|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu F, Wang L and Zhou C: Lung cancer in
China: Current and prospect. Curr Opin Oncol. 33:40–46.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL,
Kwon R, Curran WJ, Yi-Long W and Paz-Ares L: Lung cancer: current
therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 389:299–311.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
de Sousa VM and Carvalho L: Heterogeneity
in lung cancer. Pathobiology. 85:96–107. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bai X, Meng L, Sun H, Li Z, Zhang X and
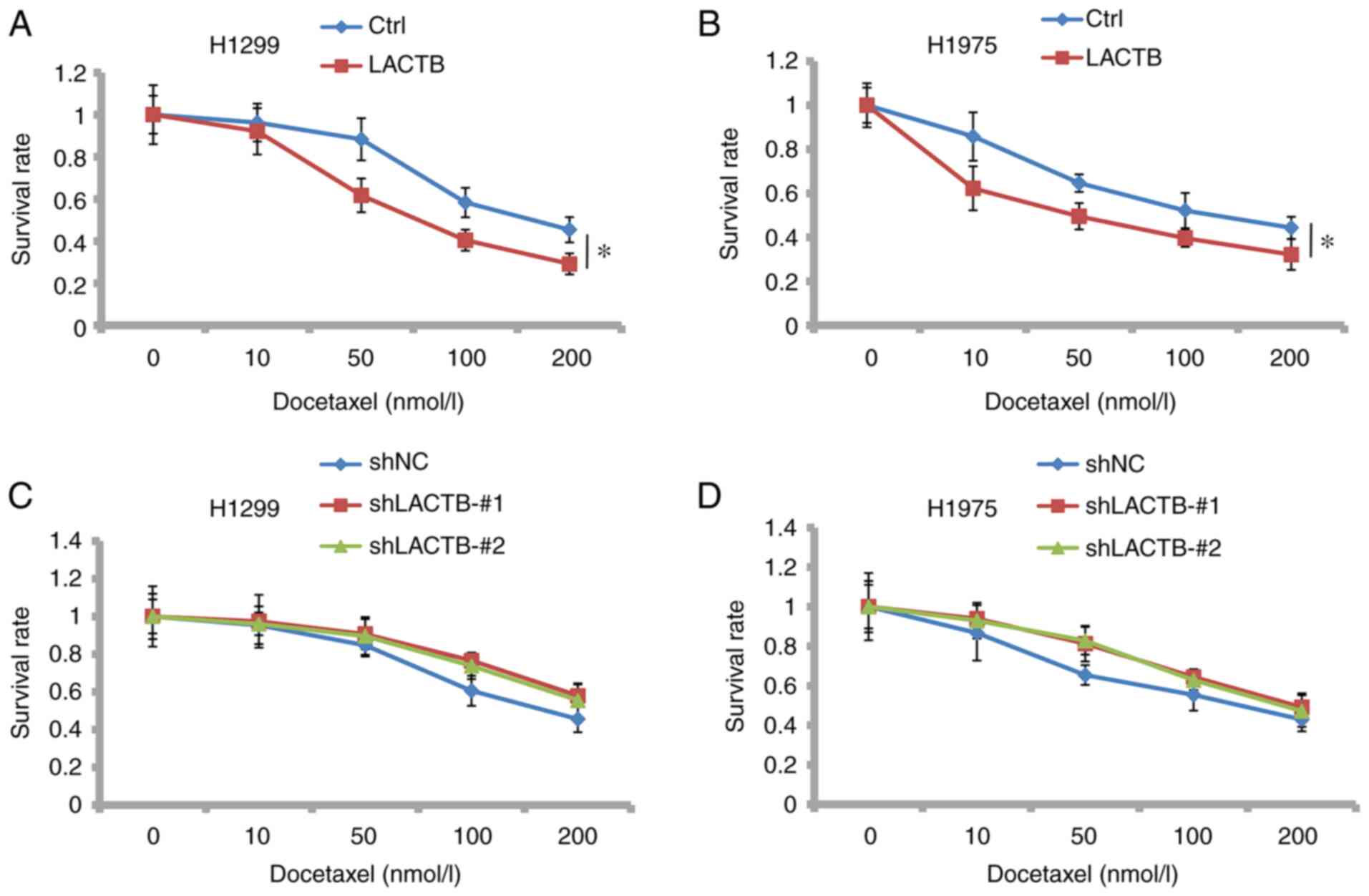
