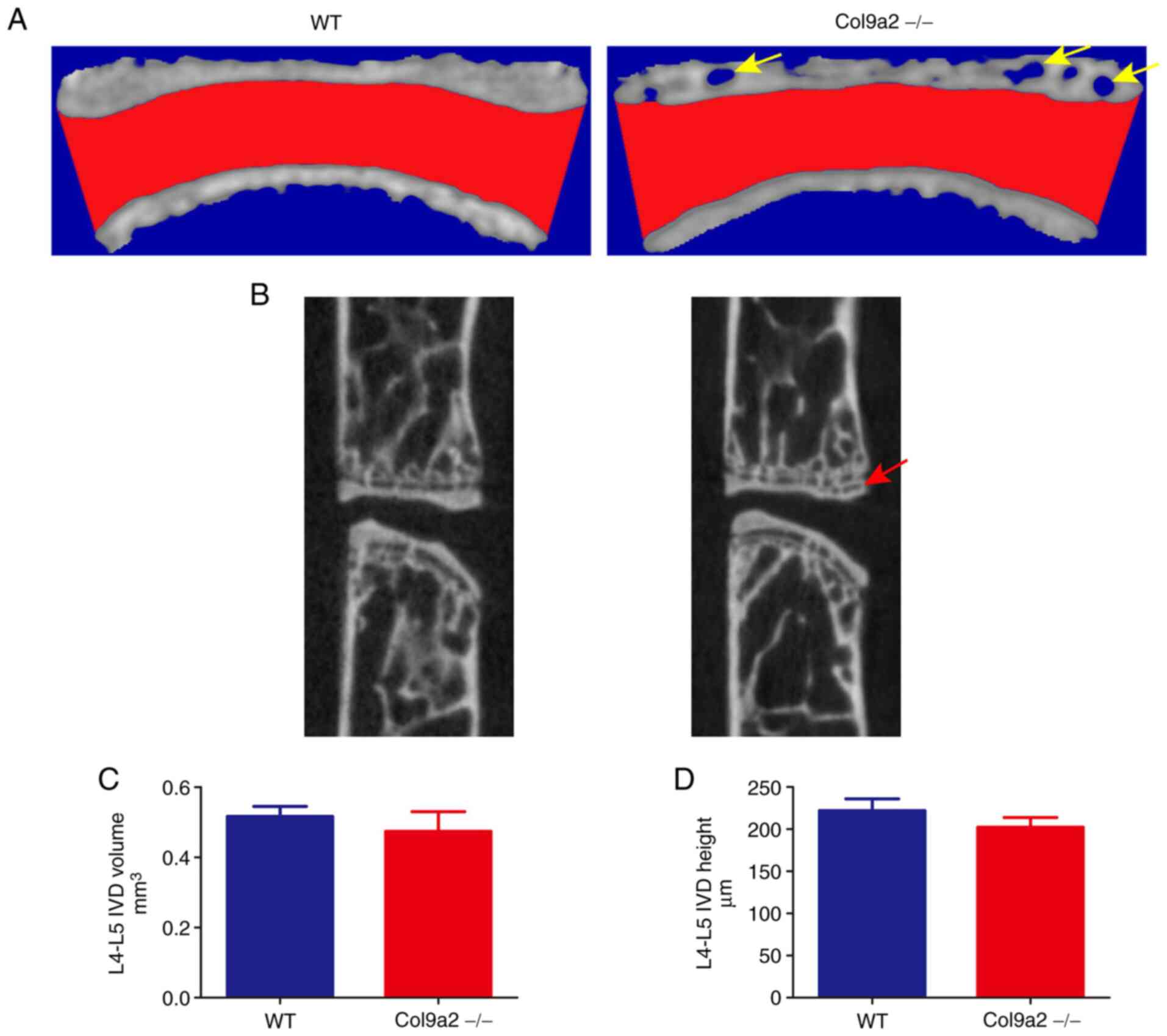
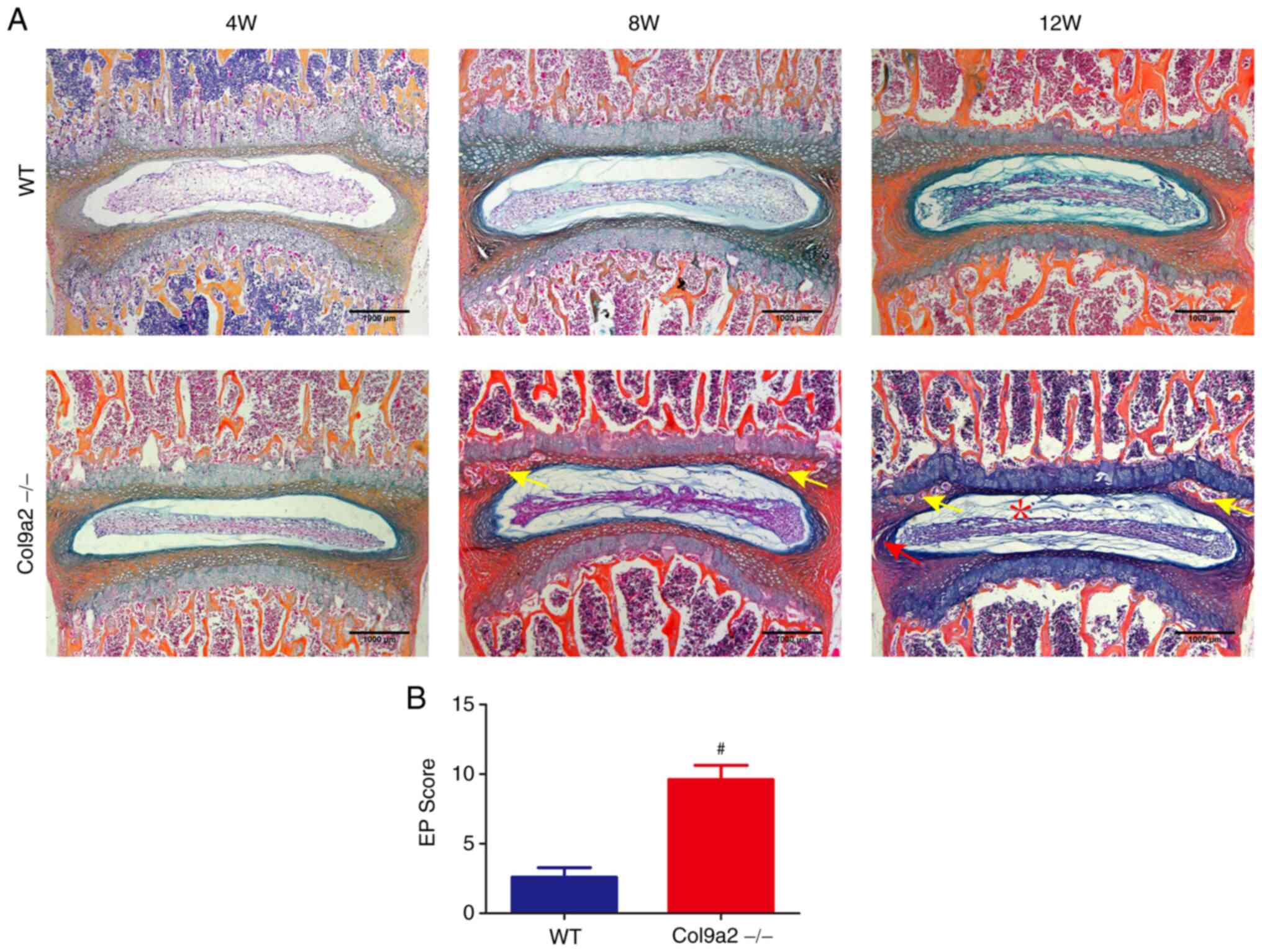
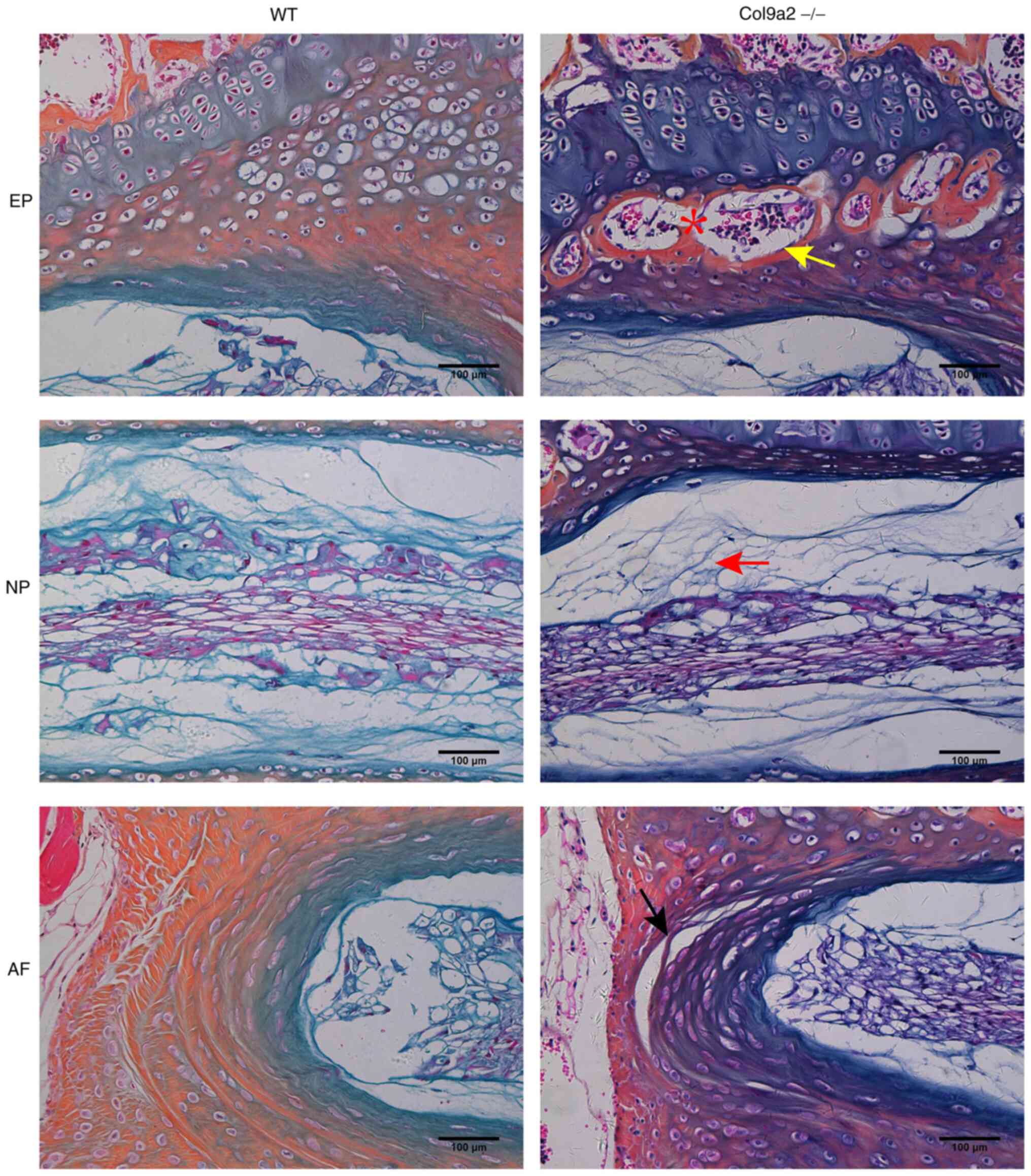
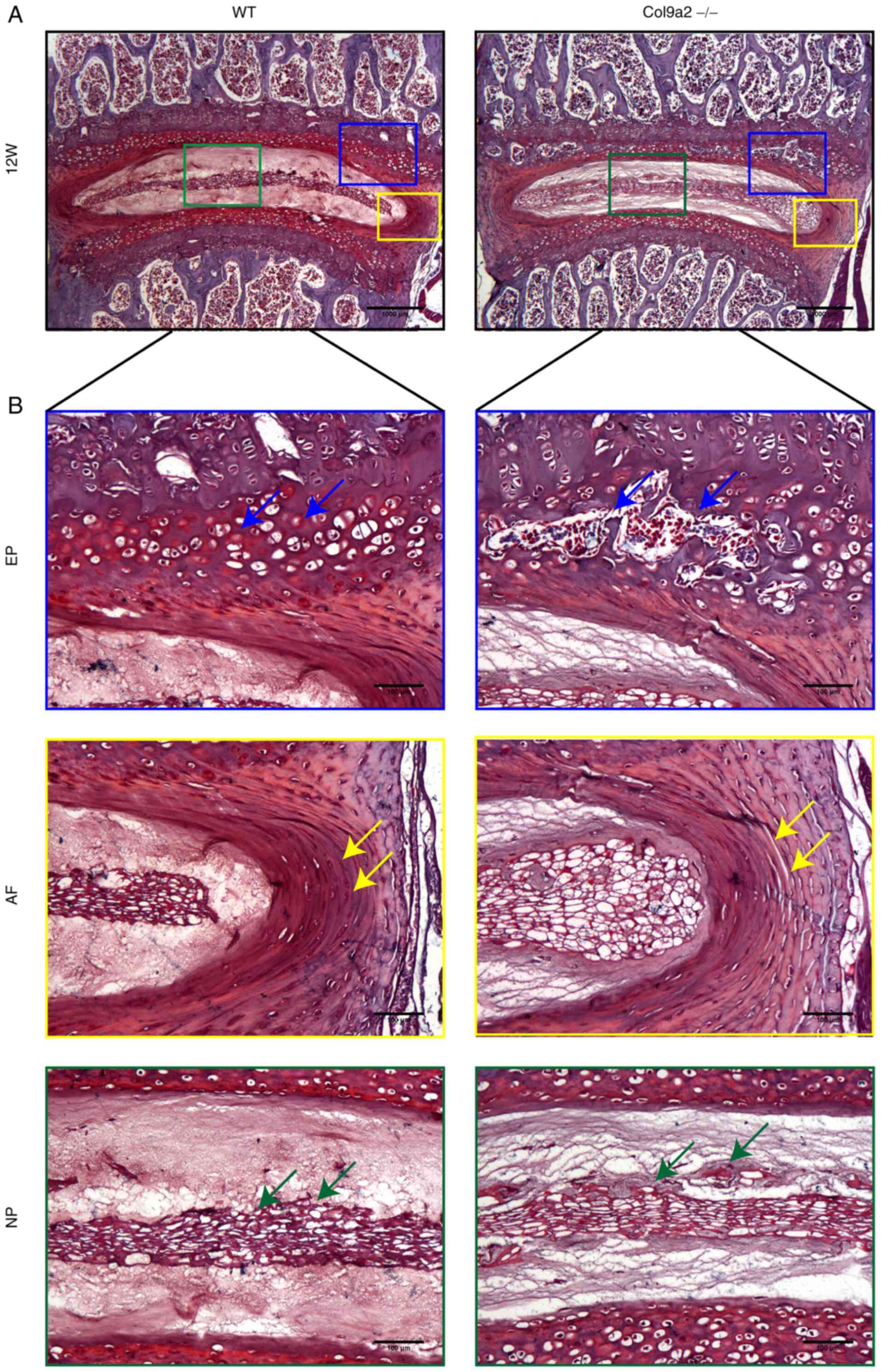
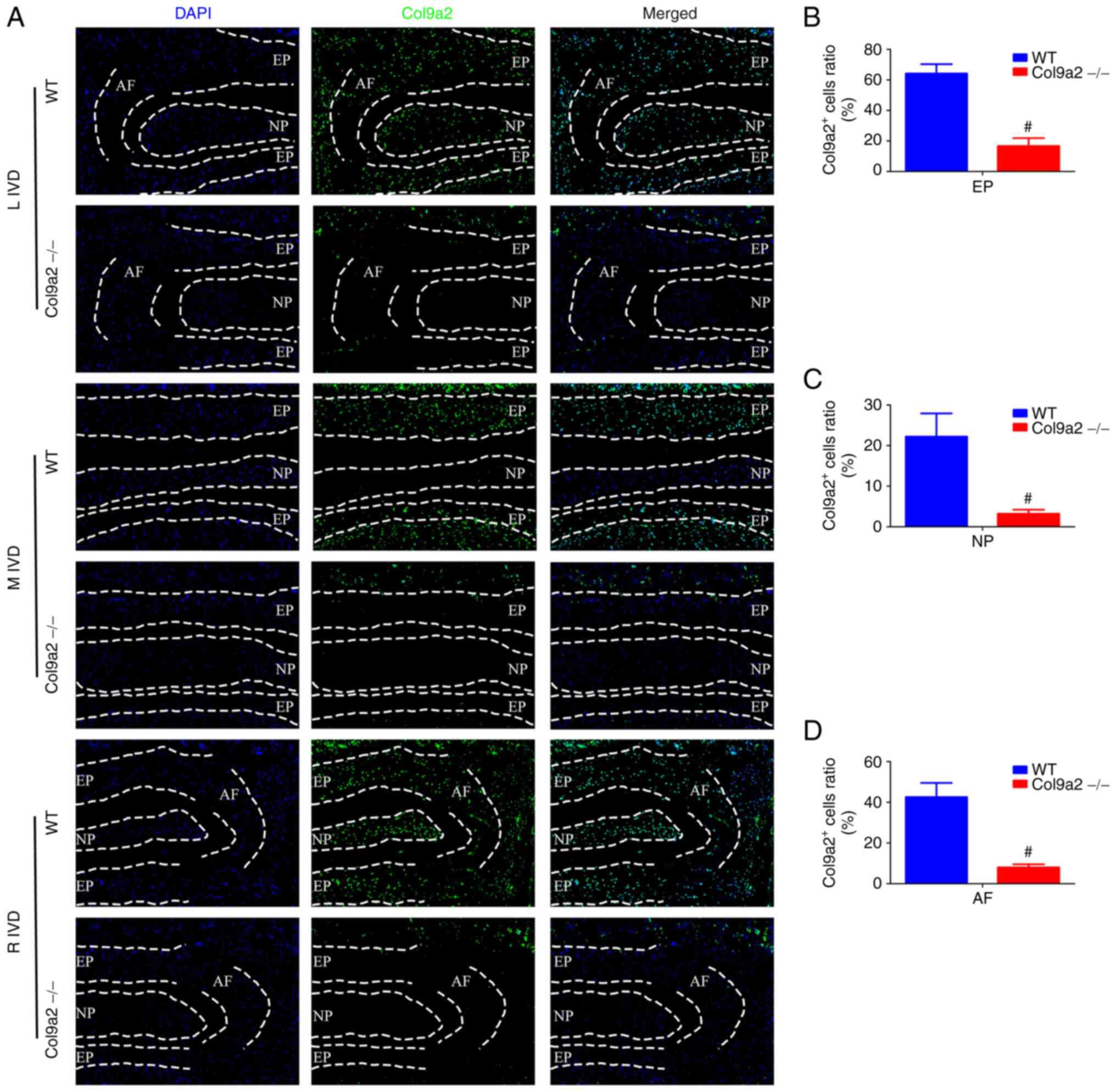
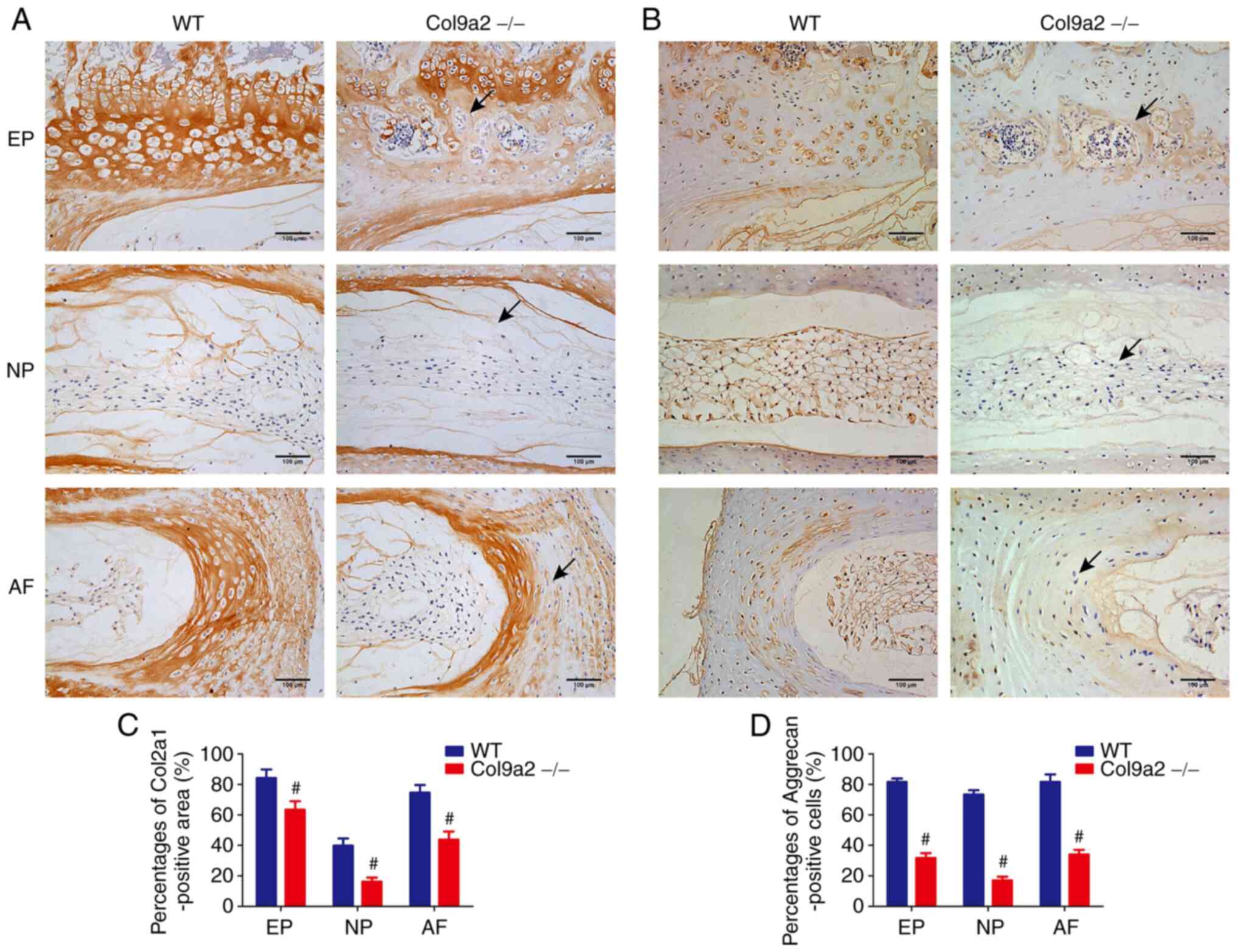
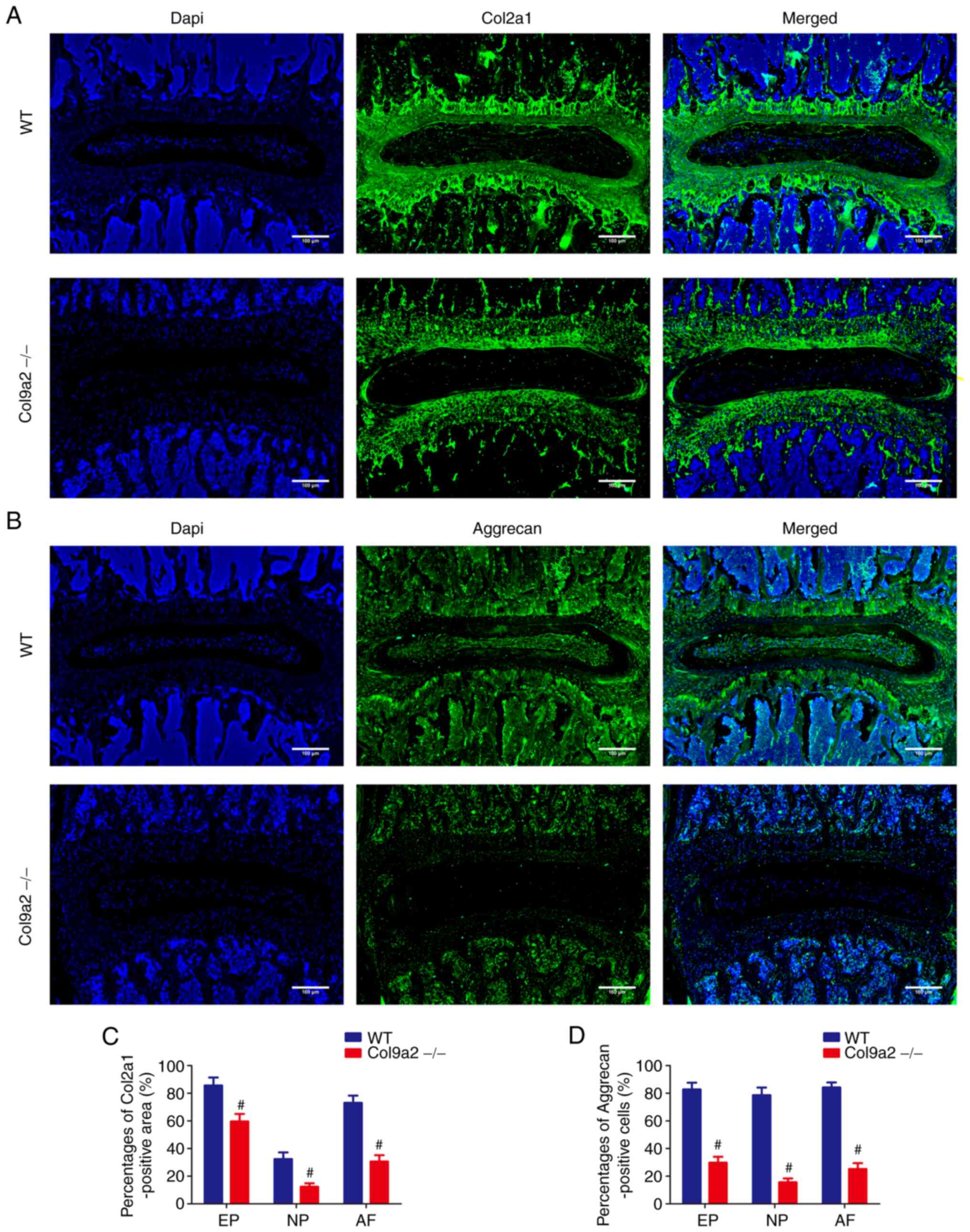
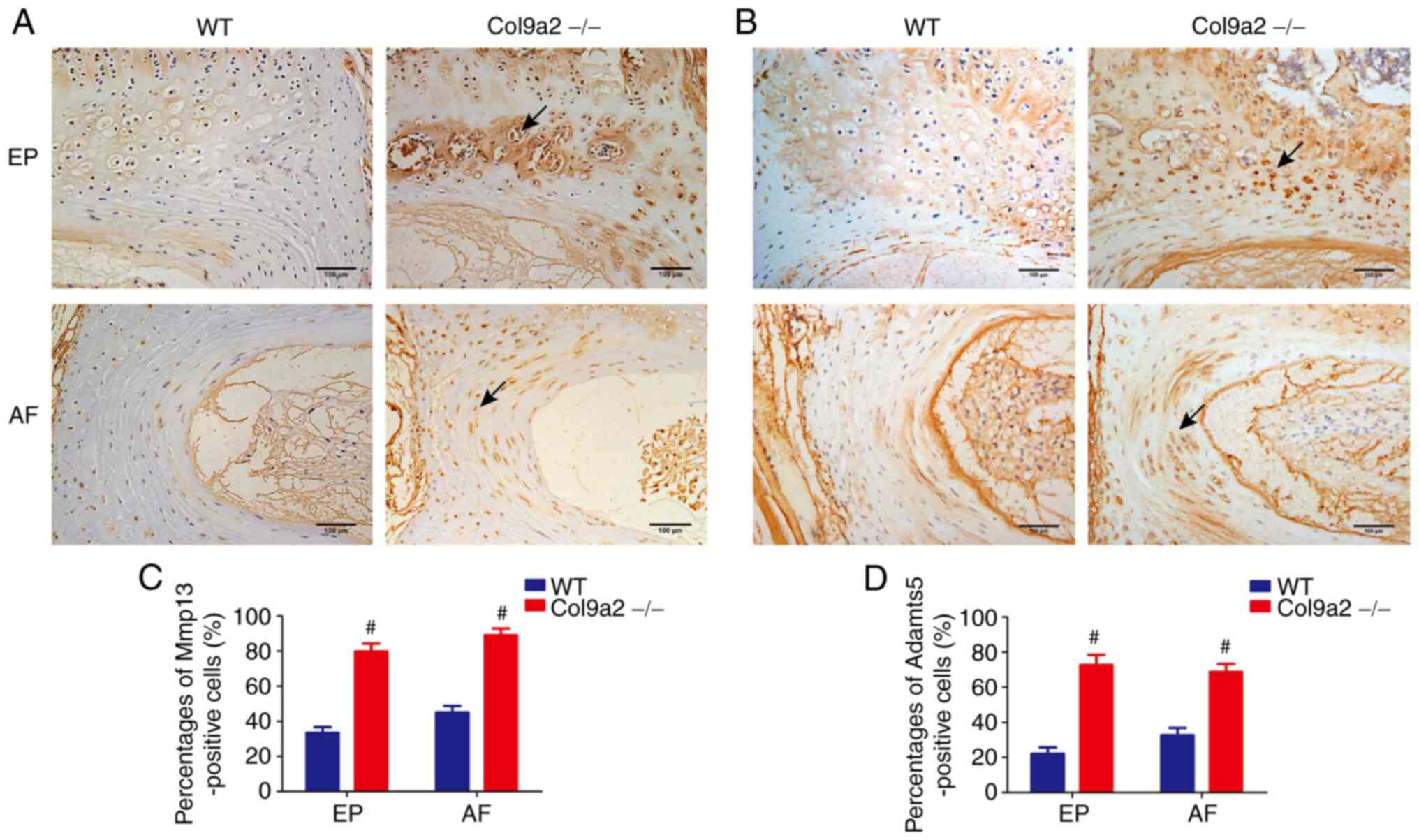
|
1
|
Luoma K, Vehmas T, Kerttula L, Gronblad M
and Rinne E: Chronic low back pain in relation to modic changes,
bony endplate lesions, and disc degeneration in a prospective MRI
study. Eur Spine J. 25:2873–2881. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Izzo R, Popolizio T, D'Aprile P and Muto
M: Spinal pain. Eur J Radiol. 84:746–756. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cazzanelli P and Wuertz-Kozak K: MicroRNAs
in intervertebral disc degeneration, apoptosis, inflammation, and
mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 21(3601)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Frapin L, Clouet J, Delplace V, Fusellier
M, Guicheux J and Le Visage C: Lessons learned from intervertebral
disc pathophysiology to guide rational design of sequential
delivery systems for therapeutic biological factors. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 149-150:49–71. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen BL, Guo JB, Zhang HW, Zhang YJ, Zhu
Y, Zhang J, Hu HY, Zheng YL and Wang XQ: Surgical versus
non-operative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 32:146–160. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wu PH, Kim HS and Jang IT: Intervertebral
disc diseases PART 2: A review of the current diagnostic and
treatment strategies for intervertebral disc disease. Int J Mol
Sci. 21(2135)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Makanji H, Schoenfeld AJ, Bhalla A and
Bono CM: Critical analysis of trends in lumbar fusion for
degenerative disorders revisited: Influence of technique on fusion
rate and clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J. 27:1868–1876.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shapiro IM, Vresilovic EJ and Risbud MV:
Is the spinal motion segment a diarthrodial polyaxial joint: What a
nice nucleus like you doing in a joint like this? Bone. 50:771–776.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen S, Fu P, Wu H and Pei M: Meniscus,
articular cartilage and nucleus pulposus: A comparative review of
cartilage-like tissues in anatomy, development and function. Cell
Tissue Res. 370:53–70. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kang R, Li H, Ringgaard S, Rickers K, Sun
H, Chen M, Xie L and Bünger C: Interference in the endplate
