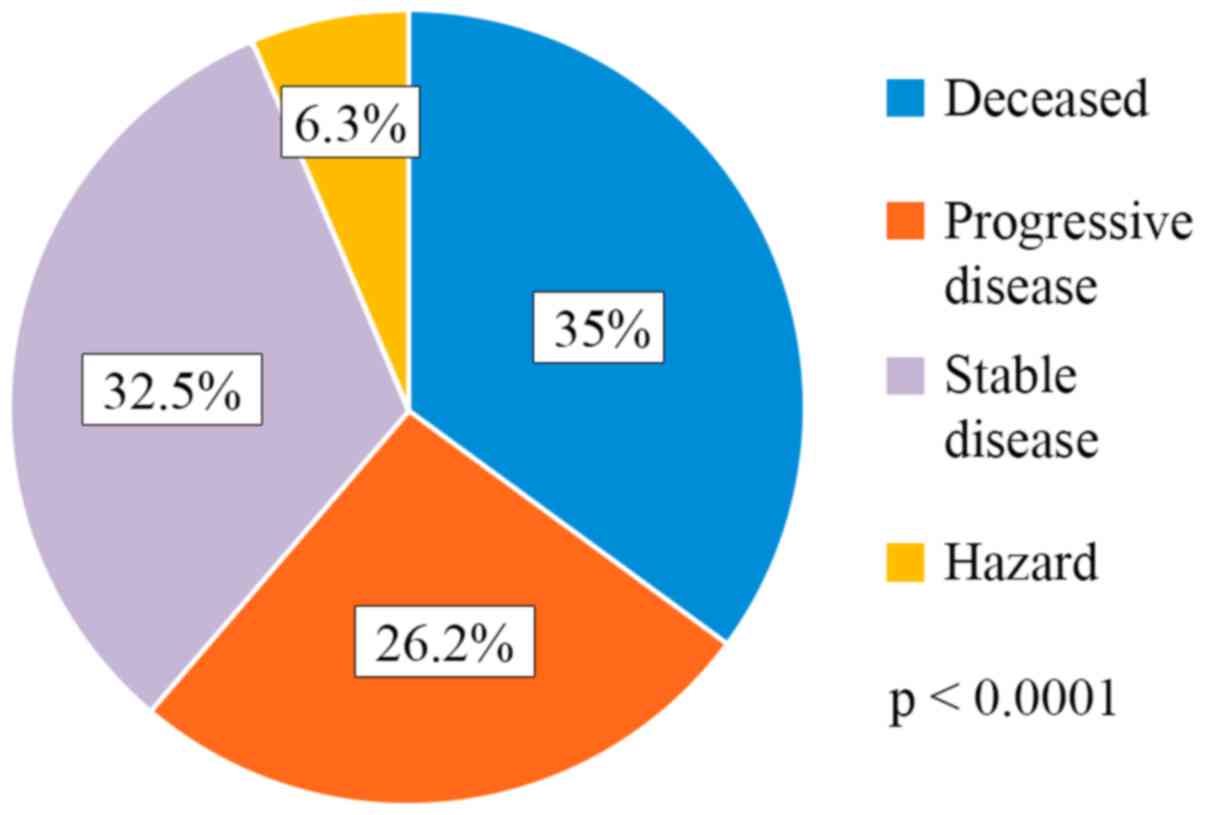
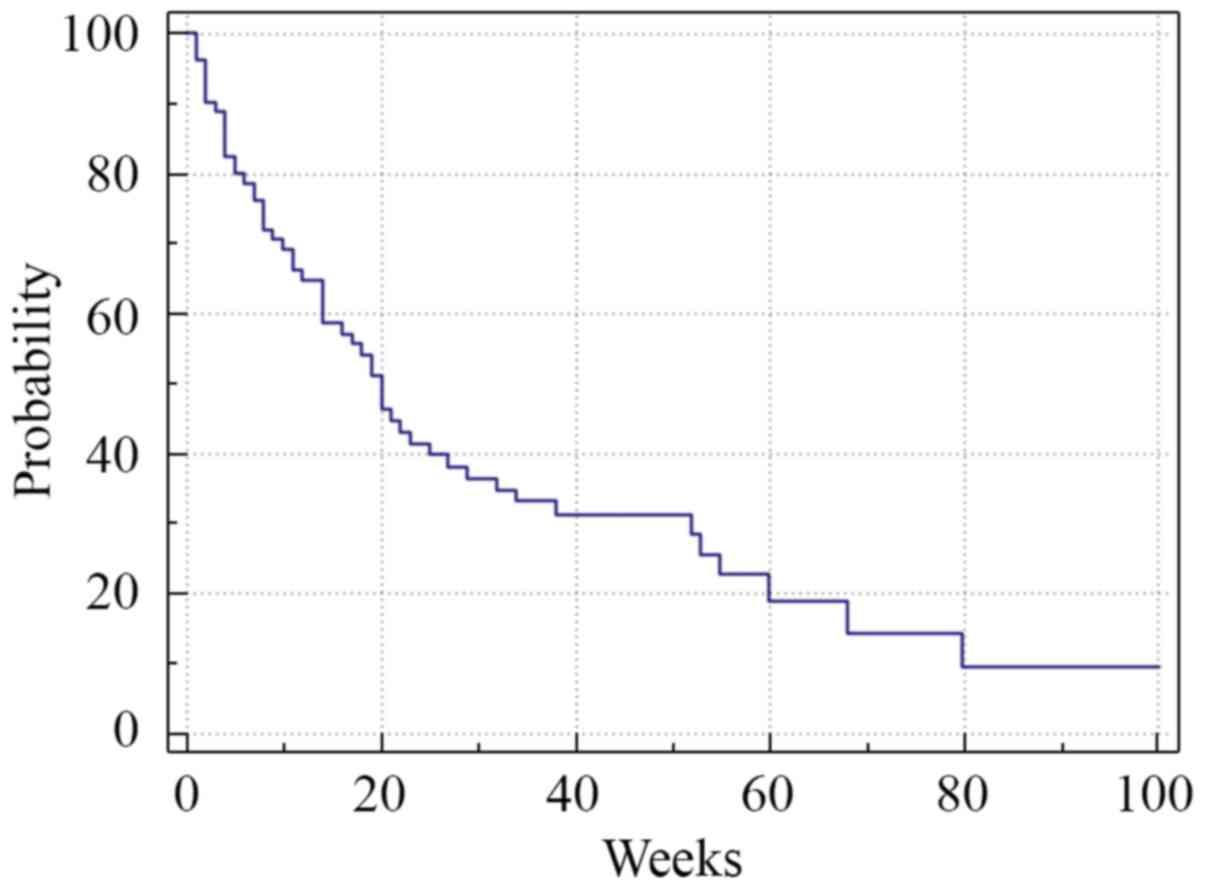
