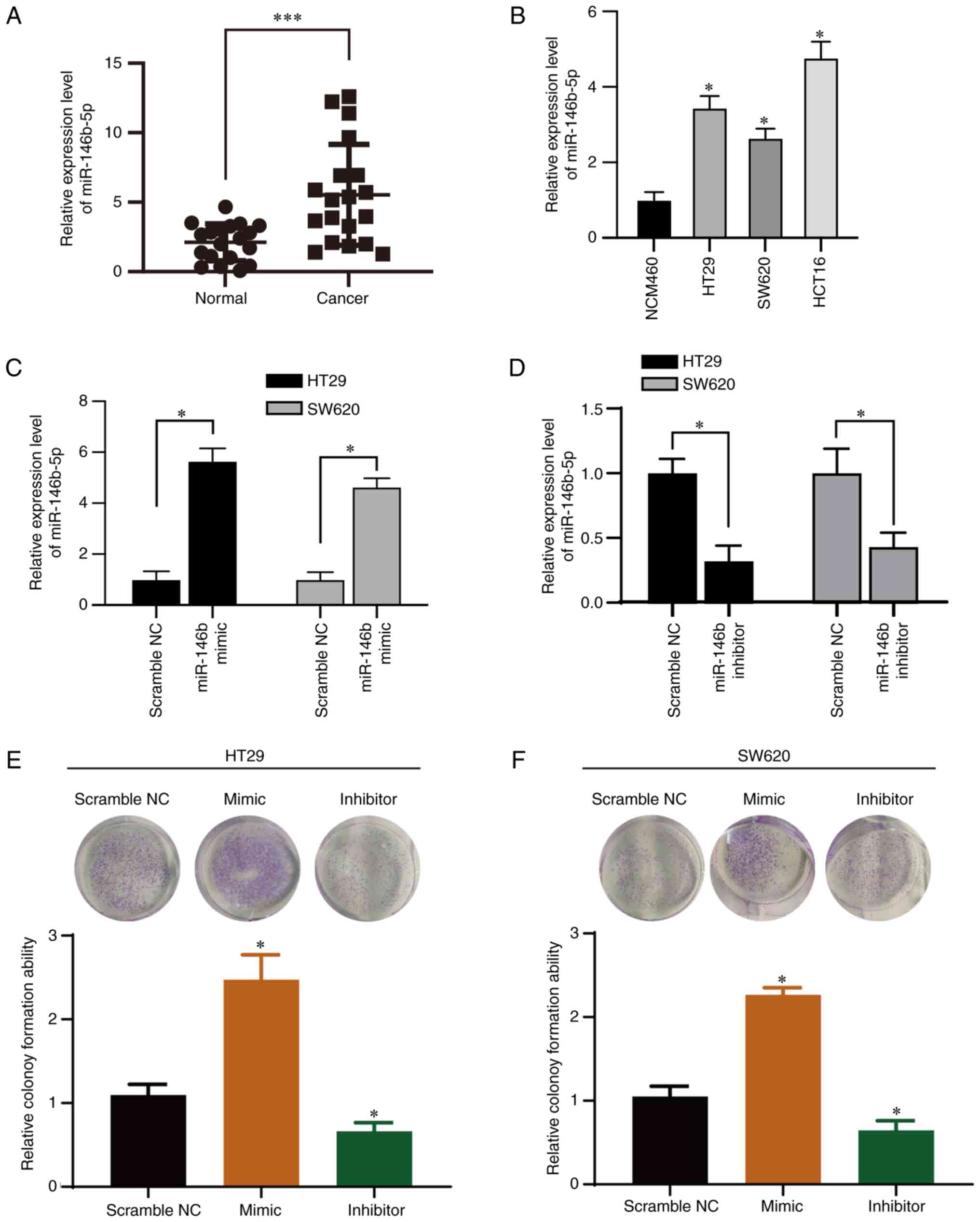
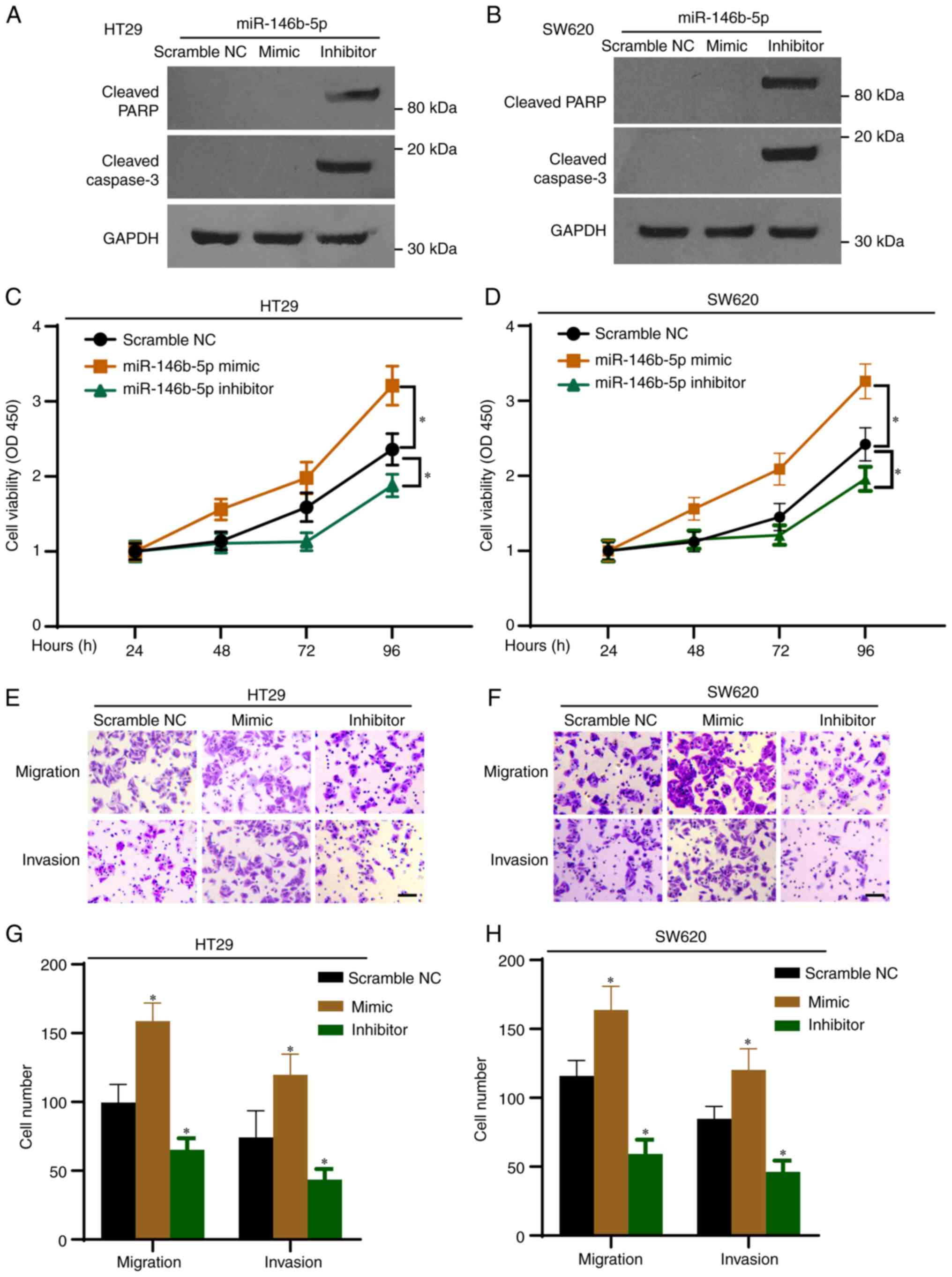
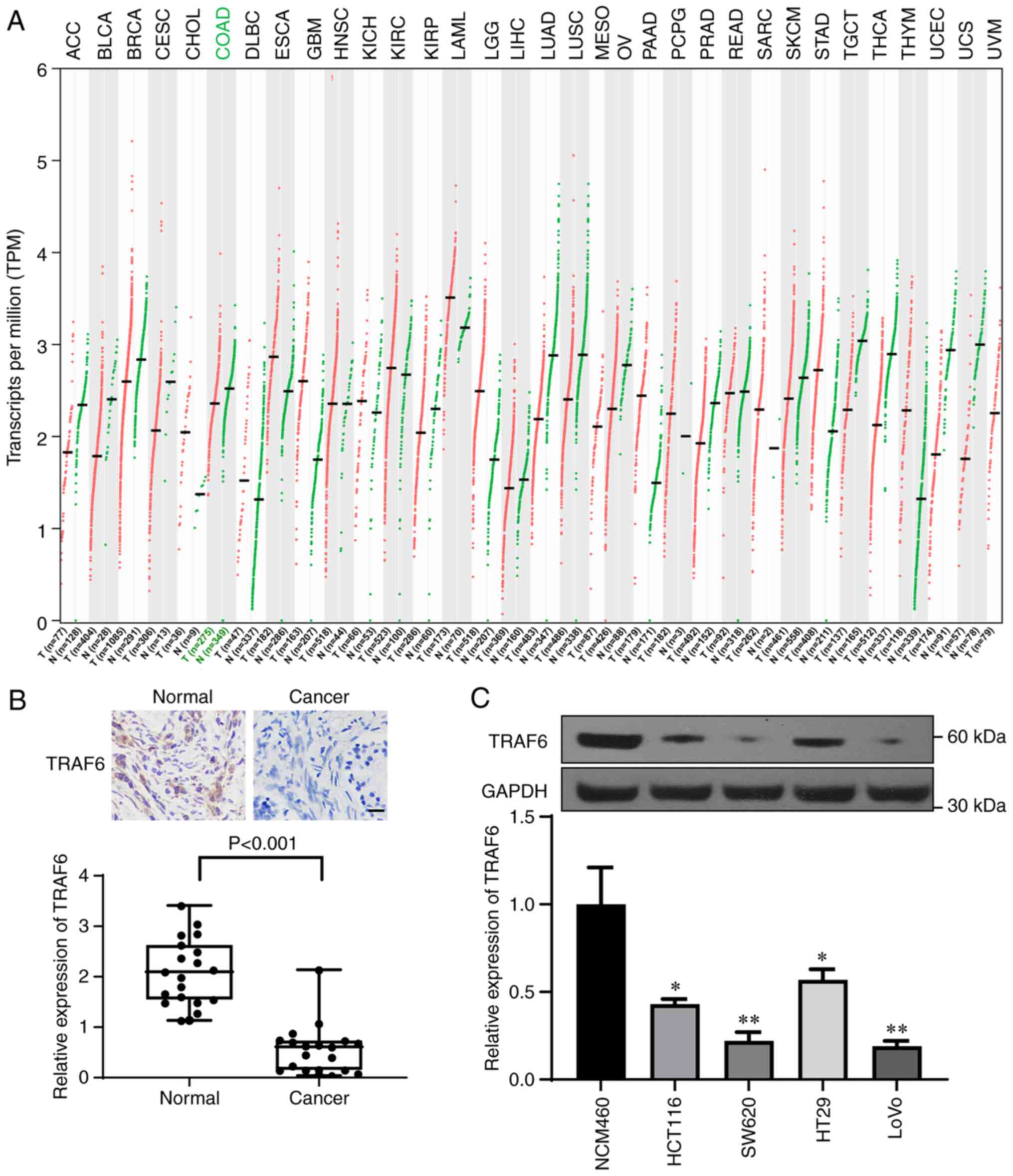
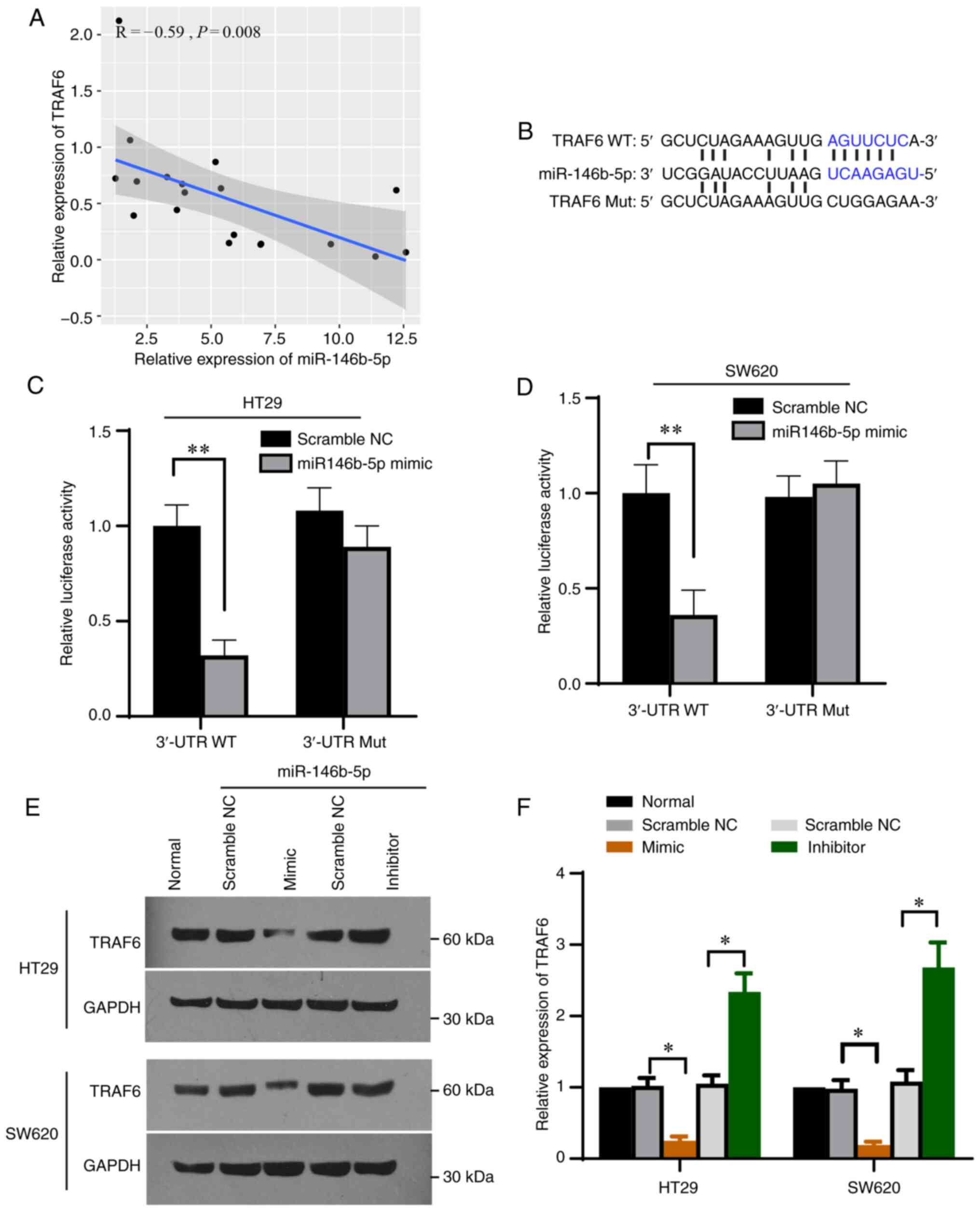
|
1
|
Labianca R, Beretta GD, Kildani B, Milesi
L, Merlin F, Mosconi S, Pessi MA, Prochilo T, Quadri A, Gatta G, et
al: Colon cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 74:106–133.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhou Z, Mo S, Dai W, Xiang W, Han L, Li Q,
Wang R, Liu L, Zhang L, Cai S and Cai G: Prognostic nomograms for
predicting cause-specific survival and overall survival of stage
I-III colon cancer patients: A large population-based study. Cancer
Cell Int. 19(355)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Freeman HJ: Early stage colon cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:8468–8473. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Klaver CEL, Kappen TM, Borstlap WAA,
Bemelman WA and Tanis PJ: Laparoscopic surgery for T4 colon cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 31:4902–4912.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hu T, Li Z, Gao CY and Cho CH: Mechanisms
of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:6876–6889. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yete S and Saranath D: MicroRNAs in oral
cancer: Biomarkers with clinical potential. Oral Oncol.