nutritional pathway causes intervertebral disc degeneration in an
immature porcine model. Int Orthop. 38:1011–1017. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tomaszewski KA, Adamek D, Konopka T,
Tomaszewska R and Walocha JA: Endplate calcification and cervical
intervertebral disc degeneration: The role of endplate marrow
contact channel occlusion. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 74:84–92.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mattei TA: Osteoporosis delays
intervertebral disc degeneration by increasing intradiscal
diffusive transport of nutrients through both mechanical and
vascular pathophysiological pathways. Med Hypotheses. 80:582–586.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Laffosse JM, Accadbled F, Molinier F,
Bonnevialle N, de Gauzy JS and Swider P: Correlations between
effective permeability and marrow contact channels surface of
vertebral endplates. J Orthop Res. 28:1229–1234. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rodriguez AG, Slichter CK, Acosta FL,
Rodriguez-Soto AE, Burghardt AJ, Majumdar S and Lotz JC: Human disc
nucleus properties and vertebral endplate permeability. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 36:512–520. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Han Y, Li X, Yan M, Yang M, Wang S, Pan J,
Li L and Tan J: Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes
calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through
ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 516:1026–1032. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Paassilta P, Pihlajamaa T, Annunen S,
Brewton RG, Wood BM, Johnson CC, Liu J, Gong Y, Warman ML, Prockop
