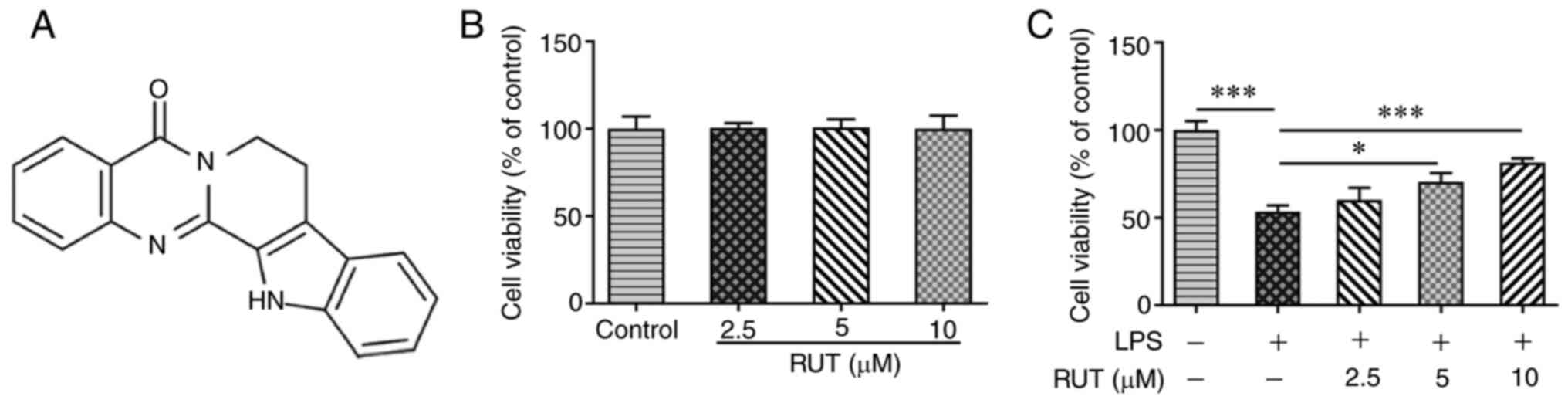
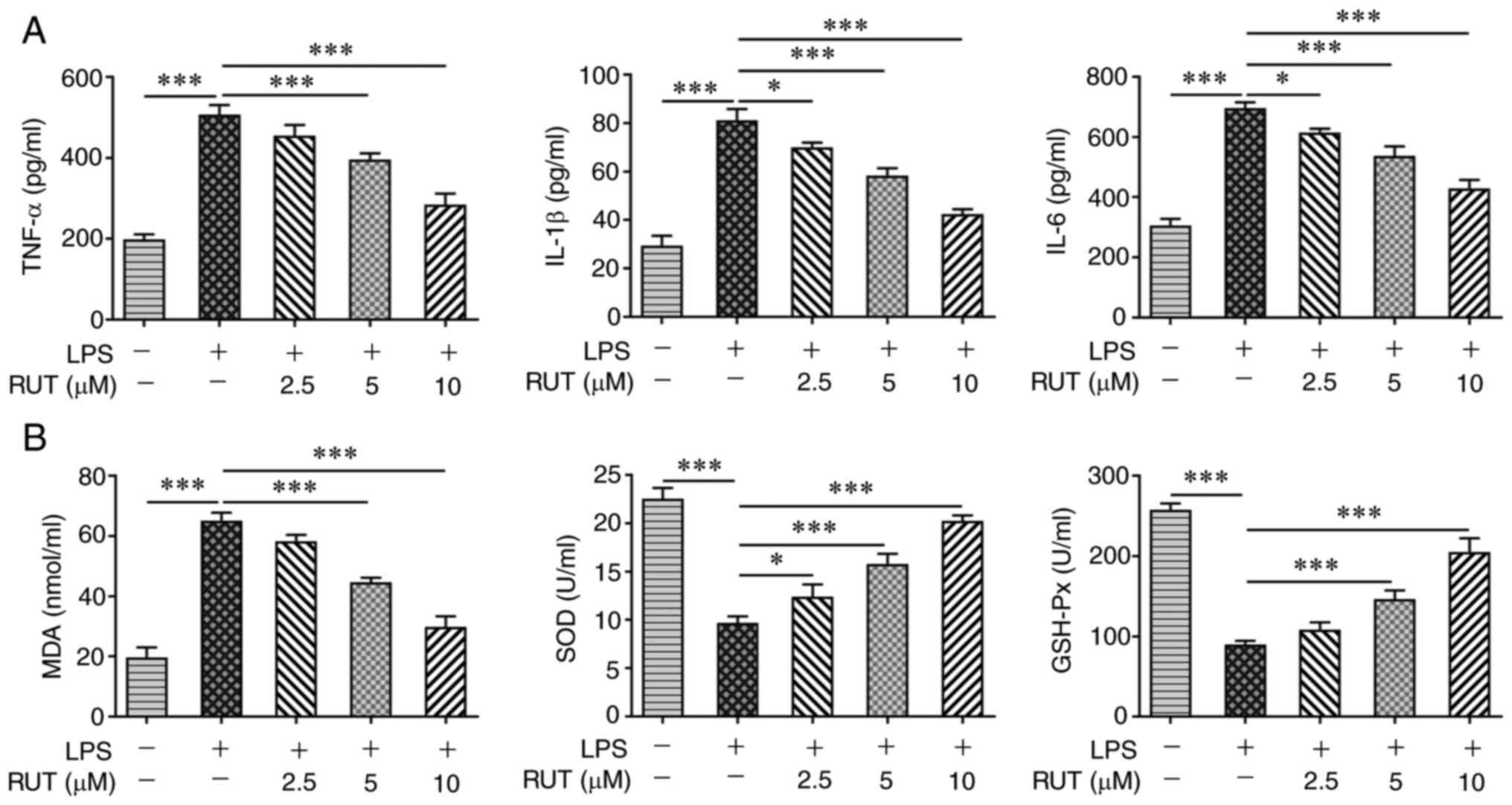
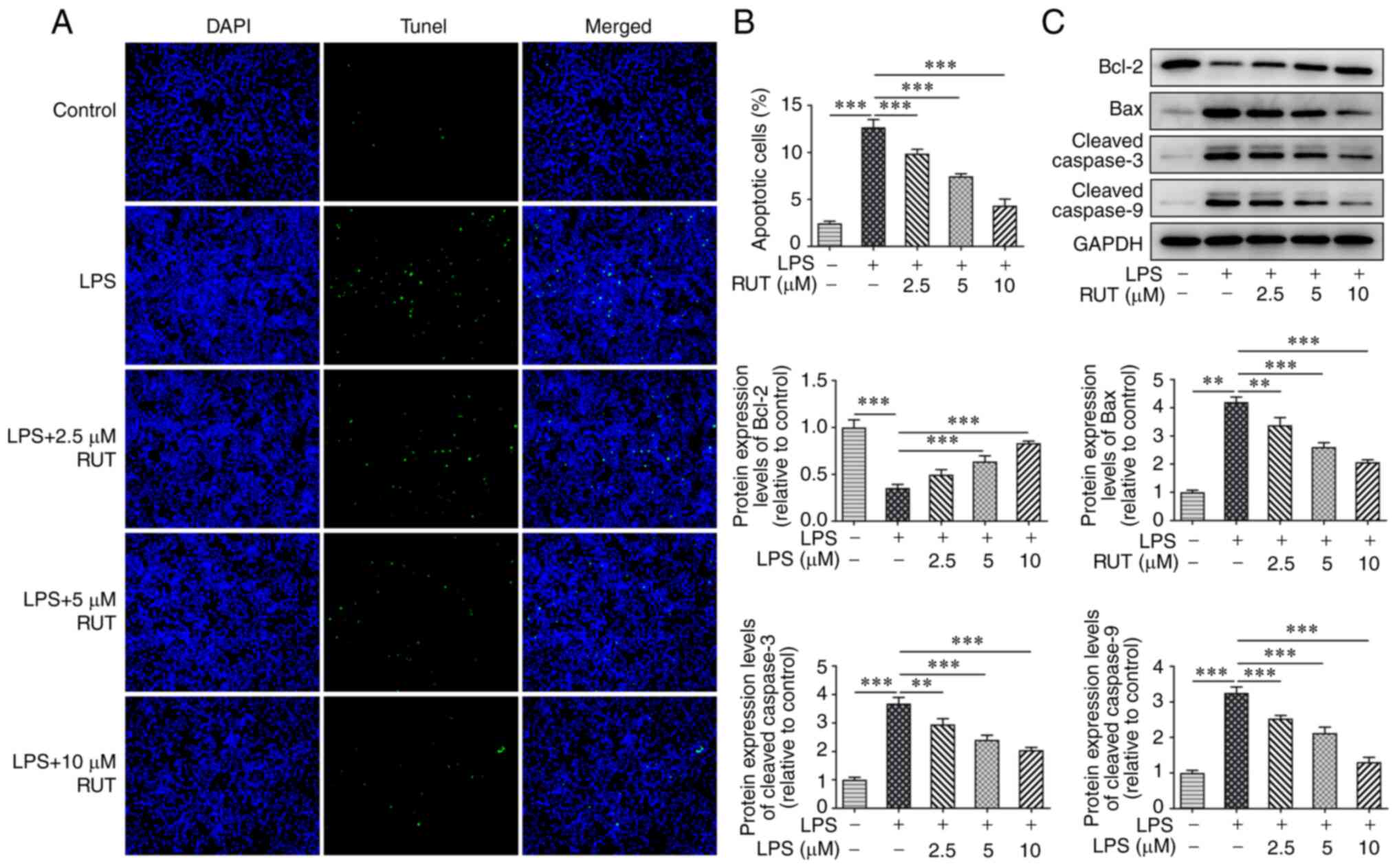
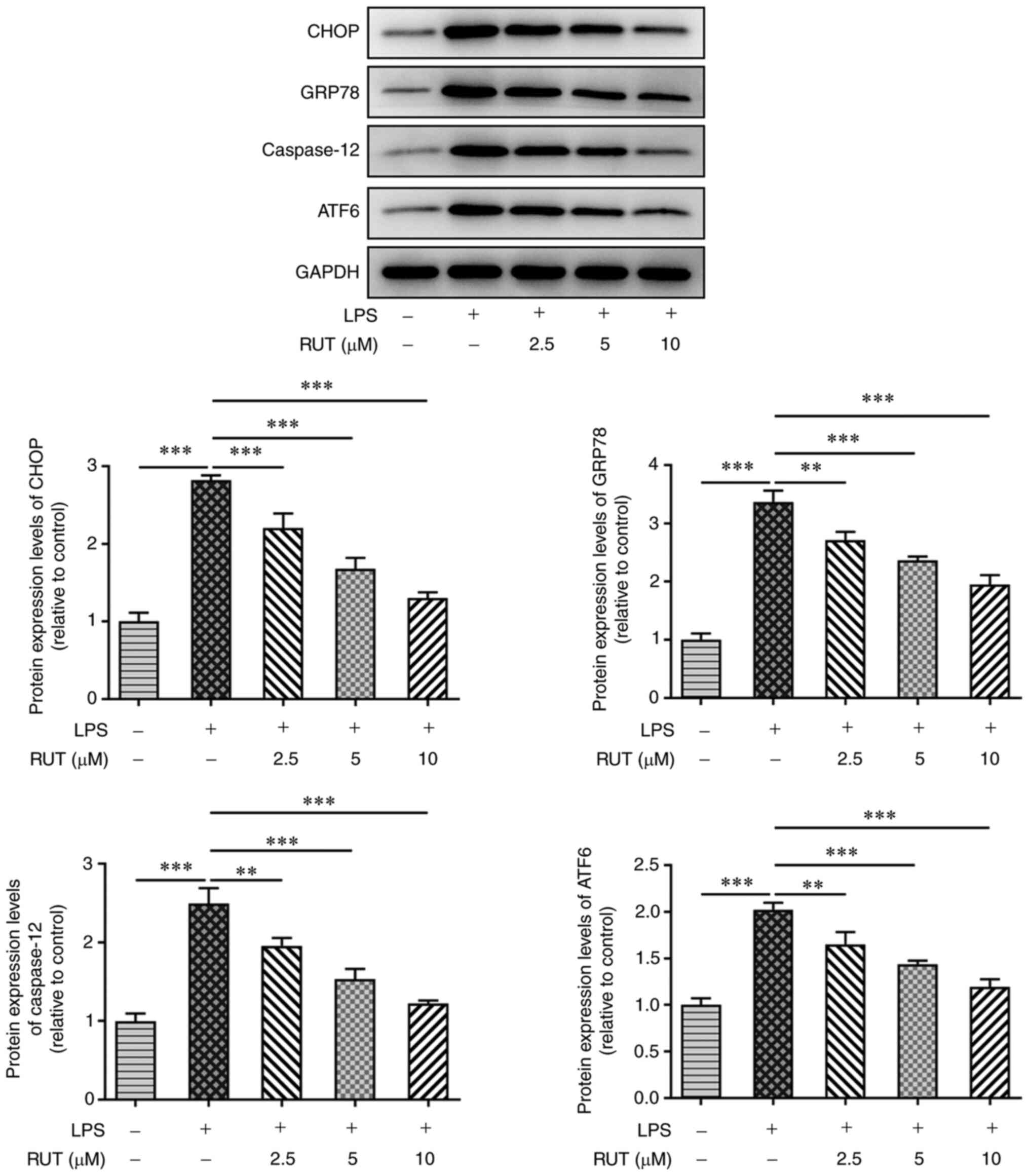
|
1
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Abedi F, Hayes AW, Reiter R and Karimi G:
Acute lung injury: The therapeutic role of Rho kinase inhibitors.
Pharmacol Res. 155(104736)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
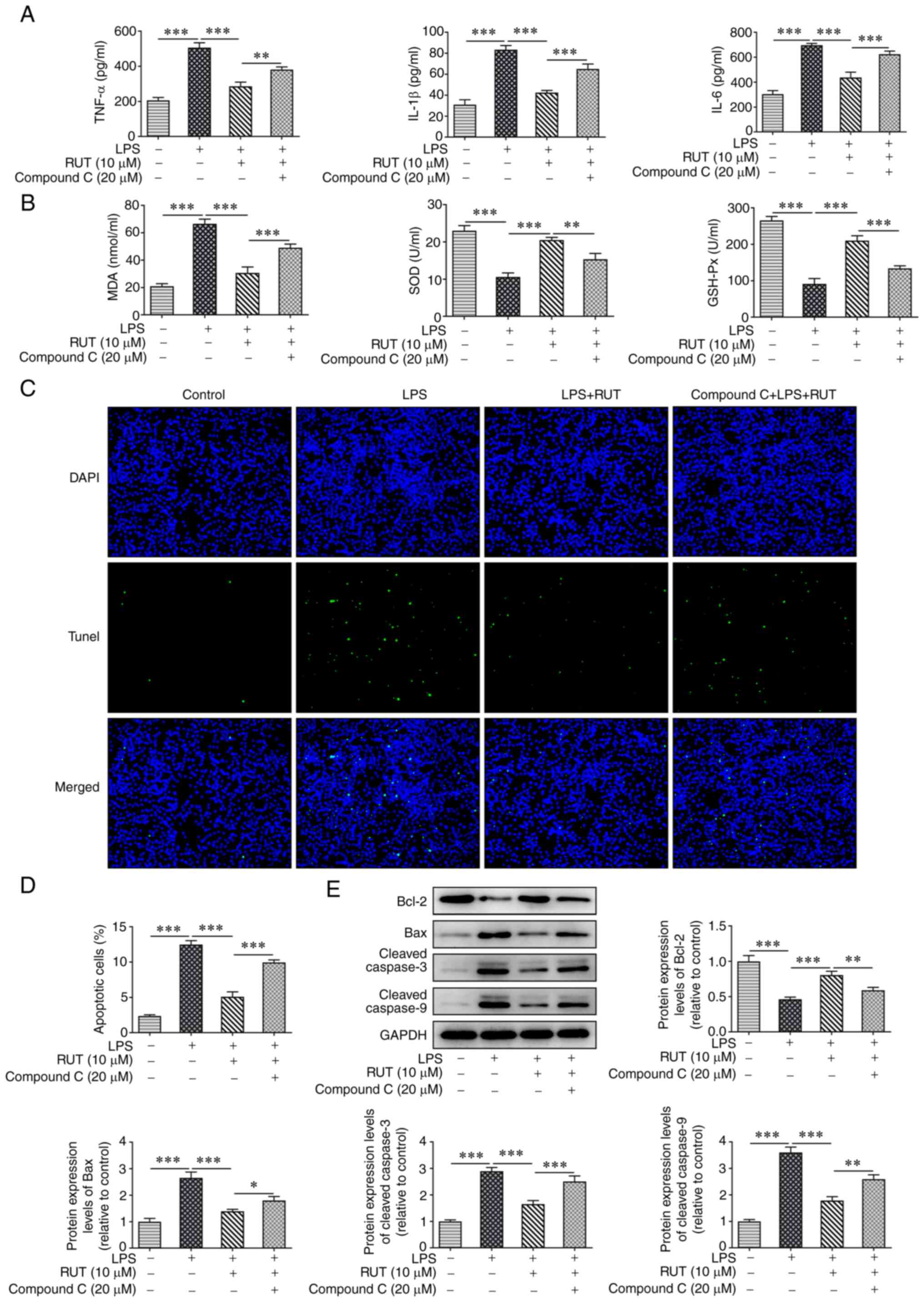
|
|
3
|
Yan J, Wang A, Cao J and Chen L:
Apelin/APJ system: An emerging therapeutic target for respiratory
diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:2919–2930. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Standiford TJ and Ward PA: Therapeutic
targeting of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Transl Res. 167:183–191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chambers ED, White A, Vang A, Wang Z,
Ayala A, Weng T, Blackburn M, Choudhary G, Rounds S and Lu Q:
Blockade of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1/2 protects
against pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute lung injury and NLRP3
inflammasome activation. FASEB J. 34:1516–1531. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao Z, Gong S, Wang S and Ma C: Effect
and mechanism of evodiamine against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer
in mice by suppressing Rho/NF-кB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
28:588–595. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jia S and Hu C: Pharmacological effects of
rutaecarpine as a cardiovascular protective agent. Molecules.
15:1873–1881. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ren S, Wei Y, Wang R, Wei S, Wen J, Yang
T, Chen X, Wu S, Jing M, Li H, et al: Rutaecarpine ameliorates
ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice by modulating genes
related to inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Front
Pharmacol. 11(600295)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Yan T, Sun D, Xie C, Wang T, Liu
X, Wang J, Wang Q, Luo Y, Wang P, et al: Rutaecarpine inhibits
KEAP1-NRF2 interaction to activate NRF2 and ameliorate dextran
sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 148:33–41.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nie XQ, Chen HH, Zhang JY, Zhang YJ, Yang
JW, Pan HJ, Song WX, Murad F, He YQ and Bian K: Rutaecarpine
