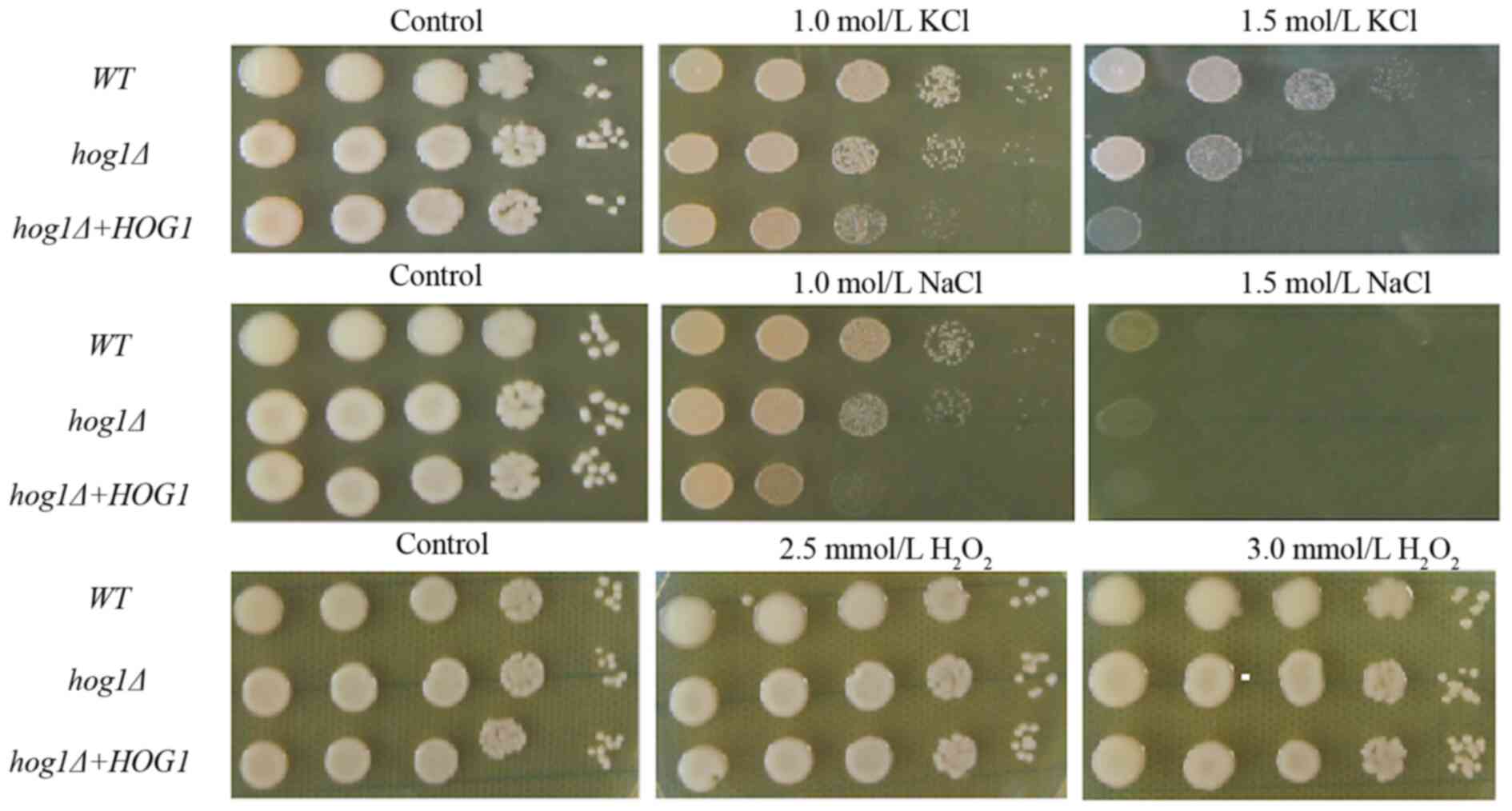
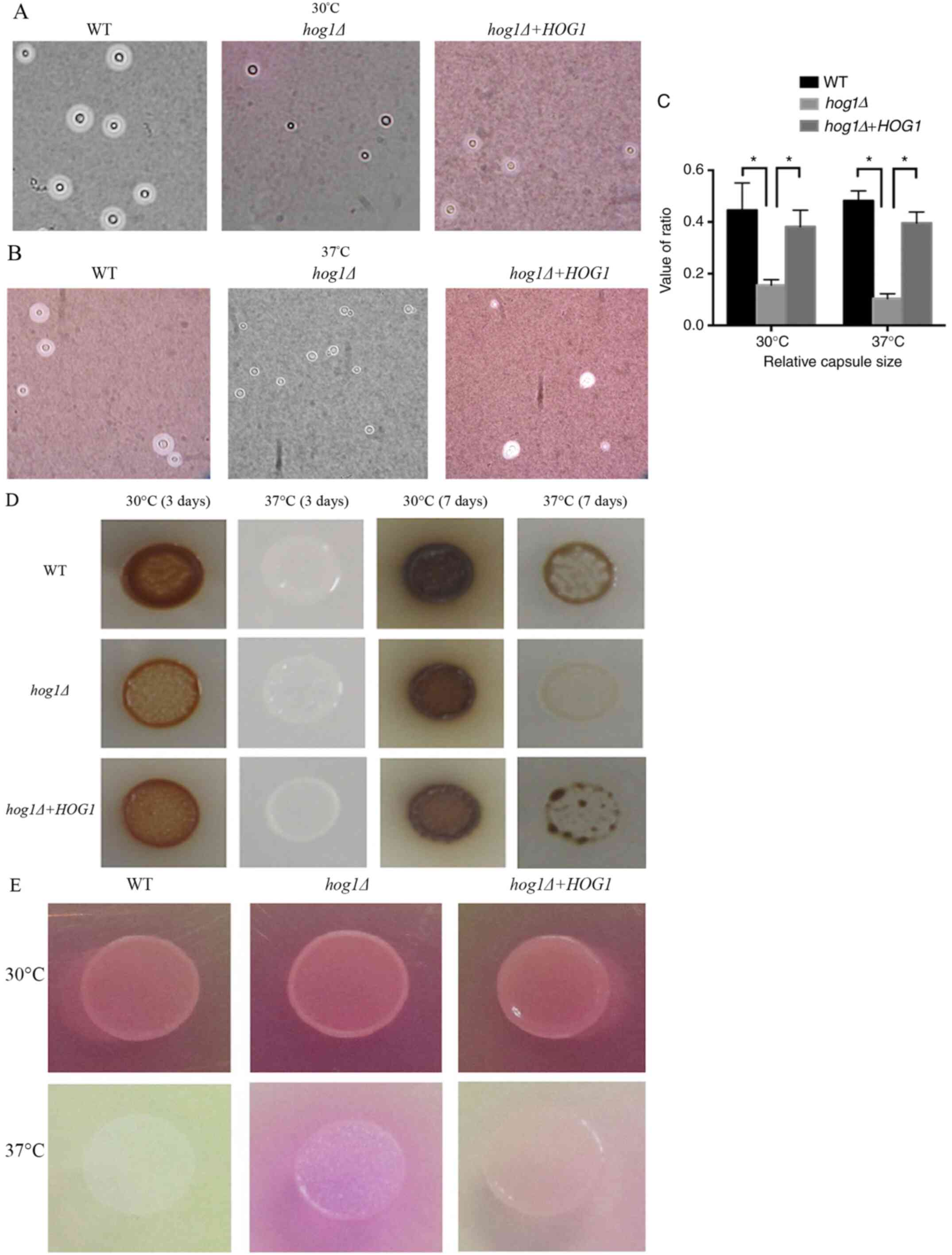
