|
1
|
Williams R, Airey M, Baxter H, Forrester
J, Kennedy-Martin T and Girach A: Epidemiology of diabetic
retinopathy and macular oedema: A systematic review. Eye (Lond).
18:963–983. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Simó R and Hernández C: Prevention and
treatment of diabetic retinopathy: Evidence from large, randomized
trials. The emerging role of fenofibrate. Rev Recent Clin Trials.
7:71–80. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Singh R, Barden A, Mori T and Beilin L:
Advanced glycation end-products: A review. Diabetologia.
44:129–146. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pardue MT and Allen RS: Neuroprotective
strategies for retinal disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 65:50–76.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kollias AN and Ulbig MW: Diabetic
retinopathy: Early diagnosis and effective treatment. Dtsch Arztebl
Int. 107:75–83; quiz 84. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moreno A, Lozano M and Salinas P: Diabetic
retinopathy. Nutr Hosp. 28 (Suppl 2):S53–S56. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wong TY, Cheung CM, Larsen M, Sharma S and
Simó R: Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2(16012)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
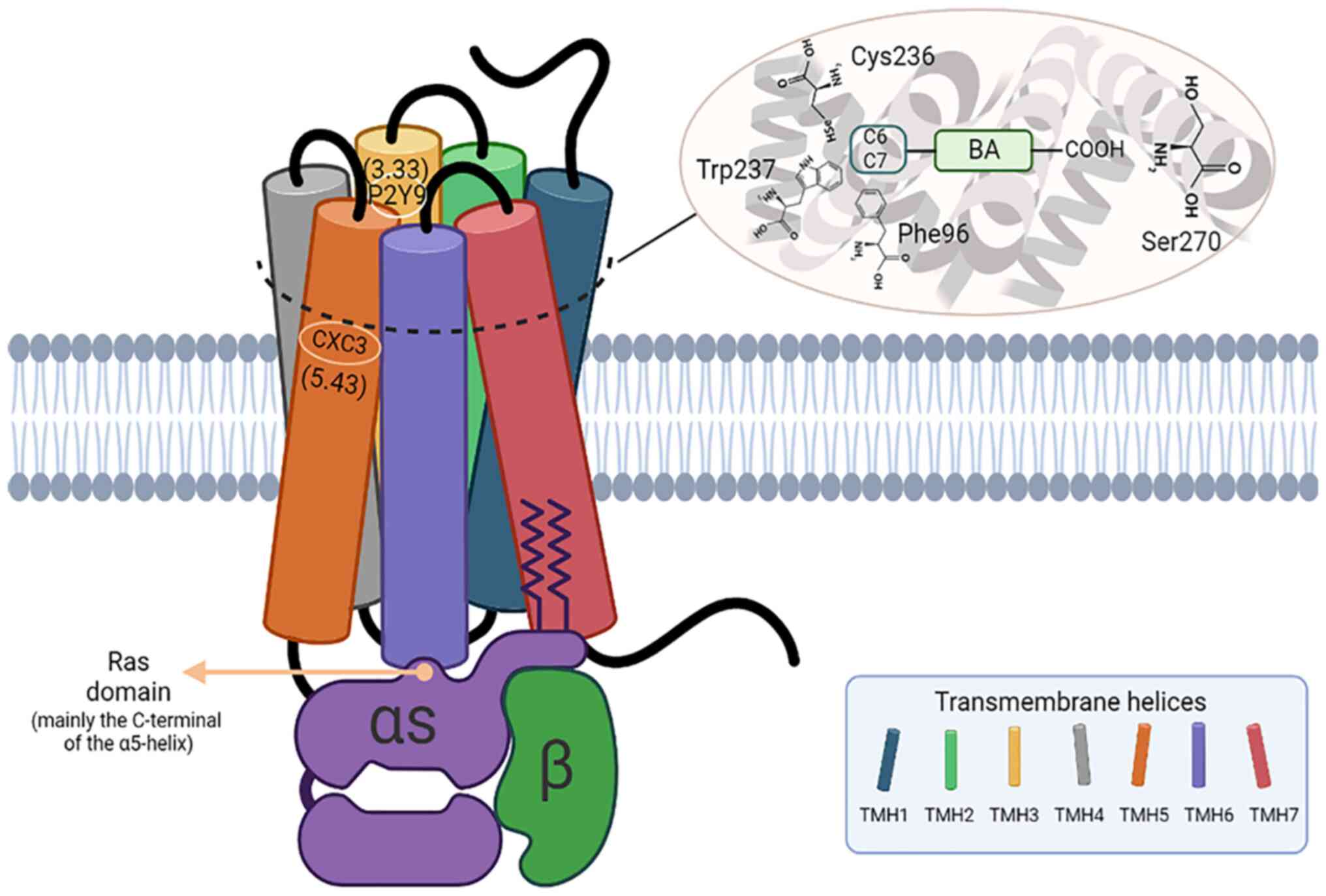
Henriques J, Vaz-Pereira S, Nascimento J
and Rosa PC: Diabetic eye disease. Acta Med Port. 28:107–113.
