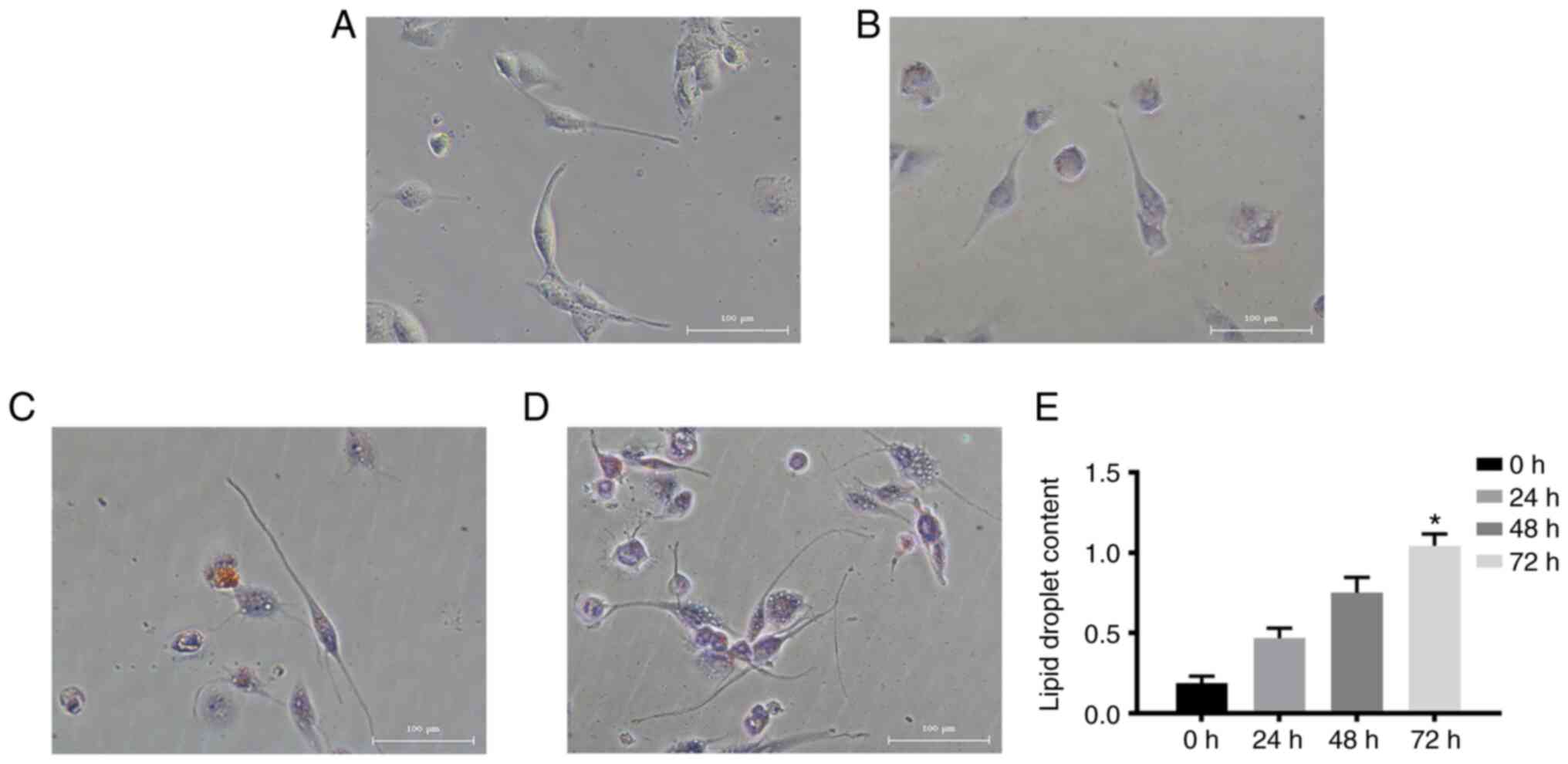
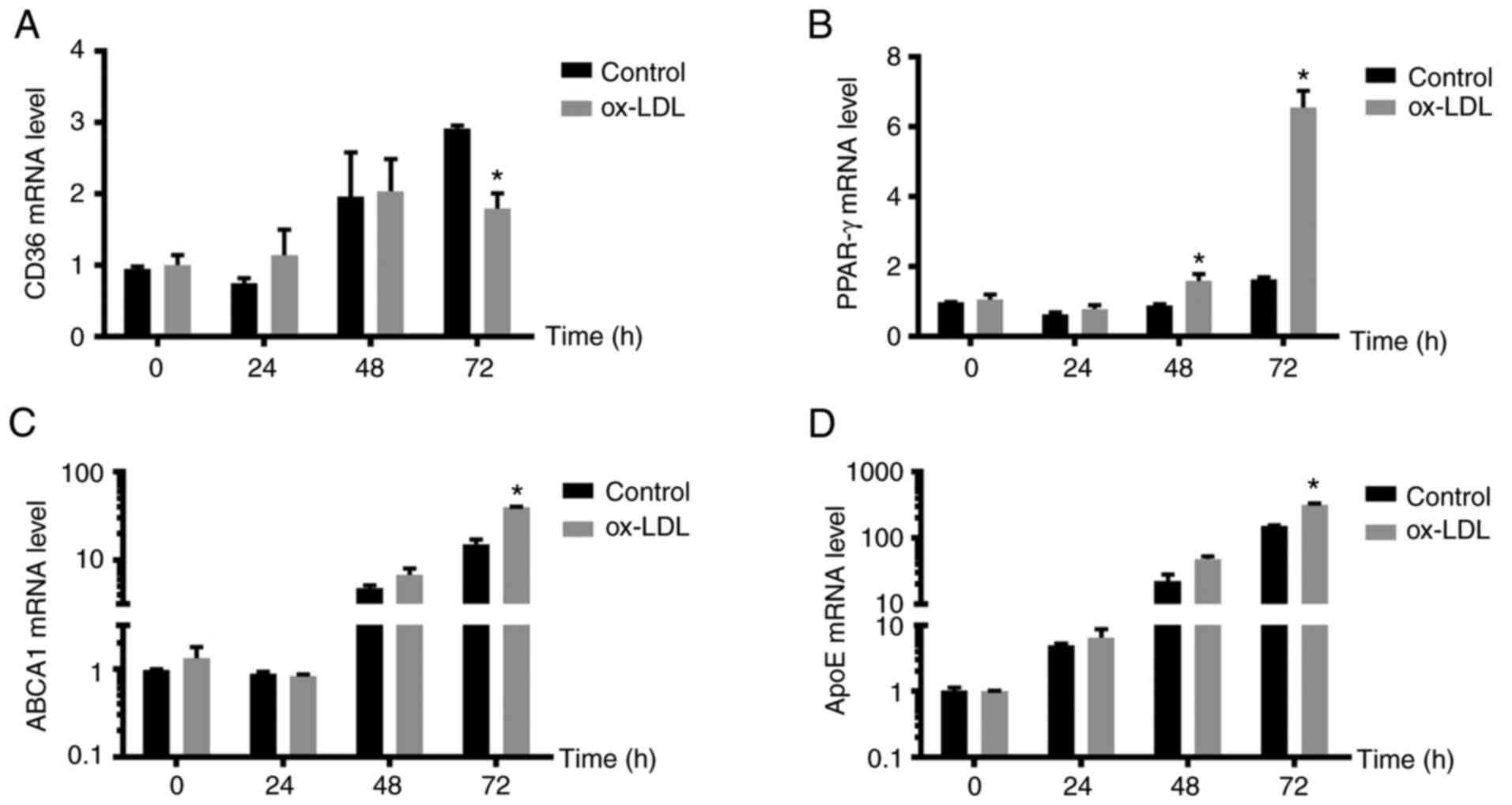
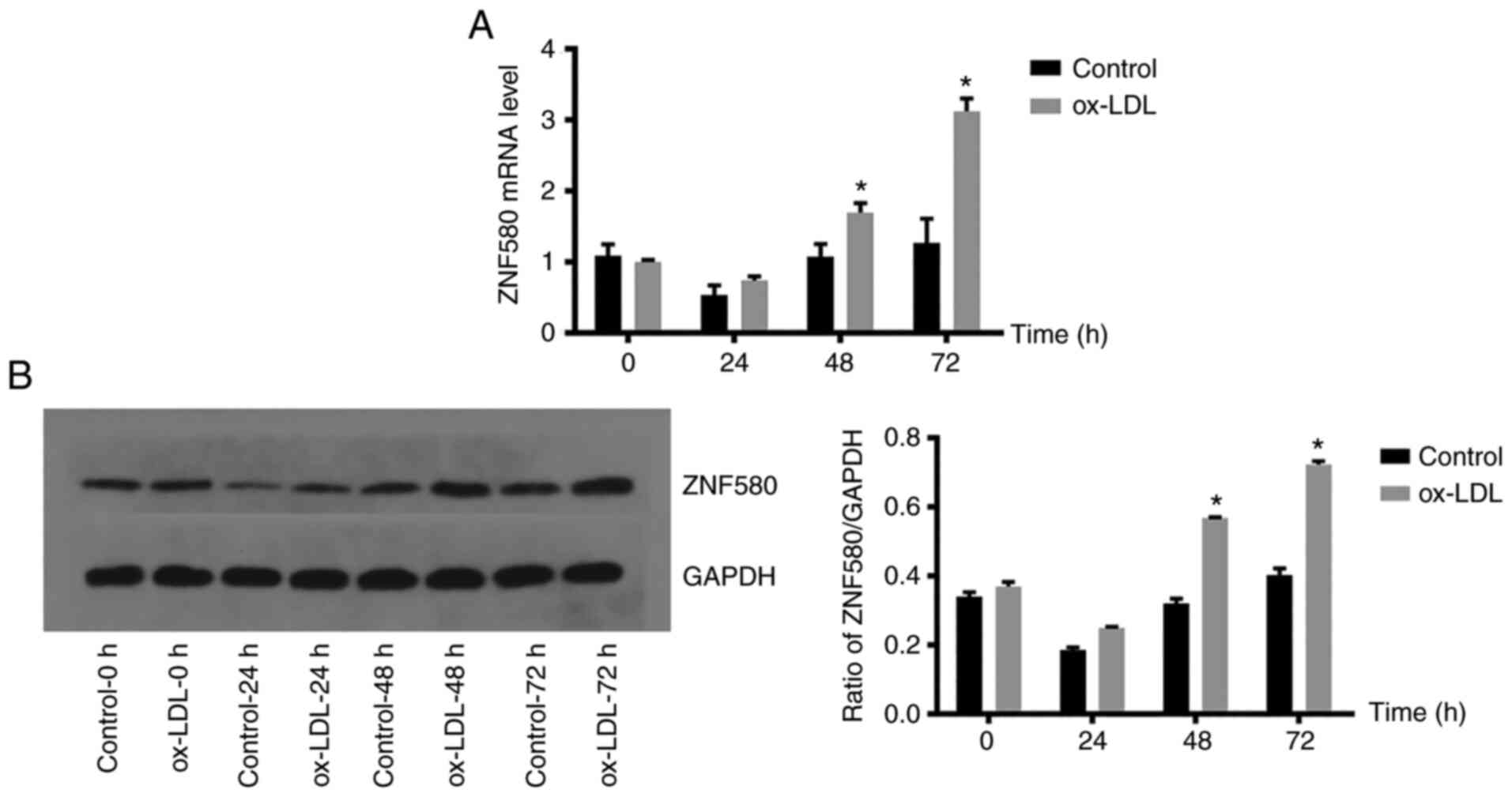
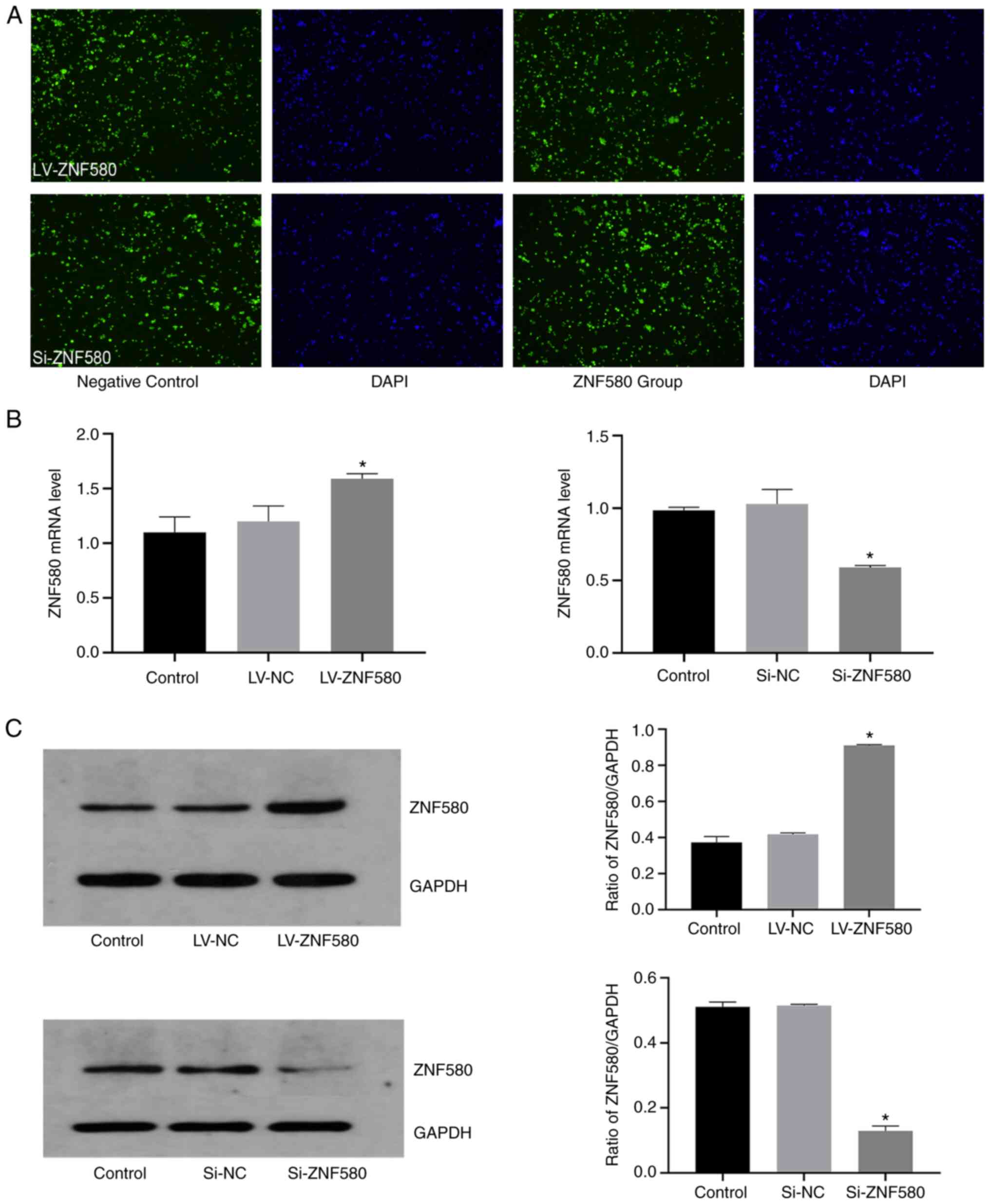
|
1
|
Kingstone LL, Currie GM and Torres C: The
pathogenesis, analysis, and imaging methods of atherosclerotic
disease of the carotid artery: Review of the literature. J Med
Imaging Radiat Sci. 43:84–94. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Nature. 420:868–874. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roy A, Saqib U, Wary K and Baig MS:
Macrophage neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS1) controls the
inflammatory response and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis.
Int Immunopharmacol. 83(106382)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Grajeda-Iglesias C and Aviram M: Specific
amino acids affect cardiovascular diseases and atherogenesis via
protection against macrophage foam cell formation: Review article.