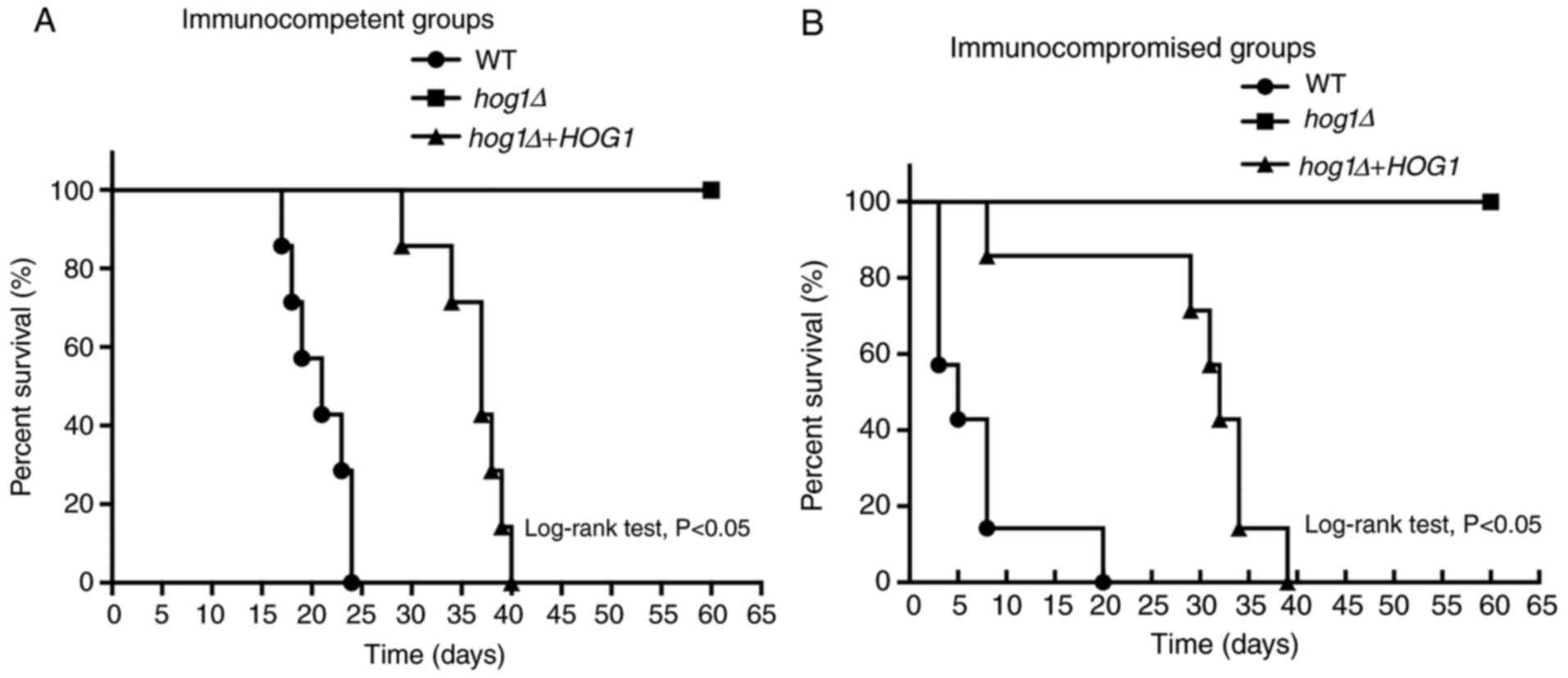
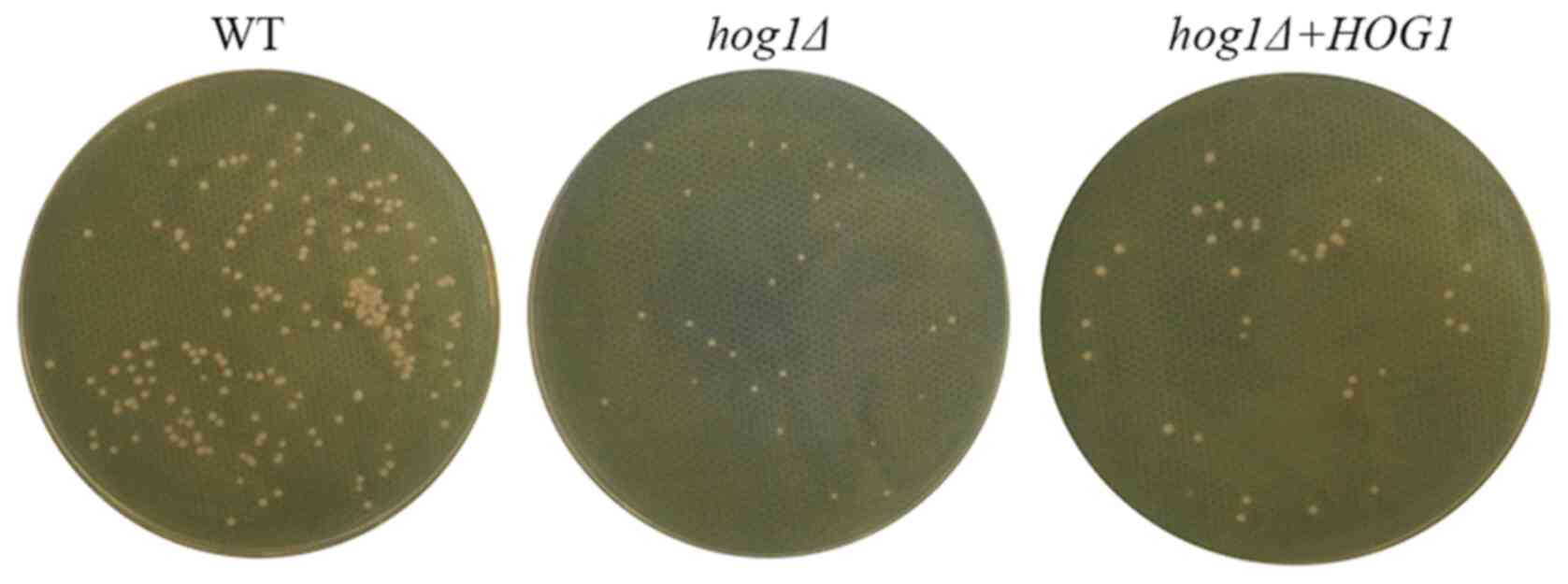
|
1
|
Heitman J: American Society for
Microbiology. (2011). ‘Cryptococcus: From human pathogen to model
yeast.’ Washington, DC, ASM Press.