110(105002)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pisarska J and Baldy-Chudzik K:
MicroRNA-based fingerprinting of cervical lesions and cancer. J
Clin Med. 9(3668)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Morishita A, Oura K, Tadokoro T, Fujita K,
Tani J and Masaki T: MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Cancers (Basel).
13(514)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Machackova T, Prochazka V, Kala Z and
Slaby O: Translational potential of MicroRNAs for preoperative
staging and prediction of chemoradiotherapy response in rectal
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(1545)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yaghoubi N, Zahedi Avval F, Khazaei M and
Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH: MicroRNAs as potential investigative and
predictive biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Cell Signal.
80(109910)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rapado-González Ó, Álvarez-Castro A,
López-López R, Iglesias-Canle J, Suárez-Cunqueiro MM and
Muinelo-Romay L: Circulating microRNAs as promising biomarkers in
colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(898)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cojocneanu R, Braicu C, Raduly L, Jurj A,
Zanoaga O, Magdo L, Irimie A, Muresan MS, Ionescu C, Grigorescu M
and Berindan-Neagoe I: Plasma and tissue specific miRNA expression
pattern and functional analysis associated to colorectal cancer
patients. Cancers (Basel). 12(843)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Morimoto Y, Mizushima T, Wu X, Okuzaki D,
Yokoyama Y, Inoue A, Hata T, Hirose H, Qian Y, Wang J, et al:
miR-4711-5p regulates cancer stemness and cell cycle progression
via KLF5, MDM2 and TFDP1 in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
122:1037–1049. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu YN, Tsai MF, Wu SG, Chang TH, Tsai TH,
Gow CH, Wang HY and Shih JY: miR-146b-5p enhances the sensitivity
of NSCLC to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors by regulating the
IRAK1/NF-κB pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:471–483.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lv YP, Shi W, Liu HX, Kong XJ and Dai DL:
Identification of miR-146b-5p in tissues as a novel biomarker for
prognosis of gallbladder carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:518–522. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li S, Hao J, Hong Y, Mai J and Huang W:
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes the proliferation, migration,
and metastasis of human breast-cancer cells by inhibiting
miR-146b-5p expression. Cancer Manag Res. 12:6091–6101.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhu Y, Wu G, Yan W, Zhan H and Sun P:
miR-146b-5p regulates cell growth, invasion, and metabolism by
targeting PDHB in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1136–1150.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Xu J, Li H, Sun C, Yu L, Li Y, Shi
C, Zhou X, Bian X, Ping Y, et al: miR-146b-5p functions as a tumor
suppressor by targeting TRAF6 and predicts the prognosis of human
gliomas. Oncotarget. 6:29129–29142. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meng G, Li G, Yang X and Xiao N:
Inhibition of miR146b-5p suppresses CT-guided renal cell carcinoma
by targeting TRAF6. J Cell Biochem: Sep 11, 2018 (Epub ahead of
print). doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27566.
|
|
22
|
Jiang M, Lu W, Ding X, Liu X, Guo Z and Wu
X: p16INK4a inhibits the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells
through regulating the miR-146b-5p/TRAF6 pathway. Biosci Rep.