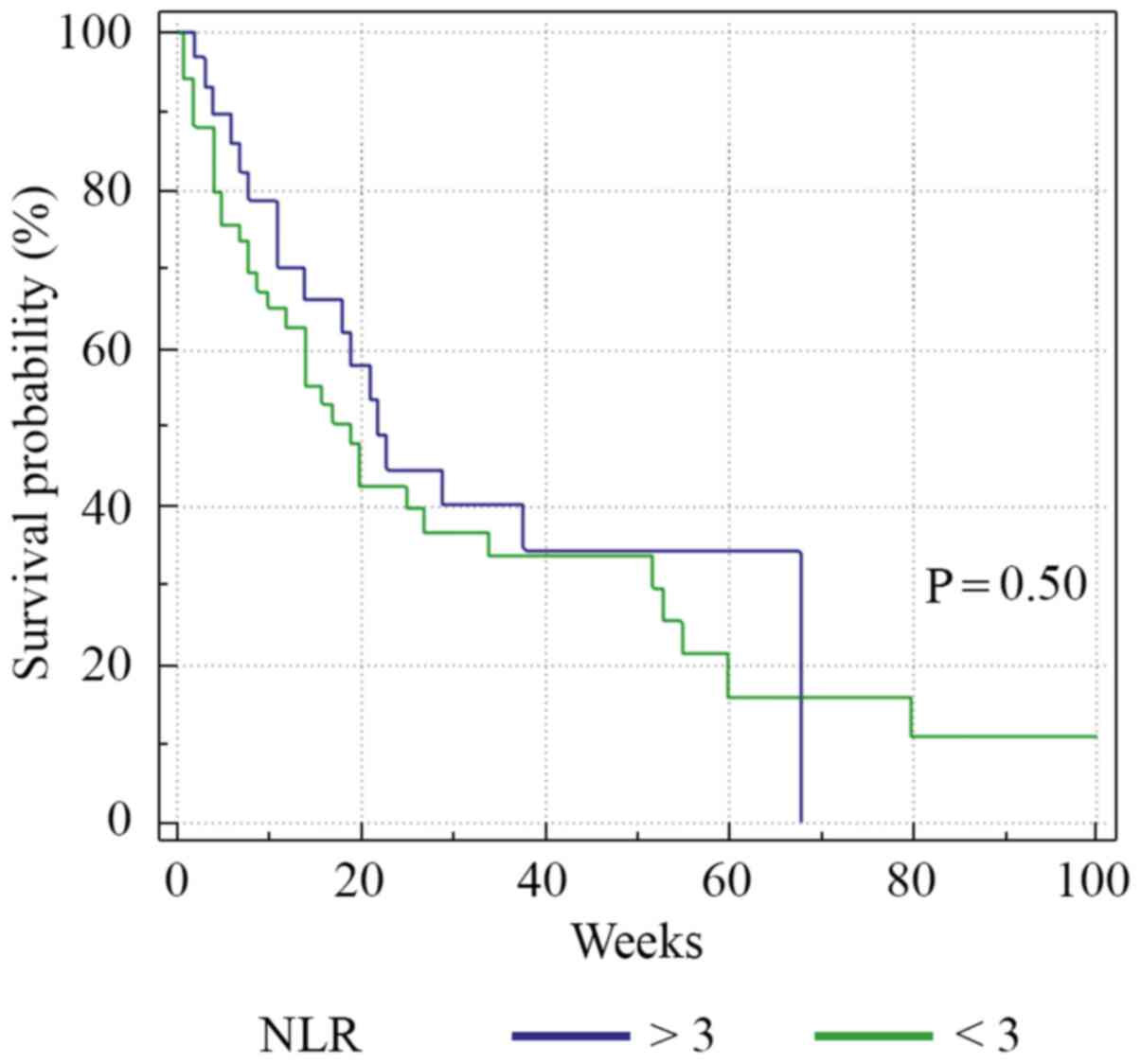