2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Portuguese).
|
|
9
|
Lechner J, O'Leary OE and Stitt AW: The
pathology associated with diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res.
139:7–14. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
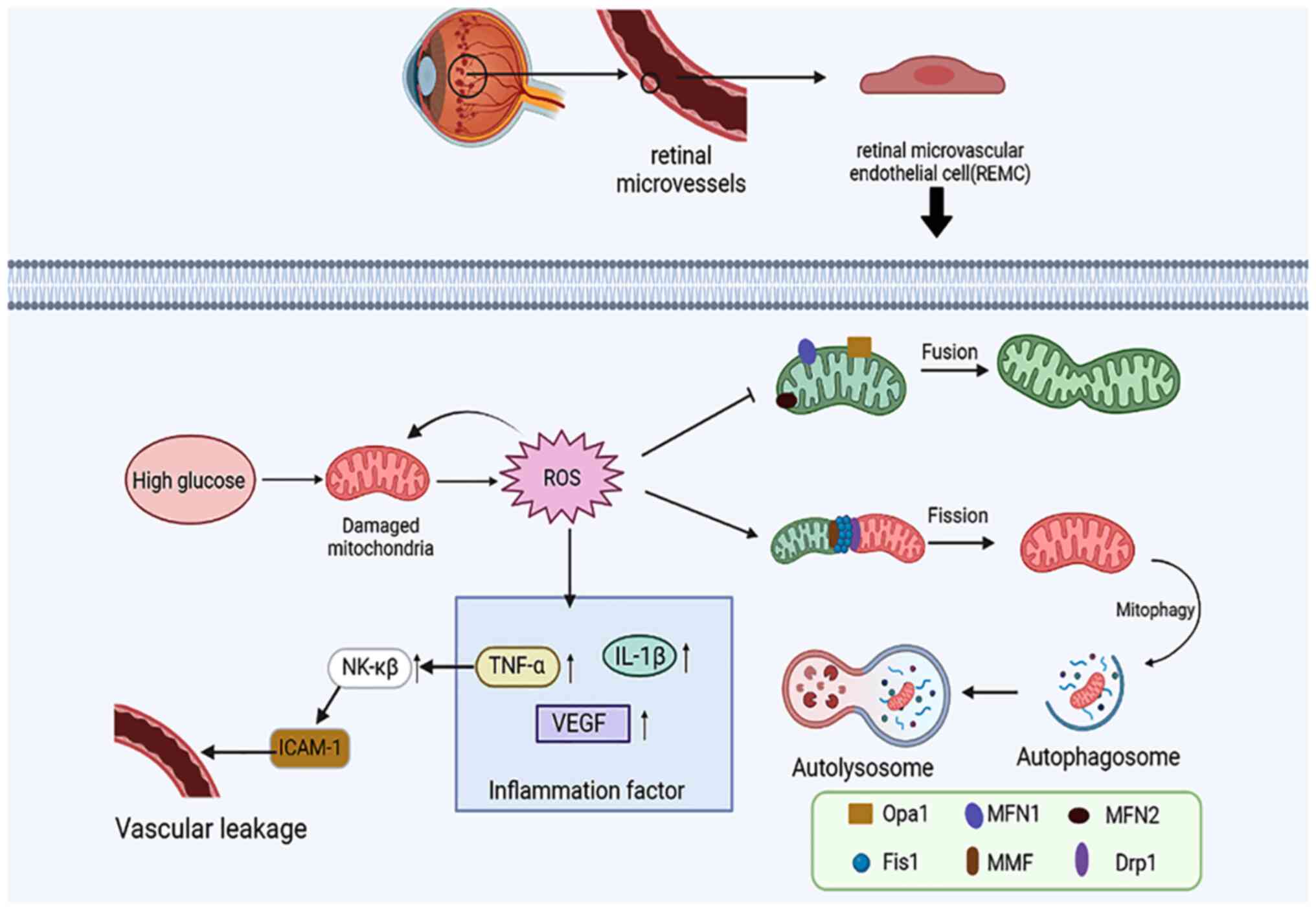
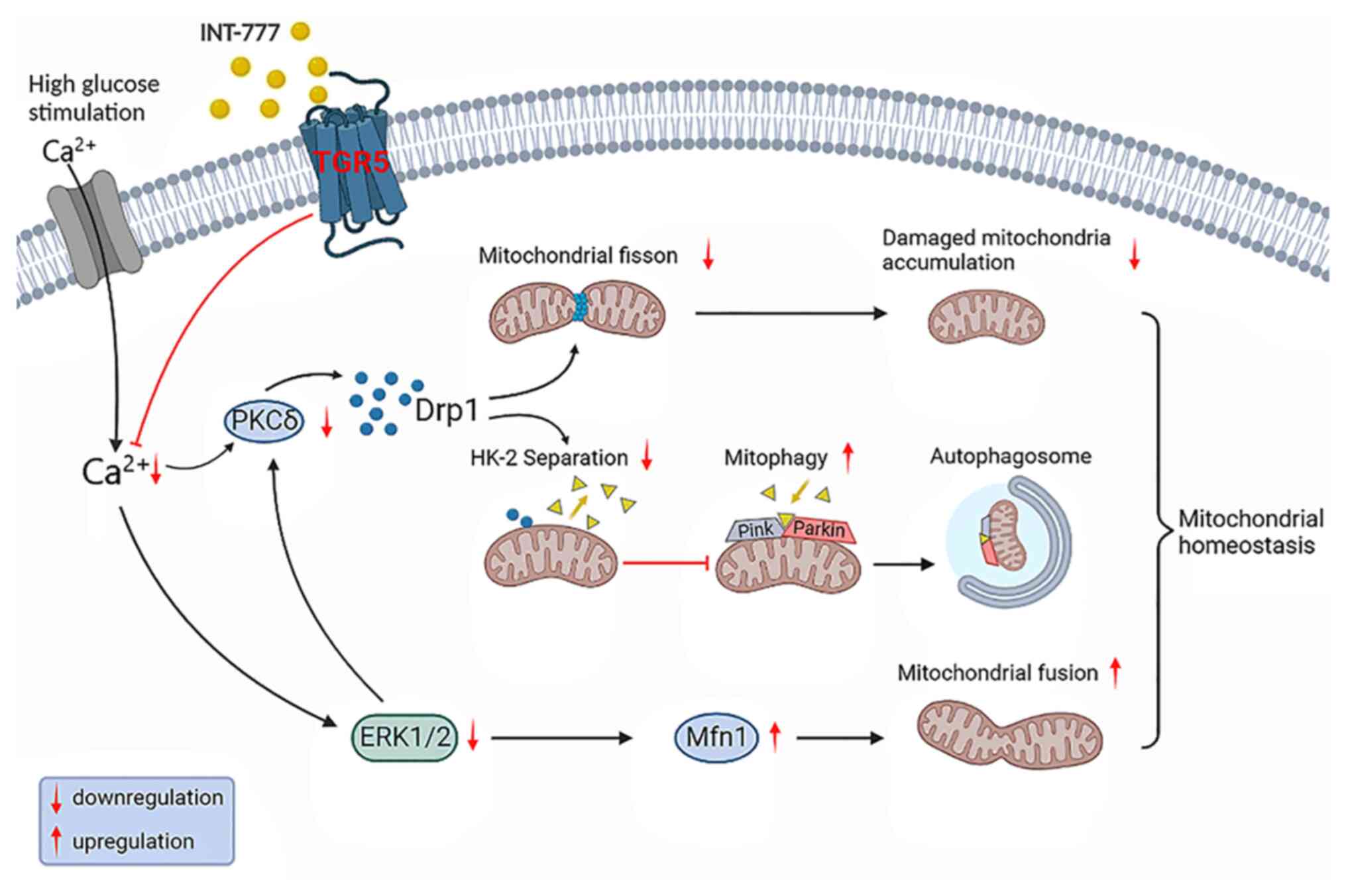
10
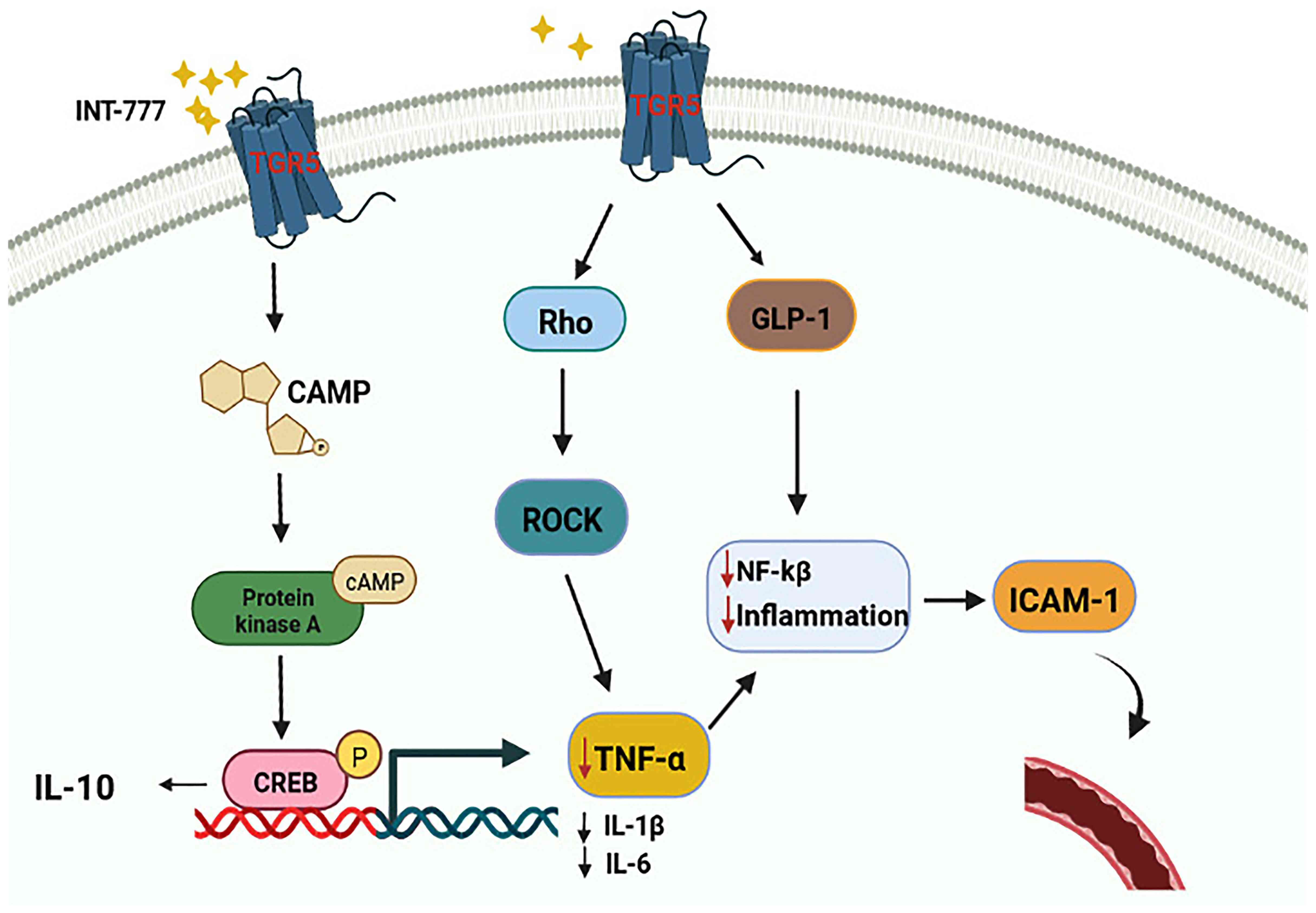
|
Shafabakhsh R, Aghadavod E, Mobini M,
Heidari-Soureshjani R and Asemi Z: Association between microRNAs
expression and signaling pathways of inflammatory markers in
diabetic retinopathy. J Cell Physiol. 234:7781–7787.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Singh LP, Yumnamcha T and Devi TS:
Mitophagy, ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in retinal pigment
epithelial cells under high glucose conditions: Implications for
Diabetic retinopathy and age-related retinal diseases. JOJ
Ophthalmol. 8:77–85. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meza CA, La Favor JD, Kim DH and Hickner
RC: Endothelial dysfunction: Is There a Hyperglycemia-induced
