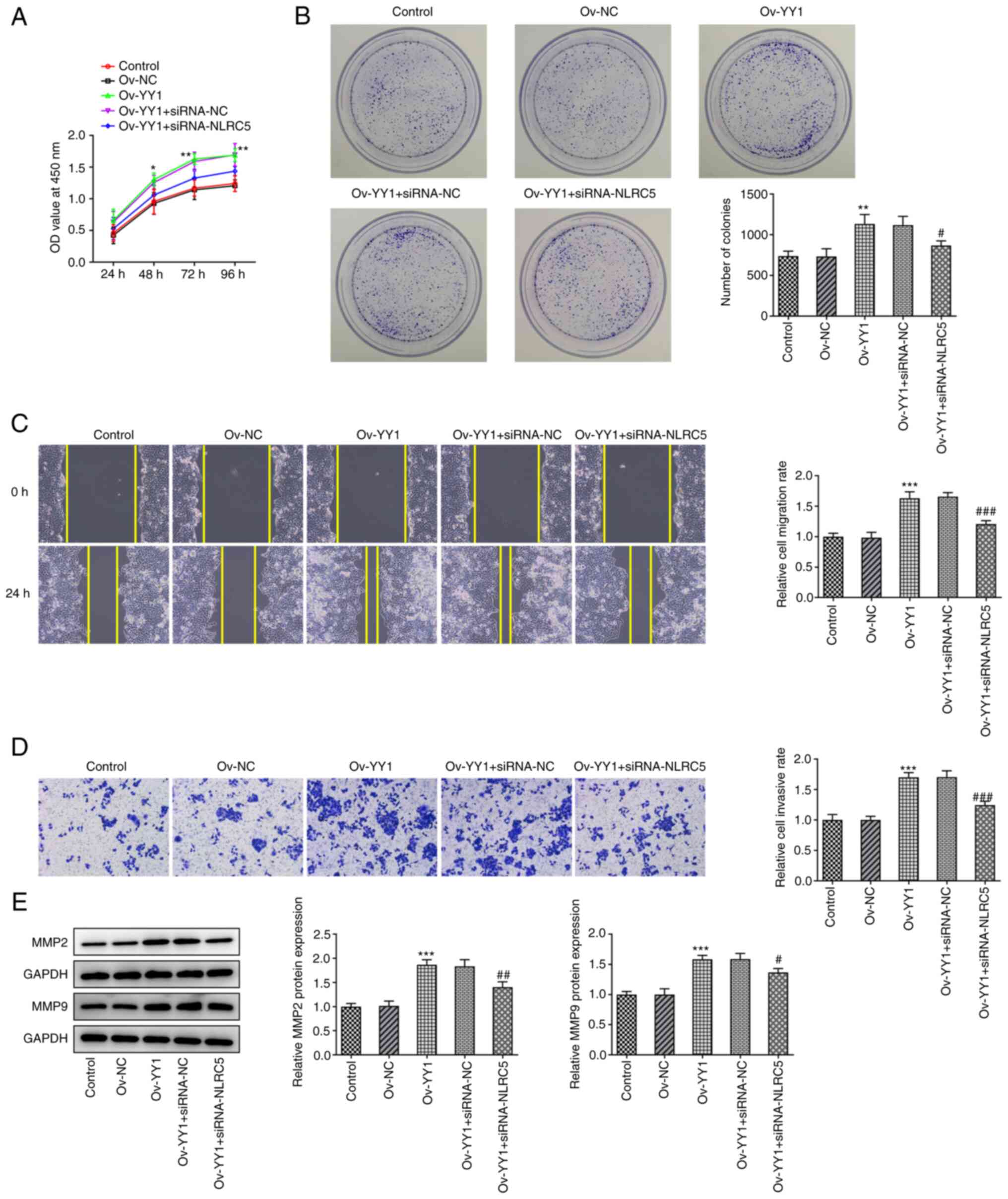
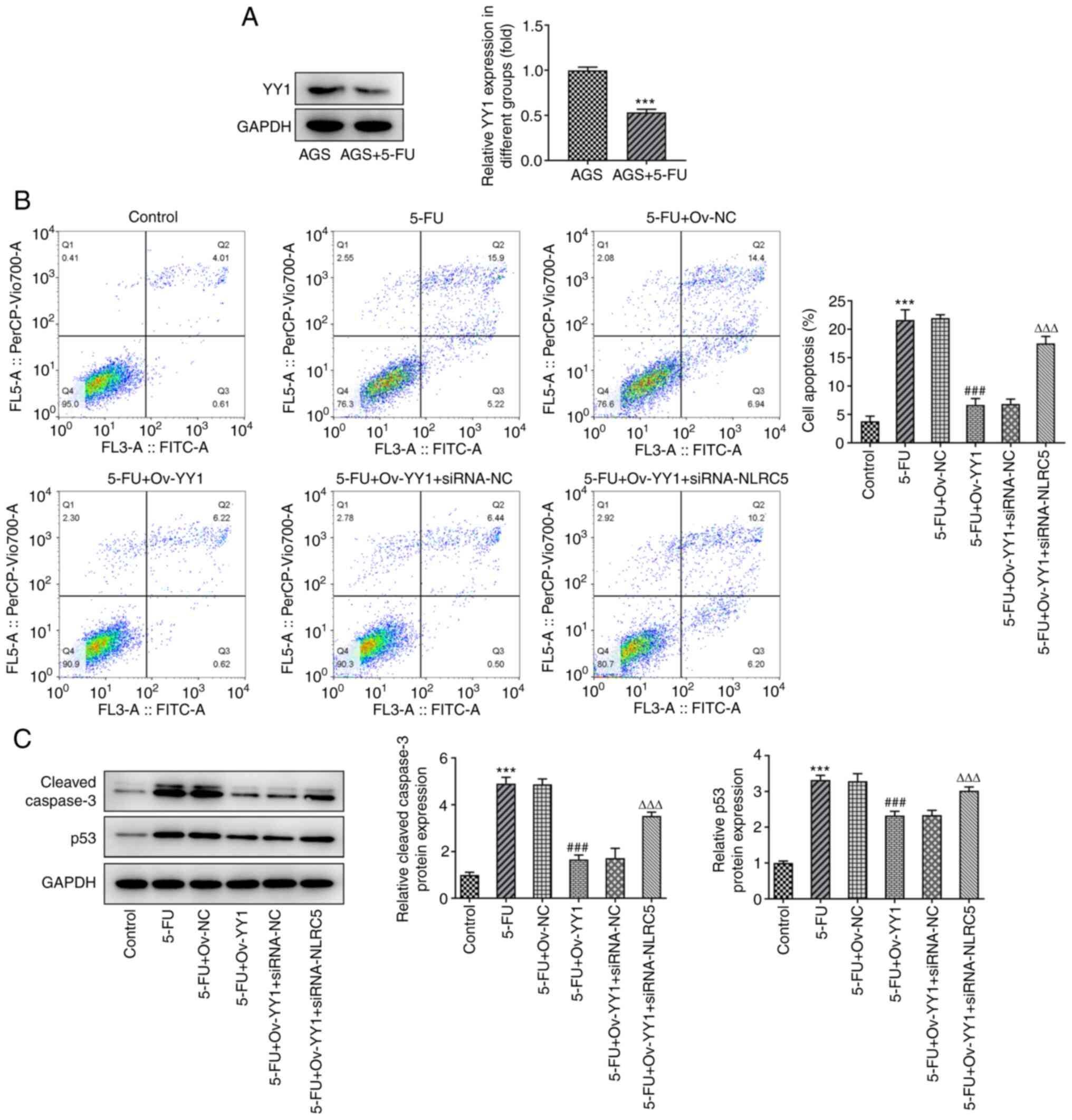
|
1
|
Correa P: Gastric cancer: Overview.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 42:211–217. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu LP, Sheng XP, Shuai TK, Zhao YX, Li B
and Li YM: Helicobacter pylori promotes invasion and metastasis of
gastric cancer by enhancing heparanase expression. World J
Gastroenterol. 27:3138–3141. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Martinez-Jimenez F, Muinos F, Sentis I,
Deu-Pons J, Reyes-Salazar I, Arnedo-Pac C, Mularoni L, Pich O,
Bonet J, Kranas H, et al: A compendium of mutational cancer driver
genes. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:555–572. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tang F, Xu Y and Zhao B: NLRC5: New cancer
buster? Mol Biol Rep. 47:2265–2277. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Ding H, He Y, Li X, Cheng Y, Xu Q,
Yang Y, Liao G, Meng X, Huang C and Li J: NLRC5 mediates cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 444:9–19. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
He YH, Li MF, Zhang XY, Meng XM, Huang C
and Li J: NLRC5 promotes cell proliferation via regulating the
AKT/VEGF-A signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Toxicology. 359-360:47–57. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Zhang M and Zheng X: High expression
of NLRC5 is associated with prognosis of gastric cancer. Open Med
(Wars). 13:443–449. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Oh SC, Sohn BH, Cheong JH, Kim SB, Lee JE,
Park KC, Lee SH, Park JL, Park YY, Lee HS, et al: Clinical and
genomic landscape of gastric cancer with a mesenchymal phenotype.
