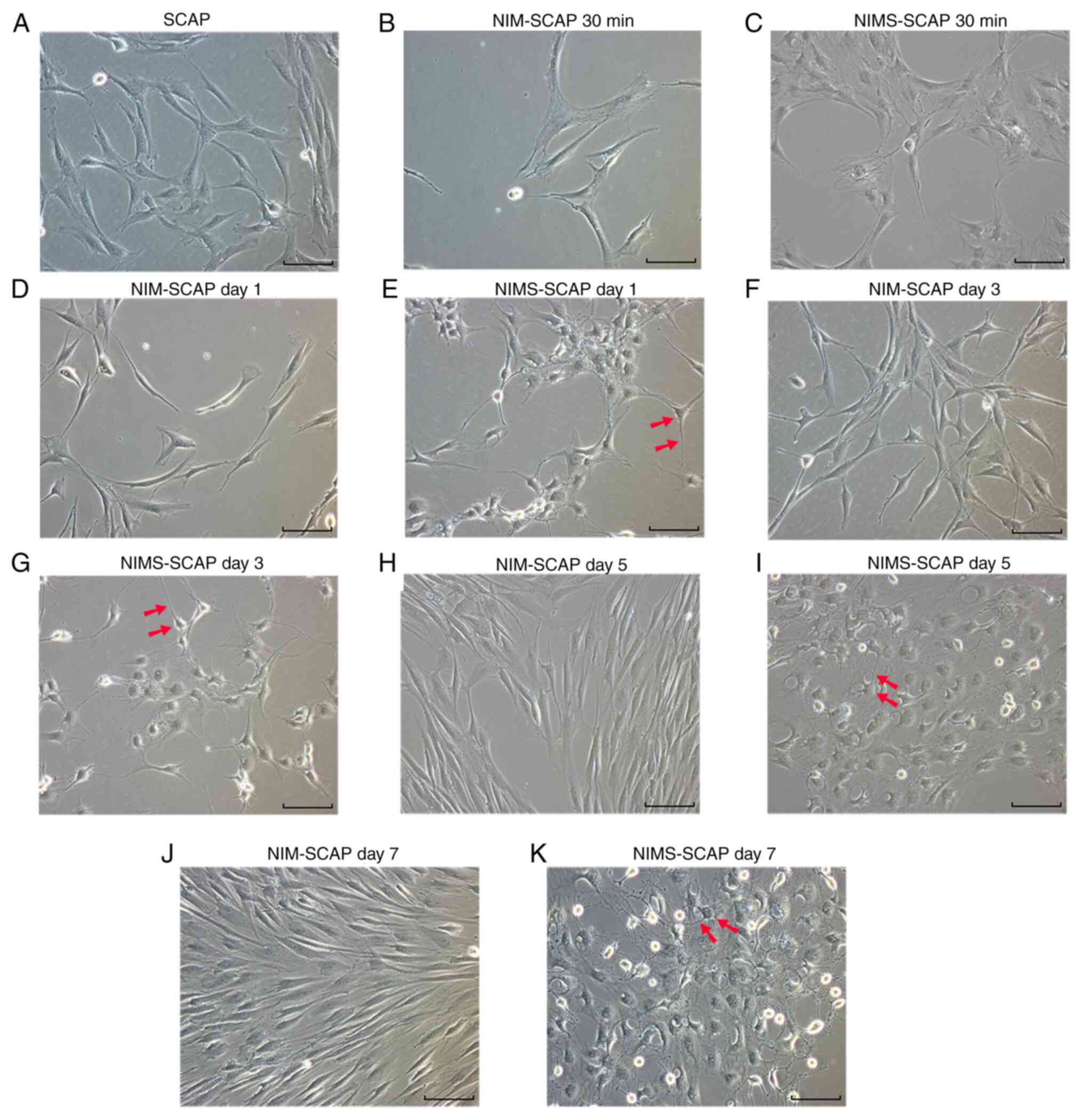
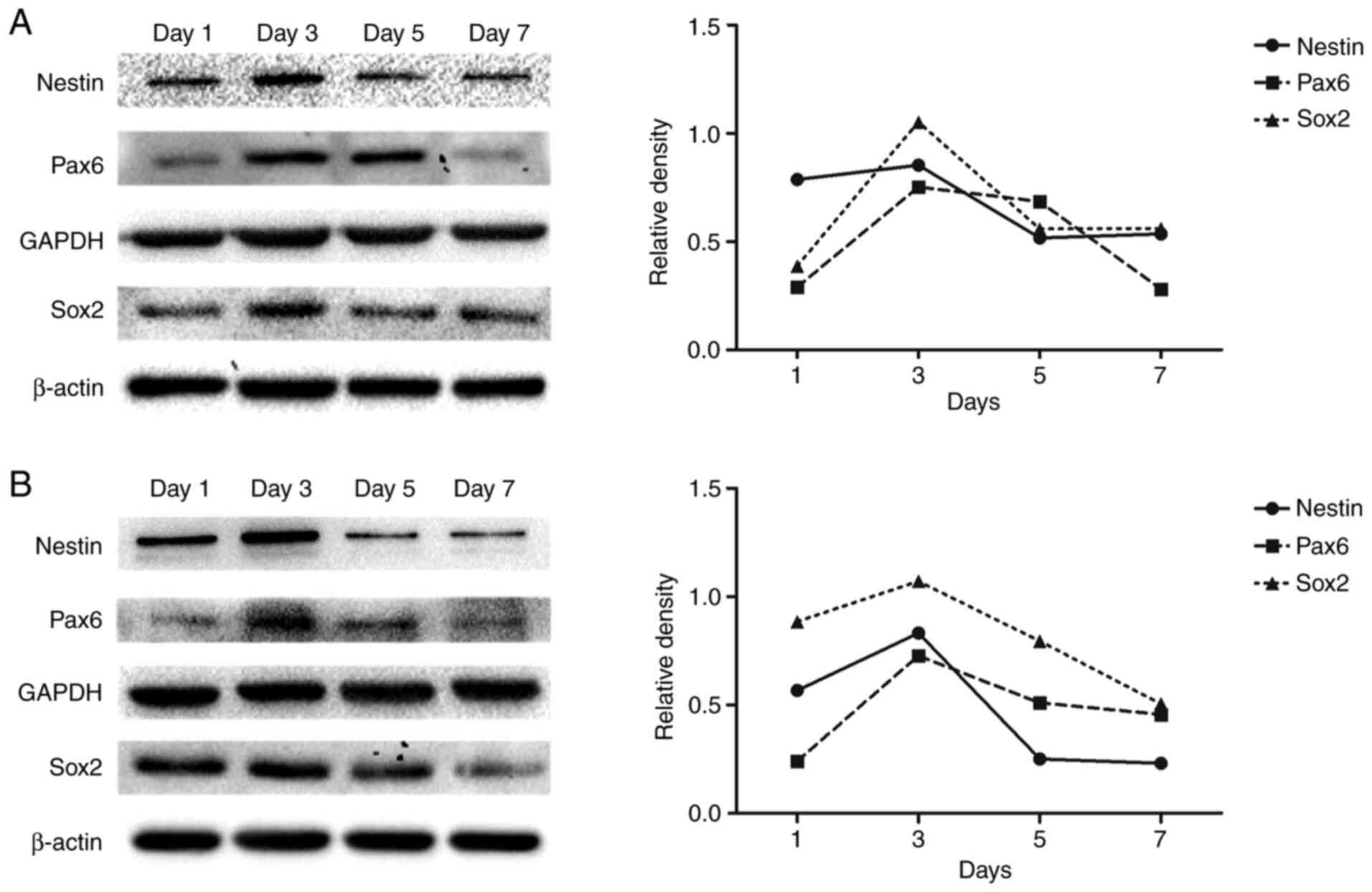
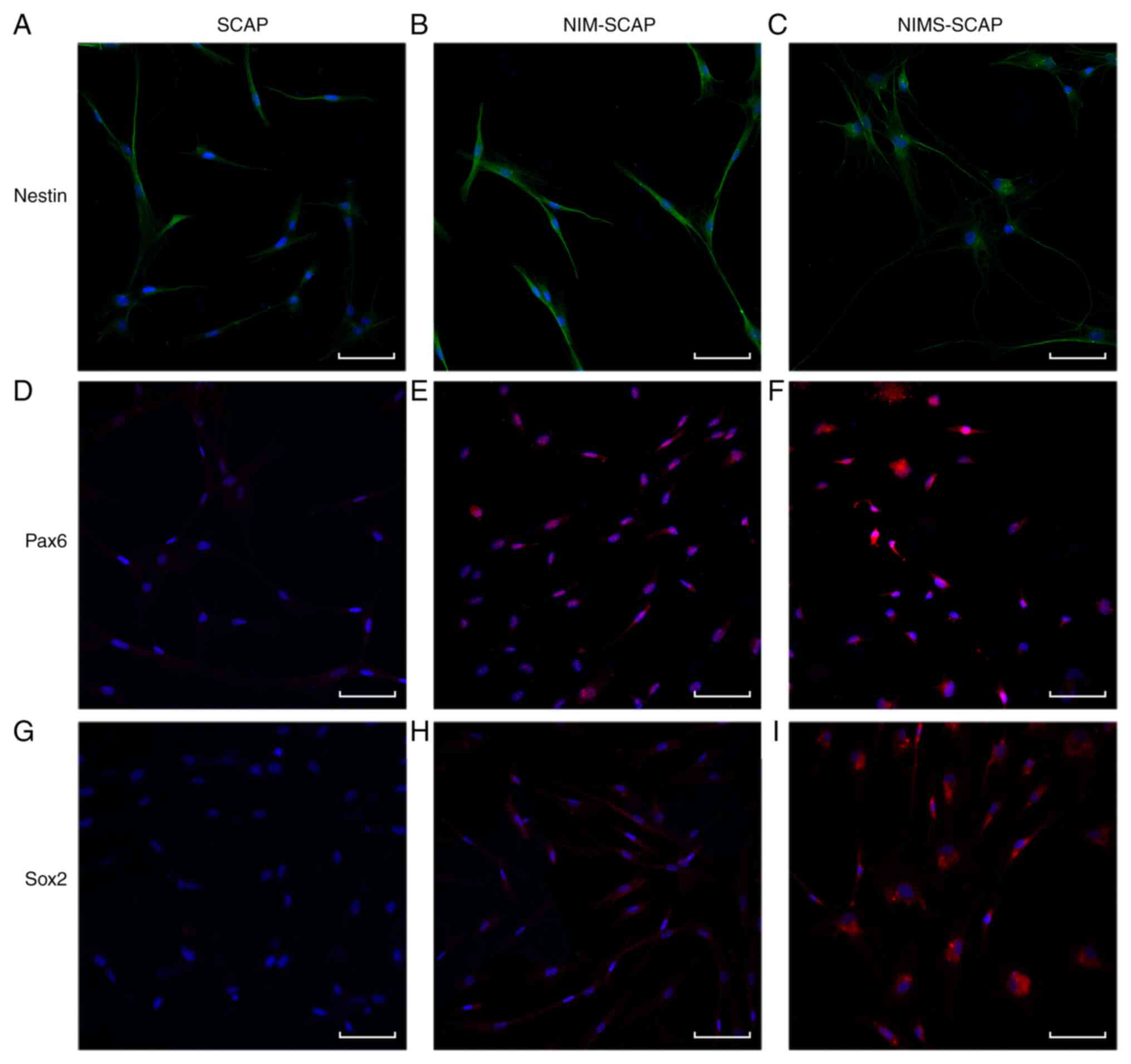
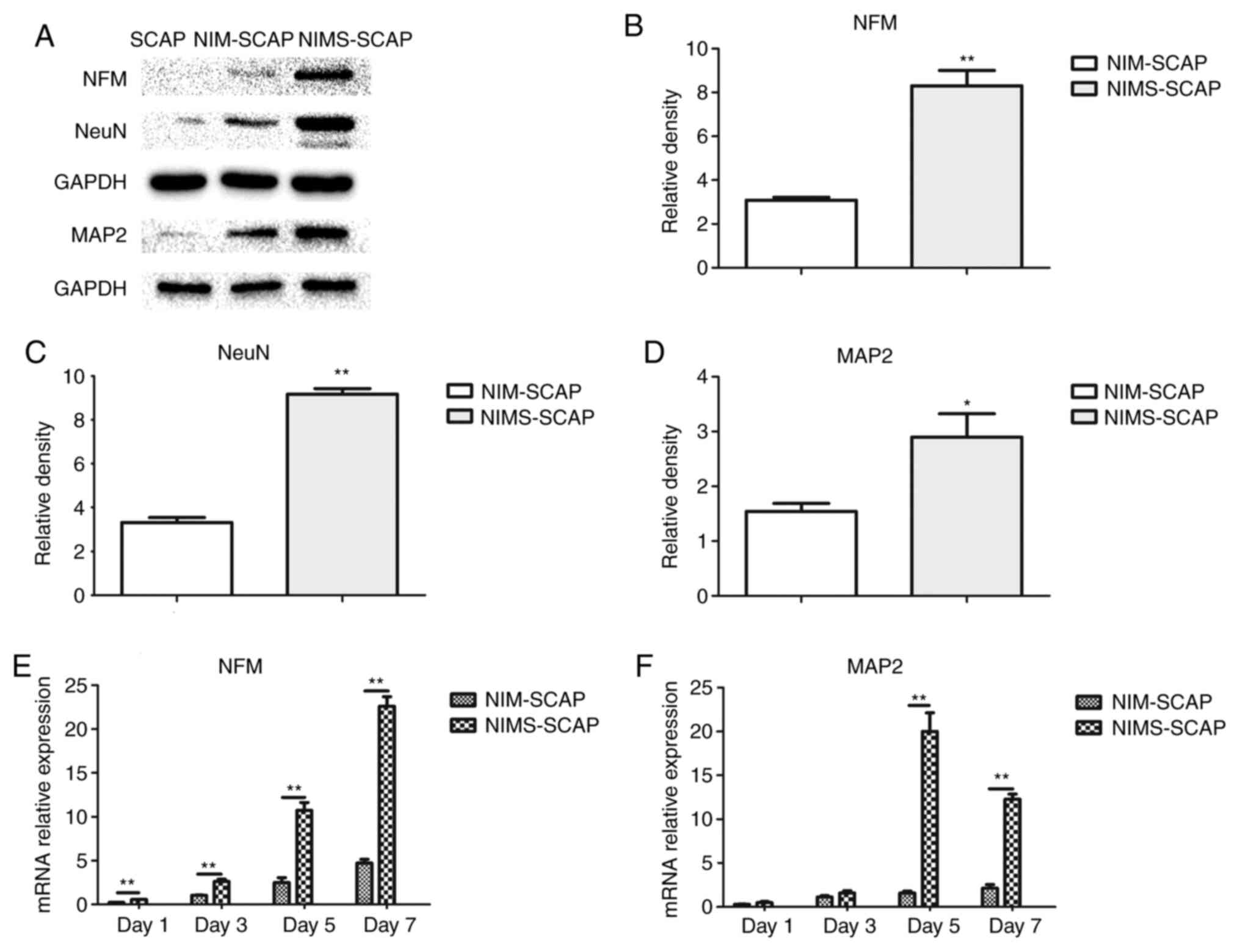
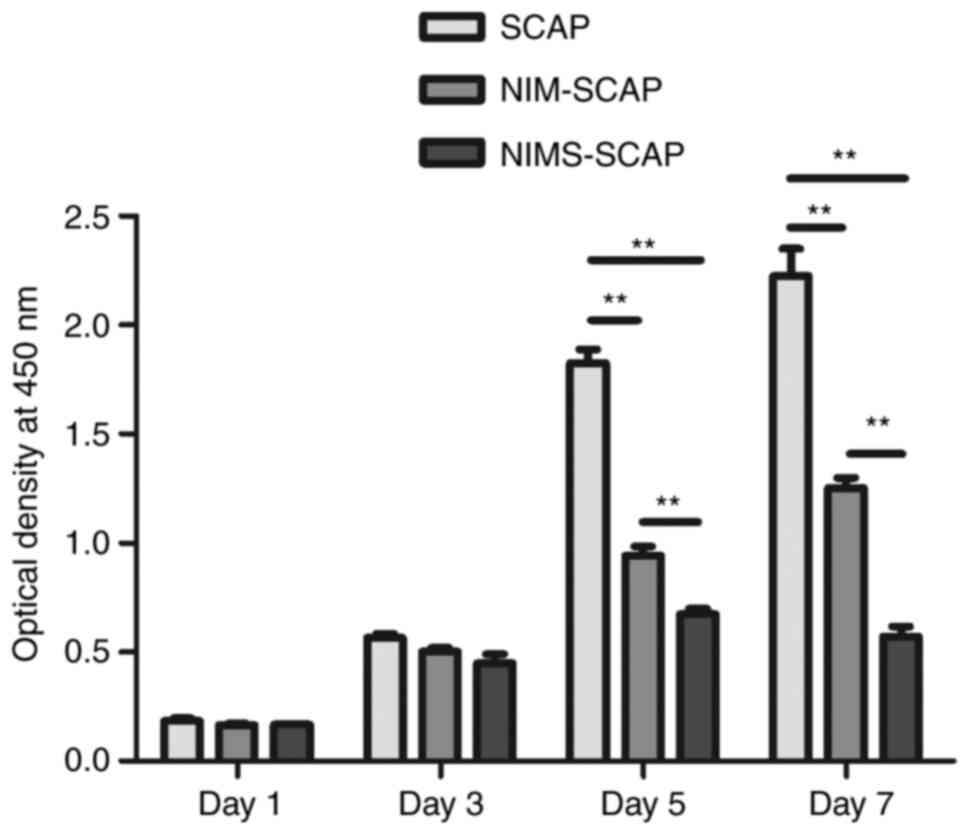
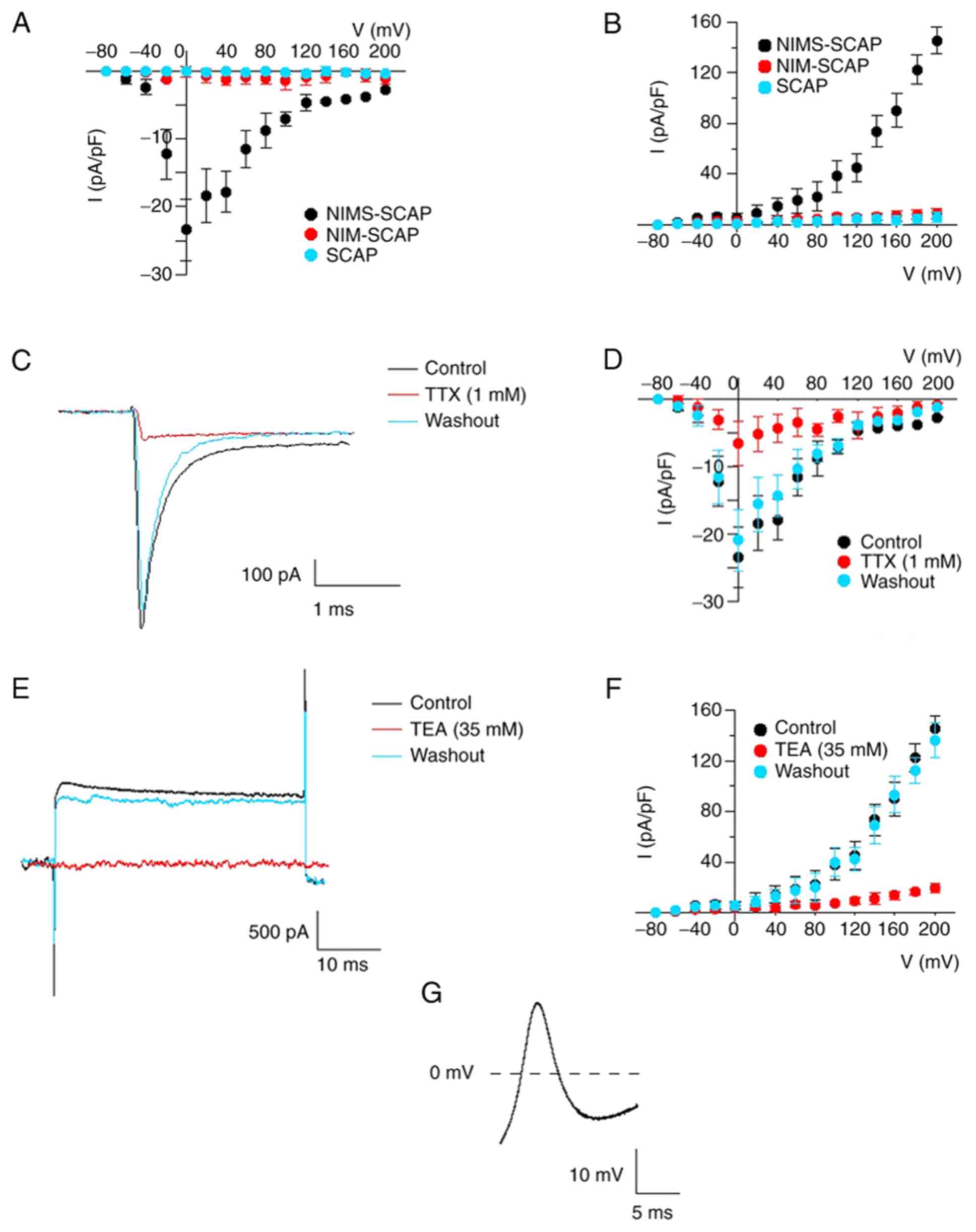
|
1
|
Wilkinson DA, Pandey AS, Thompson BG, Keep
RF, Hua Y and Xi G: Injury mechanisms in acute intracerebral
hemorrhage. Neuropharmacology. 134:240–248. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hurlbert RJ, Hadley MN, Walters BC, Aarabi
B, Dhall SS, Gelb DE, Rozzelle CJ, Ryken TC and Theodore N:
Pharmacological therapy for acute spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery.
72 (Suppl 2):S93–S105. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Panagopoulos GN, Megaloikonomos PD and
Mavrogenis AF: The present and future for peripheral nerve
regeneration. Orthopedics. 40:e141–e156. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
McComish SF and Caldwell MA: Generation of
defined neural populations from pluripotent stem cells. Philos
Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 373(20170214)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP,
Tomishima M, Sadelain M and Studer L: Highly efficient neural
conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD
signaling. Nat Biotechnol. 27:275–280. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Li ZW, Luo M, Li YJ and Zhang KQ:
Biological conduits combining bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
and extracellular matrix to treat long-segment sciatic nerve
defects. Neural Regen Res. 10:965–971. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhao H, Cheng L, Du X, Hou Y, Liu Y, Cui Z
and Nie L: Transplantation of cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor
transducted BMSCs in contusion spinal cord injury of rats:
Promotion of nerve regeneration by alleviating neuroinflammation.
Mol Neurobiol. 53:187–199. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Georgiou M, Golding JP, Loughlin AJ,
Kingham PJ and Phillips JB: Engineered neural tissue with aligned,
differentiated adipose-derived stem cells promotes peripheral nerve
regeneration across a critical sized defect in rat sciatic nerve.
Biomaterials. 3:242–251. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hsueh YY, Chang YJ, Huang TC, Fan SC, Wang
DH, Chen JJ, Wu CC and Lin SC: Functional recoveries of sciatic
nerve regeneration by combining chitosan-coated conduit and
neurosphere cells induced from adipose-derived stem cells.
Biomaterials. 35:2234–2244. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Parisi L and Manfredi E: Applicability of
tooth derived stem cells in neural regeneration. Neural Regen Res.
11:1704–1707. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lima RL, Holanda-Afonso RC, Moura-Neto V,
Bolognese AM, DosSantos MF and Souza MM: Human dental follicle
cells express embryonic, mesenchymal and neural stem cells markers.
Arch Oral Biol. 73:121–128. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Athanassiou-Papaefthymiou M, Papagerakis P
and Papagerakis S: Isolation and characterization of human adult
epithelial stem cells from the periodontal ligament. J Dent Res.
