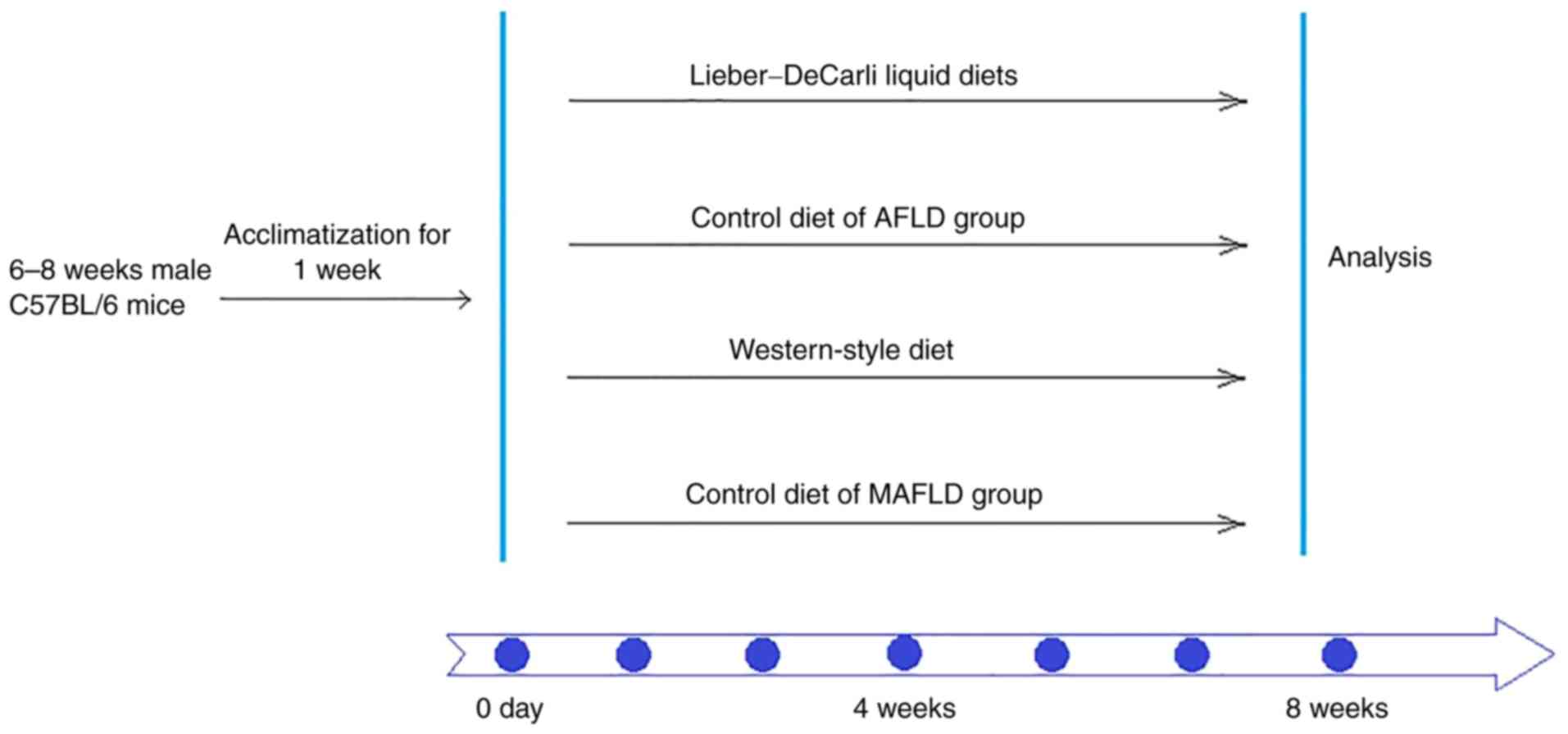
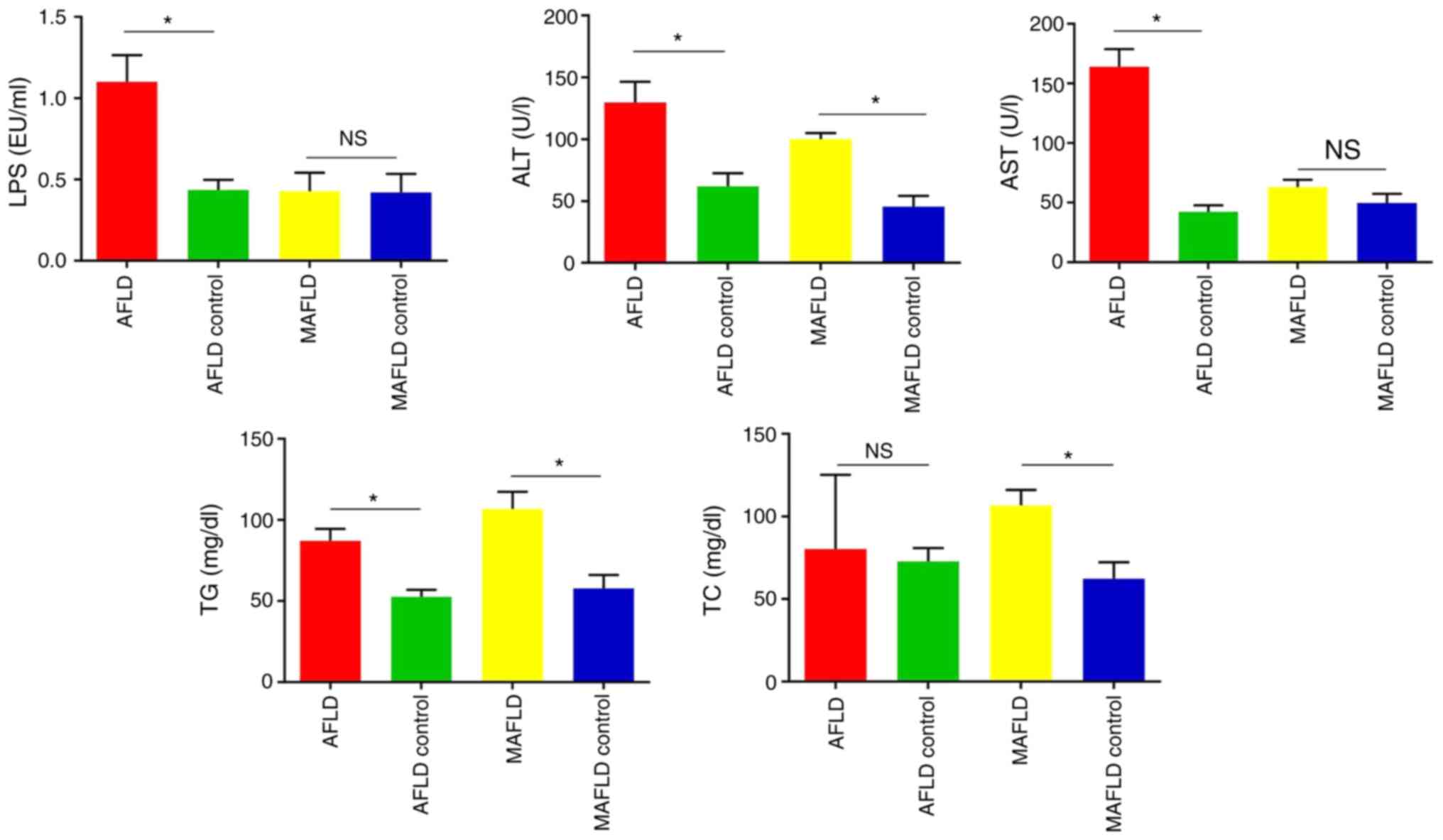
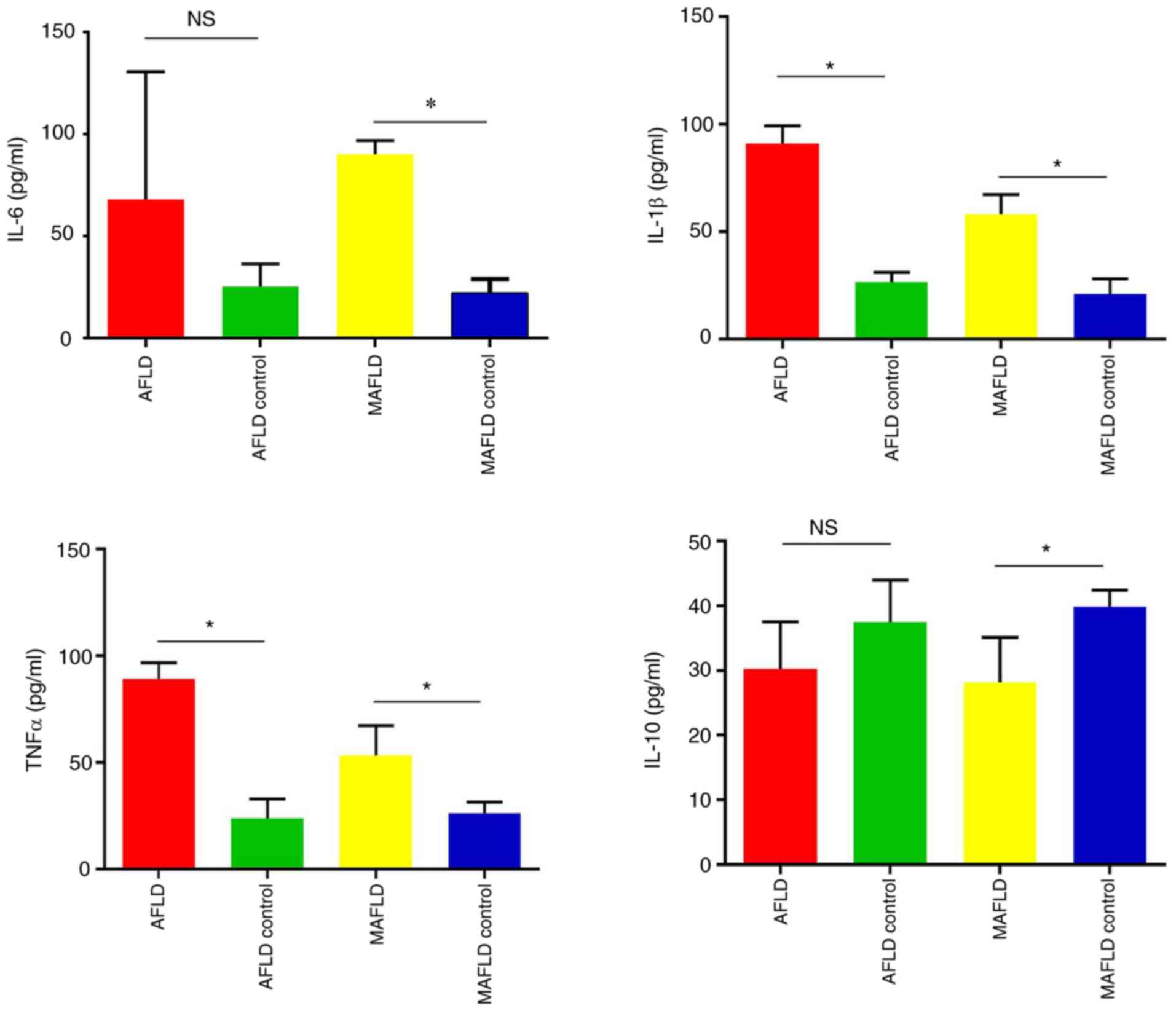
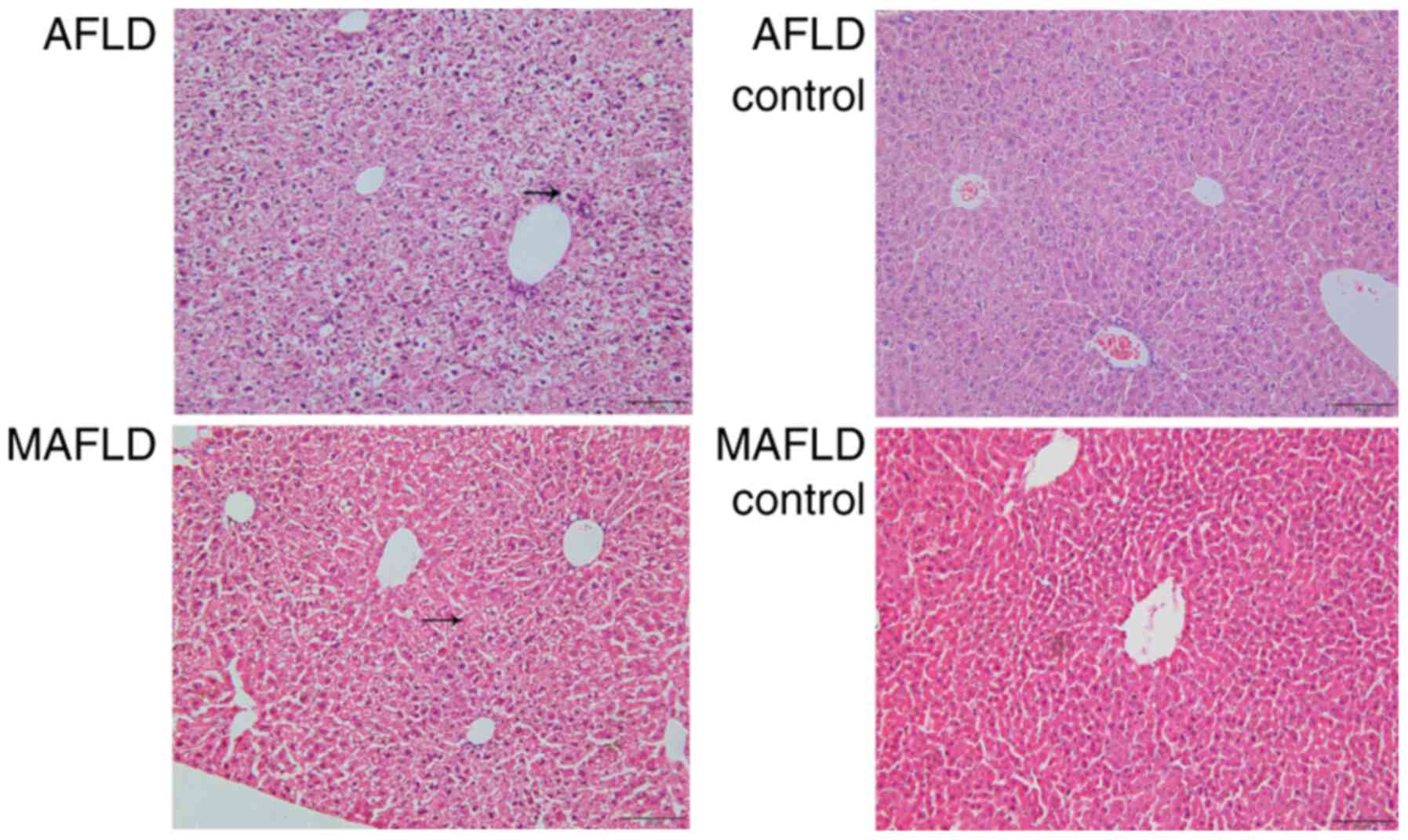
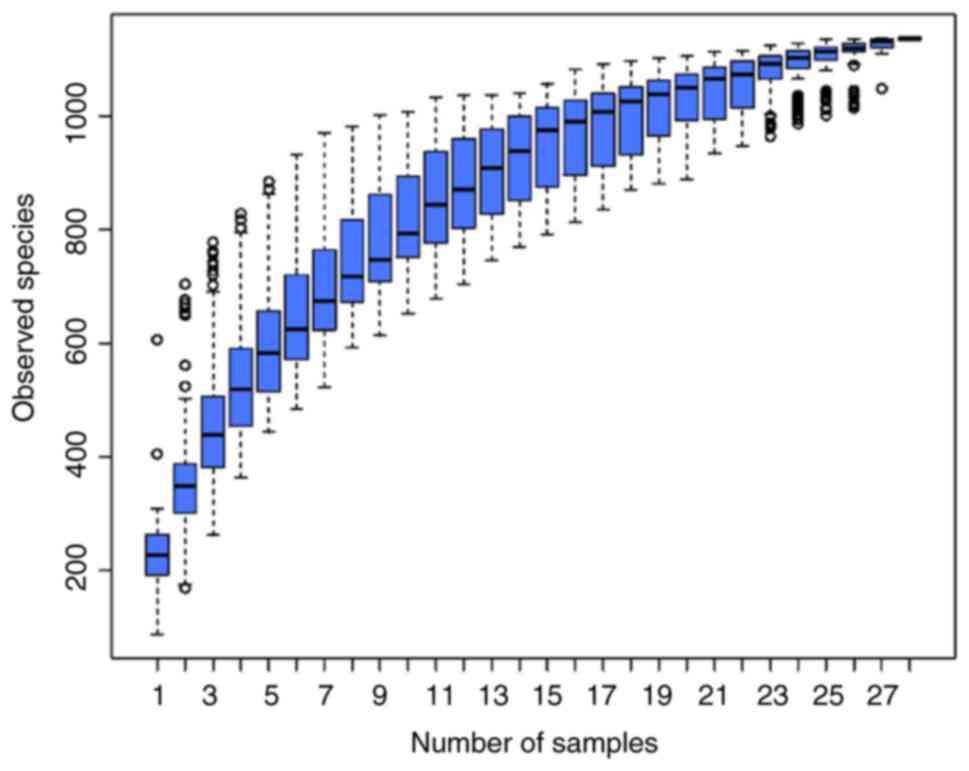
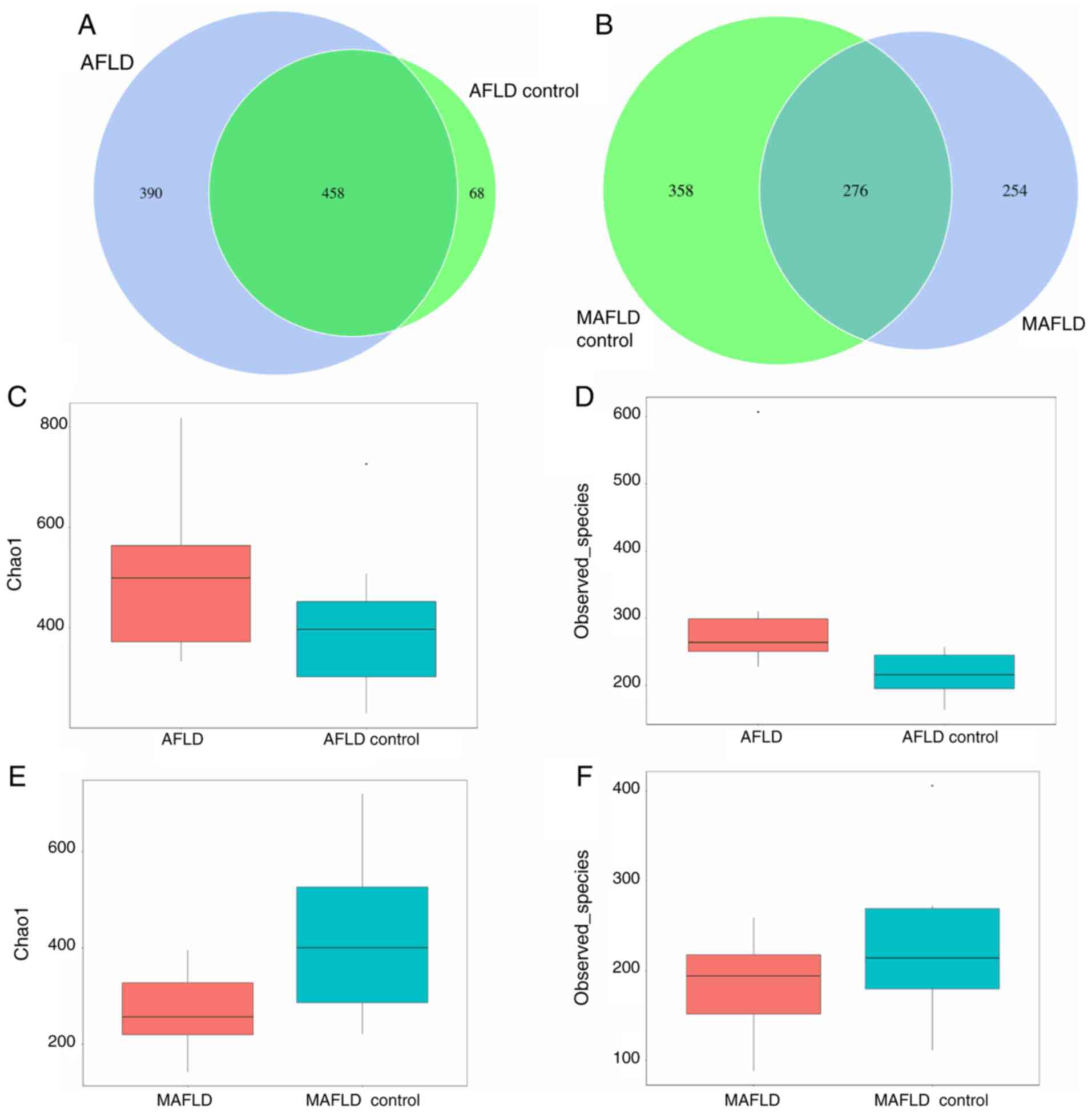
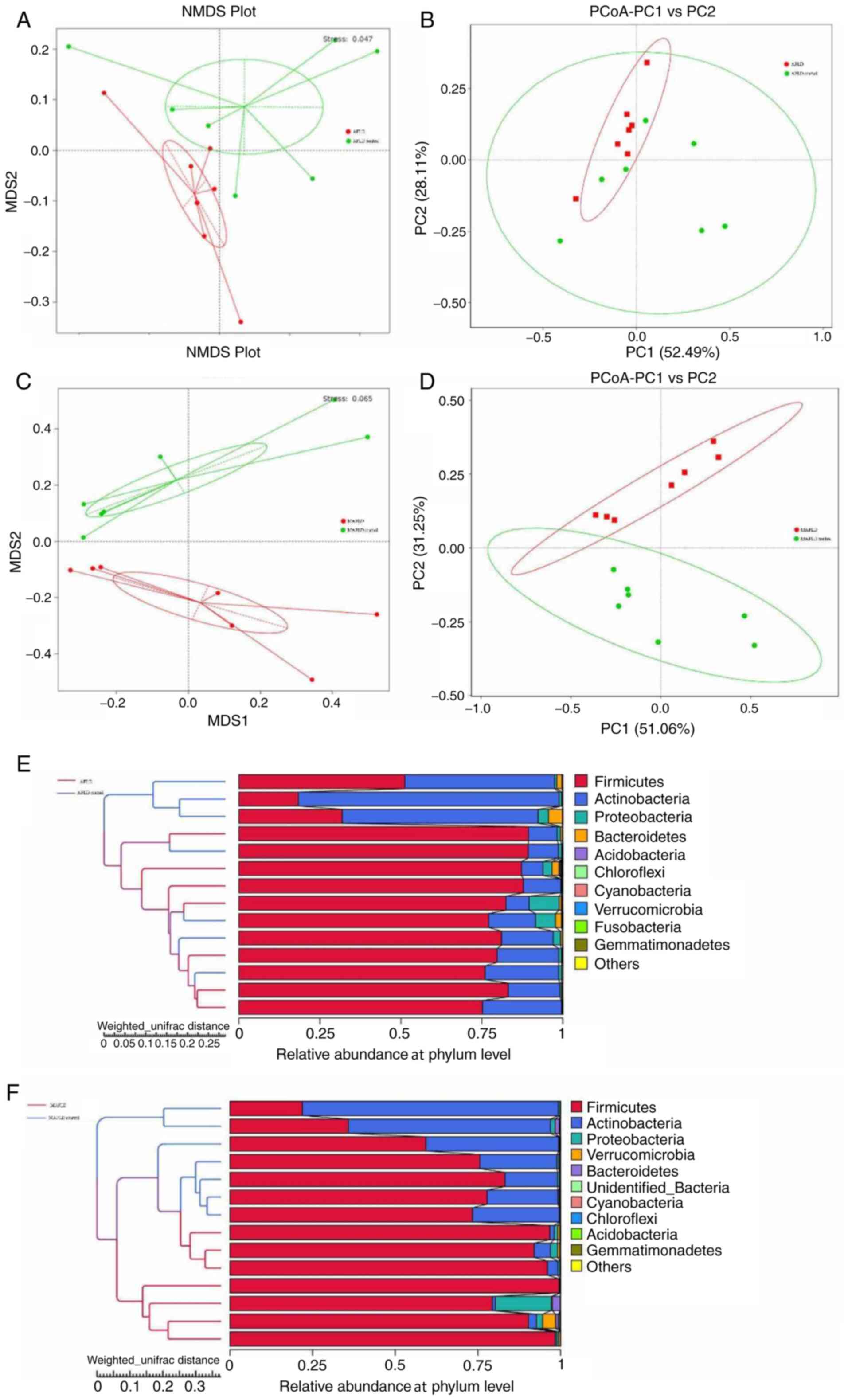
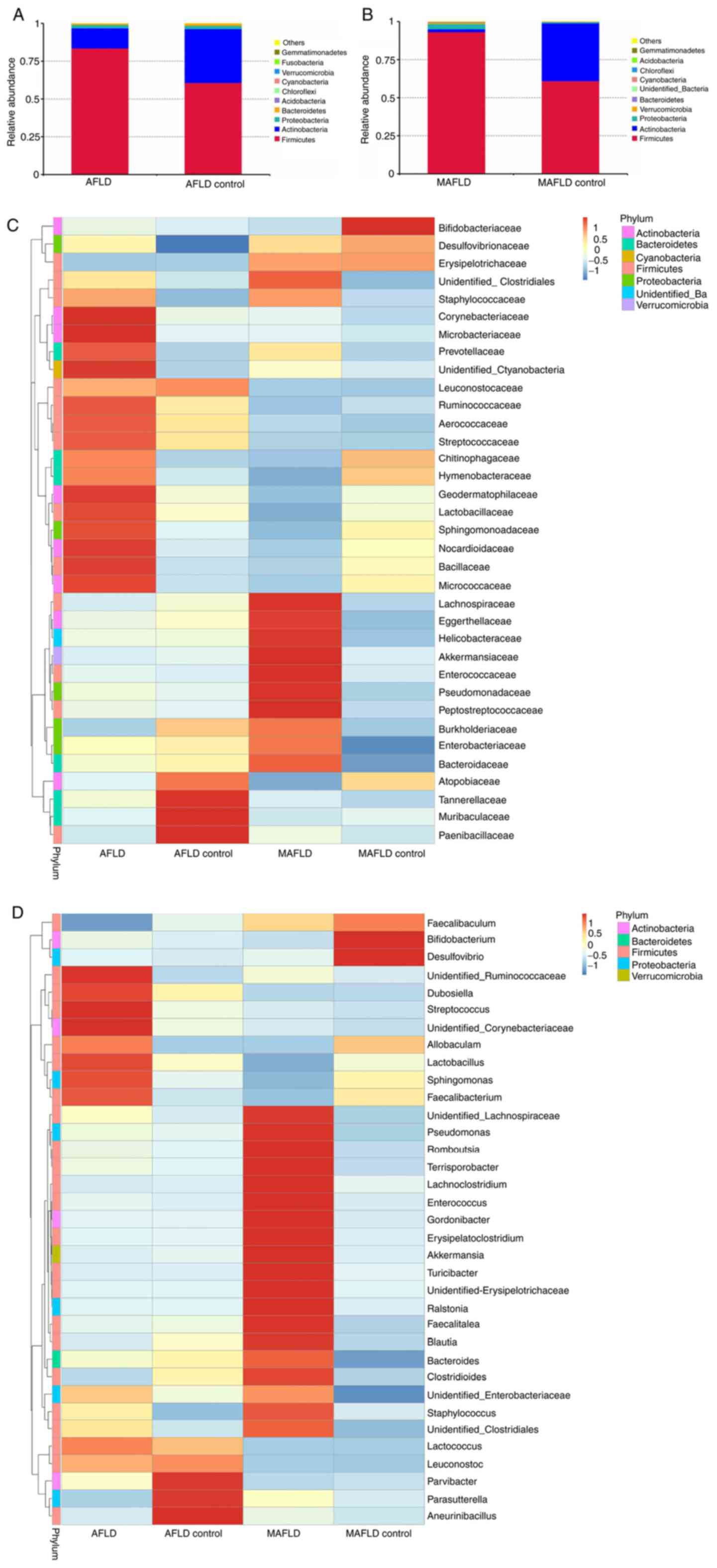
|
1
|
Szabo G, Kamath PS, Shah VH, Thursz M and
Mathurin P: EASL-AASLD Joint Meeting. Alcohol-related liver
disease: Areas of consensus, unmet needs and opportunities for
further study. Hepatology. 69:2271–2283. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Teli MR, Day CP, Burt AD, Bennett MK and
