|
1
|
Barnett R: Parkinson's disease. Lancet.
387(217)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Toulouse A and Sullivan AM: Progress in
Parkinson's disease-where do we stand? Prog Neurobiol. 85:376–392.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schapira AH: Molecular and clinical
pathways to neuroprotection of dopaminergic drugs in Parkinson
disease. Neurology. 72 (Suppl 7):S44–S50. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Beal MF: Bioenergetic approaches for
neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 53 (Suppl
3):S39–S48. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Olanow CW and Schapira AH: Therapeutic
prospects for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. 74:337–347.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schapira AH: Treatment options in the
modern management of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 64:1083–1088.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ellis JM and Reddy P: Effects of Panax
ginseng on quality of life. Ann Pharmacother. 36:375–379.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rausch WD, Liu S, Gille G and Radad K:
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars).
66:369–375. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ong WY, Farooqui T, Koh HL, Farooqui AA
and Ling EA: Protective effects of ginseng on neurological
disorders. Front Aging Neurosci. 7(129)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
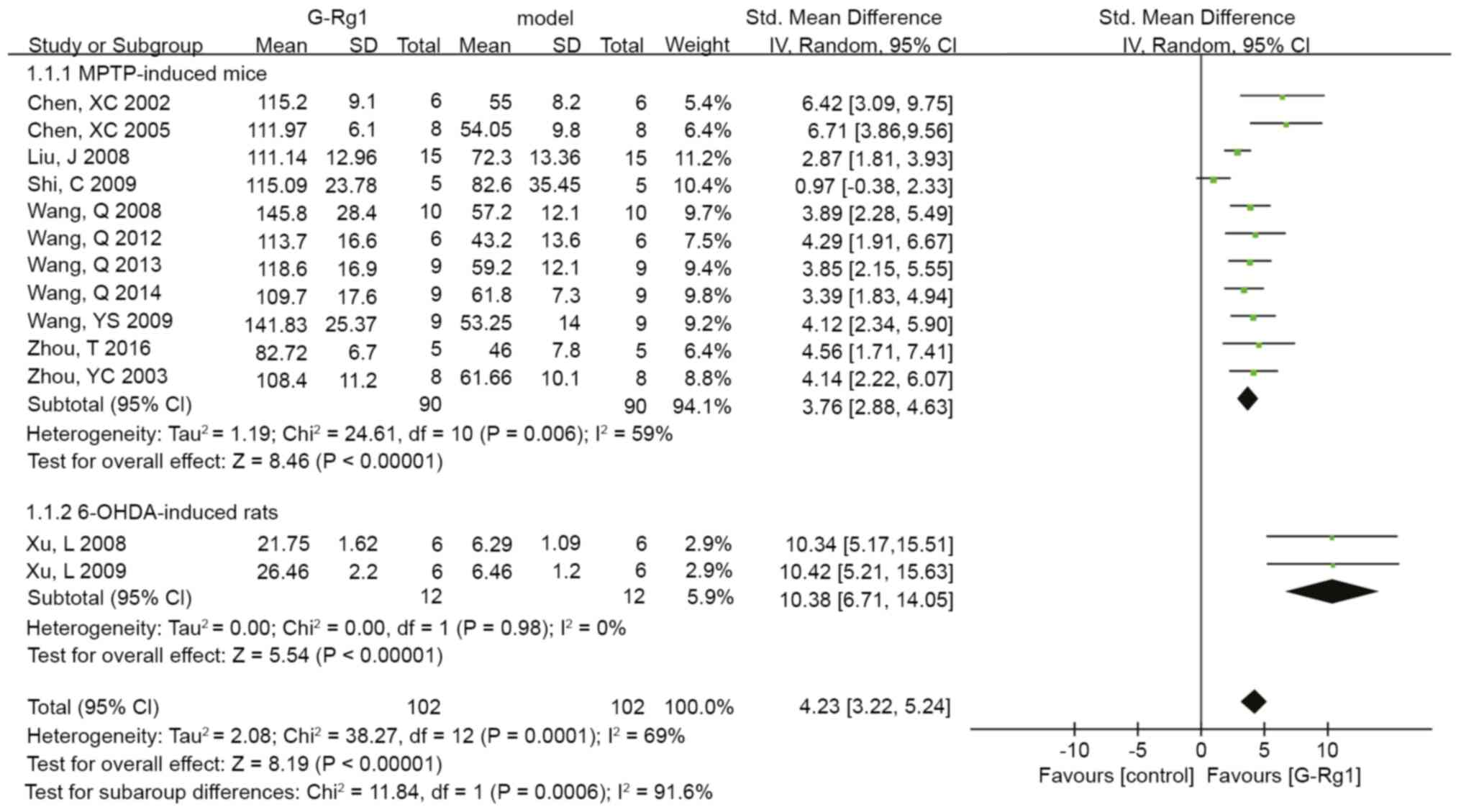
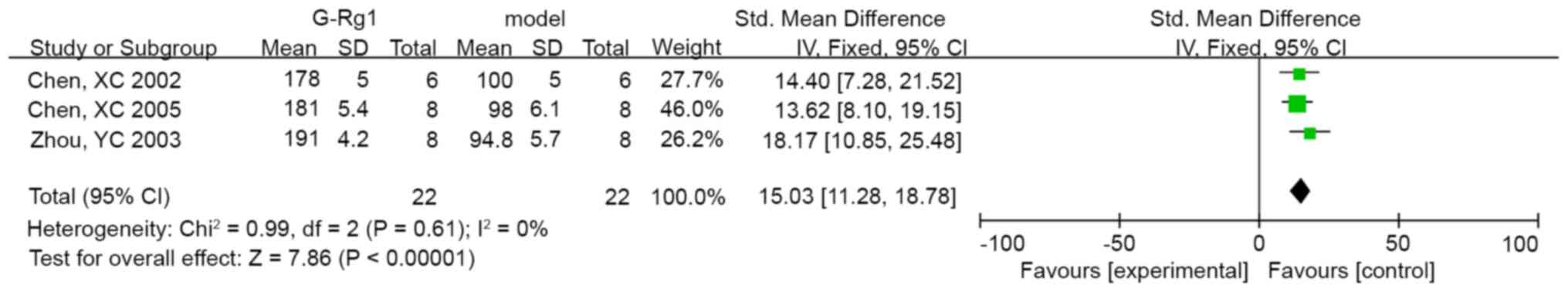
Chen XC, Fang F, Zhu YG, Chen LM, Zhou YC
and Chen Y: Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on
MPP+-induced apoptosis in SHSY5Y cells. J Neural Transm
(Vienna). 110:835–845. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Radad K, Gille G, Moldzio R, Saito H,
Ishige K and Rausch WD: Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 effects on
survival and neurite growth of MPP+-affected
mesencephalic dopaminergic cells. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
111:37–45. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Radad K, Gille G, Moldzio R, Saito H and
Rausch WD: Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 effects on mesencephalic
dopaminergic cells stressed with glutamate. Brain Res. 1021:41–53.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen XC, Chen Y, Zhu YG, Fang F and Chen
LM: Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 against MPTP-induced
apoptosis in mouse substantia nigra neurons. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
23:829–834. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
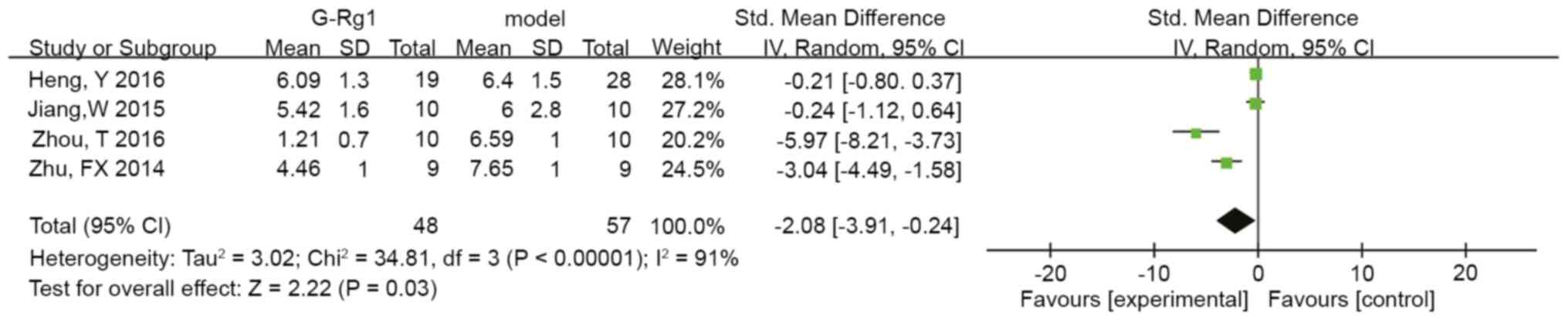
Heng Y, Zhang QS, Mu Z, Hu JF, Yuan YH and
Chen NH: Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates motor impairment and