ameliorates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia in fat-fed,
streptozotocin-treated rats via regulating the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and
AMPK/ACC2 signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:483–496.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang R, Xie Y, Qiu J and Chen J: The
effects of dexmedetomidine in a rat model of sepsis-induced lung
injury are mediated through the adenosine monophosphate-activated
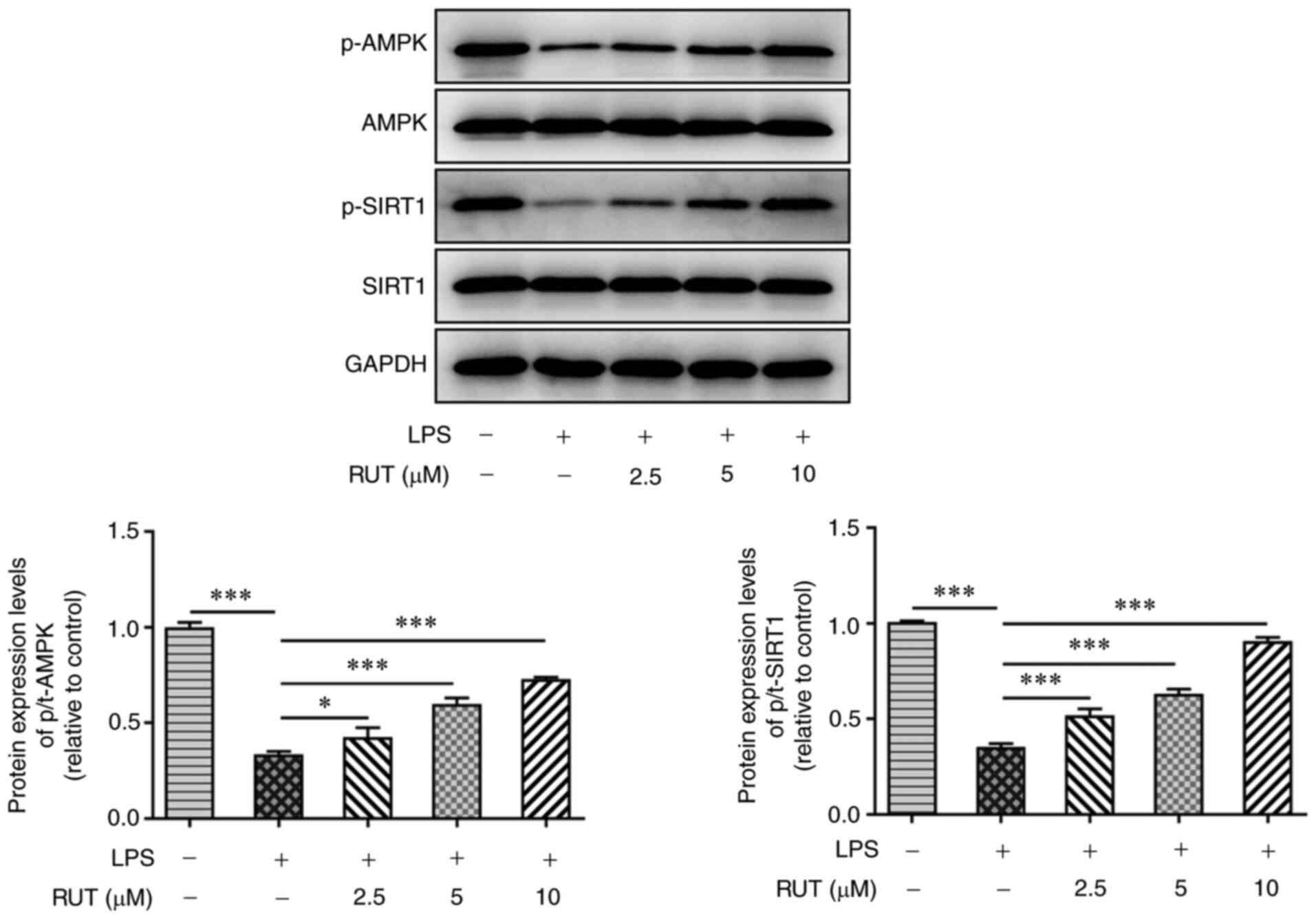
protein kinase (AMPK)/silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1)
pathway. Med Sci Monit. 26(e919213)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bao MH, Dai W, Li YJ and Hu CP:
Rutaecarpine prevents hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced myocardial cell
apoptosis via inhibition of NADPH oxidases. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 89:177–186. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Luo X, Lin B, Gao Y, Lei X, Wang X, Li Y
and Li T: Genipin attenuates mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis,
endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT
pathway in acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol.