James OF: Determinants of progression to cirrhosis or fibrosis in
pure alcoholic fatty liver. Lancet. 346:987–990. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Araújo AR, Rosso N, Bedogni G, Tiribelli C
and Bellentani S: Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: What we need in the future.
Liver Int. 38 (Suppl 1):S47–S51. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Levene AP and Goldin RD: The epidemiology,
pathogenesis and histopathology of fatty liver disease.
Histopathology. 61:141–152. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu Y, Cai J, She Z and Li H: Insights into
the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutics of nonalcoholic
fatty liver diseases. Adv Science (Weinh).
6(1801585)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Peredo-Lovillo A, Romero-Luna HE and
Jiménez-Fernández M: Health promoting microbial metabolites
produced by gut microbiota after prebiotics metabolism. Food Res
Int. 136(109473)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Willers M, Ulas T, Völlger L, Vogl T,
Heinemann AS, Pirr S, Pagel J, Fehlhaber B, Halle O, Schöning J, et
al: S100A8 and S100A9 are important for postnatal development of
gut microbiota and immune system in mice and infants.
Gastroenterology. 159:2130–2145.e5. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ruff WE, Greiling TM and Kriegel MA:
Host-microbiota interactions in immune-mediated diseases. Nat Rev
Microbiol. 18:521–538. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fan Y and Pedersen O: Gut microbiota in
human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19:55–71.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang L and Schnabl B: Gut microbiota in
liver disease: What do we know and what do we not know? Physiology
(Bethesda). 35:261–274. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lang S, Fairfied B, Gao B, Duan Y, Zhang
X, Fouts DE and Schnabl B: Changes in the fecal bacterial
microbiota associated with disease severity in alcoholic hepatitis
patients. Gut Microbes. 12(1785251)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ferrere G, Wrzosek L, Cailleux F, Turpin
W, Puchois V, Spatz M, Ciocan D, Rainteau D, Humbert L, Hugot C, et
al: Fecal microbiota manipulation prevents dysbiosis and
alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. J Hepatol. 66:806–815.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Minaya DM, Turlej A, Joshi A, Nagy T,
Weinstein N, DiLorenzo P, Hajnal A and Czaja K: Consumption of a
high energy density diet triggers microbiota dysbiosis, hepatic
lipidosis, and microglia activation in the nucleus of the solitary
tract in rats. Nutr Diabetes. 10(20)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shen F, Zheng RD, Sun XQ, Ding WJ, Wang XY
and Fan JG: Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 16:375–381.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HN, Joo EJ, Cheong HS, Kim Y, Kim HL,
Shin H, Chang Y and Ryu S: Gut microbiota and risk of persistent
nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases. J Clin Med.