imbalance of NOX and NOS? Int J Mol Sci. 20(3775)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Maldonado-Valderrama J, Wilde P,
Macierzanka A and Mackie A: The role of bile salts in digestion.
Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 165:36–46. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
van Nierop FS, Scheltema MJ, Eggink HM,
Pols TW, Sonne DP, Knop FK and Soeters MR: Clinical relevance of
the bile acid receptor TGR5 in metabolism. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 5:224–233. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
de Boer JF, Bloks VW, Verkade E,
Heiner-Fokkema MR and Kuipers F: New insights in the multiple roles
of bile acids and their signaling pathways in metabolic control.
Curr Opin Lipidol. 29:194–202. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Molinaro A, Wahlström A and Marschall HU:
Role of bile acids in metabolic control. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
29:31–41. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Thomas C, Gioiello A, Noriega L, Strehle
A, Oury J, Rizzo G, Macchiarulo A, Yamamoto H, Mataki C, Pruzanski
M, et al: TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose
homeostasis. Cell Metab. 10:167–177. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li S, Qiu M, Kong Y, Zhao X, Choi HJ,
Reich M, Bunkelman BH, Liu Q, Hu S, Han M, et al: Bile Acid G
protein-coupled membrane receptor TGR5 Modulates Aquaporin
2-Mediated water homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:2658–2670.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li T and Chiang JY: Bile acid signaling in
metabolic disease and drug therapy. Pharmacol Rev. 66:948–983.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chávez-Talavera O, Tailleux A, Lefebvre P
and Staels B: Bile acid control of metabolism and inflammation in
obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Gastroenterology. 152:1679–1694.e3. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Voiosu A, Wiese S, Voiosu T, Bendtsen F
and Møller S: Bile acids and cardiovascular function in cirrhosis.
