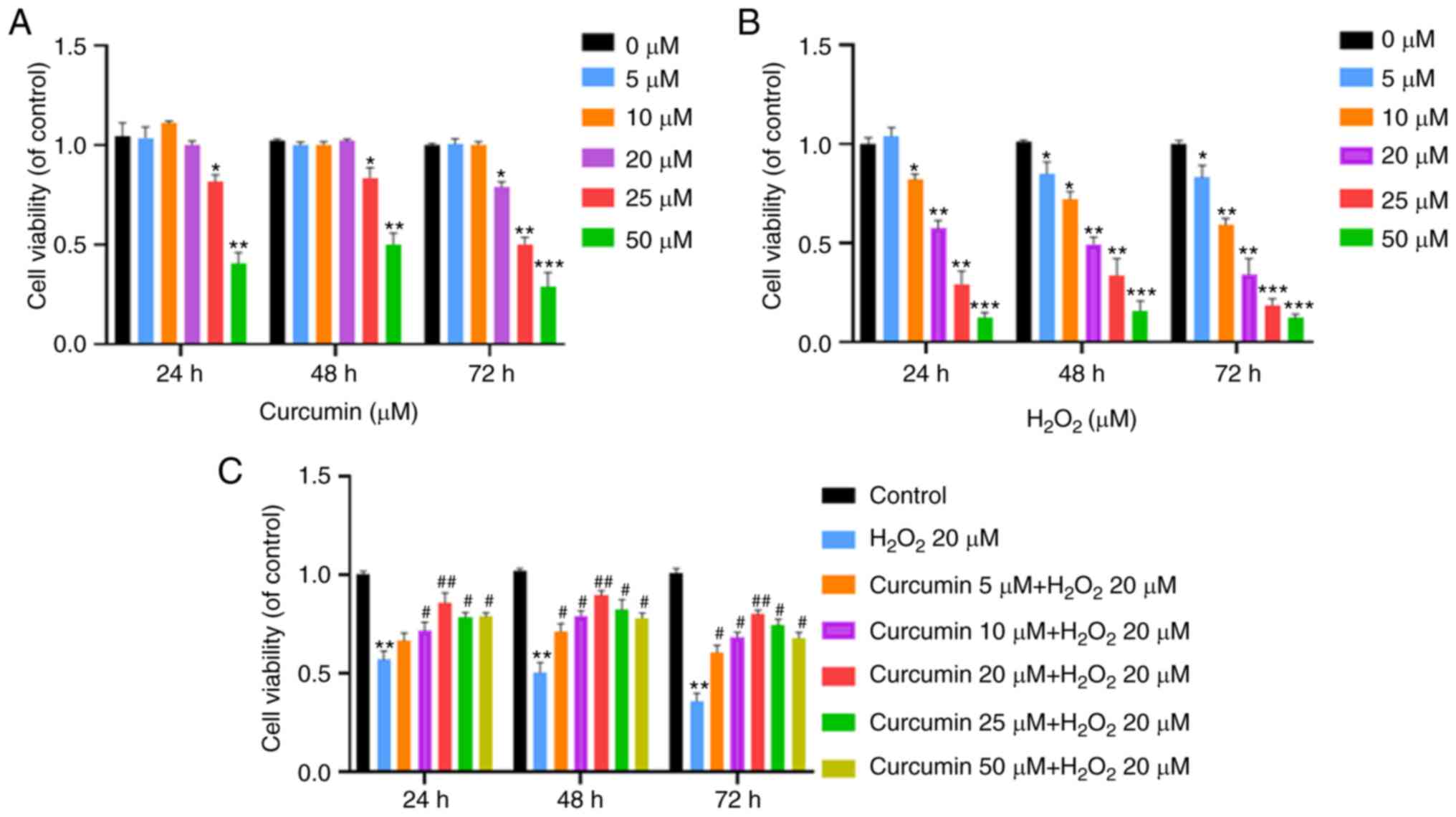
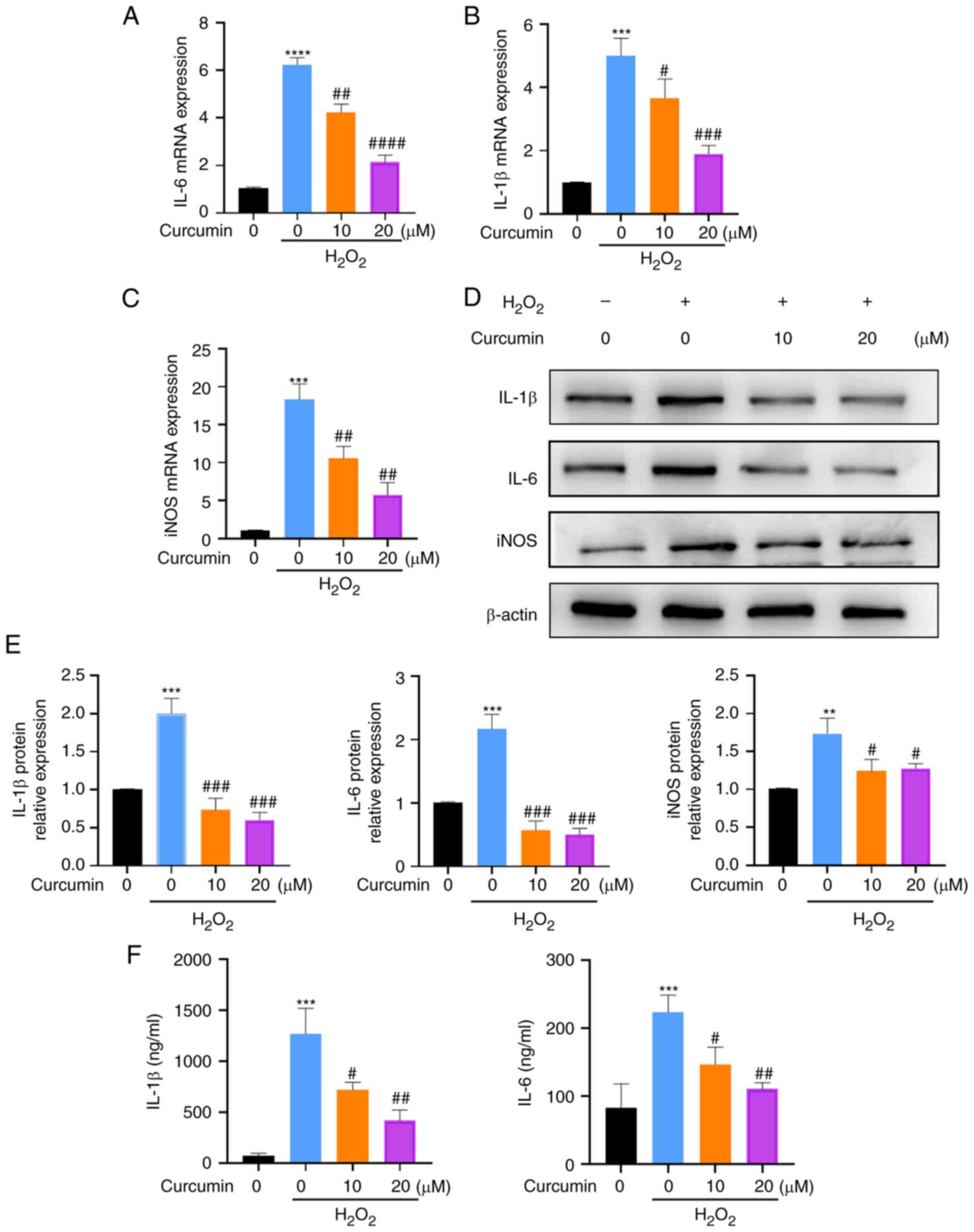
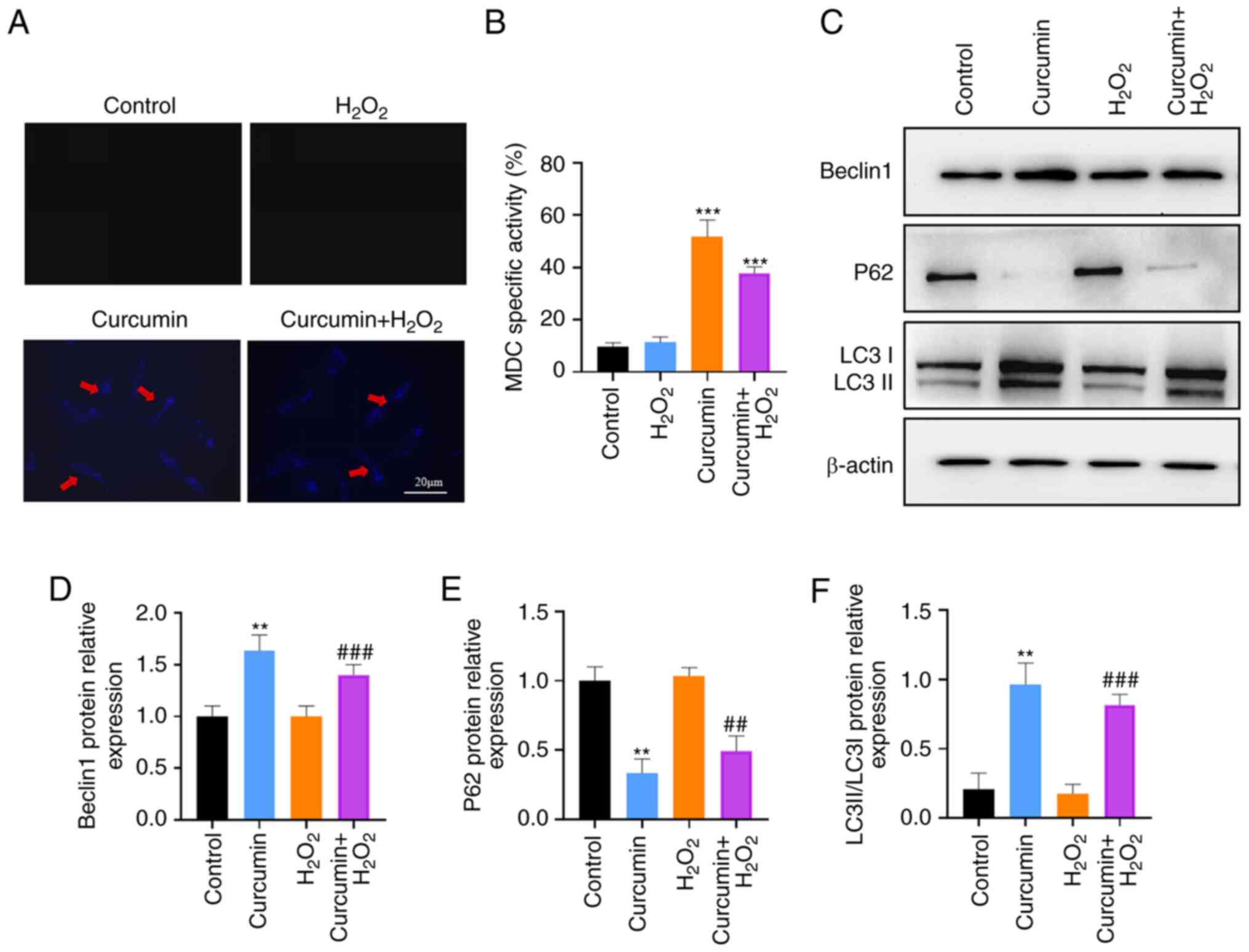
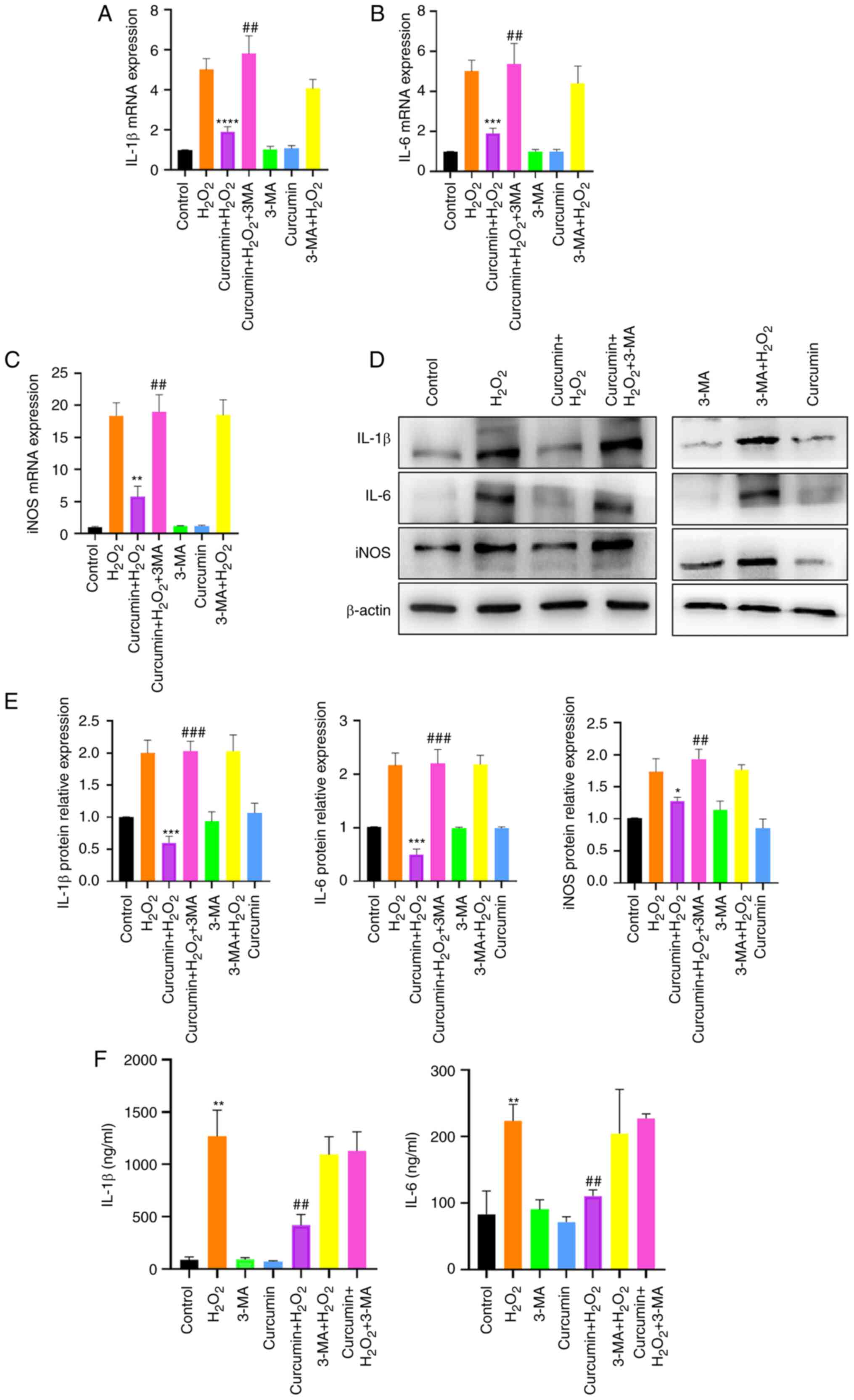
|
1
|
Norooznezhad F, Rodriguez-Merchan EC,
Asadi S and Norooznezhad AH: Curcumin: Hopeful treatment of
hemophilic arthropathy via inhibition of inflammation and
angiogenesis. Expert Rev Hematol. 13:5–11. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
de Montmollin N, Dusser D, Lorut C, Dion
J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Mouthon L, Chassagnon G, Revel MP and
Puéchal X: Tracheobronchial involvement of relapsing
polychondritis. Autoimmun Rev. 8(102353)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
D'Cruz DP and Ferrada MA: Relapsing
polychondritis and large-vessel vasculitis. J Rheumatol.