neuroinflammation in the MPTP-probenecid-induced parkinsonism mouse
model by targeting α-synuclein abnormalities in the substantia
nigra. Toxicol Lett. 243:7–21. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Song L, Xu MB, Zhou XL, Zhang DP, Zhang SL
and Zheng GQ: A preclinical systematic review of ginsenoside-Rg1 in
experimental Parkinson's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(2163053)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Stanic D, Finkelstein DI, Bourke DW, Drago
J and Horne MK: Timecourse of striatal re-innervation following
lesions of dopaminergic SNpc neurons of the rat. Eur J Neurosci.
18:1175–1188. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
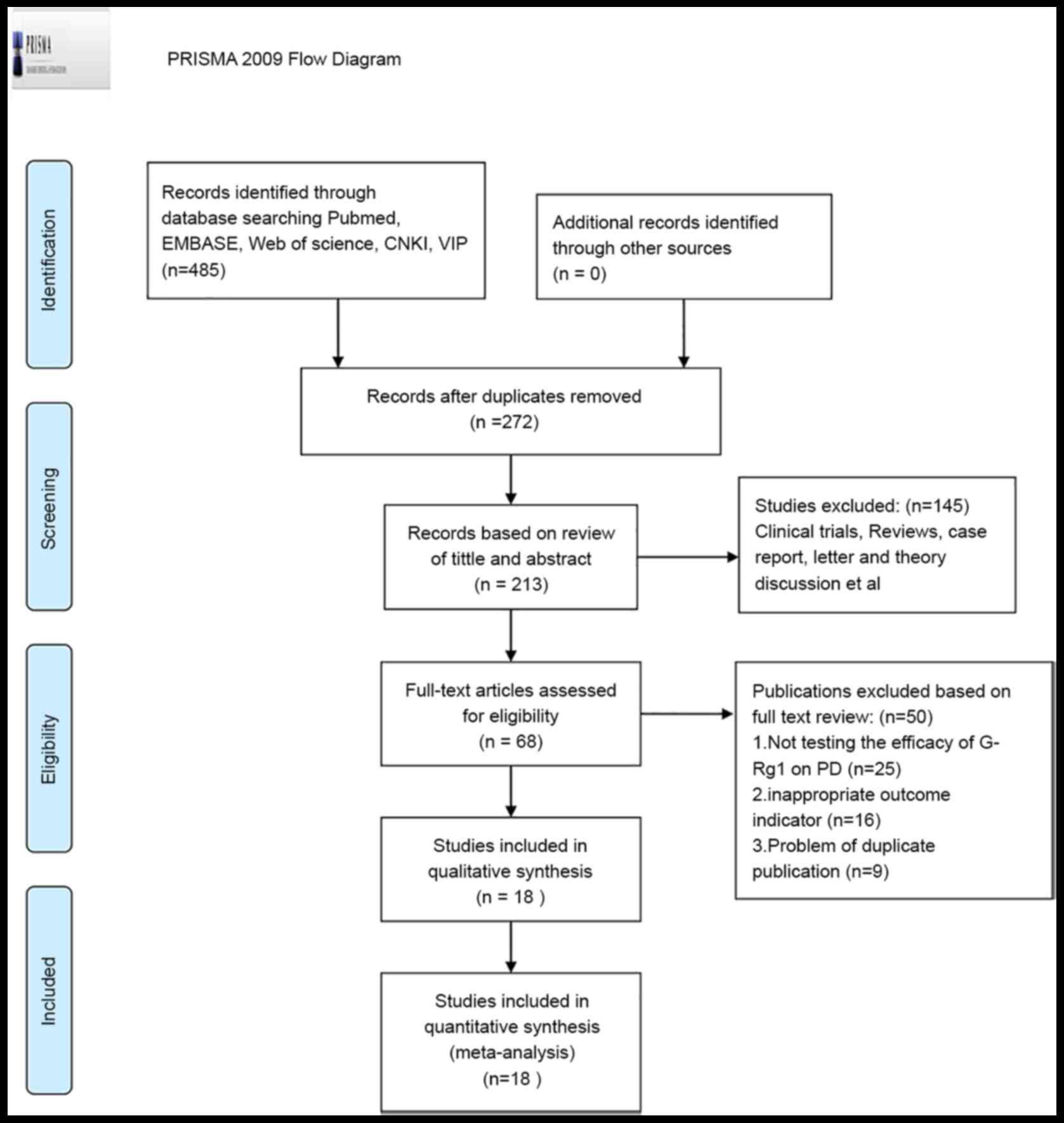
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG: PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 8:336–341.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fifel K and Cooper HM: Loss of dopamine
disrupts circadian rhythms in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 71:359–369. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Morin N, Jourdain VA and Di Paolo T:
Modeling dyskinesia in animal models of Parkinson disease. Exp
Neurol. 256:105–116. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Matsumoto M: Dopamine signals and
physiological origin of cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson's