Liver Int. 37:1420–1430. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang XX, Wang D, Luo Y, Myakala K,
Dobrinskikh E, Rosenberg AZ, Levi J, Kopp JB, Field A, Hill A, et
al: FXR/TGR5 dual agonist prevents progression of nephropathy in
diabetes and obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:118–137. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Beli E, Yan Y, Moldovan L, Vieira CP, Gao
R, Duan Y, Prasad R, Bhatwadekar A, White FA, Townsend SD, et al:
Restructuring of the gut microbiome by intermittent fasting
prevents retinopathy and prolongs survival in db/db Mice. Diabetes.
67:1867–1879. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ren S, Hylemon P, Marques D, Hall E,
Redford K, Gil G and Pandak WM: Effect of increasing the expression
of cholesterol transporters (StAR, MLN64, and SCP-2) on bile acid
synthesis. J Lipid Res. 45:2123–2131. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pellicciari R, Gioiello A, Macchiarulo A,
Thomas C, Rosatelli E, Natalini B, Sardella R, Pruzanski M, Roda A,
Pastorini E, et al: Discovery of 6alpha-ethyl-23(S)-methylcholic
acid (S-EMCA, INT-777) as a potent and selective agonist for the
TGR5 receptor, a novel target for diabesity. J Med Chem.
52:7958–7961. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Galley HF and Webster NR: Physiology of
the endothelium. Br J Anaesth. 93:105–113. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cai Z, Yuan S, Zhong Y, Deng L, Li J, Tan
X and Feng J: Amelioration of Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes:
Role of takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5. Front Pharmacol.
12(637051)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Poredos P, Poredos AV and Gregoric I:
Endothelial dysfunction and its clinical implications. Angiology.
72:604–615. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Basha B, Samuel SM, Triggle CR and Ding H:
Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: Possible involvement
of endoplasmic reticulum stress? Exp Diabetes Res.
2012(481840)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sorrentino FS, Matteini S, Bonifazzi C,
Sebastiani A and Parmeggiani F: Diabetic retinopathy and endothelin
system: Microangiopathy versus endothelial dysfunction. Eye (Lond).
32:1157–1163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fu D, Yu JY, Yang S, Wu M, Hammad SM,
Connell AR, Du M, Chen J and Lyons TJ: Survival or death: A dual
role for autophagy in stress-induced pericyte loss in diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetologia. 59:2251–2261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kowluru RA: Mitochondrial stability in
diabetic retinopathy: Lessons learned from epigenetics. Diabetes.
68:241–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Forrester JV, Kuffova L and Delibegovic M:
The role of inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Front Immunol.
11(583687)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liang Q and Kobayashi S: Mitochondrial
quality control in the diabetic heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
95:57–69. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Williams M and Caino MC: Mitochondrial
dynamics in type 2 diabetes and cancer. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 9(211)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Madsen-Bouterse SA, Mohammad G, Kanwar M
and Kowluru RA: Role of mitochondrial DNA damage in the development
of diabetic retinopathy, and the metabolic memory phenomenon
associated with its progression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 13:797–805.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kowluru RA and Mishra M: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase in the pathogenesis of diabetic
retinopathy. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 148:67–85. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhong Q and Kowluru RA: Diabetic
retinopathy and damage to mitochondrial structure and transport
machinery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:8739–8746. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Singh LP, Devi TS and Yumnamcha T: The
role of txnip in mitophagy dysregulation and inflammasome
activation in diabetic retinopathy: A new perspective. JOJ
Ophthalmol. 4(10)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Noda K, Nakao S, Ishida S and Ishibashi T:
Leukocyte adhesion molecules in diabetic retinopathy. J Ophthalmol.
2012(279037)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kaštelan S, Tomić M, Gverović Antunica A,
Salopek Rabatić J and Ljubić S: Inflammation and pharmacological
treatment in diabetic retinopathy. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(213130)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tang J and Kern TS: Inflammation in
diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 30:343–358.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shabab T, Khanabdali R, Moghadamtousi SZ,
Kadir HA and Mohan G: Neuroinflammation pathways: A general review.
Int J Neurosci. 127:624–633. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Rübsam A, Parikh S and Fort PE: Role of
inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci.
19(942)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bucolo C, Marrazzo G, Platania CB, Drago
F, Leggio GM and Salomone S: Fortified extract of red berry, Ginkgo
biloba, and white willow bark in experimental early diabetic
retinopathy. J Diabetes Res. 2013(432695)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bucolo C, Drago F, Maisto R, Romano GL,
D'Agata V, Maugeri G and Giunta S: Curcumin prevents high glucose
damage in retinal pigment epithelial cells through ERK1/2-mediated
activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J Cell Physiol.
234:17295–17304. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Platania CBM, Lazzara F, Fidilio A, Fresta
CG, Conti F, Giurdanella G, Leggio GM, Salomone S, Drago F and
Bucolo C: Blood-retinal barrier protection against high glucose
damage: The role of P2X7 receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 168:249–258.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Tassetto M, Scialdone A, Solini A and Di
Virgilio F: The P2X7 receptor: A promising pharmacological target
in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 22(7110)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Platania CBM, Drago F and Bucolo C: The
P2X7 receptor as a new pharmacological target for retinal diseases.