39(BSR20181268)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li C, Miao R, Liu S, Wan Y, Zhang S, Deng
Y, Bi J, Qu K, Zhang J and Liu C: Down-regulation of miR-146b-5p by
long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes
cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget. 8:28683–28695.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yang B, Du K, Yang C, Xiang L, Xu Y, Cao
C, Zhang J and Liu W: CircPRMT5 circular RNA promotes proliferation
of colorectal cancer through sponging miR-377 to induce E2F3
expression. J Cell Mol Med. 24:3431–3437. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4(e05005)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42 (Database Issue):D92–D97. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam
WL, Thomson AM, Lim B and Rigoutsos I: A pattern-based method for
the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their
corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 126:1203–1217. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Vejnar CE and Zdobnov EM: MiRmap:
Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:11673–11683. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45
(W1):W98–W102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Qiu Z, Tu L, Hu X, Zhou Z, Lin Y, Ye L and
Cui C: A preliminary study of miR-144 inhibiting the stemness of
colon cancer stem cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4. J
Biomed Nanotechnol. 16:1102–1109. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Marques D, Ferreira-Costa LR,
Ferreira-Costa LL, Bezerra-Oliveira AB, Correa RDS, Ramos CCO,
Vinasco-Sandoval T, Lopes KP, Vialle RA, Vidal AF, et al: Role of
miRNAs in sigmoid colon cancer: A search for potential biomarkers.
Cancers (Basel). 12(3311)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vargas-Medrano J, Yang B, Garza NT,
Segura-Ulate I and Perez RG: Up-regulation of protective neuronal
MicroRNAs by FTY720 and novel FTY720-derivatives. Neurosci Lett.
690:178–180. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wu HZY, Thalamuthu A, Cheng L, Fowler C,
Masters CL, Sachdev P and Mather KA: the Australian Imaging
Biomarkers and Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing. Differential
blood miRNA expression in brain amyloid imaging-defined Alzheimer's
disease and controls. Alzheimers Res Ther. 12(59)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ling X, Wen M, Xiao Z, Luo Z, Zhuang J, Li
Q, Du S, Zheng S and Zhu P: Lymphotoxin beta receptor is associated
with regulation of microRNAs expression and nuclear factor-kappa B
activation in lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated vascular smooth
muscle cells. Ann Palliat Med. 9:805–815. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mononen N, Lyytikäinen LP, Seppälä I,
Mishra PP, Juonala M, Waldenberger M, Klopp N, Illig T, Leiviskä J,
Loo BM, et al: Whole blood microRNA levels associate with glycemic
status and correlate with target mRNAs in pathways important to
type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. 9(8887)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen P, Li Y, Li L, Yu Q, Chao K, Zhou G,
Qiu Y, Feng R, Huang S, He Y, et al: Circulating microRNA146b-5p is
superior to C-reactive protein as a novel biomarker for monitoring
inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 49:733–743.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Tan L, Dong X, Liu L, Jiang Q, Li
H, Shi J, Yang X, Dai X, Qian Z and Dong J: MiR-146b-5p suppresses
the malignancy of GSC/MSC fusion cells by targeting SMARCA5. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:13647–13667. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pan Y, Yun W, Shi B, Cui R, Liu C, Ding Z,
Fan J, Jiang W, Tang J, Zheng T, et al: Downregulation of
miR-146b-5p via iodine involvement repressed papillary thyroid
carcinoma cell proliferation. J Mol Endocrinol. 65:1–10.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhu J and Chen G: Protective effect of
FOXP3-mediated miR-146b-5p/Robo1/NF-κB system on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Ann Transl
Med. 8(1651)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Strycharz J, Wróblewski A, Zieleniak A,
Świderska E, Matyjas T, Rucińska M, Pomorski L, Czarny P, Szemraj
J, Drzewoski J and Śliwińska A: Visceral adipose tissue of
prediabetic and diabetic females shares a set of similarly
upregulated microRNAs functionally annotated to inflammation,
oxidative stress and insulin signaling. Antioxidants (Basel).