Nat Commun. 9(1777)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Digklia A and Wagner AD: Advanced gastric
cancer: Current treatment landscape and future perspectives. World
J Gastroenterol. 22:2403–2414. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Catalano C, da Silva Filho MI, Jiraskova
K, Vymetalkova V, Levy M, Liska V, Vycital O, Naccarati A,
Vodickova L, Hemminki K, et al: Short article: Influence of
regulatory NLRC5 variants on colorectal cancer survival and
5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
30:838–842. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Naidoo K, Clay V, Hoyland JA, Swindell R,
Linton K, Illidge T, Radford JA and Byers RJ: YY1 expression
predicts favourable outcome in follicular lymphoma. J Clin Pathol.
64:125–129. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim H, Bang S, Jee S, Park S, Kim Y, Park
H, Jang K and Paik SS: Loss of YY1 expression predicts unfavorable
prognosis in stage III colorectal cancer. Indian J Pathol
Microbiol. 64 (Supplement):S78–S84. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xia W, Li Y, Wu Z, Wang Y, Xing N, Yang W
and Wu S: Transcription factor YY1 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition through the TGFβ signaling pathway in bladder cancer.
Med Oncol. 37(93)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Zhao J, Dong Y,
Wang S, Yang W, Sin FM, Ng SS, Yu J, et al: Yin Yang 1 contributes
to gastric carcinogenesis and its nuclear expression correlates
with shorter survival in patients with early stage gastric
adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med. 12(80)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Wu X, Dai W, Li J, Xiang L, Tang
W, Lin J, Zhang W, Liu G, Yang Q, et al: The CCDC43-ADRM1 axis
regulated by YY1, promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric
cancer. Cancer Lett. 482:90–101. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Zou L and Sun P: Relationship
between miR-378c and YY1 expression in patients with gastric cancer
and the clinicopathological features. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
26(12)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Messeguer X, Escudero R, Farre D, Nunez O,
Martinez J and Alba MM: PROMO: Detection of known transcription
regulatory elements using species-tailored searches.
Bioinformatics. 18:333–334. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A, van
der Lee R, Zhang X, Richmond PA, Modi BP, Correard S, Gheorghe M,
Baranašić D, et al: JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database
of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.
48:D87–D92. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
El-Rifai W and Powell SM: Molecular
biology of gastric cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 12:128–140.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Frycz BA, Murawa D, Borejsza-Wysocki M,
Wichtowski M, Spychala A, Marciniak R, Murawa P, Drews M and
Jagodziński PP: mRNA expression of steroidogenic enzymes, steroid
hormone receptors and their coregulators in gastric cancer. Oncol
Lett. 13:3369–3378. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang T, Wang R, Zhang J, Bao C, Zhang J,
Li R, Chen X, Wu S, Wen J, Wei S, et al: Mechanism of berberine in
treating Helicobacter pylori induced chronic atrophic gastritis
through IRF8-IFN-ү signaling axis suppressing. Life Sci.
248(117456)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang QY, Chen T, Chen YB and Lan DL:
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the NLR
family CARD containing five transcripts in the pig. Pol J Vet Sci.
19:753–761. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zong Z, Song Y, Xue Y, Ruan X, Liu X, Yang
C, Zheng J, Cao S, Li Z and Liu Y: Knockdown of LncRNA SCAMP1
suppressed malignant biological behaviours of glioma cells via
modulating miR-499a-5p/LMX1A/NLRC5 pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
23:5048–5062. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fan Y, Dong Z, Shi Y, Sun S, Wei B and
Zhan L: NLRC5 promotes cell migration and invasion by activating
the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in endometrial cancer. J Int Med
Res. 48(300060520925352)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li X, Guo F, Liu Y, Chen HJ, Wen F, Zou B,
Li D, Qin Q, Liu X, Shen Y and Wang Y: NLRC5 expression in tumors
and its role as a negative prognostic indicator in stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Oncol Lett. 10:1533–1540.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ito S, Sano T, Mizusawa J, Takahari D,
Katayama H, Katai H, Kawashima Y, Kinoshita T, Terashima M,
Nashimoto A, et al: A phase II study of preoperative chemotherapy
with docetaxel, cisplatin, and S-1 followed by gastrectomy with D2
plus para-aortic lymph node dissection for gastric cancer with
extensive lymph node metastasis: JCOG1002. Gastric Cancer.
20:322–331. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo XM, Liu XP, Chang GB, Xu L, Bi YL,
Wang HZ, Zhang Y, Zhu PF, Wu Y and Chen GH: Characterization of the
NLRC5 promoter in chicken: SNPs, regulatory elements and CpG
islands. Anim Genet. 47:579–587. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|