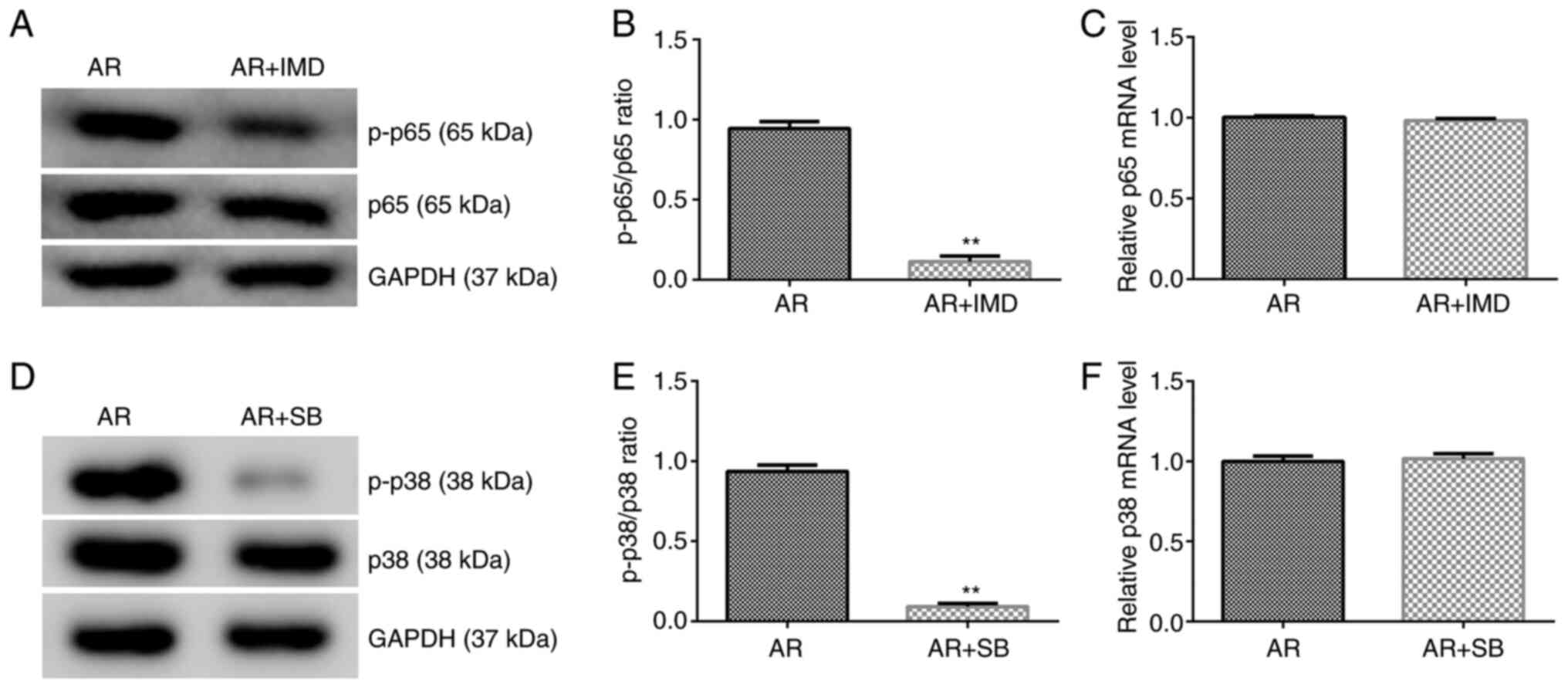
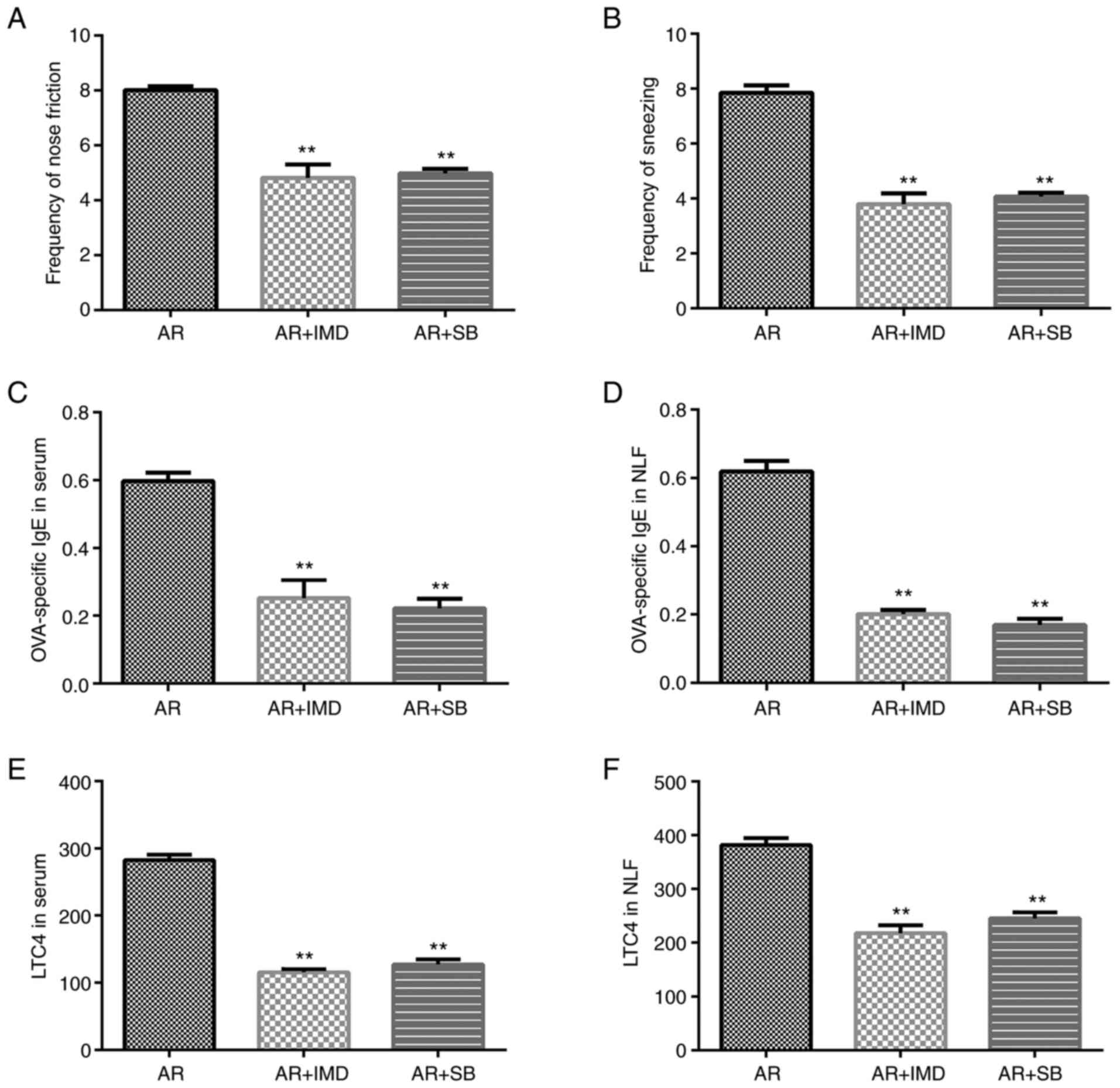
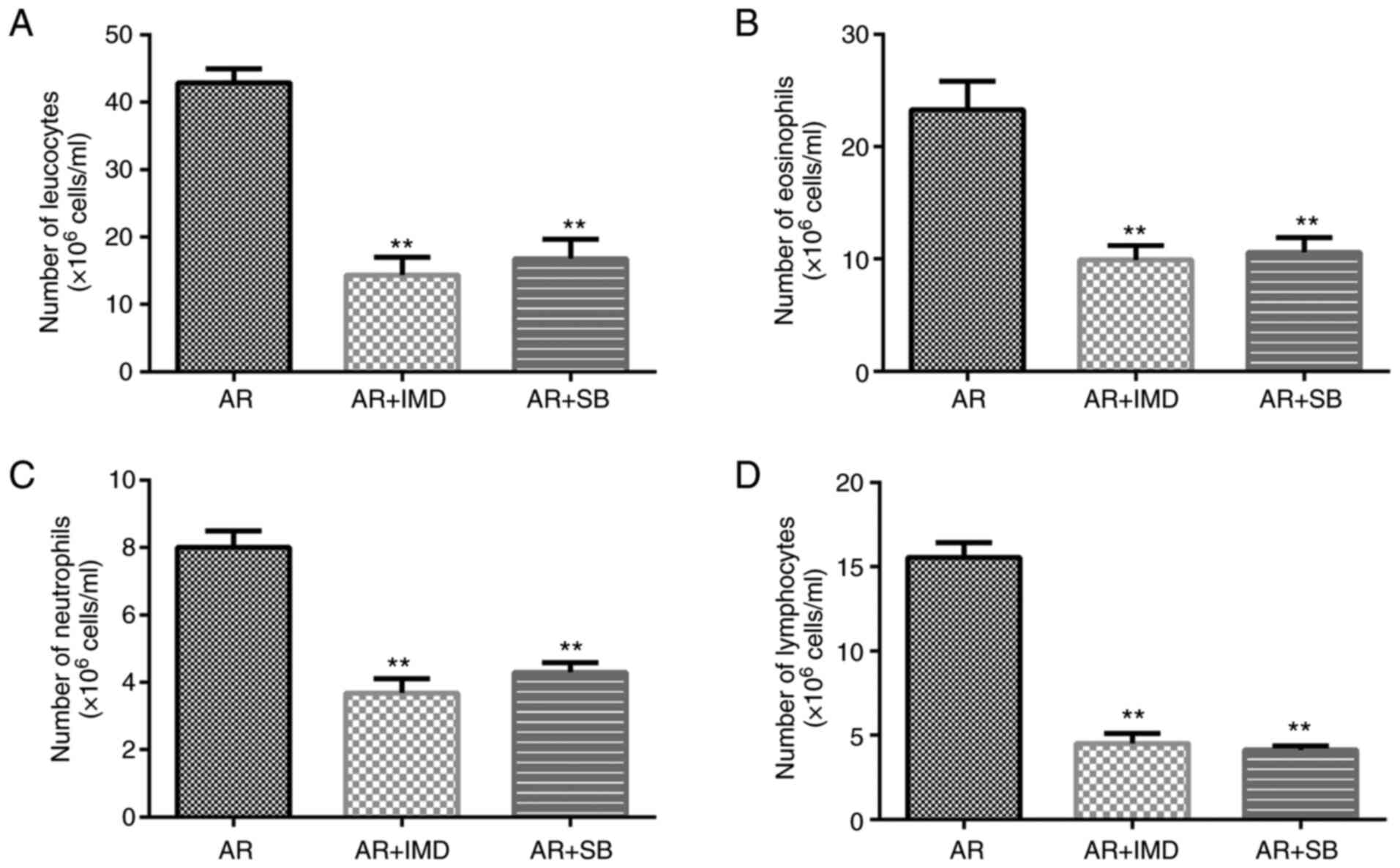
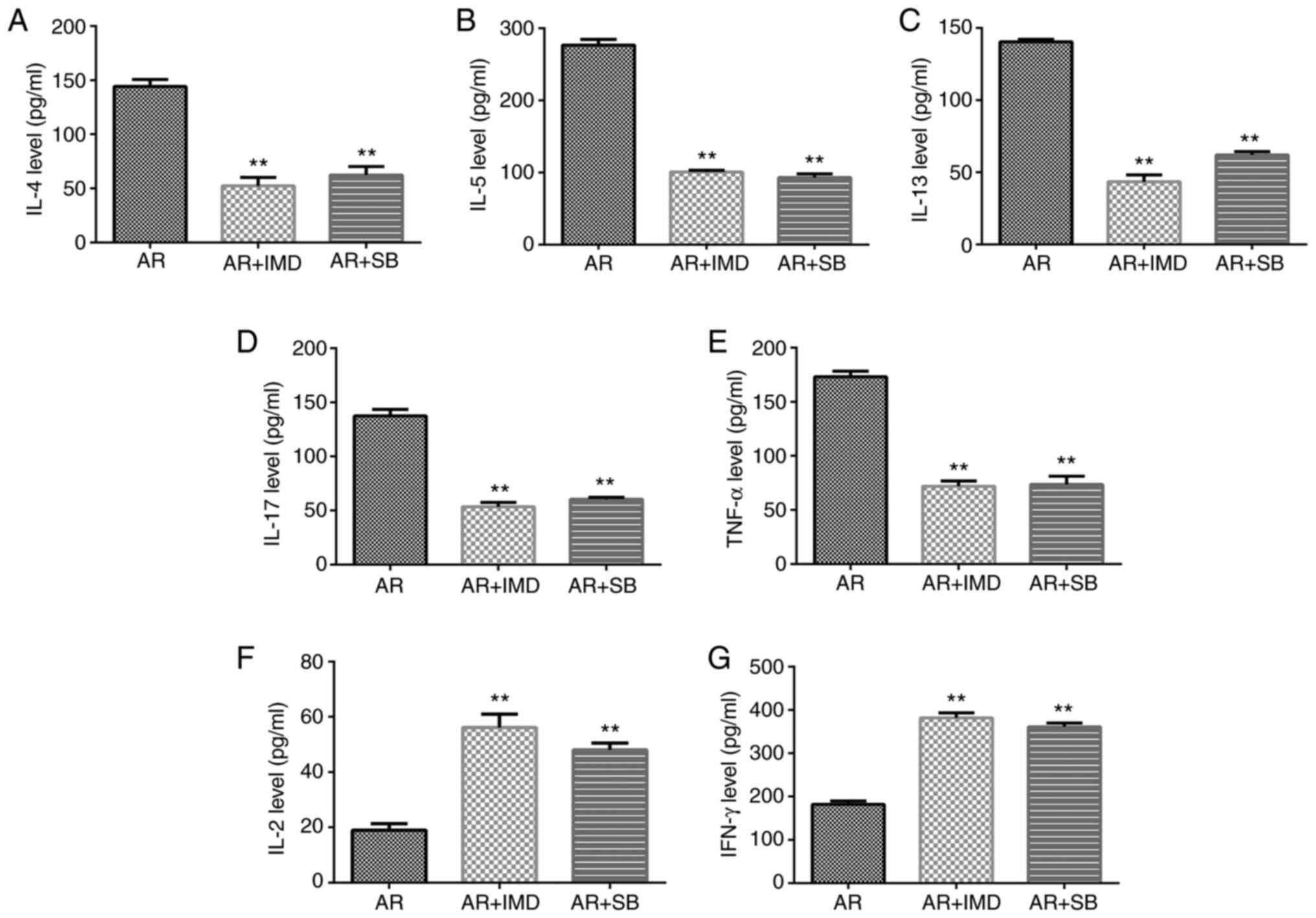
|
1
|
Incorvaia C, Cavaliere C, Frati F and
Masieri S: Allergic rhinitis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 32 (1
Suppl 1):S61–S66. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paiva Ferreira LKD, Paiva Ferreira LAM,
Monteiro TM, Bezerra GC, Bernardo LR and Piuvezam MR: Combined
allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS). Int Immunopharmacol.
74(105718)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rosati MG and Peters AT: Relationships
