|
1
|
Safiabadi Tali SH, LeBlanc JJ, Sadiq Z,
Oyewunmi OD, Camargo C, Nikpour B, Armanfard N, Sagan SM and
Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S: Tools and techniques for severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 detection.
Clin Microbiol Rev. 34:00228–20. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ahamd F, Almuayqil SN, Humayun M, Naseem
S, Khan WA and Junaid K: Prediction of COVID-19 cases using machine
learning for effective public health management. Comput Mater
Contin. 66:2265–2282. 2021.
|
|
3
|
Ntambara J and Chu M: The risk to child
nutrition during and after COVID-19 pandemic: What to expect and
how to respond. Public Health Nutr. 24:3530–3536. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Malekifar P, Pakzad R, Shahbahrami R,
Zandi M, Jafarpour A, Rezayat SA, Akbarpour S, Shabestari AN,
Pakzad I, Hesari E, et al: Viral coinfection among COVID-19 patient
groups: An update systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res
Int. 2021(5313832)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zandi M, Farahani A, Zakeri A, Akhavan
Rezayat S, Mohammadi R, Das U, Dimmock JR, Afzali S, Nakhaei MA,
Doroudi A, et al: Clinical symptoms and types of samples are
critical factors for the molecular diagnosis of symptomatic
COVID-19 patients: A systematic literature review. Int J Microbiol.
2021(5528786)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Soltani S, Zakeri A, Zandi M, Kesheh MM,
Tabibzadeh A, Dastranj M, Faramarzi S, Didehdar M, Hafezi H,
Hosseini P and Farahani A: The role of bacterial and fungal human
respiratory microbiota in covid-19 patients. Biomed Res Int.
2021(6670798)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hosseini P, Afzali S, Karimi MR, Zandi M,
Zebardast A, Latifi T, Tabibzadeh A, Ramezani A, Zakeri A, Zakeri
A, et al: The coronavirus disease 2019 and effect on liver
function: A hidden and vital interaction beyond the respiratory
system. Rev Med Microbiol. 33:e161–e179. 2022.
|
|
8
|
Tsatsakis A, Petrakis D, Nikolouzakis TK,
Docea AO, Calina D, Vinceti M, Goumenou M, Kostoff RN, Mamoulakis
C, Aschner M and Hernández AF: COVID-19, an opportunity to
reevaluate the correlation between long-term effects of
anthropogenic pollutants on viral epidemic/pandemic events and
prevalence. Food Chem Toxicol. 141(111418)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Iaccarino G, Grassi G, Borghi C, Ferri C,
Salvetti M and Volpe M: SARS-RAS Investigators. Age and
multimorbidity predict death among COVID-19 patients: Results of
the SARS-RAS study of the italian society of hypertension.
Hypertension. 76:366–372. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pedersen OB, Nissen J, Dinh KM, Schwinn M,
Kaspersen KA, Boldsen JK, Didriksen M, Dowsett J, Sørensen E,
Thørner LW, et al: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) infection fatality rate among elderly danes: A
cross-sectional study on retired blood donors. Clin Infect Dis.
73:e2962–e2969. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kadambari S, Klenerman P and Pollard AJ:
Why the elderly appear to be more severely affected by COVID-19:
The potential role of immunosenescence and CMV. Rev Med Virol.
30(e2144)2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J,
Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, et al: Clinical Characteristics
of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected
pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 323:1061–1069. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Smith PW: Nosocomial infections in the
elderly. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 3:763–777. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Plonquet A, Bastuji-Garin S, Tahmasebi F,
Brisacier C, Ledudal K, Farcet J and Paillaud E: Immune risk
phenotype is associated with nosocomial lung infections in elderly
in-patients. Immun Ageing. 8(8)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu
Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al: Clinical features of patients
infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet.
395:497–506. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kollef MH, Torres A, Shorr AF,
Martin-Loeches I and Micek ST: Nosocomial infection. Crit Care Med.