Biochem Pharmacol. 198(114942)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Maruyama T, Miyamoto Y, Nakamura T, Tamai
Y, Okada H, Sugiyama E, Nakamura T, Itadani H and Tanaka K:
Identification of membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR).
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 298:714–719. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hov JR, Keitel V, Laerdahl JK, Spomer L,
Ellinghaus E, ElSharawy A, Melum E, Boberg KM, Manke T, Balschun T,
et al: Mutational characterization of the bile acid receptor TGR5
in primary sclerosing cholangitis. PLoS One.
5(e12403)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Macchiarulo A, Gioiello A, Thomas C, Pols
TW, Nuti R, Ferrari C, Giacchè N, De Franco F, Pruzanski M, Auwerx
J, et al: Probing the binding site of bile acids in TGR5. ACS Med
Chem Lett. 4:1158–1162. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Guo C, Chen WD and Wang YD: TGR5, not only
a metabolic regulator. Front Physiol. 7(646)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen G, Wang X, Ge Y, Ma L, Chen Q, Liu H,
Du Y, Ye RD, Hu H and Ren R: Cryo-EM structure of activated bile
acids receptor TGR5 in complex with stimulatory G protein. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5(142)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Renga B, Cipriani S, Carino A, Simonetti
M, Zampella A and Fiorucci S: Reversal of Endothelial Dysfunction
by GPBAR1 agonism in portal hypertension involves a AKT/FOXOA1
dependent regulation of H2S generation and endothelin-1. PLoS One.
10(e0141082)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Carino A, Marchianò S, Biagioli M, Bucci
M, Vellecco V, Brancaleone V, Fiorucci C, Zampella A, Monti MC,
Distrutti E and Fiorucci S: Agonism for the bile acid receptor
GPBAR1 reverses liver and vascular damage in a mouse model of
steatohepatitis. FASEB J. 33:2809–2822. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Poprac P, Jomova K, Simunkova M, Kollar V,
Rhodes CJ and Valko M: Targeting free radicals in oxidative
stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 38:592–607.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Prasad S, Gupta SC and Tyagi AK: Reactive
oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative
nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 387:95–105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Shutt T, Geoffrion M, Milne R and McBride
HM: The intracellular redox state is a core determinant of
mitochondrial fusion. EMBO Rep. 13:909–915. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Sabouny R, Fraunberger E, Geoffrion M, Ng
AC, Baird SD, Screaton RA, Milne R, McBride HM and Shutt TE: The
Keap1-Nrf2 stress response pathway promotes mitochondrial
hyperfusion through degradation of the mitochondrial fission
protein Drp1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 27:1447–1459. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ferrington DA, Fisher CR and Kowluru RA:
Mitochondrial defects drive degenerative retinal diseases. Trends
Mol Med. 26:105–118. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Sabouny R and Shutt TE: Reciprocal
regulation of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Trends Biochem Sci.
45:564–577. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lutty GA: Effects of diabetes on the eye.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:ORSF81–ORSF87. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhang MY, Zhu L, Zheng X, Xie TH, Wang W,
Zou J, Li Y, Li HY, Cai J, Gu S, et al: TGR5 activation ameliorates
mitochondrial homeostasis via regulating the PKCδ/Drp1-HK2
signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9(759421)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhu L, Wang W, Xie TH, Zou J, Nie X, Wang
X, Zhang MY, Wang ZY, Gu S, Zhuang M, et al: TGR5 receptor
activation attenuates diabetic retinopathy through suppression of
RhoA/ROCK signaling. FASEB J. 34:4189–4203. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Mishra P and Chan DC: Metabolic regulation
of mitochondrial dynamics. J Cell Biol. 212:379–387.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rovira-Llopis S, Bañuls C, Diaz-Morales N,
Hernandez-Mijares A, Rocha M and Victor VM: Mitochondrial dynamics
in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiological implications. Redox Biol.
11:637–645. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Huang M, Wei R, Wang Y, Su T, Li P and
Chen X: The uremic toxin hippurate promotes endothelial dysfunction
via the activation of Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Redox
Biol. 16:303–313. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Alam NM, Mills WC IV, Wong AA, Douglas RM,
Szeto HH and Prusky GT: A mitochondrial therapeutic reverses visual
decline in mouse models of diabetes. Dis Model Mech. 8:701–710.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Huang J, Li X, Li M, Li J, Xiao W, Ma W,
Chen X, Liang X, Tang S and Luo Y: Mitochondria-targeted
antioxidant peptide SS31 protects the retinas of diabetic rats.