|
|
2
|
Kamari A, Sepahvand A and Mohammadi R:
‘Isolation and molecular characterization of Cryptococcus
species isolated from pigeon nests and Eucalyptus trees’.
Curr Med Mycol. 3:20–25. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lin KH, Lin YP and Chung WH: Two-step
method for isolating Cryptococcus species complex from
environmental material using a new selective medium. Environ
Microbiol Rep. 11:651–658. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pakshir K, Fakhim H, Vaezi A, Meis JF,
Mahmoodi M, Zomorodian K, Javidnia J, Ansari S, Hagen F and Badali
H: Molecular epidemiology of environmental Cryptococcus
species isolates based on amplified fragment length polymorphism. J
Mycol Med. 28:599–605. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bandalizadeh Z, Shokohi T, Badali H,
Abastabar M, Babamahmoudi F, Davoodi L, Mardani M, Javanian M,
Cheraghmakani H, Sepidgar AA, et al: Molecular epidemiology and
antifungal susceptibility profiles of clinical Cryptococcus
neoformans/Cryptococcus gattii species complex. J Med
Microbiol. 69:72–81. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Herkert PF, Hagen F, Pinheiro RL, Muro MD,
Meis JF and Queiroz-Telles F: Ecoepidemiology of Cryptococcus
gattii in developing countries. J Fungi (Basel).
3(62)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kwon-Chung KJ, Fraser JA, Doering TL, Wang
Z, Janbon G, Idnurm A and Bahn YS: Cryptococcus neoformans
and Cryptococcus gattii, the etiologic agents of
cryptococcosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
4(a019760)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Olave MC, Vargas-Zambrano JC, Celis AM,
Castañeda E and González JM: Infective capacity of Cryptococcus
neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii in a human
astrocytoma cell line. Mycoses. 60:447–453. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pini G, Faggi E and Campisi E: Enzymatic
characterization of clinical and environmental Cryptococcus
neoformans strains isolated in Italy. Rev Iberoam Micol.
34:77–82. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Casadevall A, Coelho C, Cordero RJ,
Dragotakes Q, Jung E, Vij R and Wear MP: The capsule of
Cryptococcus neoformans. Virulence. 10:822–831.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oliveira DL, Freire-de-Lima CG, Nosanchuk
JD, Casadevall A, Rodrigues ML and Nimrichter L: Extracellular
vesicles from Cryptococcus neoformans modulate macrophage
functions. Infect Immun. 8:1601–1609. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee D, Jang EH, Lee M, Kim SW, Lee Y, Lee
KT and Bahn YS: Unraveling melanin biosynthesis and signaling
networks in Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio. 10:e02267–19.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Caza M and Kronstad JW: The cAMP/protein
kinase a pathway regulates virulence and adaptation to host
conditions in Cryptococcus neoformans. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 9(212)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
So YS, Lee DG, Idnurm A, Ianiri G and Bahn
YS: The TOR pathway plays pleiotropic roles in growth and stress
responses of the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans.