49:169–187. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC
and Hughes JM: CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. Am
J Infect Control. 16:128–140. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Vickery K, Deva A, Jacombs A, Allan J,
Valente P and Gosbell IB: Presence of biofilm containing viable
multiresistant organisms despite terminal cleaning on clinical
surfaces in an intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 80:52–55.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wenzel RP: Perspective: Attributable
mortality-the promise of better antimicrobial therapy. J Infect
Dis. 178:917–919. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M,
Hwang T, Davis CS and Wenzel RP: The natural history of the
systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective
study. JAMA. 273:117–123. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, Beldavs
ZG, Dumyati G, Kainer MA, Lynfield R, Maloney M, McAllister-Hollod
L, Nadle J, et al: Multistate point-prevalence survey of health
care-associated infections. N Engl J Med. 370:1198–1208.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kollef MH, Shorr A, Tabak YP, Gupta V, Liu
LZ and Johannes RS: Epidemiology and outcomes of
health-care-associated pneumonia: Results from a large US database
of culture-positive pneumonia. Chest. 128:3854–3862.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Labelle A and Kollef MH:
Healthcare-associated pneumonia: Approach to management. Clin Chest
Med. 32:507–515. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kollef MH, Hamilton CW and Ernst FR:
Economic impact of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a large
matched cohort. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 33:250–256.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Du Q, Zhang D, Hu W, Li X, Xia Q, Wen T
and Jia H: Nosocomial infection of COVID-19: A new challenge for
healthcare professionals (Review). Int J Mol Med.
47(31)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schwierzeck V, König JC, Kühn J, Mellmann
A, Correa-Martínez CL, Omran H, Konrad M, Kaiser T and Kampmeier S:
First reported nosocomial outbreak of severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus 2 in a pediatric dialysis unit. Clin Infect
Dis. 72:265–270. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Carter B, Collins JT, Barlow-Pay F,
Rickard F, Bruce E, Verduri A, Quinn TJ, Mitchell E, Price A,
Vilches-Moraga A, et al: Nosocomial COVID-19 infection: Examining
the risk of mortality. The COPE-nosocomial study (COVID in Older
PEople). J Hosp Infect. 106:376–384. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kahl A, du Bois A, Harter P, Prader S,
Schneider S, Heitz F, Traut A, Alesina PF, Meier B, Walz M, et al:
Prognostic value of the age-adjusted charlson comorbidity index
(ACCI) on short- and long-term outcome in patients with advanced
primary epithelial ovarian cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:3692–3699.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brusselaers N and Lagergren J: The
charlson comorbidity index in registry-based research. Methods Inf
Med. 56:401–406. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Frenkel WJ, Jongerius EJ, Mandjes-van
Uitert MJ, van Munster BC and de Rooij SE: Validation of the
charlson comorbidity index in acutely hospitalized elderly adults:
A prospective cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 62:342–346.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Arabi YM, Fowler R and Hayden FG: Critical
care management of adults with community-acquired severe
respiratory viral infection. Intensive Care Med. 46:315–328.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sun Q, Qiu H, Huang M and Yang Y: Lower
mortality of COVID-19 by early recognition and intervention:
Experience from Jiangsu Province. Ann Intensive Care.
10(33)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pan L, Wang L and Huang X: How to face the
novel coronavirus infection during the 2019-2020 epidemic: The
experience of Sichuan provincial people's hospital. Intensive Care
Med. 46:573–575. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Neagu M, Calina D, Docea AO, Constantin C,
Filippini T, Vinceti M, Drakoulis N, Poulas K, Nikolouzakis TK,
Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis A: Back to basics in COVID-19: Antigens
and antibodies-completing the puzzle. J Cell Mol Med. 25:4523–4533.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
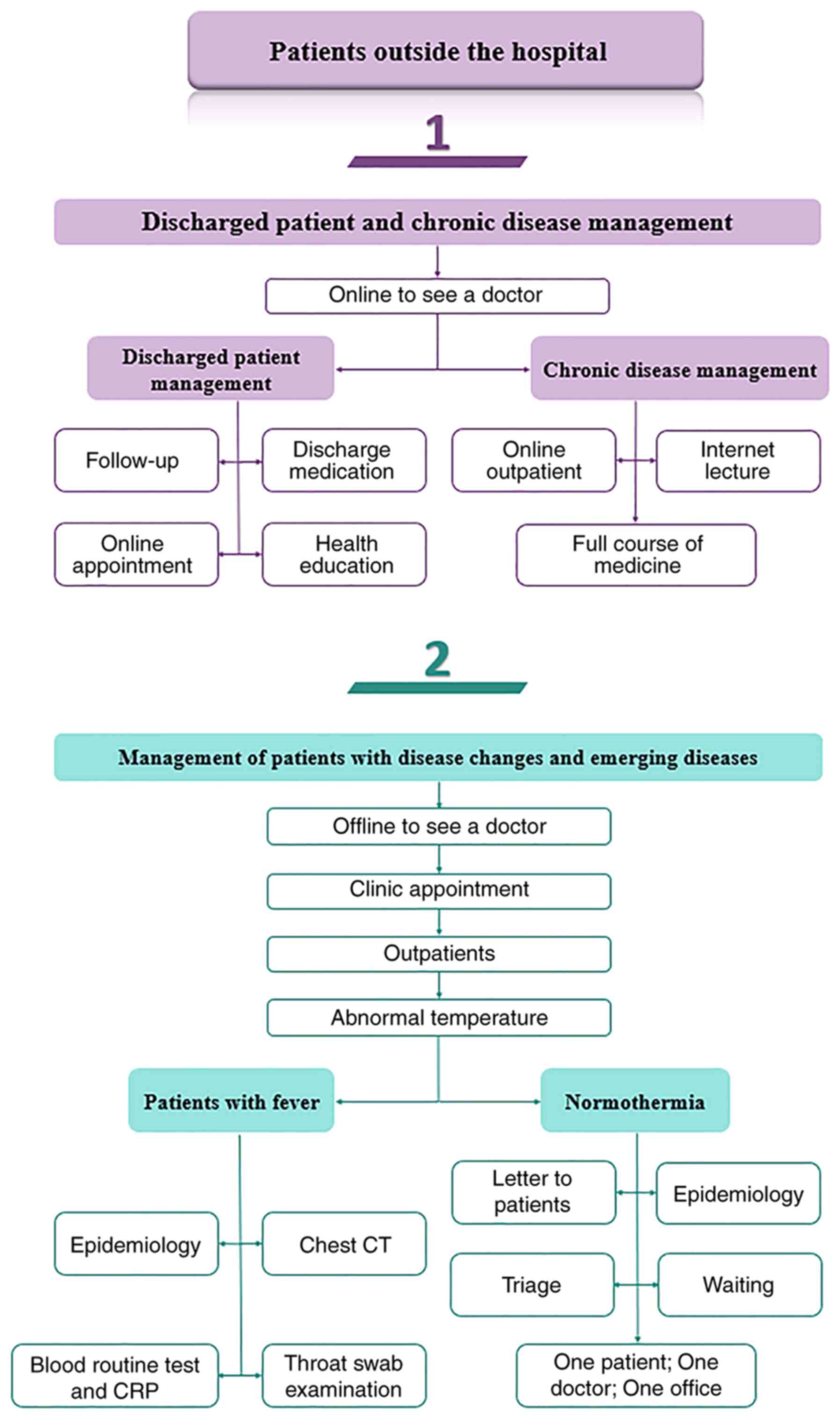
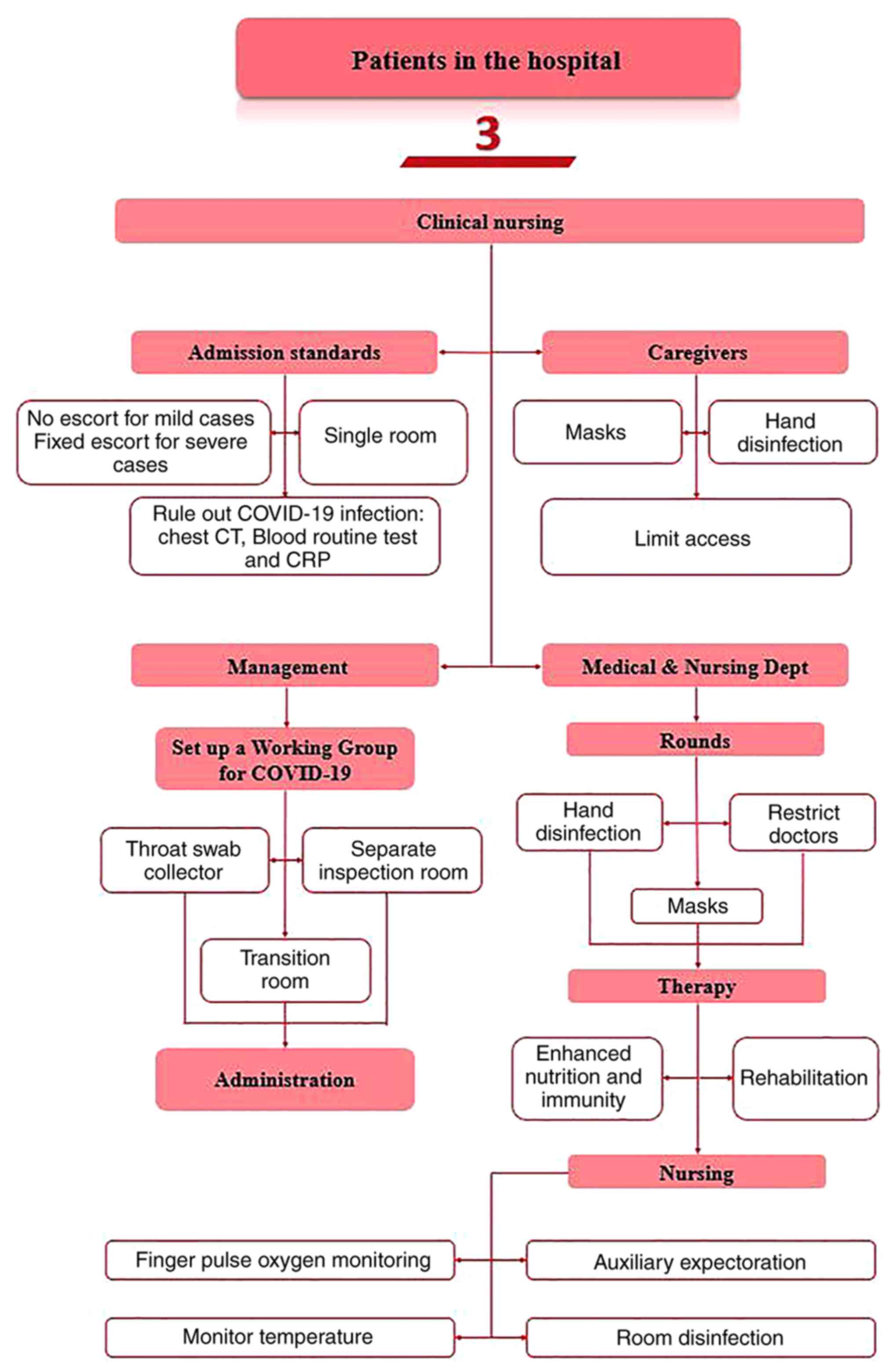
The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing
Medical University: Patient Admission Procedures During COVID-19
(Edition 7). https://book.yunzhan365.com/ymkhc/oquc/mobile/index.html.
Accessed August 27, 2020.
|
|
36
|
Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, Zhang N, Huang
M, Zeng X, Cui J, Xu W, Yang Y, Fayad ZA, et al: CT imaging
features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology.
295:202–207. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
National Health Commission of the People's
Republic of China: COVID-19 prevention and control protocols.
http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-02/22/5482010/files/310fd7316a89431d977cc8f2dbd2b3e0.pdf.
February 21, 2020.
|
|
38
|
Kok RM and Reynolds CF III: Management of
depression in older adults: A review. JAMA. 317:2114–2122.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Farver-Vestergaard I, Jacobsen D and