47:1732–1733. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yin H, Guo Q, Li X, Tang T, Li C, Wang H,
Sun Y, Feng Q, Ma C, Gao C, et al: Curcumin suppresses IL-1β
secretion and prevents inflammation through inhibition of the NLRP3
inflammasome. J Immunol. 200:2835–2846. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Burge K, Gunasekaran A, Eckert J and
Chaaban H: Curcumin and intestinal inflammatory diseases: Molecular
mechanisms of protection. Int J Mol Sci. 20(1912)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Deguchi A: Curcumin targets in
inflammation and cancer. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets.
15:88–96. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yavarpour-Bali H, Ghasemi-Kasman M and
Pirzadeh M: Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic
strategy in treatment of central nervous system disorders. Int J
Nanomedicine. 14:4449–4460. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Bordoloi D, Padmavathi G,
Monisha J, Roy NK, Prasad S and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin, the golden
nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br J
Pharmacol. 174:1325–1348. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cao Y, Chen J, Ren G, Zhang Y, Tan X and
Yang L: Punicalagin prevents inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7
macrophages by inhibiting FoxO3a/Autophagy signaling pathway.
Nutrients. 11(2794)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Matsuzawa-Ishimoto Y, Hwang S and Cadwell
K: Autophagy and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 36:73–101.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ho J, Yu J, Wong SH, Zhang L, Liu X, Wong
WT, Leung CC, Choi G, Wang MH, Gin T, et al: Autophagy in sepsis:
Degradation into exhaustion? Autophagy. 12:1073–1082.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pozuelo-Rubio M: 14-3-3 proteins are
regulators of autophagy. Cells. 1:754–773. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Martinet W, Agostinis P, Vanhoecke B,
Dewaele M and De Meyer GR: Autophagy in disease: A double-edged
sword with therapeutic potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:697–712.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kuma A, Komatsu M and Mizushima N:
Autophagy-monitoring and autophagy-deficient mice. Autophagy.
13:1619–1628. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Renga G, Oikonomou V, Stincardini C,
Pariano M, Borghi M, Costantini C, Bartoli A, Garaci E, Goldstein
AL and Romani L: Thymosin β4 limits inflammation through autophagy.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 18 (Suppl 1):S171–S175. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cui SN, Chen ZY, Yang XB, Chen L, Yang YY,
Pan SW, Wang YX, Xu JQ, Zhou T, Xiao HR, et al: Trichostatin A
modulates the macrophage phenotype by enhancing autophagy to reduce
inflammation during polymicrobial sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol.
77(105973)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tang Y, Mo Y, Xin D, Zeng L, Yue Z and Xu
C: β-ecdysterone alleviates osteoarthritis by activating autophagy
in chondrocytes through regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal pathway. Am
J Transl Res. 12:7174–7186. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang L, Chen C, Zhang X, Li X, Chen Z,
Yang C, Liang X, Zhu G and Xu Z: Neuroprotective effect of curcumin
against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via mediating autophagy and
inflammation. J Mol Neurosci. 64:129–139. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Munafó DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–3629. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Muhammad I, Wang X, Li S, Li R and Zhang
X: Curcumin confers hepatoprotection against
AFB1-induced toxicity via activating autophagy and
ameliorating inflammation involving Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Mol Biol Rep. 45:1775–1785. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shakibaei M, Mobasheri A and Buhrmann C:
Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to stimulate the MAPK
signaling pathway in human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Genes
Nutr. 6:171–179. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mobasheri A, Henrotin Y, Biesalski HK and
Shakibaei M: Scientific evidence and rationale for the development
of curcumin and resveratrol as nutraceutricals for joint health.
Int J Mol Sci. 13:4202–4232. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Csaki C, Mobasheri A and Shakibaei M:
Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol
in human articular chondrocytes: Inhibition of IL-1beta-induced
NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Arthritis Res Ther.