Genetics. 212:1241–1258. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fu C, Donadio N, Cardenas ME and Heitman
J: Dissecting the roles of the calcineurin pathway in unisexual
reproduction, stress responses, and virulence in Cryptococcus
deneoformans. Genetics. 208:639–653. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jung KW, Strain AK, Nielsen K, Jung KH and
Bahn YS: Two cation transporters Ena1 and Nha1 cooperatively
modulate ion homeostasis, antifungal drug resistance, and virulence
of Cryptococcus neoformans via the HOG pathway. Fungal Genet
Biol. 49:332–345. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meyers GL, Jung KW, Bang S, Kim J, Kim S,
Hong J, Cheong E, Kim KH and Bahn YS: The water channel protein
aquaporin 1 regulates cellular metabolism and competitive fitness
in a global fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. Environ
Microbiol Rep. 9:268–278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
So YS, Jang J, Park G, Xu J, Olszewski MA
and Bahn YS: Sho1 and Msb2 play complementary but distinct roles in
stress responses, sexual differentiation, and pathogenicity of
Cryptococcus neoformans. Front Microbiol.
9(2958)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bahn YS: Master and commander in fungal
pathogens: The two-component system and the HOG signaling pathway.
Eukaryot Cell. 7:2017–2036. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hoang LMN, Maguire JA, Doyle P, Fyfe M and
Roscoe DL: Cryptococcus neoformans infections at vancouver
hospital and health sciences centre (1997-2002): Epidemiology,
microbiology and histopathology. J Med Microbiol. 53:935–940.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nascimento E, Vitali LH, Kress MR and
Martinez R: Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii
isolates from both HIV-infected and uninfected patients: Antifungal
susceptibility and outcome of cryptococcal disease. Rev Inst Med
Trop Sao Paulo. 59(e49)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Farrer RA, Giamberardino C,
Sakthikumar S, Jones A, Yang T, Tenor JL, Wagih O, Van Wyk M,
Govender NP, et al: Microevolution of serial clinical isolates of
Cryptococcus neoformansvar grubii and C. gattii.
mBio. 8:e00166–17. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sang J, Yang Y, Fan Y, Wang G, Yi J, Fang
W, Pan W, Xu J and Liao W: Isolated iliac cryptococcosis in an
immunocompetent patient. PLoS Negl Trop Dis.
12(e0006206)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ho EC, Donaldson ME and Saville BJ:
Detection of antisense RNA transcripts by strand-specific RT-PCR.
Methods Mol Biol. 630:125–138. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Meng Y, Zhang C, Yi J, Zhou Z, Fa Z, Zhao
J, Yang Y, Fang W, Wang Y and Liao WQ: Deubiquitinase Ubp5 is
required for the growth and pathogenicity of Cryptococcus
gattii. PLoS One. 11(e0153219)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lin X, Chacko N, Wang L and Pavuluri Y:
Generation of stable mutants and targeted gene deletion strains in
Cryptococcus neoformans through electroporation. Med Mycol.
53:225–234. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory
Standards: Reference method for broth dilution antifungal
susceptibility testing of yeasts. Approved standard NCCLS document
M27-A. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne,
PA, 1997.
|
|
28
|
Liu TB and Xue C: Fbp1-mediated
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway controls Cryptococcus
neoformans virulence by regulating fungal intracellular growth
in macrophages. Infect Immun. 82:557–568. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Upadhya R, Kim H, Jung KW, Park G, Lam W,
Lodge JK and Bahn YS: Sulphiredoxin plays peroxiredoxin-dependent
and -independent roles via the HOG signalling pathway in
Cryptococcus neoformans and contributes to fungal virulence.
Mol Microbiol. 90:630–648. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Toplis B, Bosch C, Schwartz IS, Kenyon C,
Boekhout T, Perfect JR and Botha A: The virulence factor urease and
its unexplored role in the metabolism of Cryptococcus
neoformans. FEMS Yeast Res. 20(foaa031)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fang W, Fa Z and Liao W: Epidemiology of
Cryptococcus and Cryptococcosis in China. Fungal
Genet Biol. 78:7–15. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Acheson ES, Galanis E, Bartlett K, Mak S
and Klinkenberg B: Searching for clues for eighteen years:
Deciphering the ecological determinants of Cryptococcus
gattii on Vancouver Island, British Columbia. Med Mycol.