8(1089)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Martín R, Chain F, Miquel S, Motta JP,
Vergnolle N, Sokol H and Langella P: Using murine colitis models to
analyze probiotics-host interactions. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 41 (Supp
1):S49–S70. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu L, Li P, Liu Y and Zhang Y: Efficacy
of probiotics and synbiotics in patients with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease: A meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 64:3402–3412.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kirpich IA, Solovieva NV, Leikhter SN,
Shidakova NA, Lebedeva OV, Sidorov PI, Bazhukova TA, Soloviev AG,
Barve SS, McClain CJ and Cave M: Probiotics restore bowel flora and
improve liver enzymes in human alcohol-induced liver injury: A
pilot study. Alcohol. 42:675–682. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lamas-Paz A, Hao F, Nelson LJ, Vázquez MT,
Canals S, Gómez Del Moral M, Martínez-Naves E, Nevzorova YA and
Cubero FJ: Alcoholic liver disease: Utility of animal models. World
J Gastroenterol. 24:5063–5075. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhong F, Zhou X, Xu J and Gao L: Rodent
models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Digestion. 101:522–535.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yoneyama N, Crabbe JC, Ford MM, Murillo A
and Finn DA: Voluntary ethanol consumption in 22 inbred mouse
strains. Alcohol. 42:149–160. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Denucci SM, Tong M, Longato L, Lawton M,
Setshedi M, Carlson RI, Wands JR and de la Monte SM: Rat strain
differences in susceptibility to alcohol-induced chronic liver
injury and hepatic insulin resistance. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2010(312790)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lutz KA, Wang W, Zdepski A and Michael TP:
Isolation and analysis of high quality nuclear DNA with reduced
organellar DNA for plant genome sequencing and resequencing. BMC
Biotechnol. 11(54)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang L and Wang S: Bacterial community
diversity on in-shell walnut surfaces from six representative
provinces in China. Sci Rep. 7(10054)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J,
Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J and Glöckner FO: The SILVA ribosomal
RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based
tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 (Database issue):D590–D596.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C
and Knight R: UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera
detection. Bioinformatics. 27:2194–2200. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M,
Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren
E, et al: Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in
Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 21:494–504.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Edgar RC: UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU
sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 10:996–998.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Edgar RC: MUSCLE: Multiple sequence
alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids
Res. 32:1792–1797. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hadinia A, Doustimotlagh AH, Goodarzi HR,
Arya A and Jafarinia M: Circulating levels of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Iran J Immunol. 16:327–333.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Carpino G, Del Ben M, Pastori D, Carnevale
R, Baratta F, Overi D, Francis H, Cardinale V, Onori P, Safarikia
S, et al: Increased liver localization of lipopolysaccharides in
human and experimental NAFLD. Hepatology. 72:470–485.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan AW, Fouts DE, Brandl J, Stärkel P,
Torralba M, Schott E, Tsukamoto H, Nelson KE, Brenner DA and
Schnabl B: Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of
alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 53:96–105. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jung F, Lippmann T, Brandt A, Jin CJ,
Engstler AJ and Baumann A: Moderate consumption of fermented
alcoholic beverages diminishes diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease through mechanisms involving hepatic adiponectin
signaling in mice. Eur J Nutr. 59:787–799. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xiong DD, Zhang M, Li N, Gai JF, Mao L and
Li M: Mediation of inflammation, obesity and fatty liver disease by
advanced glycation endoproducts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:5172–5178. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ishihara K and Hirano T: IL-6 in
autoimmune disease and chronic inflammatory proliferative disease.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:357–368. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jorge ASB, Andrade JMO, Paraíso AF, Jorge
G, Silveira CM, de Souza LR, Santos EP, Guimaraes A, Santos S and
De-Paula A: Body mass index and the visceral adipose tissue
expression of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with the
morphological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in
individuals with class III obesity. Obes Res Clin Pract. 12 (Suppl
2):S1–S8. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sheron N, Bird G, Goka J, Alexander G and
Williams R: Elevated plasma interleukin-6 and increased severity
and mortality in alcoholic hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 84:449–453.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schmidt-Arras D and Rose-John S: IL-6
pathway in the liver: From physiopathology to therapy. J Hepatol.
64:1403–1415. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bird GL, Sheron N, Goka AK, Alexander GJ
and Williams RS: Increased plasma tumor necrosis factor in severe
alcoholic hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 112:917–920. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tilg H, Moschen AR and Szabo G:
Interleukin-1 and inflammasomes in alcoholic liver disease/acute
alcoholic hepatitis and nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 64:955–965.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hill DB, D'Souza NB, Lee EY, Burikhanov R,
Deaciuc IV and de Villiers WJ: A role for interleukin-10 in
alcohol-induced liver sensitization to bacterial
lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 26:74–82. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Paredes-Turrubiarte G, González-Chávez A,
Pérez-Tamayo R, Salazar-Vázquez BY, Hernández VS, Garibay-Nieto N,
Fragoso JM and Escobedo G: Severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease is associated with high systemic levels of tumor necrosis
factor α and low serum interleukin 10 in morbidly obese patients.
Clin Exp Med. 16:193–202. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang L, Wu YN, Chen T, Ren CH, Li X and
Liu GX: Relationship between intestinal microbial dysbiosis and
primary liver cancer. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 18:149–157.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang W, Gu Y, Chen Y, Deng H, Chen L,
Chen S, Zhang G and Gao Z: Intestinal flora imbalance results in
altered bacterial translocation and liver function in rats with
experimental cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1481–1486.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Duan Y, Llorente C, Lang S, Brandl K, Chu
H, Jiang L, White RC, Clarke TH, Nguyen K, Torralba M, et al:
Bacteriophage targeting of gut bacterium attenuates alcoholic liver
disease. Nature. 575:505–511. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Manfredo Vieira S, Hiltensperger M, Kumar
V, Zegarra-Ruiz D, Dehner C, Khan N, Costa FRC, Tiniakou E,
Greiling T, Ruff W, et al: Translocation of a gut pathobiont drives
autoimmunity in mice and humans. Science. 359:1156–1161.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Çolakoğlu M, Xue J and Trajkovski M:
Bacteriophage prevents alcoholic liver disease. Cell. 180:218–220.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Llorente C, Jepsen P, Inamine T, Wang L,
Bluemel S, Wang HJ, Loomba R, Bajaj JS, Schubert ML, Sikaroodi M,
et al: Gastric acid suppression promotes alcoholic liver disease by
inducing overgrowth of intestinal Enterococcus. Nat Commun.
8(837)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nakayama T, Takeuchi D, Matsumura T, Akeda
Y, Fujinaga Y and Oishi K: Alcohol consumption promotes the
intestinal translocation of Streptococcus suis infections.