Rambam Maimonides Med J. 9(e0022)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu XH, Fu YC, Zhang DW, Yin K and Tang CK:
Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 424:245–252.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ghodsian N, Yeandle A and Gieseg SP: Foam
cell formation but not oxLDL cytotoxicity is inhibited by CD36 down
regulation by the macrophage antioxidant 7,8-dihydroneopterin. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 133(105918)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chávez-Sánchez L, Garza-Reyes MG,
Espinosa-Luna JE, Chávez-Rueda K, Legorreta-Haquet MV and
Blanco-Favela F: The role of TLR2, TLR4 and CD36 in macrophage
activation and foam cell formation in response to ox-LDL in humans.
Hum Immunol. 75:322–329. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Maréchal L, Laviolette M, Rodrigue-Way A,
Sow B, Brochu M, Caron V and Tremblay A: The CD36-PPARγ pathway in
metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 19(1529)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ozasa H, Ayaori M, Iizuka M, Terao Y,
Uto-Kondo H, Yakushiji E, Takiguchi S, Nakaya K, Hisada T, Uehara
Y, et al: Pioglitazone enhances cholesterol efflux from macrophages
by increasing ABCA1/ABCG1 expressions via PPARγ/LXRα pathway:
findings from in vitro and ex vivo studies. Atherosclerosis.
219:141–150. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Du M, Yang L, Liu B, Yang L, Mao X, Liang
M and Huang K: Inhibition of NFAT suppresses foam cell formation
and the development of diet-induced atherosclerosis. FASEB J.
35(e21951)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Su B, Gao B, Zhou J, Ren XK, Guo
J, Xia S, Zhang W and Feng Y: Cascaded bio-responsive delivery of
eNOS gene and ZNF580 gene to collaboratively treat hindlimb
ischemia via pro-angiogenesis and anti-inflammation. Biomater Sci.
8:6545–6560. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luo Y, Zhao Y, Li X, Zhao J and Zhang W:
ZNF580 mediates eNOS expression and endothelial cell
migration/proliferation via the TGF-β1/ALK5/Smad2 pathway. Mol Cell
Biochem. 393:199–207. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
DangLi R, HeKong W, JiQin L, MingHua Z and
WenCheng Z: ROS-induced ZNF580 expression: A key role for
H2O2/NF-κB signaling pathway in vascular endothelial inflammation.
Mol Cell Biochem. 359:183–191. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu HJ, Wang XL, Zhang L, Qiu Y, Li TJ, Li
R, Wu MC, Wei LX and Rui YC: Inhibitions of vascular endothelial
growth factor expression and foam cell formation by EGb 761, a
special extract of Ginkgo biloba, in oxidatively modified
low-density lipoprotein-induced human THP-1 monocytes cells.
Phytomedicine. 16:138–145. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fu Y, Luo N, Lopes-Virella MF and Garvey
WT: The adipocyte lipid binding protein (ALBP/aP2) gene facilitates
foam cell formation in human THP-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis.
165:259–269. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cao H, Jia Q, Yan L, Chen C, Xing S and
Shen D: Quercetin suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by
regulating MST1-Mediated autophagy in ox-LDL-Induced RAW264.7
macrophage foam cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20(6093)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu JX: The effects of ZNF580
overexpression on the balloon-injury model of Rat (unpublished PhD
thesis). Hebei Medical University, 2013.
|
|
18
|
Yu HL: The role of ZFP580 in ROS mediated
the process of myocardial oxidative stress injury (unpublished PhD
thesis). Hebei Medical University, 2014.
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y: The effects of ZNF580 on the
expression of e NOS induced by TGF-β in endothelial cell
(unpublished PhD thesis). Hebei Medical University, 2013.
|
|
20
|
Daigneault M, Preston JA, Marriott HM,
Whyte MK and Dockrell DH: The identification of markers of
macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and
monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS One. 5(e8668)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hamilton TA, Major JA and Chisolm GM: The
effects of oxidized low density lipopmteins on inducible mouse
macmphage gene expression are gene and stimulus dependent. J Clin
Invest. 95:2020–2027. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT
and Murray CJ: Global and regional burden of disease and risk
factors, 2001: Systematic analysis of population health data.