6:129–144. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Firacative C, Torres G, Meyer W and
Escandón P: Clonal dispersal of Cryptococcus gattii VGII in
an endemic region of Cryptococcosis in Colombia. J Fungi
(Basel). 5(32)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Day AM, McNiff MM, da Silva Dantas A, Gow
NA and Quinn J: Hog1 regulates stress tolerance and virulence in
the emerging fungal pathogen Candida auris. mSphere. 3:e00506–18.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kojima K, Bahn YS and Heitman J:
Calcineurin, Mpk1 and Hog1 MAPK pathways independently control
fludioxonil antifungal sensitivity in Cryptococcus
neoformans. Microbiology (Reading). 152:591–604.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Guirao-Abad JP, Sánchez-Fresneda R, Román
E, Pla J, Argüelles JC and Alonso-Monge R: The MAPK Hog1 mediates
the response to amphotericin B in Candida albicans. Fungal
Genet Biol. 136(103302)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shiraishi K, Hioki T, Habata A, Yurimoto H
and Sakai Y: Yeast Hog1 proteins are sequestered in stress granules
during high-temperature stress. J Cell Sci.
131(jcs209114)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sharmeen N, Sulea T, Whiteway M and Wu C:
The adaptor protein Ste50 directly modulates yeast MAPK signaling
specificity through differential connections of its RA domain. Mol
Biol Cell. 30:794–807. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Petelenz-Kurdziel E, Kuehn C, Nordlander
B, Klein D, Hong KK, Jacobson T, Dahl P, Schaber J, Nielsen J,
Hohmann S and Klipp E: Quantitative analysis of glycerol
accumulation, glycolysis and growth under hyper osmotic stress.
PLoS Comput Biol. 9(e1003084)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ko YJ, Yu YM, Kim GB, Lee GW, Maeng PJ,
Kim S, Floyd A, Heitman J and Bahn YS: Remodeling of global
transcription patterns of Cryptococcus neoformans genes
mediated by the stress-activated HOG signaling pathways. Eukaryot
Cell. 8:1197–1217. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Geddes JM, Caza M, Croll D, Stoynov N,
Foster LJ and Kronstad JW: Analysis of the protein kinase
a-regulated proteome of Cryptococcus neoformans identifies a
role for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in capsule formation.
mBio. 7:e01862–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huston SM, Ngamskulrungroj P, Xiang RF,
Ogbomo H, Stack D, Li SS, Timm-McCann M, Kyei SK, Oykhman P,
Kwon-Chung KJ and Mody CH: Cryptococcus gattii capsule
blocks surface recognition required for dendritic cell maturation
independent of internalization and antigen processing. J Immunol.
196:1259–1271. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Maybruck BT, Lam WC, Specht CA, Ilagan MX,
Donlin MJ and Lodge JK: The aminoalkylindole BML-190 negatively
regulates chitosan synthesis via the Cyclic AMP/protein kinase A1
pathway in Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio. 10:e02264–19.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bruni GO, Battle B, Kelly B, Zhang Z and
Wang P: Comparative proteomic analysis of Gib2 validating its
adaptor function in Cryptococcus neoformans. PLoS One.
12(e0180243)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fu MS, Coelho C, De Leon-Rodriguez CM,
Rossi DC, Camacho E, Jung EH, Kulkarni M and Casadevall A:
Cryptococcus neoformans urease affects the outcome of
intracellular pathogenesis by modulating phagolysosomal pH. PLoS
Pathog. 14(e1007144)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Squizani ED, Oliveira NK, Reuwsaat JC,
Marques BM, Lopes W, Gerber AL, de Vasconcelos AT, Lev S,
Djordjevic JT, Schrank A, et al: Cryptococcal dissemination to the
central nervous system requires the vacuolar calcium transporter
Pmc1. Cell Microbiol: Feb 20, 2018 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
47
|
Kronstad J, Saikia S, Nielson ED,
Kretschmer M, Jung W, Hu G, Geddes JM, Griffiths EJ, Choi J,
Cadieux B, et al: Adaptation of Cryptococcus neoformans to
mammalian hosts: Integrated regulation of metabolism and virulence.
Eukaryot Cell. 11:109–118. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Do E, Park M, Hu G, Caza M, Kronstad JW
and Jung WH: The lysine biosynthetic enzyme Lys4 influences iron
metabolism, mitochondrial function and virulence in Cryptococcus
neoformans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 77:706–711.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chang AL, Kang Y and Doering TL: Cdk8 and
Ssn801 regulate oxidative stress resistance and virulence in
Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio. 10:e02818–18. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|