among allergic rhinitis, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J
Rhinol Allergy. 30:44–47. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prenner BM and Schenkel E: Allergic
rhinitis: Treatment based on patient profiles. Am J Med.
119:230–237. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sur DK and Plesa ML: Treatment of allergic
rhinitis. Am Fam Physician. 92:985–992. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bernstein DI, Schwartz G and Bernstein JA:
Allergic rhinitis: Mechanisms and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin
North Am. 36:261–278. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Steelant B, Farré R, Wawrzyniak P, Belmans
J, Dekimpe E, Vanheel H, Van Gerven L, Kortekaas Krohn I, Bullens
DM, Ceuppens JL, et al: Impaired barrier function in patients with
house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis is accompanied by
decreased occludin and zonula occludens-1 expression. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 137:1043–1053.e5. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin S, Jin P, Shao C, Lu W, Xiang Q, Jiang
Z, Zhang Y and Bian J: Lidocaine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and protects
against endotoxemia in mice by suppressing HIF1α-induced
glycolysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 80(106150)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Leng T, Lin S, Xiong Z and Lin J:
Lidocaine suppresses glioma cell proliferation by inhibiting TRPM7
channels. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 9:8–15.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Křikava I, Nováková M and Ševčík P: The
effects of trimecaine on bupivacaine induced cardiotoxicity in the
isolated rat heart: A pilot study. Physiol Res. 57(18)2008.