Hua S: MicroRNA-196b inhibits cell growth and metastasis of lung
cancer cells by targeting Runx2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:757–767.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Devlin JR and Verschuren EW: More than a
tumor suppressor: E-Cadherin loss drives lung cancer metastasis. Am
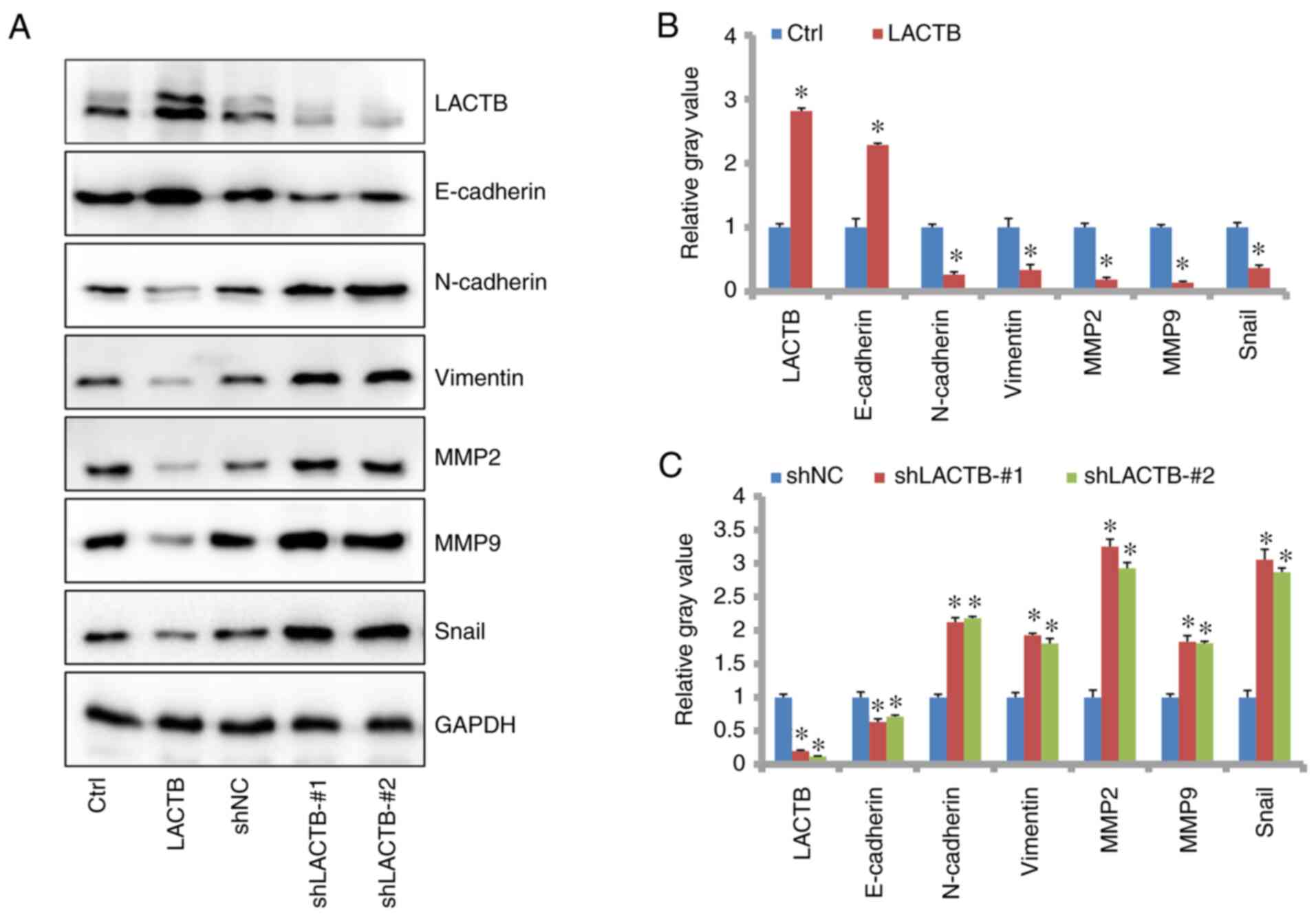
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 59:141–142. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ma Y, Wang L, He F, Yang J, Ding Y, Ge S,
Fan X, Zhou Y, Xu X and Jia R: LACTB suppresses melanoma
progression by attenuating PP1A and YAP interaction. Cancer Lett.