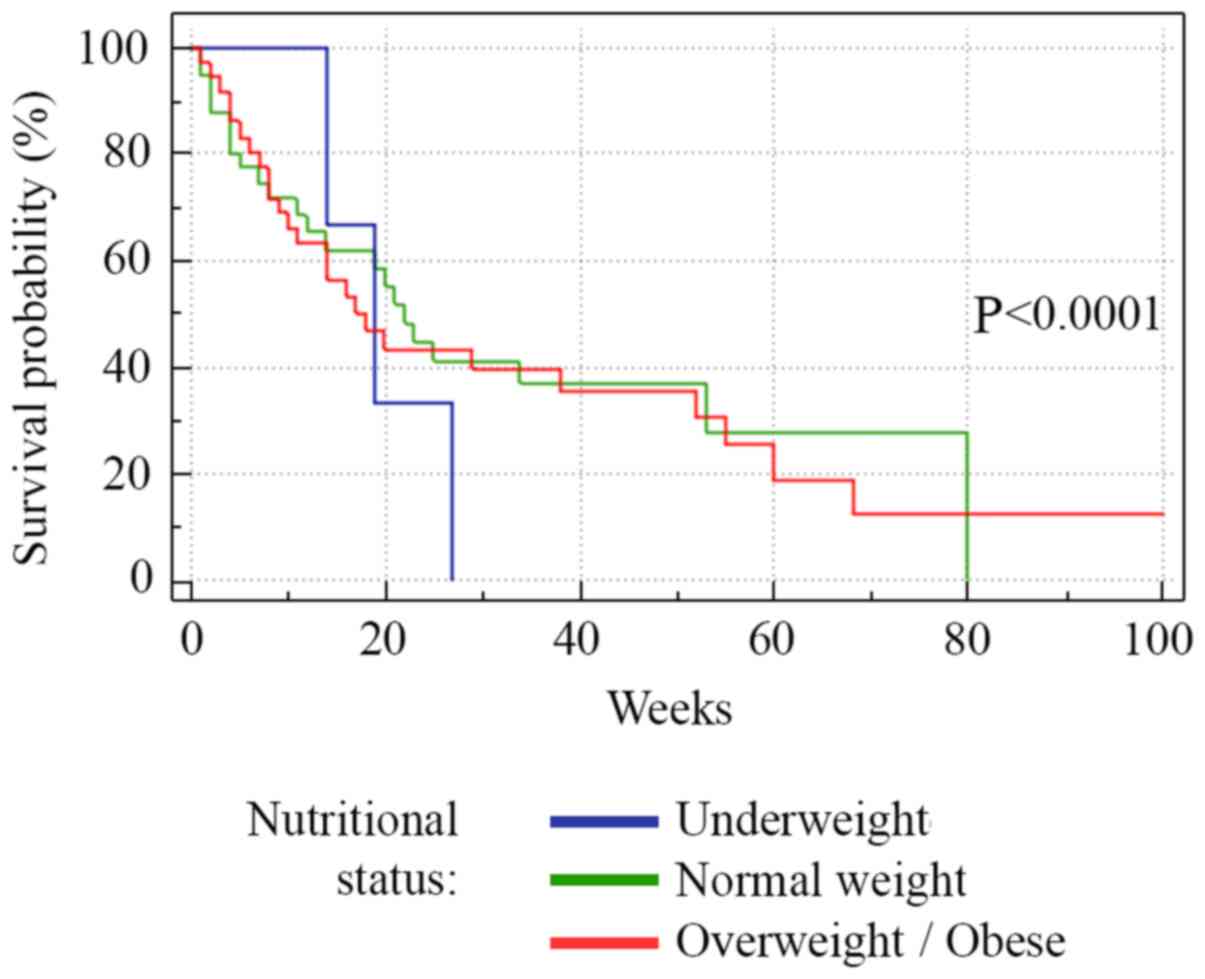
|
1
|
World Health Organization. Lung cancer.
