induced apoptotic cells and an Alzheimer's disease
mouse model via modulation oxidative stress. Appl Biochem
Biotechnol. 190:634–644. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Alvariño R, Alonso E, Abbasov ME, Chaheine
CM, Conner ML, Romo D, Alfonso A and Botana LM: Gracilin A
derivatives target early events in Alzheimer's disease: In vitro
effects on neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. ACS Chem
Neurosci. 10:4102–4111. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bagherniya M, Butler AE, Barreto GE and
Sahebkar A: The effect of fasting or calorie restriction on
autophagy induction: A review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev.
47:183–197. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Castillo K, Valenzuela V, Oñate M and Hetz
C: A molecular reporter for monitoring autophagic flux in nervous
system in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 588:109–131. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Reddy PH and Oliver DM: Amyloid beta and
phosphorylated tau-induced defective autophagy and mitophagy in
Alzheimer's disease. Cells. 8(488)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Correia SC, Resende R, Moreira PI and
Pereira CM: Alzheimer's disease-related misfolded proteins and
dysfunctional organelles on autophagy menu. DNA Cell Biol.
34:261–273. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Damme M, Suntio T, Saftig P and Eskelinen
EL: Autophagy in neuronal cells: General principles and
physiological and pathological functions. Acta Neuropathol.
129:337–362. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gao L, Li X, Meng S, Ma T, Wan L and Xu S:
Chlorogenic acid alleviates Aβ25-35-induced autophagy
and cognitive impairment via the mTOR/TFEB signaling pathway. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 14:1705–1716. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Farhood HB, Balas M, Gradinaru D, Margina
D and Dinischiotu A: Hepatoprotective effects of chlorogenic acid
under hyperglycemic conditions. Rom Biotechnol Lett. 1–10.
2017.
|
|
21
|
Heitman E and Ingram DK: Cognitive and
neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid. Nutr Neurosci.
20:32–39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tajik N, Tajik M, Mack I and Enck P: The
potential effects of chlorogenic acid, the main phenolic components
in coffee, on health: A comprehensive review of the literature. Eur
J Nutr. 56:2215–2244. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Wang N and Zheng G: Enhanced
effect of combining chlorogenic acid on selenium nanoparticles in
inhibiting amyloid β aggregation and reactive oxygen species
formation in vitro. Nanoscale Res Lett. 13(303)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Taram F, Winter AN and Linseman DA:
Neuroprotection comparison of chlorogenic acid and its metabolites
against mechanistically distinct cell death-inducing agents in
cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Brain Res. 1648:69–80.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang XJ, Wang LY, Fu Y, Wu J, Tang XC,
Zhao WM and Zhang HY: Promising effects on ameliorating
mitochondrial function and enhancing Akt signaling in SH-SY5Y cells
by (M)-bicelaphanol A, a novel dimeric podocarpane type
trinorditerpene isolated from Celastrus orbiculatus. Phytomedicine.
20:1064–1070. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zheng Y, Ma L, Liu N, Tang X, Guo S, Zhang
B and Jiang Z: Autophagy and apoptosis of porcine ovarian granulosa
cells during follicular development. Animals (Basel).
9(1111)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shi C, Zhao L, Zhu B, Li Q, Yew DT, Yao Z
and Xu J: Dosage effects of EGb761 on hydrogen peroxide-induced
cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact. 180:389–397.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang W, Sun F, An Y, Ai H, Zhang L, Huang
W and Li L: Morroniside protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol.
613:19–23. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yu BW, Li JL, Guo BB, Fan HM, Zhao WM and
Wang HY: Chlorogenic acid analogues from Gynura nepalensis protect
H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against H2O2-induced
apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:1413–1422. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chao X, Ni HM and Ding WX: Insufficient
autophagy: A novel autophagic flux scenario uncovered by impaired
liver TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis from chronic
alcohol-drinking mice. Autophagy. 14:1646–1648. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Aghdaei HA, Kadijani AA, Sorrentino D,
Mirzaei A, Shahrokh S, Balaii H, Geraci M and Zali MR: An increased
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in circulating inflammatory cells predicts primary
response to infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease patients.
United European Gastroenterol J. 6:1074–1081. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao T, Fu Y, Sun H and Liu X:
Ligustrazine suppresses neuron apoptosis via the Bax/Bcl-2 and
caspase-3 pathway in PC12 cells and in rats with vascular dementia.
IUBMB Life. 70:60–70. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Katsuragi Y, Ichimura Y and Komatsu M:
p62/SQSTM1 functions as a signaling hub and an autophagy adaptor.