Curr Mol Med. 13:935–945. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Dikalov SI, Nazarewicz RR, Bikineyeva A,
Hilenski L, Lassègue B, Griendling KK, Harrison DG and Dikalova AE:
Nox2-induced production of mitochondrial superoxide in angiotensin
II-mediated endothelial oxidative stress and hypertension. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 20:281–294. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Verónica Donoso M, Hernández F, Villalón
T, Acuña-Castillo C and Pablo Huidobro-Toro J: Pharmacological
dissection of the cellular mechanisms associated to the spontaneous
and the mechanically stimulated ATP release by mesentery
endothelial cells: Roles of thrombin and TRPV. Purinergic Signal.
14:121–139. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Chen C, Huang J, Shen J and Bai Q:
Quercetin improves endothelial insulin sensitivity in obese mice by
inhibiting Drp1 phosphorylation at serine 616 and mitochondrial
fragmentation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 51:1250–1257.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Slupe AM, Merrill RA, Flippo KH, Lobas MA,
Houtman JC and Strack S: A calcineurin docking motif (LXVP) in
dynamin-related protein 1 contributes to mitochondrial
fragmentation and ischemic neuronal injury. J Biol Chem.
288:12353–12365. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Bo T, Yamamori T, Suzuki M, Sakai Y,
Yamamoto K and Inanami O: Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
(CaMKII) mediates radiation-induced mitochondrial fission by
regulating the phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1)
at serine 616. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:1601–1607.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Cho B, Cho HM, Jo Y, Kim HD, Song M, Moon
C, Kim H, Kim K, Sesaki H, Rhyu IJ, et al: Constriction of the
mitochondrial inner compartment is a priming event for
mitochondrial division. Nat Commun. 8(15754)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Cook SJ, Stuart K, Gilley R and Sale MJ:
Control of cell death and mitochondrial fission by ERK1/2 MAP
kinase signalling. FEBS J. 284:4177–4195. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Chakrabarti R, Ji WK, Stan RV, de Juan
Sanz J, Ryan TA and Higgs HN: INF2-mediated actin polymerization at
the ER stimulates mitochondrial calcium uptake, inner membrane
constriction, and division. J Cell Biol. 217:251–268.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Schmukler E, Solomon S, Simonovitch S,
Goldshmit Y, Wolfson E, Michaelson DM and Pinkas-Kramarski R:
Altered mitochondrial dynamics and function in APOE4-expressing
astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 11(578)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Xu S and Herschman HR: A Tumor agnostic
therapeutic strategy for hexokinase 1-Null/Hexokinase 2-positive
cancers. Cancer Res. 79:5907–5914. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Li M, Shao J, Guo Z, Jin C, Wang L, Wang
F, Jia Y, Zhu Z, Zhang Z, Zhang F, et al: Novel
mitochondrion-targeting copper(II) complex induces HK2 malfunction
and inhibits glycolysis via Drp1-mediating mitophagy in HCC. J Cell
Mol Med. 24:3091–3107. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Clausell N, Kalil P, Biolo A, Molossi S
and Azevedo M: Increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha
in diabetic macrovasculopathy. Cardiovasc Pathol. 8:145–151.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Zhou X and Guan Z, Jin X, Zhao J, Chen G,
Ding J, Ren Y, Zhai X, Zhou Q and Guan Z: Reversal of alopecia
areata, osteoporosis follow treatment with activation of Tgr5 in
mice. Biosci Rep. 41(BSR20210609)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Wang TY, Tao SY, Wu YX, An T, Lv BH, Liu
JX, Liu YT and Jiang GJ: Quinoa Reduces High-Fat diet-induced
obesity in mice via potential microbiota-gut-brain-liver
interaction mechanisms. Microbiol Spectr.
10(e0032922)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Malik S, Suchal K, Khan SI, Bhatia J,
Kishore K, Dinda AK and Arya DS: Apigenin ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via
MAPK-NF-κB-TNF-α and TGF-β1-MAPK-fibronectin pathways. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 313:F414–F422. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Xiang E, Han B, Zhang Q, Rao W, Wang Z,
Chang C, Zhang Y, Tu C, Li C and Wu D: Human umbilical cord-derived
mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of early diabetic
nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation and fibrosis. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 11(336)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Khaloo P, Qahremani R, Rabizadeh S, Omidi
M, Rajab A, Heidari F, Farahmand G, Bitaraf M, Mirmiranpour H,
Esteghamati A and Nakhjavani M: Nitric oxide and TNF-α are
correlates of diabetic retinopathy independent of hs-CRP and HbA1c.