Available at: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx.
Accessed June 4, 2020.
|
|
2
|
Inamura K: Lung cancer: Understanding its
molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO classification. Front Oncol.
7(193)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Onoi K, Chihara Y, Uchino J, Shimamoto T,
Morimoto Y, Iwasaku M, Kaneko Y, Yamada T and Takayama K: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors for lung cancer treatment: A review. J Clin
Med. 9(1362)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Malhotra J, Jabbour SK and Aisner J:
Current state of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 6:196–211. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Han F, Liu Y, Cheng S, Sun Z, Sheng C, Sun
X, Shang X, Tian W, Wang X, Li J, et al: Diagnosis and survival
values of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and red blood cell
distribution width (RDW) in esophageal cancer. Clin Chim Acta.
488:150–158. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B,
Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G,
Knox JJ, Tran B, et al: Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 106(dju124)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Woodall MJ, Neumann S, Campbell K,
Pattison ST and Young SL: The effects of obesity on anti-cancer
immunity and cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel).
12(1230)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cortellini A, Bersanelli M, Buti S,
Cannita K, Santini D, Perrone F, Giusti R, Tiseo M, Michiara M, Di
Marino P, et al: A multicenter study of body mass index in cancer
patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors:
When overweight becomes favorable. J Immunother Cancer.
7(57)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Naik GS, Waikar SS, Johnson AE, Buchbinder
EI, Haq R, Hodi RS, Schoenfeld JD and Ott PA: Complex
inter-relationship of body mass index, sex and serum creatinine on
survival: Exploring the obesity paradox in melanoma patients
treated with checkpoint inhibition. J Immunother Cancer.
7(89)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
McQuade JL, Daniel CR, Hess KR, Mak C,
Wang DY, Rai RR, Park JJ, Haydu LE, Spencer C, Wongchenko M, et al:
Association of body-mass index and outcomes in patients with
metastatic melanoma treated with targeted therapy, immunotherapy,
or chemotherapy: A retrospective, multicohort analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 19:310–22. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ozyurek BA, Ozdemirel TS, Ozden SB,
Erdogan Y, Kaplan B and Kaplan T: Prognostic value of the
neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in lung cancer cases. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:1417–1421. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fouad TM, Kogawa T, Liu DD, Shen Y, Masuda
H, El-Zein R, Woodward WA, Chavez-MacGregor M, Alvarez RH, Arun B,
et al: Erratum: Overall survival differences between patients with
inflammatory and noninflammatory breast cancer presenting with
distant metastasis at diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
152:407–416. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Faur CI, Pop DL, Motoc AGM, Folescu R,
Grigoraş ML, Gurguş D, Zamfir CL, Iacob M, Vermeşan D, Deleanu BN,
et al: Large giant cell tumor of the posterior iliac bone-an
atypical location. A case report and literature review. Rom J
Morphol Embryol. 61:247–252. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS,
Horgan PG, McMillan DC and Clarke SJ: The systemic
inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in
patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:218–230.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hao S, Andersen M and Yu H: Detection of
immune suppressive neutrophils in peripheral blood samples of
cancer patients. Am J Blood Res. 3:239–245. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pillay J, Kamp VM, van Hoffen E, Visser T,
Tak T, Lammers JW, Ulfman LH, Leenen LP, Pickkers P and Koenderman
L: A subset of neutrophils in human systemic inflammation inhibits
T cell responses through mac-1. J Clin Invest. 122:327–336.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pillay J, Tak T, Kamp VM and Koenderman L:
Immune suppression by neutrophils and granulocytic myeloid-derived
suppressor cells: Similarities and differences. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:3813–3827. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Uribe-Querol E and Rosales C: Neutrophils
in cancer: Two sides of the same coin. J Immunol Res.