|
|
11
|
Martí-Carvajal AJ, Simancas-Racines D,
Anand V and Bangdiwala S: Prophylactic lidocaine for myocardial
infarction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2015(CD008553)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nakazawa M, Okumura A, Niijima S,
Yamashita S, Shimono K, Hirose S and Shimizu T: Oral mexiletine for
lidocaine-responsive neonatal epilepsy. Brain Dev. 35:667–669.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Slaton RM, Thomas RH and Mbathi JW:
Evidence for therapeutic uses of nebulized lidocaine in the
treatment of intractable cough and asthma. Ann Pharmacother.
47:578–585. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chinn E, Friedman BW, Naeem F, Irizarry E,
Afrifa F, Zias E, Jones MP, Pearlman S, Chertoff A, Wollowitz A and
Gallagher EJ: Randomized trial of intravenous lidocaine versus
hydromorphone for acute abdominal pain in the emergency department.
Ann Emerg Med. 74:233–240. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Dilger JP and Lin J: Lidocaine
suppresses viability and migration of human breast cancer Cells:
TRPM7 as a target for some breast cancer cell lines. Cancers
(Basel). 13(234)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhao L, Ma N, Liu G, Mao N, Chen F and Li
J: Lidocaine inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development by
modulating circ_ITCH/miR-421/CPEB3 axis. Dig Dis Sci. 66:4384–4397.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee U, Choi YJ, Choi GJ and Kang H:
Intravenous lidocaine for effective pain relief after bimaxillary
surgery. Clin Oral Investig. 21:2645–2652. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guang F, Liu S, Wang GL and Liu GJ:
Lidocaine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
through inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Pharmacology. 81:32–40.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin S, Jin P, Shao C, Lu W, Xiang Q, Jiang
Z, Zhang Y and Bian J: Lidocaine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and protects
against endotoxemia in mice by suppressing HIF1α-induced
glycolysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 80(106150)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Leon-Constantin MM, Alexa-Stratulat T,
Luca A, Tamba BI, Trandafir LM, Harabagiu V and Cojocaru E: The
morphofunctional impact of topical lidocaine formulation in
inflammatory pain-experimental study. Rom J Morphol Embryol.
60:869–874. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Wang M, Li S, Wu H, Shen Q, Zhang
S, Fang L and Liu R: Nebulized lidocaine ameliorates allergic
airway inflammation via downregulation of TLR2. Mol Immunol.
97:94–100. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xiao L, Jiang L, Hu Q and Li Y:
MicroRNA-133b ameliorates allergic inflammation and symptom in
murine model of allergic rhinitis by targeting Nlrp3. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:901–912. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu H, Shu H, Zhu J and Song J: Inhibition
of TLR4 inhibits allergic responses in murine allergic rhinitis by
regulating the NF-κB pathway. Exp Ther Med. 18:761–768.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zheng Y, Hou X and Yang S: Lidocaine
potentiates SOCS3 to attenuate inflammation in microglia and
suppress neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 39:1081–1092.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Khan DA: Allergic rhinitis and asthma:
Epidemiology and common pathophysiology. Allergy Asthma Proc.
35:357–361. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mandhane SN, Shah JH and Thennati R:
Allergic rhinitis: An update on disease, present treatments and
future prospects. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:1646–1662.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Casale TB and Dykewicz MS: Clinical
implications of the allergic rhinitis-asthma link. Am J Med Sci.