Endocrine. 69:536–541. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Mikelis CM, Simaan M, Ando K, Fukuhara S,
Sakurai A, Amornphimoltham P, Masedunskas A, Weigert R, Chavakis T,
Adams RH, et al: RhoA and ROCK mediate histamine-induced vascular
leakage and anaphylactic shock. Nat Commun. 6(6725)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Hu X, Yan J, Huang L, Araujo C, Peng J,
Gao L, Liu S, Tang J, Zuo G and Zhang JH: INT-777 attenuates
NLRP3-ASC inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via TGR5/cAMP/PKA
signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain
Behav Immun. 91:587–600. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Haselow K, Bode JG, Wammers M, Ehlting C,
Keitel V, Kleinebrecht L, Schupp AK, Häussinger D and Graf D: Bile
acids PKA-dependently induce a switch of the IL-10/IL-12 ratio and
reduce proinflammatory capability of human macrophages. J Leukoc
Biol. 94:1253–1264. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Kolka CM and Bergman RN: The endothelium
in diabetes: Its role in insulin access and diabetic complications.
Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 14:13–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Sampedro J, Bogdanov P, Ramos H,
Solà-Adell C, Turch M, Valeri M, Simó-Servat O, Lagunas C, Simó R
and Hernández C: New insights into the mechanisms of action of
topical administration of GLP-1 in an experimental model of
diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Med. 8(339)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wang LY, Cheng KC, Li Y, Niu CS, Cheng JT
and Niu HS: Glycyrrhizic acid increases glucagon like peptide-1
secretion via TGR5 activation in type 1-like diabetic rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:599–604. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Claybaugh T, Decker S, McCall K, Slyvka Y,
Steimle J, Wood A, Schaefer M, Thuma J and Inman S: L-Arginine
supplementation in type II diabetic rats preserves renal function
and improves insulin sensitivity by altering the nitric oxide
pathway. Int J Endocrinol. 2014(171546)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Kida T, Tsubosaka Y, Hori M, Ozaki H and
Murata T: Bile acid receptor TGR5 agonism induces NO production and
reduces monocyte adhesion in vascular endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:1663–1669. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Gloerich M and Bos JL: Epac: Defining a
new mechanism for cAMP action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
50:355–375. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Lezoualc'h F, Fazal L, Laudette M and
Conte C: Cyclic AMP Sensor EPAC proteins and their role in
cardiovascular function and disease. Circ Res. 118:881–897.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Gündüz D, Troidl C, Tanislav C, Rohrbach
S, Hamm C and Aslam M: Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signalling in
cAMP/Epac-Mediated endothelial barrier stabilisation. Front
Physiol. 10(1387)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Yuan Y, Engler AJ, Raredon MS, Le A,
Baevova P, Yoder MC and Niklason LE: Epac agonist improves barrier
function in iPSC-derived endothelial colony forming cells for whole
organ tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 200:25–34. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Garcia-Morales V, Friedrich J, Jorna LM,
Campos-Toimil M, Hammes HP, Schmidt M and Krenning G: The
microRNA-7-mediated reduction in EPAC-1 contributes to vascular
endothelial permeability and eNOS uncoupling in murine experimental
retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 54:581–591. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ramos CJ, Lin C, Liu X and Antonetti DA:
The EPAC-Rap1 pathway prevents and reverses cytokine-induced
retinal vascular permeability. J Biol Chem. 293:717–730.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Liu L, Jiang Y, Chahine A, Curtiss E and
Steinle JJ: Epac1 agonist decreased inflammatory proteins in
retinal endothelial cells, and loss of Epac1 increased inflammatory
proteins in the retinal vasculature of mice. Mol Vis. 23:1–7.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Luchetti F, Crinelli R, Cesarini E,
Canonico B, Guidi L, Zerbinati C, Di Sario G, Zamai L, Magnani M,
Papa S and Iuliano L: Endothelial cells, endoplasmic reticulum
stress and oxysterols. Redox Biol. 13:581–587. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Song J, Li J, Hou F, Wang X and Liu B:
Mangiferin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated
thioredoxin-interacting protein/NLRP3 inflammasome activation with
regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells. Metabolism. 64:428–437.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Fiorentino TV, Procopio T, Mancuso E,
Arcidiacono GP, Andreozzi F, Arturi F, Sciacqua A, Perticone F,
Hribal ML and Sesti G: SRT1720 counteracts glucosamine-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and endothelial dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Res. 107:295–306. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Sasaki T, Kuboyama A, Mita M, Murata S,
Shimizu M, Inoue J, Mori K and Sato R: The exercise-inducible bile
acid receptor Tgr5 improves skeletal muscle function in mice. J
Biol Chem. 293:10322–10332. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Dicks N, Gutierrez K, Currin L, de Macedo
MP, Glanzner WG, Mondadori RG, Michalak M, Agellon LB and Bordignon
V: Tauroursodeoxycholic acid/TGR5 signaling promotes survival and
early development of glucose-stressed porcine embryos†. Biol
Reprod. 105:76–86. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Dicks N, Gutierrez K, Currin L, Priotto de
Macedo M, Glanzner W, Michalak M, Agellon LB and Bordignon V:
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid acts via TGR5 receptor to facilitate DNA
damage repair and improve early porcine embryo development. Mol
Reprod Dev. 87:161–173. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|