94:1591–1600. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yamagata M, Yamamoto A, Kako E, Kaneko N,
Matsubara K, Sakai K, Sawamoto K and Ueda M: Human dental
pulp-derived stem cells protect against hypoxic-ischemic brain
injury in neonatal mice. Stroke. 44:551–554. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shamir C, Venugopal C and Dhanushkodi A:
Dental pulp stem cells for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Neural Regen Res. 10:1910–1911. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang GT, Sonoyama W, Liu Y, Liu H, Wang S
and Shi S: The hidden treasure in apical papilla: The potential
role in pulp/dentin regeneration and bioroot engineering. J Endod.
34:645–651. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
De Berdt P, Vanacker J, Ucakar B, Elens L,
Diogenes A, Leprince JG, Deumens R and des Rieux A: Dental apical
papilla as therapy for spinal cord injury. J Dent Res.
94:1575–1581. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kolar MK, Itte VN, Kingham PJ, Novikov LN,
Wiberg M and Kelk P: The neurotrophic effects of different human
dental mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 7(12605)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hu W, Qiu B, Guan W, Wang Q, Wang M, Li W,
Gao L, Shen L, Huang Y, Xie G, et al: Direct conversion of normal
and Alzheimer's disease human fibroblasts into neuronal cells by
small molecules. Cell Stem Cell. 17:204–212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Heng BC, Jiang S, Yi B, Gong T, Lim LW and
Zhang C: Small molecules enhance neurogenic differentiation of
dental-derived adult stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 102:26–38.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alt E, Yan Y, Gehmert S, Song YH, Altman
A, Gehmert S, Vykoukal D and Bai X: Fibroblasts share mesenchymal
phenotypes with stem cells, but lack their differentiation and
colony-forming potential. Biol cell. 103:197–208. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ruparel NB, de Almeida JF, Henry MA and
Diogenes A: Characterization of a stem cell of apical papilla cell
line: Effect of passage on cellular phenotype. J Endod. 39:357–363.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li D, Zou XY, El-Ayachi I, Romero LO, Yu
Z, Iglesias-Linares A, Cordero-Morales JF and Huang GT: Human
dental pulp stem cells and gingival mesenchymal stem cells display
action potential capacity in vitro after neuronogenic
differentiation. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:67–81. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lai PL, Lin H, Chen SF, Yang SC, Hung KH,
Chang CF, Chang HY, Lu FL, Lee YH, Liu YC, et al: Efficient
generation of chemically induced mesenchymal stem cells from human
dermal fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 7(44534)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cheng L, Hu W, Qiu B, Zhao J, Yu Y, Guan
W, Wang M, Yang W and Pei G: Generation of neural progenitor cells
by chemical cocktails and hypoxia. Cell Res. 24:665–679.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheng L, Gao L, Guan W, Mao J, Hu W, Qiu
B, Zhao J, Yu Y and Pei G: Direct conversion of astrocytes into
neuronal cells by drug cocktail. Cell Res. 25:1269–1272.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fu Y, Huang C, Xu X, Gu H, Ye Y, Jiang C,
Qiu Z and Xie X: Direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts into
cardiomyocytes with chemical cocktails. Cell Res. 25:1013–1024.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sayed N, Wong WT, Ospino F, Meng S, Lee J,
Jha A, Dexheimer P, Aronow BJ and Cooke JP: Transdifferentiation of
human fibroblasts to endothelial cells: Role of innate immunity.
Circulation. 131:300–309. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xie M, Cao N and Ding S: Small molecules
for cell reprogramming and heart repair: Progress and perspective.
ACS Chem Biol. 9:34–44. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huangfu D, Maehr R, Guo W, Eijkelenboom A,
Snitow M, Chen AE and Melton DA: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells by defined factors is greatly improved by small-molecule
compounds. Nat Biotechnol. 26:795–797. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ladewig J, Mertens J, Kesavan J, Doerr J,
Poppe D, Glaue F, Herms S, Wernet P, Kögler G, Müller FJ, et al:
Small molecules enable highly efficient neuronal conversion of
human fibroblasts. Nat Methods. 9:575–578. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gafni O, Weinberger L, Mansour AA, Manor
YS, Chomsky E, Ben-Yosef D, Kalma Y, Viukov S, Maza I, Zviran A, et
al: Derivation of novel human ground state naive pluripotent stem
cells. Nature. 504:282–286. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
PLOS ONE Staff. Correction: Neurotrophic
requirements of human motor neurons defined using amplified and
purified stem cell-derived cultures. PLoS One.