11(R165)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen T, Zhou R, Chen Y, Fu W, Wei X, Ma G,
Hu W and Lu C: Curcumin ameliorates IL-1β-induced apoptosis by
activating autophagy and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in
rat primary articular chondrocytes. Cell Biol Int. 45:976–988.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco
FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal
cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62:791–801. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Settembre C, Arteaga-Solis E, McKee MD, de
Pablo R, Al Awqati Q, Ballabio A and Karsenty G: Proteoglycan
desulfation determines the efficiency of chondrocyte autophagy and
the extent of FGF signaling during endochondral ossification. Genes
Dev. 22:2645–2650. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Patergnani S, Missiroli S, Morciano G,
Perrone M, Mantovani CM, Anania G, Fiorica F, Pinton P and Giorgi
C: Understanding the role of autophagy in cancer formation and
progression is a real opportunity to treat and cure human cancers.
Cancers (Basel). 13(5622)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ikeda S, Zablocki D and Sadoshima J: The
role of autophagy in death of cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
165:1–8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Farber E, Hanut A, Tadmor H, Ruth A,
Nakhoul F and Nakhoul N: Autophagy and diabetic nephropathy.
Harefuah. 160:740–745. 2021.PubMed/NCBI(In Hebrew).
|
|
31
|
Zhou JC, Wang JL, Ren HZ and Shi XL:
Autophagy plays a double-edged sword role in liver diseases. J
Physiol Biochem. Oct 18, 2021. (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1007/s13105-021-00844-7.
|
|
32
|
Wu MY, Wang EJ, Feng D, Li M, Ye RD and Lu
JH: Pharmacological insights into autophagy modulation in
autoimmune diseases. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:3364–3378.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sriram N and Sah MK: Regulatory insights
into progression of cancer and Alzheimer's disorder from autophagy
perspective. Mol Biol Rep. 48:8227–8232. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Leonardi L, Sibéril S, Alifano M, Cremer I
and Joubert PE: Autophagy modulation by viral infections influences
tumor development. Front Oncol. 11(743780)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ravanan P, Srikumar IF and Talwar P:
Autophagy: The spotlight for cellular stress responses. Life Sci.
188:53–67. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chang CP, Su YC, Hu CW and Lei HY:
TLR2-dependent selective autophagy regulates NF-κB lysosomal
degradation in hepatoma-derived M2 macrophage differentiation. Cell
Death Differ. 20:515–523. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Qing G, Yan P, Qu Z, Liu H and Xiao G:
Hsp90 regulates processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 involving protection
of NF-kappa B2 p100 involving protection of NF-kappa B-inducing
kinase (NIK) from autophagy-mediated degradation. Cell Res.
17:520–530. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: p62 at the
crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell. 137:1001–004.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi
K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou YS, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, et
al: The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress
responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:213–223. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Song C, Mitter SK, Qi X, Beli E, Rao HV,
Ding J, Ip CS, Gu H, Akin D, Dunn WA Jr, et al: Oxidative
stress-mediated NFκB phosphorylation upregulates p62/SQSTM1 and
promotes retinal pigmented epithelial cell survival through
increased autophagy. PLoS One. 12(e0171940)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Puéchal X, Terrier B, Mouthon L,
Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Guillevin L and Le Jeunne C: Relapsing
polychondritis. Joint Bone Spine. 81:118–124. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vitale A, Sota J, Rigante D, Lopalco G,
Molinaro F, Messina M, Iannone F and Cantarini L: Relapsing
polychondritis: An update on pathogenesis, clinical features,
diagnostic tools, and therapeutic perspectives. Curr Rheumatol Rep.
18(3)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qin Y, Zheng B, Yang GS, Yang HJ, Zhou J,
Yang Z, Zhang XH, Zhao HY, Shi JH and Wen JK: Salvia
miltiorrhiza-derived Sal-miR-58 induces autophagy and attenuates
inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 21:492–511. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|