disease. Mov Disord. 30:472–483. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jagmag SA, Tripathi N, Shukla SD, Maiti S
and Khurana S: Evaluation of models of Parkinson's disease. Front
Neurosci. 9(503)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vesterinen HM, Sena ES, Egan KJ, Hirst TC,
Churolov L, Currie GL, Antonic A, Howells DW and Macleod MR:
Meta-analysis of data from animal studies: A practical guide. J
Neurosci Methods. 221:92–102. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
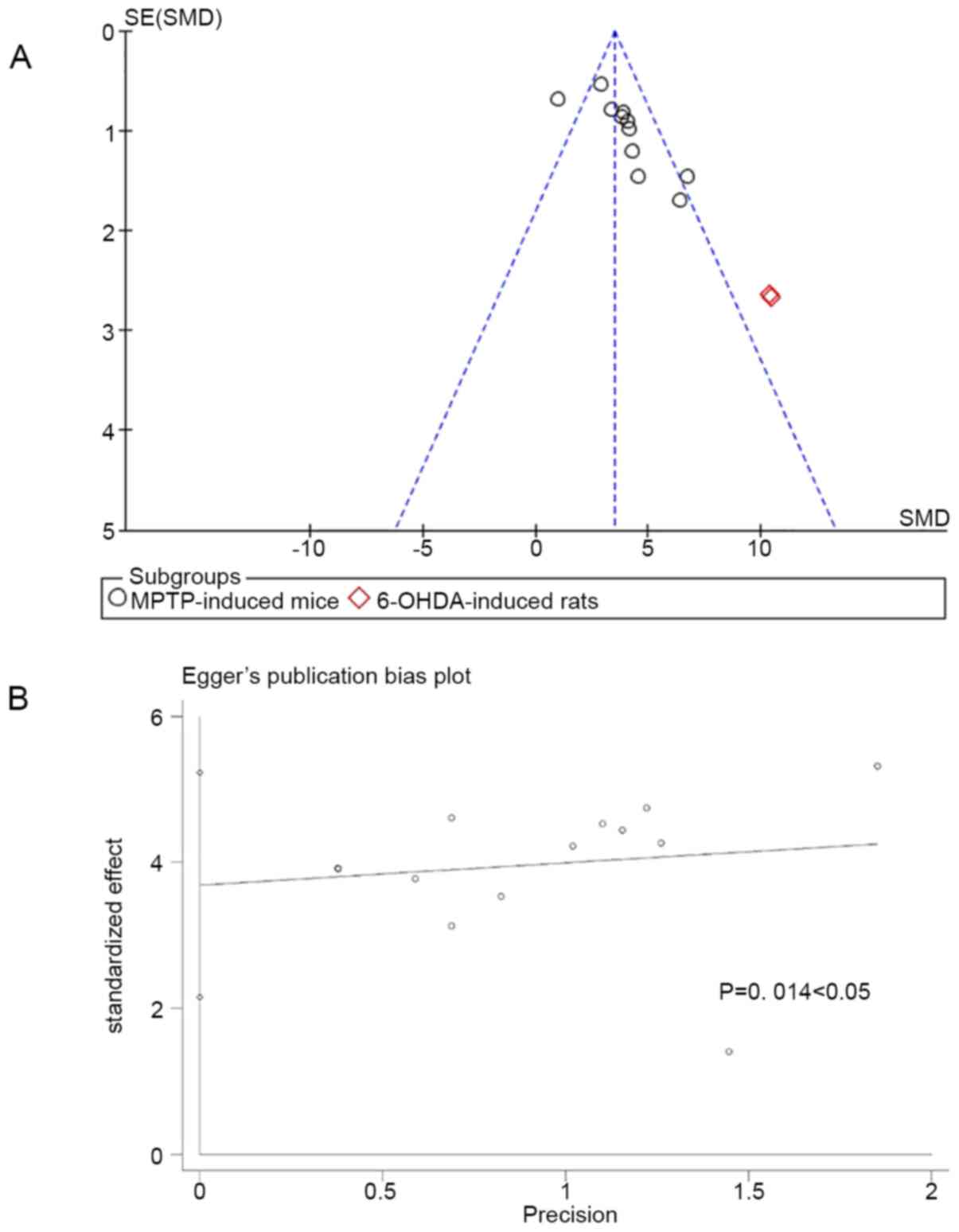
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen XC, Zhou YC, Chen Y, Zhu YG, Fang F
and Chen LM: Ginsenoside Rg1 reduces MPTP-induced substantia nigra
neuron loss by suppressing oxidative stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
26:56–62. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang W, Wang Z, Jiang Y, Lu M and Li X:
Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates motor function in an animal model of
Parkinson's disease. Pharmacology. 96:25–31. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Li R, Liu LN, Zhang XW, Zhang YX
and Zhang ZF: Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on jnk signaling
pathway mediatethe loss of nigral nurons in the mice model of
Parkinson. Mod Prev Med. 35:1973–1975. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Shi C, Zhang YX and Zhang ZF: Effect of
