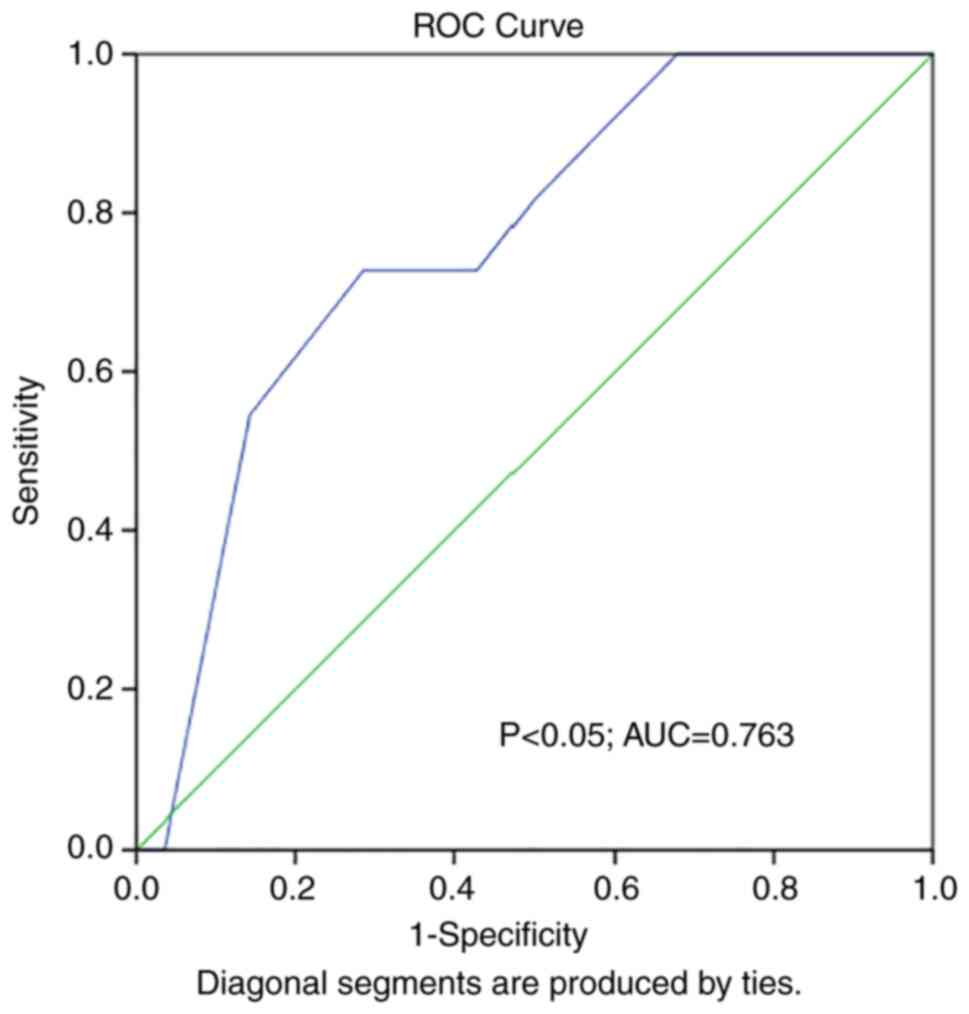
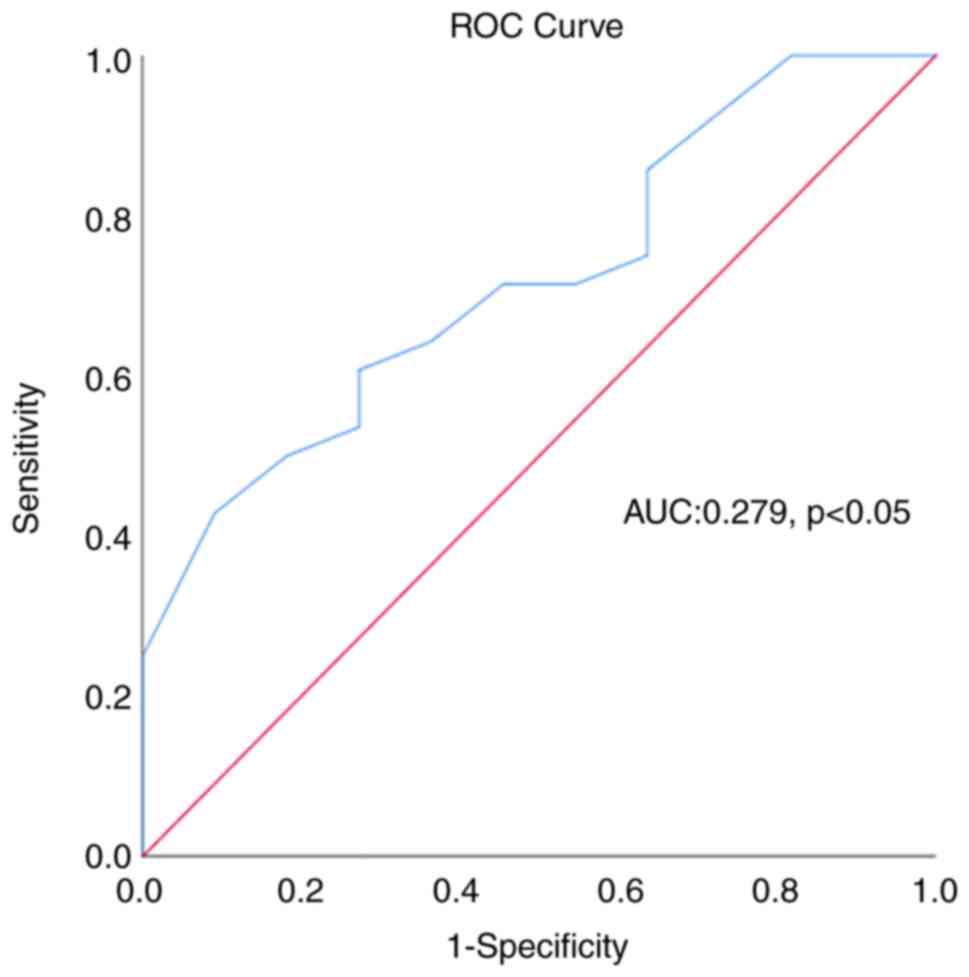
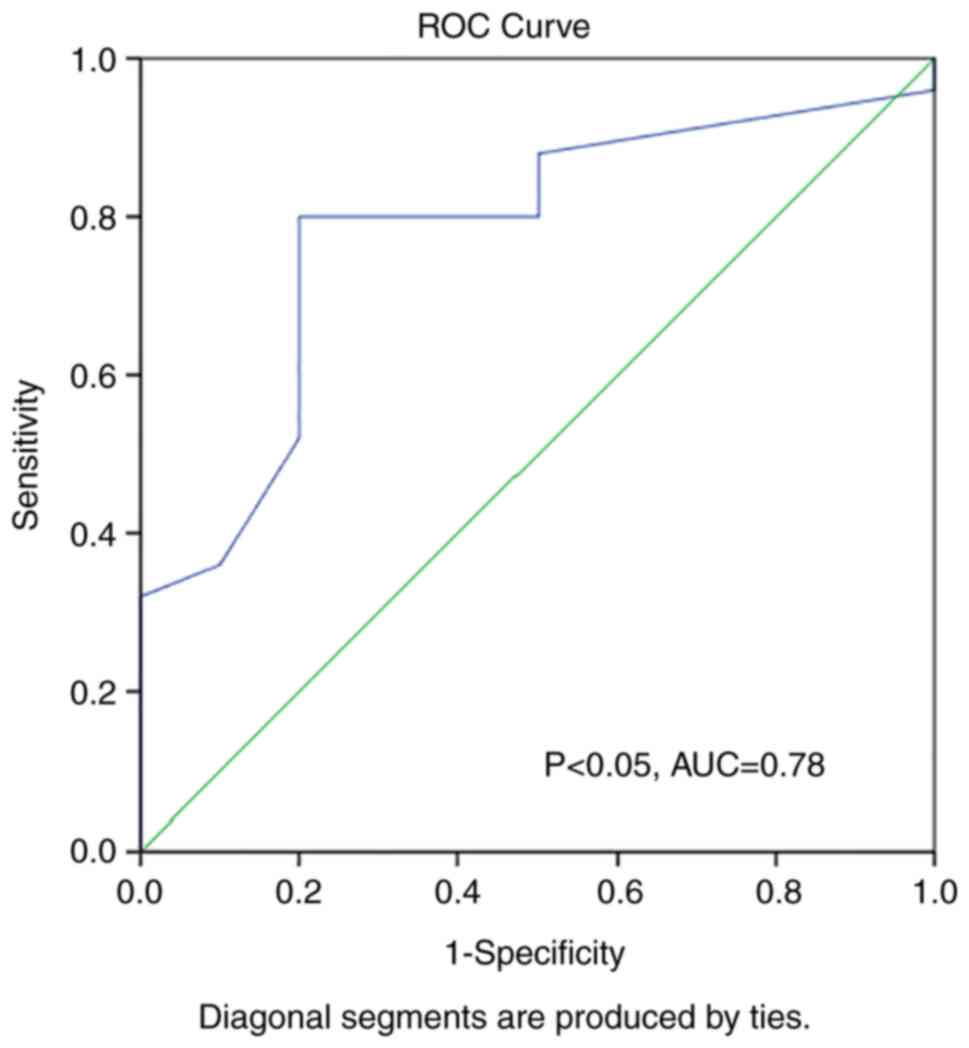
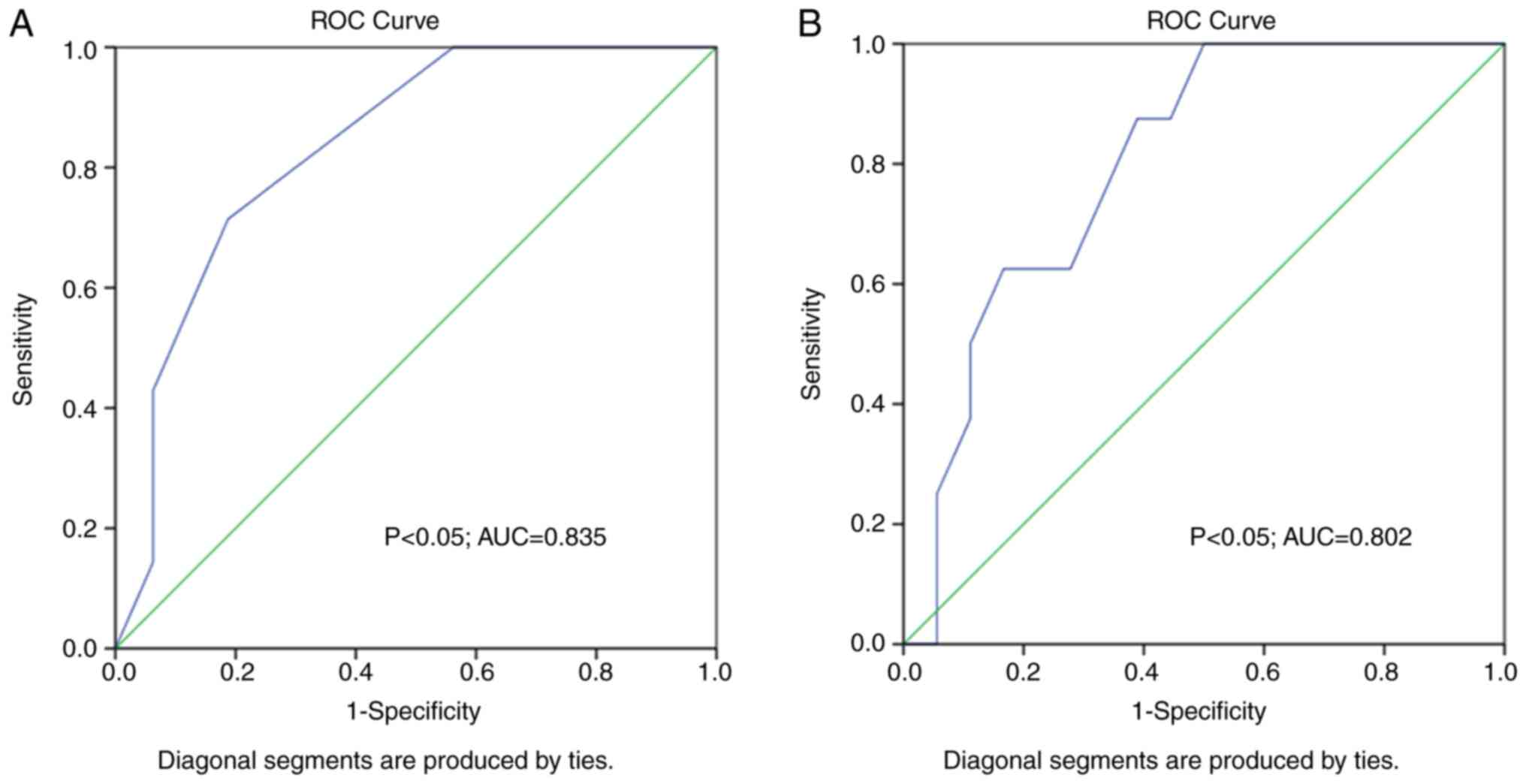
|
1
|
D'Silva A, Bhuva AN, van Zalen J,
Bastiaenen R, Abdel-Gadir A, Jones S, Nadarajan N, Medina KD, Ye Y,
Augusto J, et al: Cardiovascular remodeling experienced by
real-world, unsupervised, young novice marathon runners. Front
Physiol. 11(232)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lee DC, Pate RR, Lavie CJ, Sui X, Church
TS and Blair SN: Leisure-time running reduces all-cause and
cardiovascular mortality risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:472–481.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gabrielli L, Sitges M, Chiong M, Jalil J,
Ocaranza M, Llevaneras S, Herrera S, Fernandez R, Saavedra R, Yañez
F, et al: Potential adverse cardiac remodelling in highly trained
athletes: Still unknown clinical significance. Eur J Sport Sci.