327:127–138. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal
A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Brignardello-Petersen R,
Canonica GW, Casale T, Chavannes NH, et al: Allergic rhinitis and
its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 140:950–958. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Drazdauskaitė G, Layhadi JA and Shamji MH:
Mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis. Curr
Allergy Asthma Rep. 21(2)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu S and Xiao D: Effect of curcumin on
nasal symptoms and airflow in patients with perennial allergic
rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 117:697–702.e1.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yu S, Han B, Liu S, Wang H, Zhuang W,
Huang Y and Zhang R: Derp1-modified dendritic cells attenuate
allergic inflammation by regulating the development of T helper
type1(Th1)/Th2 cells and regulatory T cells in a murine model of
allergic rhinitis. Mol Immunol. 90:172–181. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li J, Lin XY, Liu X, Ma ZQ and Li Y:
Baicalin regulates Treg/Th17 cell imbalance by inhibiting autophagy
in allergic rhinitis. Mol Immunol. 125:162–171. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bae JS, Kim JH, Kim EH and Mo JH: The role
of IL-17 in a lipopolysaccharide-induced rhinitis model. Allergy
Asthma Immunol Res. 9:169–176. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bachert C, Zhang L and Gevaert P: Current
and future treatment options for adult chronic rhinosinusitis:
Focus on nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 136:1431–1440.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Deo SS, Mistry KJ, Kakade AM and Niphadkar
PV: Role played by Th2 type cytokines in IgE mediated allergy and
asthma. Lung India. 27:66–71. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Coffman RL, Seymour BW, Hudak S, Jackson J
and Rennick D: Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced
eosinophilia in mice. Science. 245:308–310. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jung HW, Jung JK and Park YK: Comparison
of the efficacy of KOB03, ketotifen, and montelukast in an
experimental mouse model of allergic rhinitis. Int Immunopharmacol.
16:254–260. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Piao CH, Fan YJ, Nguyen TV, Song CH and
Chai OH: Mangiferin alleviates ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis
via Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
21(3415)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1(a001651)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Vanden Berghe W, Plaisance S, Boone E, De
Bosscher K, Schmitz ML, Fiers W and Haegeman G: p38 and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways are required for nuclear factor-kappaB p65
transactivation mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem.
273:3285–3290. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dodeller F, Skapenko A, Kalden JR, Lipsky
PE and Schulze-Koops H: The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
regulates effector functions of primary human CD4 T cells. Eur J
Immunol. 35:3631–3642. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dodeller F and Schulze-Koops H: The p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in CD4 T cells.
Arthritis Res Ther. 8(205)2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ono K and Han J: The p38 signal
transduction pathway: Activation and function. Cell Signal.
12:1–13. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kang OH, Jang HJ, Chae HS, Oh YC, Choi JG,
Lee YS, Kim JH, Kim YC, Sohn DH, Park H and Kwon DY:
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of resveratrol in activated HMC-1
cells: Pivotal roles of NF-kappaB and MAPK. Pharmacol Res.
59:330–337. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu J, Liu L, Cui Y, Zhang J and Jiang H:
p38 MAPK regulates Th2 cytokines release in PBMCs in allergic
rhinitis rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 30:222–225.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gao X, Li N and Zhang J: SB203580, a
p38MAPK inhibitor, attenuates olfactory dysfunction by inhibiting
OSN apoptosis in AR mice (activation and involvement of the p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase in olfactory sensory neuronal
apoptosis of OVA-induced allergic rhinitis). Brain Behav.
9(e01295)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jiang R, Liao J, Yang MC, Deng J, Hu YX,
Li P and Li MT: Lidocaine mediates the progression of cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting the activation
of NF-κB p65 and p38 MAPK. Ann Transl Med. 8(548)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen LJ, Ding YB, Ma PL, Jiang SH, Li KZ,
Li AZ, Li MC, Shi CX, Du J and Zhou HD: The protective effect of
lidocaine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
through NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathway and excessive
inflammatory responses. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2099–2108.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Haller I, Hausott B, Tomaselli B, Keller
C, Klimaschewski L, Gerner P and Lirk P: Neurotoxicity of lidocaine
involves specific activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase, but not extracellular signal-regulated or c-jun N-terminal
kinases, and is mediated by arachidonic acid metabolites.
Anesthesiology. 105:1024–1033. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jin H and Yu J: Lidocaine protects H9c2
cells from hypoxia-induced injury through regulation of the
MAPK/ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 18:4125–4131.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Niu L, Wei J, Li X, Jin Y and Shi X:
Inhibitory activity of narirutin on RBL-2H3 cells degranulation.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 43:68–76. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
van der Wal SE, van den Heuvel SA, Radema
SA, van Berkum BF, Vaneker M, Steegers MA, Scheffer GJ and Vissers
KC: The in vitro mechanisms and in vivo efficacy of intravenous
lidocaine on the neuroinflammatory response in acute and chronic
pain. Eur J Pain. 20:655–674. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|