DJ, et al: Complete sequence of the 23-kilobase human COL9A3 gene.
Detection of Gly-X-Y triplet deletions that represent neutral
variants. J Biol Chem. 274:22469–22475. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pihlajamaa T, Vuoristo MM, Annunen S,
Perala M, Prockop DJ and Ala-Kokko L: Human COL9A1 and COL9A2
genes. Two genes of 90 and 15 kb code for similar polypeptides of
the same collagen molecule. Matrix Biol. 17:237–241.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kamper M, Paulsson M and Zaucke F: Absence
of collagen IX accelerates hypertrophic differentiation in the
embryonic mouse spine through a disturbance of the Ihh-PTHrP
feedback loop. Cell Tissue Res. 367:359–367. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kamper M, Hamann N, Prein C,
Clausen-Schaumann H, Farkas Z, Aszodi A, Niehoff A, Paulsson M and
Zaucke F: Early changes in morphology, bone mineral density and
matrix composition of vertebrae lead to disc degeneration in aged
collagen IX -/- mice. Matrix Biol. 49:132–143. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Eyre DR, Pietka T, Weis MA and Wu JJ:
Covalent cross-linking of the NC1 domain of collagen type IX to
collagen type II in cartilage. J Biol Chem. 279:2568–2574.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bruckner P: Suprastructures of
extracellular matrices: Paradigms of functions controlled by
aggregates rather than molecules. Cell Tissue Res. 339:7–18.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Noponen-Hietala N, Kyllonen E, Mannikko M,
Kyllönen E, Männikkö M, Ilkko E, Karppinen J, Ott J and Ala-Kokko
L: Sequence variations in the collagen IX and XI genes are
associated with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Ann Rheum Dis.