76(105842)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS and Matthay
MA: Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 14:523–535. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xie X, Sun S, Zhong W, Soromou LW, Zhou X,
Wei M, Ren Y and Ding Y: Zingerone attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 19:103–109. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yeh CC, Lin CC, Wang SD, Chen YS, Su BH
and Kao ST: Protective and anti-inflammatory effect of a
traditional Chinese medicine, Xia-Bai-San, by modulating lung local
cytokine in a murine model of acute lung injury. Int
Immunopharmacol. 6:1506–1514. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Deng G, He H, Chen Z, OuYang L, Xiao X, Ge
J, Xiang B, Jiang S and Cheng S: Lianqinjiedu decoction attenuates
LPS-induced inflammation and acute lung injury in rats via
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:148–152.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fu PK, Wu CL, Tsai TH and Hsieh CL:
Anti-inflammatory and anticoagulative effects of paeonol on
LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012(837513)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang KL, Chen CS, Hsu CW, Li MH, Chang H,
Tsai SH and Chu SJ: Therapeutic effects of baicalin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Am J Chin
Med. 36:301–311. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lu Z, Yang H, Cao H, Huo C, Chen Y, Liu D,
Xie P, Zhou H, Liu J and Yu L: Forsythoside A protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through up-regulating
microRNA-124. Clin Sci (Lond). 134:2549–2563. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang Q and Xiao L: Isochlorogenic acid A
attenuates acute lung injury induced by LPS via Nf-κB/NLRP3
signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 11:7018–7026. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin SW, Hwang YP, Choi CY, Kim HG, Kim SJ,
Kim Y, Chung YC, Lee KJ, Jeong TC and Jeong HG: Protective effect
of rutaecarpine against t-BHP-induced hepatotoxicity by
upregulating antioxidant enzymes via the CaMKII-Akt and Nrf2/ARE
pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 100:138–148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yan L, Li QF, Rong YT, Chen YH, Huang ZH,
Wang ZZ and Peng J: The protective effects of rutaecarpine on acute
pancreatitis. Oncol Lett. 15:3121–3126. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Han M, Hu L and Chen Y: Rutaecarpine may
improve neuronal injury, inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and
oxidative stress by regulating the expression of ERK1/2 and
Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:2923–2931. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shumin C, Wei X, Yunfeng L, Jiangshui L,
Youguang G, Zhongqing C and Tao L: Genipin alleviates vascular
hyperpermeability following hemorrhagic shock by up-regulation of