Zachariae R: Efficacy of psychosocial interventions on
psychological and physical health outcomes in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Psychother Psychosom. 84:37–50. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sarris J, Moylan S, Camfield DA, Pase MP,
Mischoulon D, Berk M, Jacka FN and Schweitzer I: Complementary
medicine, exercise, meditation, diet, and lifestyle modification
for complementary medicine, exercise, meditation, diet, and
lifestyle modification for anxiety disorders: A review of current
evidence. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012(809653)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Messika J, Kalfon P and Ricard JD:
Adjuvant therapies in critical care: Music therapy. Intensive Care
Med. 44:1929–1931. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lim KK, Lee VSY, Tan CS, Kwan YH, Lim ZHX,
Wee HL, Østbye T and Low LL: Examining the heterogeneity inexcess
risks of coronary heart disease, stroke, dialysis, and lower
extremity amputation associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus
across demographic subgroups in an Asian population: A
population-based matched cohort study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
171(108551)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Austin PC: Variance estimation when using
inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) with survival
analysis. Stat Med. 35:5642–5655. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Austin PC and Stuart EA: Moving towards
best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting
(IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment
effects in observational studies. Stat Med. 34:3661–3679.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shoffner M, Owen P, Mostafa J, Lamm B,
Wang X, Schmitt CP and Ahalt SC: The secure medical research
workspace: An IT infrastructure to enable secure research on
clinical data. Clin Transl Sci. 6:222–225. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ou HT, Lee TY, Du YF and Li CY:
Comparative risks of diabetes-related complications of basal
insulins: A longitudinal population-based cohort of type 1 diabetes
1999-2013 in Taiwan. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 84:379–391.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
VanderWalde NA, Meyer AM, Deal AM, Layton
JB, Liu H, Carpenter WR, Weissler MC, Hayes DN, Fleming ME and
Chera BS: Effectiveness of chemoradiation for head and neck cancer
in an older patient population. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
89:30–37. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liang KY and Zeger SL: Longitudinal data
analysis using generalised linear models. Biometrika. 73:13–22.