62:1208–1214. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hyun SJ, Park BG, Rhim SC, Bae CW, Lee JK,
Roh SW and Jeon SR: A haplotype at the COL9A2 gene locus
contributes to the genetic risk for lumbar spinal stenosis in the
Korean population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:1273–1278.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, Weiler C,
Spratt KF and Nerlich AG: Classification of age-related changes in
lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 volvo award in basic science.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2631–2644. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Masuda K, Aota Y, Muehleman C, Imai Y,
Okuma M, Thonar EJ, Andersson GB and An HS: A novel rabbit model of
mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture:
Correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and
histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 30:5–14. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ruiz Wills C, Foata B, Gonzalez Ballester
MA, Karppinen J and Noailly J: Theoretical explorations generate
new hypotheses about the role of the cartilage endplate in early
intervertebral disk degeneration. Front Physiol.
9(1210)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jiang C, Guo Q, Jin Y, Xu JJ, Sun ZM, Zhu
DC, Lin JH, Tian NF, Sun LJ, Zhang XL and Wu YS: Inhibition of EZH2
ameliorates cartilage endplate degeneration and attenuates the
progression of intervertebral disc degeneration via demethylation
of Sox-9. EBioMedicine. 48:619–629. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yuan FL, Xu RS, Ye JX, Zhao MD, Ren LJ and
Li X: Apoptotic bodies from endplate chondrocytes enhance the
oxidative stress-induced mineralization by regulating PPi
metabolism. J Cell Mol Med. 23:3665–3675. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dudli S, Ballatori A, Bay-Jensen AC,
McCormick ZL, O'Neill CW, Demir-Deviren S, Krug R, Heggli I,
Juengel A, Karppinen J, et al: Serum biomarkers for connective
tissue and basement membrane remodeling are associated with
vertebral endplate bone marrow lesions as seen on MRI (Modic
changes). Int J Mol Sci. 21(3791)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Easson GW, Zhao J, Makki N, Ahituv
N, Hilton MJ, Tang SY and Gray RS: Dysregulation of STAT3 signaling
is associated with endplate-oriented herniations of the
intervertebral disc in Adgrg6 mutant mice. PLoS Genet.
15(e1008096)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rade M, Määttä JH, Freidin MB, Airaksinen
O, Karppinen J and Williams FM: Vertebral endplate defect as
initiating factor in intervertebral disc degeneration: Strong
association between endplate defect and disc degeneration in the
general population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 43:412–419.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Herrero CF, Garcia SB, Garcia LV and
Aparecido Defino HL: Endplates changes related to age and vertebral
segment. Biomed Res Int. 2014(545017)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jackson AR, Huang CY and Gu WY: Effect of
endplate calcification and mechanical deformation on the
distribution of glucose in intervertebral disc: A 3D finite element
study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 14:195–204.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li X and Yang S, Han L, Mao K and Yang S:
Ciliary IFT80 is essential for intervertebral disc development and
maintenance. FASEB J. 34:6741–6756. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang T, Dai Y, Zhang L, Tian Y, Li Z and
Wang J: Effects of edible oils with different n-6/n-3 PUFA ratios
on articular cartilage degeneration via regulating the NF-κB
signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 68:12641–12650.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
McCann MR, Veras MA, Yeung C, Lalli G,
Patel P, Leitch KM, Holdsworth DW, Dixon SJ and Séguin CA:
Whole-body vibration of mice induces progressive degeneration of
intervertebral discs associated with increased expression of Il-1β
and multiple matrix degrading enzymes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
25:779–789. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kita K, Kimura T, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa H
and Nakano T: PI3K/Akt signaling as a key regulatory pathway for
chondrocyte terminal differentiation. Genes Cells. 13:839–850.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang S, Zhang F, Ma J and Ding W:
Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic
effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 57(100978)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Q, Shen Y, Zhao S, Jiang Y, Zhou D
and Zhang Y: Exosomes miR-15a promotes nucleus pulposus-mesenchymal
stem cells chondrogenic differentiation by targeting MMP-3. Cell
Signal. 86(110083)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hristova GI, Jarzem P, Ouellet JA,
Roughley PJ, Epure LM, Antoniou J and Mwale F: Calcification in
human intervertebral disc degeneration and scoliosis. J Orthop Res.
29:1888–1895. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sun MM and Beier F: Chondrocyte
hypertrophy in skeletal development, growth, and disease. Birth
Defects Res C Embryo Today. 102:74–82. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, Huang M, Wang X, Xu X, Ni M and
Wang Y: Negative effects of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 on endplate
cartilage differentiation. J Orthop Res. 30:1238–1243.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Iwata M, Aikawa T, Hakozaki T, Arai K,
Ochi H, Haro H, Tagawa M, Asou Y and Hara Y: Enhancement of Runx2
expression is potentially linked to β-catenin accumulation in
canine intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol.
230:180–190. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|