SIRT3/autophagy. Cell Death Discov. 4(52)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Khan MM, Yang WL, Brenner M, Bolognese AC
and Wang P: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) causes
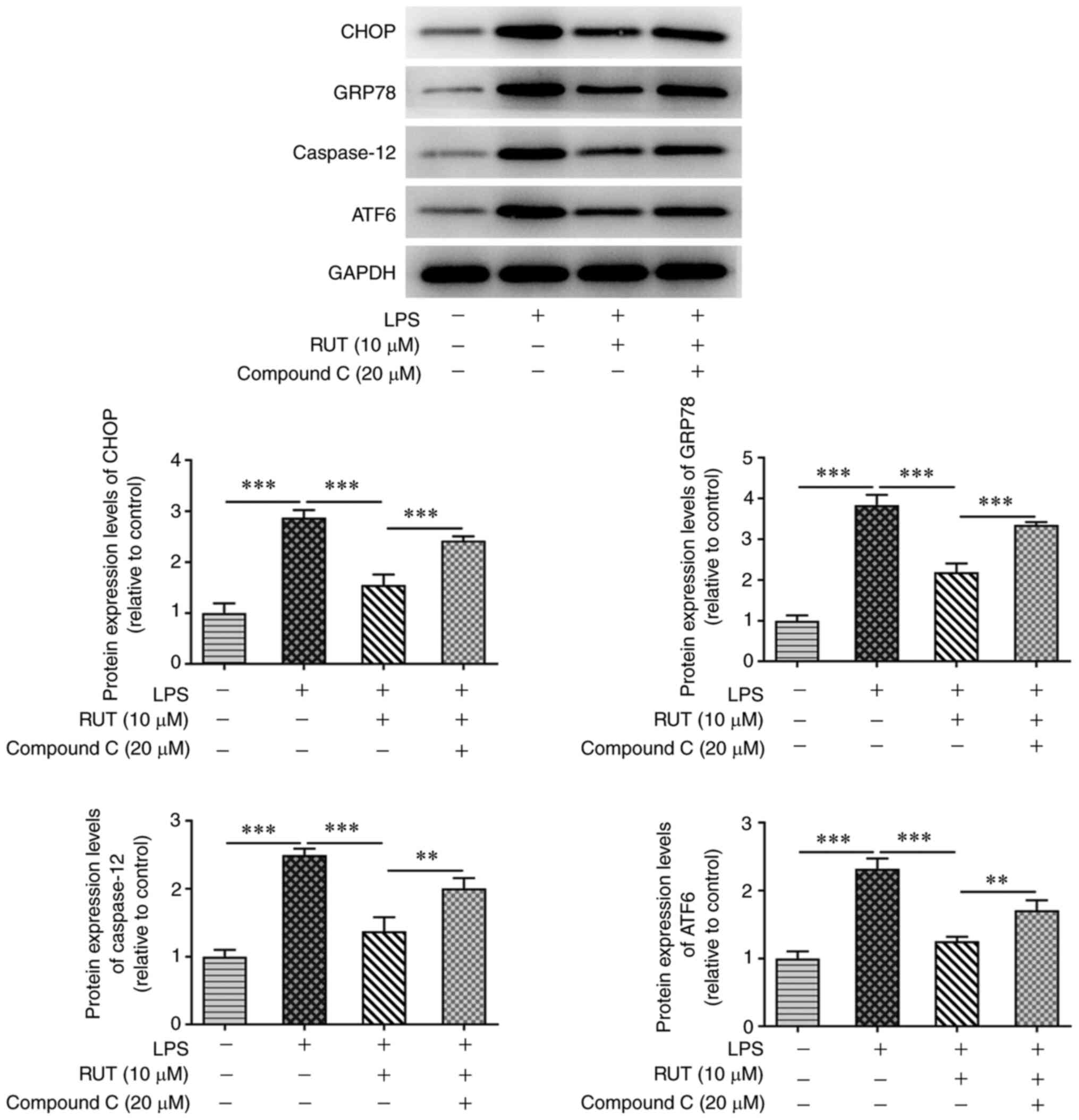
sepsis-associated acute lung injury via induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Sci Rep. 7(41363)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu R, Chen ZF, Yan J, Li QF, Huang Y, Xu
H, Zhang XP and Jiang H: Endoplasmic reticulum stress of
neutrophils is required for ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung
injury. J Immunol. 195:4802–4809. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Du Y, Zhu P, Wang X, Mu M, Li H, Gao Y,
Qin X, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Qu G, et al: Pirfenidone alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by accentuating BAP31
regulation of ER stress and mitochondrial injury. J Autoimmun.
112(102464)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bi XG, Li ML, Xu W, You JY, Xie D, Yuan XF
and Xiang Y: Helix B surface peptide protects against acute lung
injury through reducing oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum
stress via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 24:6919–6930. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Yang M, Peng Y, Gao M and Yang B:
Rutaecarpine ameliorated sepsis-induced peritoneal resident
macrophages apoptosis and inflammation responses. Life Sci.
228:11–20. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee GH, Kim CY, Zheng C, Jin SW, Kim JY,
Lee SY, Kim MY, Han EH, Hwang YP and Jeong HG: Rutaecarpine
increases nitric oxide synthesis via eNOS phosphorylation by
TRPV1-dependent CaMKII and CaMKKβ/AMPK signaling pathway in human
endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22(9407)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
He Y, Xu K, Wang Y, Chao X, Xu B, Wu J,
Shen J, Ren W and Hu Y: AMPK as a potential pharmacological target
for alleviating LPS-induced acute lung injury partly via NLRC4
inflammasome pathway inhibition. Exp Gerontol.
125(110661)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang N, Li P, Lin H, Shuo T, Ping F, Su L
and Chen G: IL-10 ameliorates PM2.5-induced lung injury by
activating the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 86(103659)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li X, Jamal M, Guo P, Jin Z, Zheng F, Song
X, Zhan J and Wu H: Irisin alleviates pulmonary epithelial barrier
dysfunction in sepsis-induced acute lung injury via activation of
AMPK/SIRT1 pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
118(109363)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen X, Wang T, Song L and Liu X:
Activation of multiple Toll-like receptors serves different roles
in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 18:443–450.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|