phosphorylated-ERK1/2 on inducible nitric oxide synthase expression
in the substantia nigra of mice with MPTP-induced Parkinson
disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 29:60–63. 2009.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Xu HM, Yang HD, Du XX, Jiang H and
Xie JX: Rg1 reduces nigral iron levels of MPTP-treated C57BL6 mice
by regulating certain iron transport proteins. Neurochem Int.
54:43–48. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Zhang H and Liu M: Influence of
NF-κB on i-NOS expression in substantia nigra of mouse models of
Parkinson's disease induced by MPTP. J Hebei United Univ.
15:297–299. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Wang Q, Zhang H, Liu M, Li QJ, Geng LX,
Sun MH, Tian QY and Zhang YX: Influence of ginsenoside Rg1 in
expressions of FADD and FLIP in substantia nigra of Parkinson's
disease model mice. J Jilin Univ Med Ed. 40:962–966. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Wang Q, Zhang H, Zhang ZF, Wei ZF, Wang
YS, Zhou HX, et al: Role of P38 MAPK in regulating expression of
NF-κB and COX-2 in substantia-nigra of MPTP Parkinson's disease
mice model. China J Mod Med. 22:15–20. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Wang Q, Zhang YX and Zhang ZF: Influence
of NF-κB on COX-2 expression insubstantia nigra of mouse models of
Parkinson's disease induced by MPTP. J Fourth Mil Med Univ.