FEBS J. 282:4672–4678. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ahsan A, Zheng Y, Ma S, Liu M, Cao M, Li
Y, Zheng W, Zhou X, Xin M, Hu WW, et al: Tomatidine protects
against ischemic neuronal injury by improving lysosomal function.
Eur J Pharmacol. 882(173280)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Schaaf MB, Houbaert D, Meçe O, To SK,
Ganne M, Maes H and Agostinis P: Lysosomal pathways and autophagy
distinctively control endothelial cell behavior to affect tumor
vasculature. Front Oncol. 9(171)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pierzyńska-Mach A, Janowski PA and
Dobrucki JW: Evaluation of acridine orange, LysoTracker Red, and
quinacrine as fluorescent probes for long-term tracking of acidic
vesicles. Cytometry A. 85:729–737. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Thapa A and Carroll NJ: Dietary modulation
of oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Sci.
18(1583)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pohanka M: Alzheimer's disease and
oxidative stress: A review. Curr Med Chem. 21:356–364.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gubandru M, Margina D, Tsitsimpikou C,
Goutzourelas N, Tsarouhas K, Ilie M, Tsatsakis AM and Kouretas D:
Alzheimer's disease treated patients showed different patterns for
oxidative stress and inflammation markers. Food Chem Toxicol.
61:209–214. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee HJ, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A, Margina
D, Izotov BN and Yang SH: Neuroprotective effects of Scrophularia
buergeriana extract against glutamate-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y
cells. Int J Mol Med. 43:2144–2152. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Costa C, Tsatsakis A, Mamoulakis C,
Teodoro M, Briguglio G, Caruso E, Tsoukalas D, Margina D, Dardiotis
E, Kouretas D and Fenga C: Current evidence on the effect of
dietary polyphenols intake on chronic diseases. Food Chem Toxicol.
110:286–299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kato M, Ochiai R, Kozuma K, Sato H and
Katsuragi Y: Effect of chlorogenic acid intake on cognitive
function in the elderly: A pilot study. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2018(8608497)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Martini-Stoica H, Xu Y, Ballabio A and
Zheng H: The autophagy-lysosomal pathway in neurodegeneration: A
TFEB perspective. Trends Neurosci. 39:221–234. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang D, Zhang J, Jiang W, Cao Z, Zhao F,
Cai T, Aschner M and Luo W: The role of NLRP3-CASP1 in
inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and autophagy dysfunction
in manganese-induced, hippocampal-dependent impairment of learning
and memory ability. Autophagy. 13:914–927. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ntsapi C, Lumkwana D, Swart C, du Toit A
and Loos B: New insights into autophagy dysfunction related to
amyloid beta toxicity and neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease.
Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 336:321–361. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tanida I and Waguri S: Measurement of
autophagy in cells and tissues. Methods Mol Biol. 648:193–214.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lamark T, Svenning S and Johansen T:
Regulation of selective autophagy: The p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays
Biochem. 61:609–624. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Colacurcio DJ, Pensalfini A, Jiang Y and
Nixon RA: Dysfunction of autophagy and endosomal-lysosomal
pathways: Roles in pathogenesis of down syndrome and Alzheimer's
disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 114:40–51. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chai YL, Chong JR, Weng J, Howlett D,
Halsey A, Lee JH, Attems J, Aarsland D, Francis PT, Chen CP and Lai
MKP: Lysosomal cathepsin D is upregulated in Alzheimer's disease
neocortex and may be a marker for neurofibrillary degeneration.
Brain Pathol. 29:63–74. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Vidoni C, Follo C, Savino M, Melone MA and
Isidoro C: The role of cathepsin D in the pathogenesis of human
neurodegenerative disorders. Med Res Rev. 36:845–870.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ye B, Wang Q, Hu H, Shen Y, Fan C, Chen P,
Ma Y, Wu H and Xiang M: Restoring autophagic flux attenuates
cochlear spiral ganglion neuron degeneration by promoting TFEB
nuclear translocation via inhibiting MTOR. Autophagy. 15:998–1016.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tramutola A, Triplett JC, Di Domenico F,
Niedowicz DM, Murphy MP, Coccia R, Perluigi M and Butterfield DA:
Alteration of mTOR signaling occurs early in the progression of
Alzheimer disease (AD): Analysis of brain from subjects with
pre-clinical AD, amnestic mild cognitive impairment and late-stage
AD. J Neurochem. 133:739–749. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kou X, Chen D and Chen N: Physical
activity alleviates cognitive dysfunction of Alzheimer's disease
through regulating the mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci.
20(1591)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|