506:67–82. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li HT, Dong DY, Liu Q, Xu YQ and Chen L:
Overexpression of LACTB, a mitochondrial protein that inhibits
proliferation and invasion in glioma cells. Oncol Res. 27:423–429.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Al-Ostoot FH, Salah S, Khamees HA and
Khanum SA: Tumor angiogenesis: Current challenges and therapeutic
opportunities. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 28(100422)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zeng K, Chen X, Hu X, Liu X, Xu T, Sun H,
Pan Y, He B and Wang S: LACTB, a novel epigenetic silenced tumor
suppressor, inhibits colorectal cancer progression by attenuating
MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation. Oncogene.
37:5534–5551. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Peng LX, Wang MD, Xie P, Yang JP, Sun R,
Zheng LS, Mei Y, Meng DF, Peng XS, Lang YH, et al: LACTB promotes
metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activation of
ERBB3/EGFR-ERK signaling resulting in unfavorable patient survival.
Cancer Lett. 498:165–177. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xie J, Peng Y, Chen X, Li Q, Jian B, Wen Z
and Liu S: LACTB mRNA expression is increased in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma and high expression indicates a poor prognosis. PLoS
One. 16(e0245908)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vasan N, Baselga J and Hyman DM: A view on
drug resistance in cancer. Nature. 575:299–309. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang F, Yan Z, Nie W, Cheng X, Liu Z, Wang
W, Shao C, Fu G and Yu Y: LACTB induced apoptosis of
oxaliplatin-resistant gastric cancer through regulating
autophagy-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Am J Transl
Res. 13:601–616. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dibgre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jiang L, Huang J, Hu Y, Lu P, Luo Q and
Wang L: Gli promotes tumor progression through regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer. J
Cardiothorac Surg. 15(18)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu W, Yu M, Qin J, Luo Y and Zhong M:
LACTB regulates PIK3R3 to promote autophagy and inhibit EMT and
proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 12:5181–5200. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmitten TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Heberle E and Bardet AF: Sensitivity of
transcription factors to DNA methylation. Essays Biochem.
63:727–741. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xue C, He Y, Zhu W, Chen X, Yu Y, Hu Q,
Chen J, Liu L, Ren F, Ren Z, et al: Low expression of LACTB
promotes tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 10:4152–4162.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Senga SS and Grose RP: Hallmarks of
cancer-the new testament. Open Biol. 11(200358)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mohammadian J, Sabzichi M, Molavi O,
Shanehbandi D and Samadi N: Combined treatment with stattic and
docetaxel alters the Bax/Bcl-2 gene expression ratio in human
prostate cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:5031–5035.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Wang J, Wong YK, Sun X, Chen Y,
Wang L, Yang L, Lu L, Shen HM and Huang D: Docetaxel enhances
lysosomal function through TFEB activation. Cell Death Dis.
9(614)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Colli LM, Machiela MJ, Zhang H, Myers TA,
Jessop L, Delattre O, Yu K and Chanock SJ: Landscape of combination
immunotherapy and targeted therapy to improve cancer management.
Cancer Res. 77:3666–3671. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Asna N, Livoff A, Batash R, Debbi R,
Schaffer P, Rivkind T and Schaffer M: Radiation therapy and
immunotherapy-a potential combination in cancer treatment. Curr
Oncol. 25:e454–e460. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tulchinsky E, Demidov O, Kriajeska M,
Barlev NA and Imyanitov E: EMT: A mechanism for escape from
EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1871:29–39. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chae YK, Chang S, Ko T, Anker J, Agte S,
Iams W, Choi WM, Lee K and Cruz M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) signature is inversely associated with T-cell
infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Sci Rep.
8(2918)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ribatti D, Tamma R and Annese T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: A historical overview.