29:1757–1760. 2008.
|
|
33
|
Wang YS, Li H, Zhang YX, Wei SP, Zhang ZF
and Tian QY: Influence of ginsenoside Rg1 on p-c-jun and cox-2
epression in substantia nigra of the MPTP mouse model of subacute
Parkinson's disease. Chin J Neuroanat. 25:432–436. 2009.
|
|
34
|
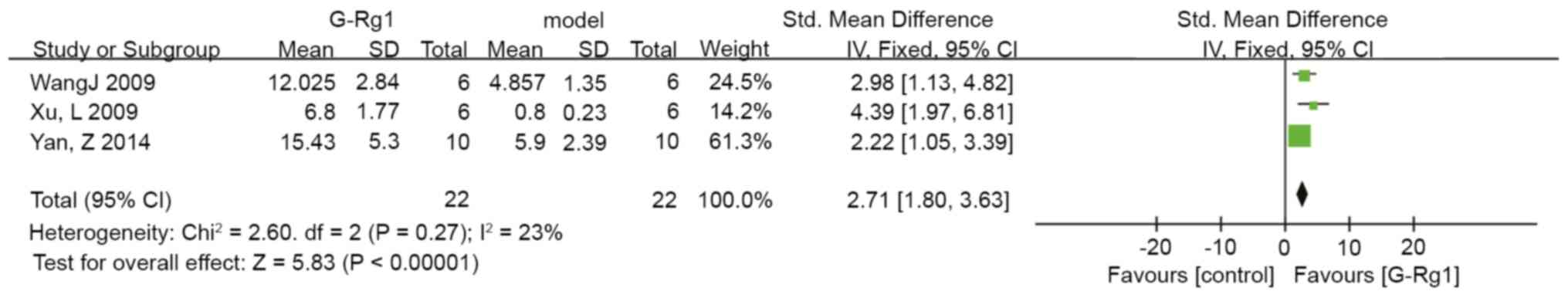
Xu L, Chen WF and Wong MS: Ginsenoside Rg1
protects dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
through the IGF-I receptor signalling pathway. Br J Pharmacol.
158:738–748. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xu L, Liu LX, Chen LX, Xie JX and Huang
WX: The protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on dopaminergic
neurons of substantia in the ovariectomized rat model of
Parkinson's disease. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi.
24:1–5. 2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Yan Z, Wu L, Xue D, Gao XQ and Chen WF:
Effects of gesenoside Rg1 and insulin-like growth factor on
dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson. Acta Acad Med Qingdao Univ.
50:283–288. 2014.
|
|
37
|
Zhou T, Zu G, Zhang X, Wang X, Li S, Gong
X, Liang Z and Zhao J: Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1
through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in both in vivo and in
vitro models of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology.
101:480–489. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou YC, Chen XC, Zhu YG, Fang F and Chen
LM: Down-regulation of oxidative stress is the possible mechanism
of ginsenoside Rg1 protecting the substantia nigra neurons in PD
mice. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 8:2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Zhu FX, Chang HM, Duan Y, Li PY and Wang
SX: Effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on the expressions of tyrosine
hydroxylase,ephrin B2 and phosphorylated c-Jun in substantia nigra
of mice with Parkinson's disease. J Xinxiang Med Univ. 31:781–785.