2015(983698)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cools-Lartigue J, Spicer J, Najmeh S and
Ferri L: Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer progression. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 71:4179–4194. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Galdiero MR, Garlanda C, Jaillon S, Marone
G and Mantovani A: Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in
tumor progression. J Cell Physiol. 228:1404–1412. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW,
Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS, Verstegen NJ, Ciampricotti M,
Hawinkels LJ, Jonkers J and de Visser KE: IL-17-producing γδ T
cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 522:345–348. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fridlender ZG, Albelda SM and Granot Z:
Promoting metastasis: Neutrophils and T cells join forces. Cell
Res. 25:765–766. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, Daemen T
and Nijman HW: The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating
lymphocytes in cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J
Cancer. 105:93–103. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sarraf KM, Belcher E, Raevsky E, Nicholson
AG, Goldstraw P and Lim E: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and its
association with survival after complete resection in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 137:425–428.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Geng Y, Shao Y, He W, Hu W, Xu Y, Chen J,
Wu C and Jiang J: Prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
in lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:1560–1571. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zeng DQ, Yu YF, Ou QY, Li XY, Zhong RZ,
Xie CM and Hu QG: Prognostic and predictive value of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for clinical therapeutic research in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
7:13765–13781. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bagley SJ, Kothari S, Aggarwal C, Bauml
JM, Alley EW, Evans TL, Kosteva JA, Ciunci CA, Gabriel PE, Thompson
JC, et al: Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker
of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 106:1–7. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ferrucci PF, Gandini S, Battaglia A,
Alfieri S, Di Giacomo AM, Giannarelli D, Cappellini GC, De Galitiis
F, Marchetti P, Amato G, et al: Baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio is associated with outcome of ipilimumab-treated metastatic
melanoma patients. Br J Cancer. 112:1904–1910. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Nakaya A, Kurata T, Yoshioka H, Takeyasu
Y, Niki M, Kibata K, Satsutani N, Ogata M, Miyara T and Nomura S:
Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte ratio as an early marker of outcomes in
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with
nivolumab. Int J Clin Oncol. 23:634–640. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wolin KY, Carson K and Colditz GA: Obesity
and cancer. Oncologist. 15:556–565. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
De Pergola G and Silvestris F: Obesity as
a major risk factor for cancer. J Obes. 2013(291546)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Reeves GK, Pirie K, Beral V, Green J,
Spencer E and Bull D: Million Women Study Collaboration. Cancer
incidence and mortality in relation to body mass index in the
million women study: Cohort study. BMJ. 335(1134)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vucenik I and Stains JP: Obesity and
cancer risk: Evidence, mechanisms, and recommendations. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1271:37–43. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tobias DK, Pan A, Jackson CL, O'Reilly EJ,
Ding EL, Willett WC, Manson JE and Hu FB: Body-Mass index and
mortality among adults with incident type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med.
370:233–244. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Andersen KK and Olsen TS: The obesity
paradox in stroke: Lower mortality and lower risk of readmission
for recurrent stroke in obese stroke patients. Int J Stroke.
10:99–104. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Curtis JP, Selter JG, Wang Y, Rathore SS,
Jovin IS, Jadbabaie F, Kosiborod M, Portnay EL, Sokol SI, Bader F,
et al: The obesity paradox: Body mass index and outcomes in
patients with heart failure. Arch Intern Med. 168:55–61. 2005.2008.
PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Silva TH, Schilithz AO, Peres WAF and
Murad LB: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and nutritional status are
clinically useful in predicting prognosis in colorectal cancer
patients. Nutr Cancer. 72:1345–1354. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kichenadasse G, Miners JO, Mangoni AA,
Rowland A, Hopkins AM and Sorich MJ: Association between body mass
index and overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy
for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 6:512–518.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cortellini A, Bersanelli M, Santini D,
Buti S, Tiseo M, Cannita K, Perrone F, Giusti R, De Tursi M,
Zoratto F, et al: Another side of the association between body mass
index (BMI) and clinical outcomes of cancer patients receiving
programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/Programmed cell death-ligand
1 (PD-L1) checkpoint inhibitors: A multicentre analysis of
immune-related adverse events. Eur J Cancer. 128:17–26.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wallis CJD, Butaney M, Satkunasivam R,
Freedland SJ, Patel SP, Hamid O, Pal SK and Klaassen Z: Association
of patient sex with efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors and
overall survival in advanced cancers: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 5:529–536. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sagerup CMT, Småstuen M, Johannesen TB,
Helland A and Brustugun OT: Sex-Specific trends in lung cancer
incidence and survival: A population study of 40 118 cases. Thorax.
66:301–307. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|