1986.
|
|
49
|
Allison PD: Longitudinal data analysis
using stata. Statistical Horison, Stockholm, 2018.
|
|
50
|
Koo TK and Li MY: A guideline of selecting
and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability
research. J Chiropr Med. 15:155–163. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wu X, Wu L, Han J, Wu Y, Cao T, Gao Y,
Wang S, Wang S, Liu Q, Li H, et al: Evaluation of the sexual
quality of life and sexual function of cervical cancer survivors
after cancer treatment: A retrospective trial. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
304:999–1006. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liu TT, Li R, Huo C, Li JP, Yao J, Ji XL
and Qu YQ: Identification of CDK2-related immune forecast model and
ceRNA in lung adenocarcinoma, a pan-cancer analysis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9(682002)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sun D, Tian L, Zhu Y, Wo Y, Liu Q, Liu S,
Li H and Hou H: Subunits of ARID1 serve as novel biomarkers for the
sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitors and prognosis of
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Med. 26(78)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hardin JW and Hilbe JM: Generalized
estimating equations. 2nd edition. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press,
London, 2012.
|
|
55
|
Li C, Duan J, Liu S, Meng X, Fu C, Zeng C
and Wu A: Assessing the risk and disease burden of clostridium
difficile infection among patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia
at a university hospital in Central China. Infection. 45:621–628.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li C, Wen X, Ren N, Zhou P, Huang X, Gong
R, Feng L, Wu H, Liu Z, Fu C, et al: Point-prevalence of
healthcare-associated infection in China in 2010: A large
multicenter epidemiological survey. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol.
35:1436–1437. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cho SJ and Stout-Delgado HW: Aging and
lung disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 82:433–459. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zdravkovic M, Berger-Estilita J, Sorbello
M and Hagberg CA: An international survey about rapid sequence
intubation of 10,003 anaesthetists and 16 airway experts.
Anaesthesia. 75:313–322. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hirai J, Sakanashi D, Haranaga S, Kinjo T,
Hagihara M, Kato H, Suematsu H, Yamagishi Y, Fujita J and Mikamo H:
Case-control study of pneumonia patients with Streptococcus
anginosus group bacteria in their sputum. J Infect Chemother.
22:794–799. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Sangro B, Martínez-Urbistondo D, Bester L,
Bilbao JI, Coldwell DM, Flamen P, Kennedy A, Ricke J and Sharma RA:
Prevention and treatment of complications of selective internal
radiation therapy: Expert guidance and systematic review.
Hepatology. 66:969–982. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Eraslan Doganay G and Cirik MO:
Determinants of prognosis in geriatric patients followed in
respiratory ICU; either infection or malnutrition. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100(e27159)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Song P, Man Q, Li Y, Jia S, Yu D, Liu Z
and Zhang J: Trends of underweight malnutrition among chinese
residents aged 60 years and above-China, 1992-2015. China CDC Wkly.
3:232–236. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Shah FA, Pike F, Alvarez K, Angus D,
Newman AB, Lopez O, Tate J, Kapur V, Wilsdon A, Krishnan JA, et al:
Bidirectional relationship between cognitive function and
pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 188:586–592. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Yu P, Xia Z, Fei J and Jha SK: An
application review of artificial intelligence in prevention and
cure of COVID-19 pandemic. Comput Mater Contin. 65:743–760.
2020.
|
|
65
|
Bischoff SC, Austin P, Boeykens K,
Chourdakis M, Cuerda C, Jonkers-Schuitema C, Lichota M, Nyulasi I,
Schneider SM, Stanga Z and Pironi L: Espen guideline on home
enteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. 39:5–22. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Cena H and Chieppa M: Coronavirus disease
(COVID-19-SARS-CoV-2) and nutrition: Is infection in Italy
suggesting a connection? Front Immunol. 11(944)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Willig A, Wright L and Galvin TA: Practice
paper of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: Nutrition
intervention and human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Acad
Nutr Diet. 118:486–498. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Kris-Etherton PM, Petersen KS, Hibbeln JR,
Hurley D, Kolick V, Peoples S, Rodriguez N and Woodward-Lopez G:
Nutrition and behavioral health disorders: Depression and anxiety.
Nutr Rev. 79:247–260. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Mandell LA and Niederman MS: Aspiration
pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 380:651–663. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang B, Wang J, Sun L and
Xiao Q: Gastric-tube versus post-pyloric feeding in critical
patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of pulmonary
aspiration- and nutrition-related outcomes. Eur J Clin Nutr.
75:1337–1348. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Alkhawaja S, Martin C, Butler RJ and
Gwadry-Sridhar F: Post-pyloric versus gastric tube feeding for
preventing pneumonia and improving nutritional outcomes in
critically ill adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2015(CD008875)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|