Lancet. 367:1747–1757. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gonzalez L and Trigatti BL: Macrophage
apoptosis and necrotic core development in atherosclerosis: A
rapidly advancing field with clinical relevance to imaging and
therapy. Can J Cardiol. 33:303–312. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Greenberg ME, Sun M, Zhang R, Febbraio M,
Silverstein R and Hazen SL: Oxidized phosphatidylserine-CD36
interactions play an essential role in macrophage-dependent
phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Exp Med. 203:2613–2625.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Luan Y and Griffiths HR: Ceramides reduce
CD36 cell surface expression and oxidised LDL uptake by monocytes
and macrophages. Arch Biochem Biophys. 450:80–99. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Coburn CT, Knapp FF Jr, Febbraio M, Beets
AL, Silverstein RL and Abumrad NA: Defective uptake and utilization
of long chain fatty acids in muscle and adipose tissues of CD36
knockout mice. J Biol Chem. 275:32523–32529. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhuang JL, Liu YY, Li ZZ, Zhuang QZ, Tang
WZ, Xiong Y and Huang XZ: Amentoflavone prevents ox-LDL-induced
lipid accumulation by suppressing the PPARγ/CD36 signal pathway.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 431(115733)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tan YL, Zeng Y, Mo ZC, He PP, Ou YX, Yao
F, Xie W, Tang CK and Yi GH: Regulation of PPAR γ on the expression
of CD36 and lipid accumulation induced by high glucose in THP-1
macrophages. Chin J Mod Med. 24:18–23. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Wu XH, Cheng B, Guo XJ, Wu QQ, Sun S and
He P: PPARα/γ signaling pathways are involved in chlamydia
pneumoniae-induced foam cell formation via upregulation of SR-A1
and ACAT1 and downregulation of ABCA1/G1. Microb Pathog.
161(105284)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li AC, Binder CJ, Gutierrez A, Brown KK,
Plotkin CR, Pattison JW, Valledor AF, Davis RA, Willson TM, Witztum
JL, et al: Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell
formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPAR-α,β/δ and γ. J
Clin Invest. 114:1564–1576. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bayliak MM, Dmytriv TR, Melnychuk AV,
Strilets NV, Storey KB and Lushchak VI: Chamomile as a potential
remedy for obesity and metabolic syndrome. EXCLI J. 20:1261–1286.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ahmadian M, Suh JM, Hah N, Liddle C,
Atkins AR, Downes M and Evans RM: PPARγ signaling and metabolism:
The good, the bad and the future. Nat Med. 19:557–566.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li K, Yao W, Zheng X and Liao K: Berberine
promotes the development of atherosclerosis and foam cell formation
by inducing scavenger receptor A expression in macrophage. Cell
Res. 19:1006–1017. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Owen JS, Wilson MD, Li H, Griffiths
GL, Thomas MJ, Hiltbold EM, Fessler MB and Parks JS: Macrophage
ABCA1 reduces MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor trafficking to
lipid rafts by reduction of lipid raft cholesterol. J Lipid Res.
51:3196–3206. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yu XH, Chen JJ, Deng WY, Xu XD, Liu QX,
Shi MW and Ren K: Biochanin A mitigates atherosclerosis by
inhibiting lipid accumulation and inflammatory response. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2020(8965047)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Shi Q, Hu Y and Li X: Silibinin
augments the effect of clopidogrel on atherosclerosis in diabetic
ApoE deficiency mice. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 80:353–361.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Siest G, Pillot T, Régis-Bailly A,
Leininger-Muller B, Steinmetz J, Galteau MM and Visvikis S:
Apolipoprotein E: An important gene and protein to follow in
laboratory medicine. Clin Chem. 41:1068–1086. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Di Pietro N, Formoso G and Pandolfi A:
Physiology and pathophysiology of ox-LDL uptake by vascular wall
cells in atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 84:1–7. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Xu W, Wei Z, Dong J, Duan F, Chen K, Chen
C, Liu J, Yang X, Chen L, Xiao H and Liu A: Global metabolomics
reveals the metabolic dysfunction in ox-LDL induced
macrophage-derived foam cells. Front Pharmacol.
8(586)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Meng FP: The role and molecular mechanism
of zinc finger gene ZFP580/ZNF580 in GDF-15 attenuating
ischemia/reperfusion induced no reflow injury (unpublished PhD
thesis). Hebei Medical University, 2016.
|