10(e0119195)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu ML, Zang T, Zou Y, Chang JC, Gibson
JR, Huber KM and Zhang CL: Small molecules enable neurogenin 2 to
efficiently convert human fibroblasts into cholinergic neurons. Nat
Commun. 4(2183)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu S, Ambasudhan R, Sun W, Kim HJ,
Talantova M, Wang X, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Laurent T, Parker J, et al:
Small molecules enable OCT4-mediated direct reprogramming into
expandable human neural stem cells. Cell Res. 24:126–129.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Huo S, Fang Y, Zou T, Gu X, Tao Q
and Xu H: ROCK inhibitor Y27632 induced morphological shift and
enhanced neurite outgrowth-promoting property of olfactory
ensheathing cells via YAP-dependent up-regulation of L1-CAM. Front
Cell Neurosci. 12(489)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Zou T, Xue L, Yin ZQ, Huo S and Xu
H: TGF-β1 enhances phagocytic removal of neuron debris and neuronal
survival by olfactory ensheathing cells via integrin/MFG-E8
signaling pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci. 85:45–56. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bernal A and Arranz L: Nestin-expressing
progenitor cells: Function, identity and therapeutic implications.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:2177–2195. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sakayori N, Kikkawa T and Osumi N: Reduced
proliferation and excess astrogenesis of Pax6 heterozygous neural
stem/progenitor cells. Neurosci Res. 74:116–121. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Han DW, Tapia N, Hermann A, Hemmer K,
Höing S, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Zaehres H, Wu G, Frank S, Moritz S, et
al: Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by
defined factors. Cell Stem Cell. 10:465–472. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ichida JK, Blanchard J, Lam K, Son EY,
Chung JE, Egli D, Loh KM, Carter AC, Di Giorgio FP, Koszka K, et
al: A small-molecule inhibitor of TGF-beta signaling replaces sox2
in reprogramming by inducing nanog. Cell Stem Cell. 5:491–503.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li W, Zhou H, Abujarour R, Zhu S, Young
Joo J, Lin T, Hao E, Schöler HR, Hayek A and Ding S: Generation of
human-induced pluripotent stem cells in the absence of exogenous
Sox2. Stem Cells. 27:2992–3000. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Maherali N and Hochedlinger K: Tgfbeta
signal inhibition cooperates in the induction of iPSCs and replaces
Sox2 and cMyc. Curr Biol. 19:1718–1723. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Steinschneider R, Delmas P, Nedelec J,
Gola M, Bernard D and Boucraut J: Appearance of neurofilament
subunit epitopes correlates with electrophysiological maturation in
cortical embryonic neurons cocultured with mature astrocytes. Dev
Brain Res. 95:15–27. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Weyer A and Schilling K: Developmental and
cell type-specific expression of the neuronal marker NeuN in the
murine cerebellum. J Neurosci Res. 73:400–409. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Soltani MH, Pichardo R, Song Z, Sangha N,
Camacho F, Satyamoorthy K, Sangueza OP and Setaluri V:
Microtubule-associated protein 2, a marker of neuronal
differentiation, induces mitotic defects, inhibits growth of
melanoma cells, and predicts metastatic potential of cutaneous
melanoma. Am J Pathol. 166:1841–1850. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pfisterer U, Ek F, Lang S, Soneji S,
Olsson R and Parmar M: Small molecules increase direct neural
conversion of human fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 6(38290)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gervois P, Struys T, Hilkens P, Bronckaers
A, Ratajczak J, Politis C, Brône B, Lambrichts I and Martens W:
Neurogenic maturation of human dental pulp stem cells following
neurosphere generation induces morphological and
electrophysiological characteristics of functional neurons. Stem
Cells Dev. 24:296–311. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang Q, Nguyen PD, Shi S, Burrell JC, Xu
Q, Cullen KD and Le AD: Neural crest stem-like cells
non-genetically induced from human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem
cells promote facial nerve regeneration in rats. Mol Neurobiol.
55:6965–6983. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|