2014.
|
|
40
|
Fleming SM, Salcedo J, Fernagut PO,
Rockenstein E, Masliah E, Levine MS and Chesselet MF: Early and
progressive sensorimotor anomalies in mice overexpressing wild-type
human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci. 24:9434–9440. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Macleod MR, O'Collins T, Howells DW and
Donnan GA: Pooling of animal experimental data reveals influence of
study design and publication bias. Stroke. 35:1203–1208.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad
AR, Moher M, Tugwell P and Klassen TP: Does quality of reports of
randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy
reported in meta-analyses? Lancet. 352:609–613. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bebarta V, Luyten D and Heard K: Emergency
medicine animal research: Does use of randomization and blinding
affect the results? Acad Emerg Med. 10:684–687. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bowenkamp KE, David D, Lapchak PL, Henry
MA, Granholm AC, Hoffer BJ and Mahalik TJ: 6-hydroxydopamine
induces the loss of the dopaminergic phenotype in substantia nigra
neurons of the rat. A possible mechanism for restoration of the
nigrostriatal circuit mediated by glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor. Exp Brain Res. 111:1–7. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ara J, Przedborski S, Naini AB,
Jackson-Lewis V, Trifiletti RR, Horwitz J and Ischiropoulos H:
Inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nitration following
exposure to peroxynitrite and
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 95:7659–7663. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kuhn DM, Aretha CW and Geddes TJ:
Peroxynitrite inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase: Mediation by
sulfhydryl oxidation, not tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci.
19:10289–10294. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Blanchard-Fillion B, Souza JM, Friel T,
Jiang GC, Vrana K, Sharov V, Barrón L, Schöneich C, Quijano C,
Alvarez B, et al: Nitration and inactivation of tyrosine
hydroxylase by peroxynitrite. J Biol Chem. 276:46017–46023.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jackson-Lewis V and Przedborski S:
Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Nat
Protoc. 2:141–151. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhao Q, Yang M, Deng Y, Yu H, Wang L, Teng
F, Cho K, Ma H, Wu P, Li X, et al: The safety evaluation of
salvianolic acid B and ginsenoside Rg1 combination on mice. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:29345–29356. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang ZL, Fan Y and Liu ML: Ginsenoside
Rg1 inhibits autophagy in H9c2 cardiomyocytes exposed to
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Mol Cell Biochem. 365:243–250.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lu D, Zhu LH, Shu XM, Zhang CJ, Zhao JY,
Qi RB, Wang HD and Lu DX: Ginsenoside Rg1 relieves tert-Butyl
hydroperoxide-induced cell impairment in mouse microglial BV2
cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 17:930–945. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li SS, Ye JM, Deng ZY, Yu LX, Gu XX and
Liu QF: Ginsenoside-Rg1 inhibits endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction in
rats. Ren Fail. 37:890–895. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu Y, Yi L, Wang L, Chen L, Chen X and
Wang Y: Ginsenoside Rg1 protects human umbilical cord blood-derived
stromal cells against tert-Butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis
through Akt-FoxO3a-Bim signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
421:75–87. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Huo DS, Zhang M, Cai ZP, Dong CX, Wang H
and Yang ZJ: The role of nerve growth factor in ginsenoside
Rg1-induced regeneration of injured rat sciatic nerve. J Toxicol
Environ Health A. 78:1328–1337. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Miao HH, Zhen Y, Ding GN, Hong FX, Xie ZC
and Tian M: Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates isoflurane-induced caspase-3
activation via inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed Environ
Sci. 28:116–126. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liao B, Newmark H and Zhou R:
Neuroprotective effects of ginseng total saponin and ginsenosides
Rb1 and Rg1 on spinal cord neurons in vitro. Exp Neurol.
173:224–234. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhang YF, Fan XJ, Li X, Peng LL, Wang GH,
Ke KF and Jiang ZL: Ginsenoside Rg1 protects neurons from
hypoxic-ischemic injury possibly by inhibiting Ca2+
influx through NMDA receptors and L-type voltage-dependent
Ca2+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 586:90–99.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Liu Z, Qi Y, Cheng Z, Zhu X, Fan C and Yu
SY: The effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on chronic stress induced
depression-like behaviors, BDNF expression and the phosphorylation
of PKA and CREB in rats. Neuroscience. 322:358–369. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|