10(101)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jia M, Shi Y, Li Z, Lu X and Wang J:
MicroRNA-146b-5p as an oncomiR promotes papillary thyroid carcinoma
development by targeting CCDC6. Cancer Lett. 443:145–156.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tong L, Tang C, Cai C and Guan X:
Upregulation of the microRNA rno-miR-146b-5p may be involved in the
development of intestinal injury through inhibition of Kruppel-like
factor 4 in intestinal sepsis. Bioengineered. 11:1334–1349.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ranjha R, Aggarwal S, Bopanna S, Ahuja V
and Paul J: Site-specific MicroRNA expression may lead to different
subtypes in ulcerative colitis. PLoS One.
10(e0142869)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li LY, Zhai Z and
Shu HB: VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered
IFN-beta signaling. Mol Cell. 19:727–740. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lad SP, Yang G, Scott DA, Chao TH, Correia
Jda S, de la Torre JC and Li E: Identification of MAVS splicing
variants that interfere with RIGI/MAVS pathway signaling. Mol
Immunol. 45:2277–2287. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Starczynowski DT, Lockwood WW, Deléhouzée
S, Chari R, Wegrzyn J, Fuller M, Tsao MS, Lam S, Gazdar AF, Lam WL
and Karsan A: TRAF6 is an amplified oncogene bridging the RAS and
NF-κB pathways in human lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 121:4095–4105.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rong Y, Wang D, Wu W, Jin D, Kuang T, Ni
X, Zhang L and Lou W: TRAF6 is over-expressed in pancreatic cancer
and promotes the tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cells. Med
Oncol. 31(260)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sun H, Li XB, Meng Y, Fan L, Li M and Fang
J: TRAF6 upregulates expression of HIF-1α and promotes tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 73:4950–4959. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang T, Wang H and Han L: Expression and
clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated
factor 6 in patients with colon cancer. Iran Red Crescent Med J.
18(e23931)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wei C, Lei L, Hui H and Tao Z:
MicroRNA-124 regulates TRAF6 expression and functions as an
independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett.
18:856–863. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wu H, Lu XX, Wang JR, Yang TY, Li XM, He
XS, Li Y, Ye WL, Wu Y, Gan WJ, et al: TRAF6 inhibits colorectal
cancer metastasis through regulating selective autophagic
CTNNB1/β-catenin degradation and is targeted for
GSK3B/GSK3β-mediated phosphorylation and degradation. Autophagy.
15:1506–1522. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sheng ZX, Yao H and Cai ZY: The role of
miR-146b-5p in TLR4 pathway of glomerular mesangial cells with
lupus nephritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1737–1743.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Echavarria R, Mayaki D, Neel JC, Harel S,
Sanchez V and Hussain SN: Angiopoietin-1 inhibits toll-like
receptor 4 signalling in cultured endothelial cells: Role of
miR-146b-5p. Cardiovasc Res. 106:465–477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yang G and Zhao Y: Overexpression of
miR-146b-5p ameliorates neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy by
inhibiting IRAK1/TRAF6/TAK1/NF-αB signaling. Yonsei Med J.
61:660–669. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Dong Y, Fan Y, Li Y, Zhao
C, Wang C, Liu J, Li X, Dong M, et al: MiR-146b-5p functions as a
suppressor miRNA and prognosis predictor in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Cancer. 8:1704–1716. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|