Microb Pathog. 65:14–20. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Posteraro B, Paroni Sterbini F, Petito V,
Rocca S, Cubeddu T, Graziani C, Arena V, Vassallo GA, Mosoni C,
Lopetuso L, et al: Liver injury, endotoxemia, and their
relationship to intestinal microbiota composition in
alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 42:2313–2325.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang DY, Zhu L, Liu HN, Tseng YJ, Weng
SQ, Liu TT, Dong L and Shen XZ: The protective effect and mechanism
of the FXR agonist obeticholic acid via targeting gut microbiota in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Des Devel Ther.
13:2249–2270. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang Y, Yang F, Huang M, Wu H, Yang C,
Zhang X, Yang L, Chen G, Li S, Wang Q, et al: Fatty liver and
alteration of the gut microbiome induced by diallyl disulfide. Int
J Mol Med. 44:1908–1920. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhu L, Baker SS, Gill C, Liu W, Alkhouri
R, Baker RD and Gill SR: Characterization of gut microbiomes in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between
endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology. 57:601–609.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM, Probert CS,
Ratcliffe NM, Smith S, Greenwood R, Sikaroodi M, Lam V, Crotty P,
et al: Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in
obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:868–875. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Boursier J, Mueller O, Barret M, Machado
M, Fizanne L, Araujo-Perez F, Guy CD, Seed PC, Rawls JF, David LA,
et al: The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is
associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function
of the gut microbiota. Hepatology. 63:764–775. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Luo D, Chen K, Li J, Fang Z, Pang H, Yin
Y, Rong X and Guo J: Gut microbiota combined with metabolomics
reveals the metabolic profile of the normal aging process and the
anti-aging effect of FuFang Zhenshu TiaoZhi(FTZ) in mice. Biomed
Pharmacother. 121(109550)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Smith-Brown P, Morrison M, Krause L and
Davies PS: Dairy and plant based food intakes are associated with
altered faecal microbiota in 2 to 3 year old Australian children.
Sci Rep. 6(32385)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Du J, Huang P, Qian Y, Yang X, Cui S, Lin
Y, Gao C, Zhang P, He Y, Xiao Q and Chen S: Fecal and blood
microbial 16s rRNA gene alterations in Chinese patients with
multiple system atrophy and its subtypes. J Parkinsons Dis.
9:711–721. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Nistal E, Sáenz de Miera LE, Ballesteros
Pomar M, Sánchez-Campos S, García-Mediavilla MV, Álvarez-Cuenllas
B, Linares P, Olcoz JL, Arias-Loste MT, García-Lobo JM, et al: An
altered fecal microbiota profile in patients with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease (NAFLD) associated with obesity. Rev Esp Enferm
Dig. 111:275–282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Sen T, Cawthon CR, Ihde BT, Hajnal A,
DiLorenzo PM, de La Serre CB and Czaja K: Diet-driven microbiota
dysbiosis is associated with vagal remodeling and obesity. Physiol
Behav. 173:305–317. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yano JM, Yu K, Donaldson GP, Shastri GG,
Ann P, Ma L, Nagler CR, Ismagilov RF, Mazmanian SK and Hsiao EY:
Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin
biosynthesis. Cell. 161:264–276. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Horiuchi H, Kamikado K, Aoki R, Suganuma
N, Nishijima T, Nakatani A and Kimura I: Bifidobacterium
animalis subsp. lactis GCL2505 modulates host energy metabolism via
the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Sci Rep.
10(4158)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Liang Y, Lin C, Zhang Y, Deng Y, Liu C and
Yang Q: Probiotic mixture of Lactobacillus and
Bifidobacterium alleviates systemic adiposity and
inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats through
Gpr109a and the commensal metabolite butyrate.
Inflammopharmacology. 26:1051–1055. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P
and Bäckhed F: From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain
fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 165:1332–1345.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Schwenger KJP, Chen L, Chelliah A, Da
Silva HE, Teterina A, Comelli EM, Taibi A, Arendt BM, Fischer S and
Allard JP: Markers of activated inflammatory cells are associated
with disease severity and intestinal microbiota in adults with
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med. 42:2229–2237.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Oo KM, Lwin AA, Kyaw YY, Tun WM, Fukada K,
Goshima A, Shimada T and Okada S: Safety and long-term effect of
the probiotic FK-23 in patients with hepatitis C virus infection.
Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 35:123–128. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Duque-Correa MA, Karp NA, McCarthy C,
Forman S, Goulding D, Sankaranarayanan G, Jenkins TP, Reid AJ,
Cambridge EL, Ballesteros Reviriego C, et al: Exclusive dependence
of IL-10Rα signalling on intestinal microbiota homeostasis and
control of whipworm infection. PLoS Pathog.
15(e1007265)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lu J, Ma SS, Zhang WY and Duan JP: Changes
in peripheral blood inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-6) and
intestinal flora in AIDS and HIV-positive individuals. J Zhejiang
Univ Sci B. 20:793–802. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Mou H, Yang F, Zhou J and Bao C:
Correlation of liver function with intestinal flora, vitamin
deficiency and IL-17A in patients with liver cirrhosis. Exp Ther
Med. 16:4082–4088. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Guo S, Guo Y, Ergun A, Lu L, Walker WA and
Ganguli K: Secreted metabolites of Bifidobacterium infantis
and lactobacillus acidophilus protect immature human enterocytes
from IL-1β-induced inflammation: A transcription profiling
analysis. PLoS One. 10(e124549)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|