Transl Oncol. 13(100773)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Villarejo A, Cortés-Cabrera A,
Molina-Ortiz P, Portillo F and Cano A: Differential role of Snail1
and Snail2 zinc fingers in E-cadherin repression and epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 289:930–941. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shen W, Pang H, Liu J, Zhou J, Zhang F and
Liu L, Ma N, Zhang N, Zhang H and Liu L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition contributes to docetaxel resistance in human non-small
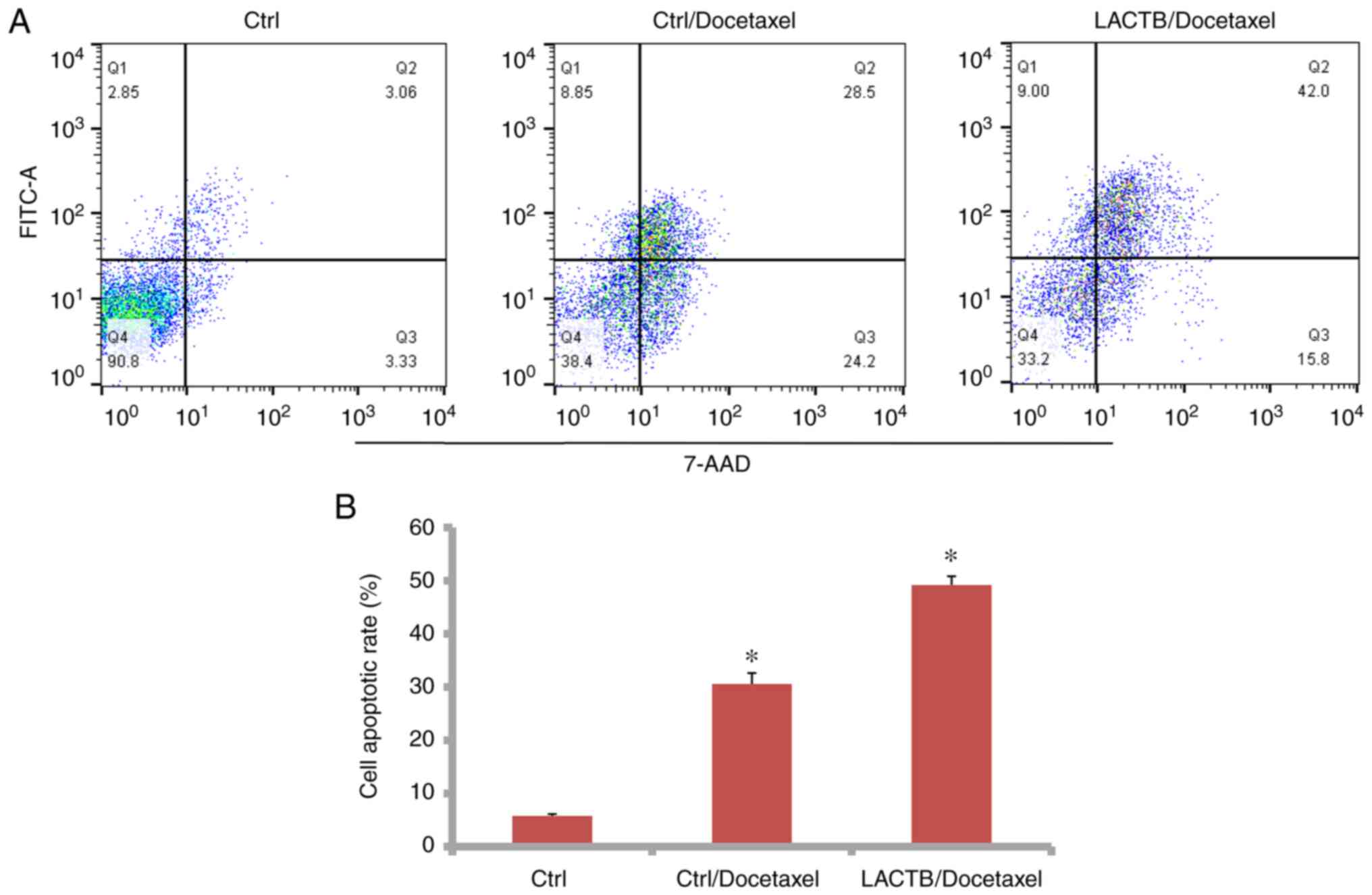
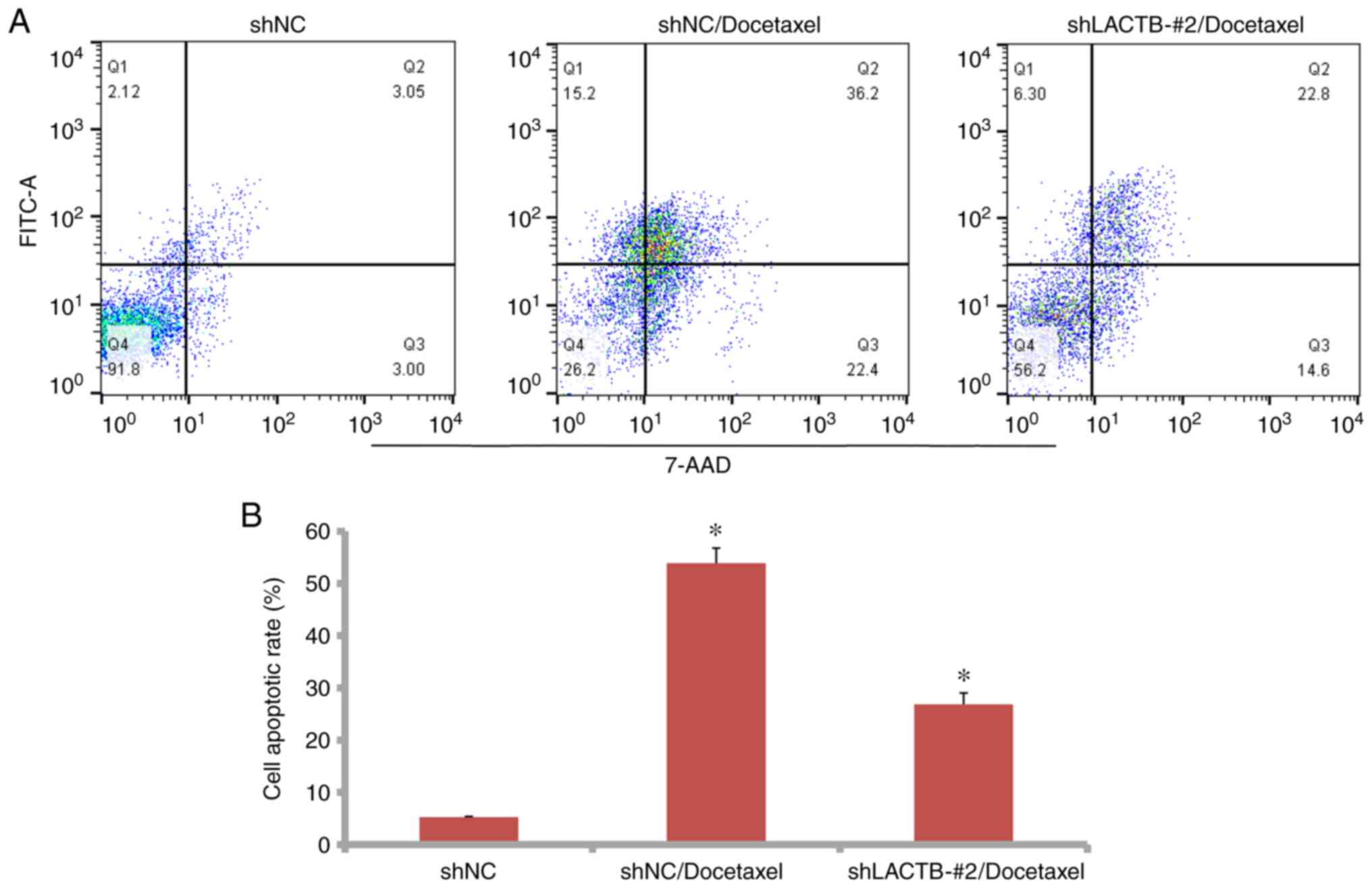
cell lung cancer. Oncol Res. 22:47–55. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|