18:1288–1297. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Arbab-Zadeh A, Perhonen M, Howden E,
Peshock RM, Zhang R, Adams-Huet B, Haykowsky MJ and Levine BD:
Cardiac remodeling in response to 1 year of intensive endurance
training. Circulation. 130:2152–2161. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zilinski JL, Contursi ME, Isaacs SK,
Deluca JR, Lewis GD, Weiner RB, Hutter AM Jr, d'Hemecourt PA,
Troyanos C, Dyer KS and Baggish AL: Myocardial adaptations to
recreational marathon training among middle-aged men. Circ
Cardiovasc Imaging. 8(e002487)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Krzeminski K, Buraczewska M, Miskiewicz Z,
Dąbrowski J, Steczkowska M, Kozacz A and Ziemba A: Effect of
ultra-endurance exercise on left ventricular performance and plasma
cytokines in healthy trained men. Biol Sport. 33:63–69.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Samaras A, Tsarouhas K, Paschalidis E,
Giamouzis G, Triposkiadis F, Tsitsimpikou C, Becker AT,
Goutzourelas N and Kouretas D: Effect of a special
carbohydrate-protein bar and tomato juice supplementation on
oxidative stress markers and vascular endothelial dynamics in
ultra-marathon runners. Food Chem Toxicol. 69:231–236.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Domke I, Cremer P and Huchtemann M:
Therapeutic drug monitoring on COBAS INTEGRA 400-evaluation
results. Clin Lab. 46:509–515. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB,
Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward
J, Shanewise JS, et al: Recommendations for chamber quantification:
A report from the American society of echocardiography's guidelines
and standards committee and the chamber quantification writing
group, developed in conjunction with the European association of
echocardiography, a branch of the European society of cardiology. J
Am Soc Echocardiogr. 18:1440–1463. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mosteller RD: Simplified calculation of
body-surface area. N Engl J Med. 317(1098)1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, Hua L,
Handschumacher MD, Chandrasekaran K, Solomon SD, Louie EK and
Schiller NB: Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the
right heart in adults: A report from the American society of
Echocardiography endorsed by the European association of
echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of
cardiology, and the canadian society of echocardiography. J Am Soc
Echocardiogr. 23:685–713. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mantero A, Gentile F, Azzollini M, Barbier
P, Beretta L, Casazza F, Corno R, Faletra F, Giagnoni E,
Gualtierotti C, et al: Effect of sample volume location on
Doppler-derived transmitral inflow velocity values in 288 normal
subjects 20 to 80 years old: An echocardiographic, two-dimensional
color Doppler cooperative study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 11:280–288.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim YJ and Sohn DW: Mitral annulus
velocity in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressure:
Prospective study in 200 patients. J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
13:980–985. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bruch C, Schmermund A, Marin D, Katz M,
Bartel T, Schaar J and Erbel R: Tei-index in patients with
mild-to-moderate congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J.
21:1888–1895. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tei C, Dujardin KS, Hodge DO, Bailey KR,
McGoon MD, Tajik AJ and Seward SB: Doppler echocardiographic index
for assessment of global right ventricular function. J Am Soc
Echocardiogr. 9:838–847. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Alvi R, Sklyar E, Gorski R, Atoui M,
Afshar M and Bella JN: Athens QRS score as a predictor of coronary
artery disease in patients with chest pain and normal exercise
stress test. J Am Heart Assoc. 5(e002832)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Foale R, Nihoyannopoulos P, McKenna W,
Kleinebenne A, Nadazdin A, Rowland E and Smith G: Echocardiographic
measurement of the normal adult right ventricle. Br Heart J.
56:33–44. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Du N, Bai S, Oguri K, Kato Y, Matsumoto I,
Kawase H and Matsuoka T: Heart rate recovery after exercise and
neural regulation of heart rate variability in 30-40 year old
female marathon runners. J Sports Sci Med. 4:9–17. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mann TN, Webster C, Lamberts RP and
Lambert MI: Effect of exercise intensity on post-exercise oxygen
consumption and heart rate recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol.
114:1809–1820. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Clauss S, Wakili R, Hildebrand B, Kääb S,
Hoster E, Klier I, Martens E, Hanley A, Hanssen H, Halle M and
Nickel T: MicroRNAs as biomarkers for acute atrial remodeling in
marathon runners (The miRathon Study-A Sub-Study of the Munich
Marathon Study). PLoS One. 11(e0148599)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, Totsuka M,
Sato K and Sugawara K: Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive
exercise. Cytokine kinetics. Exerc Immunol Rev. 8:6–48.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wallberg L, Mattsson CM, Enqvist JK and
Ekblom B: Plasma IL-6 concentration during ultra-endurance
exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 111:1081–1088. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bernecker C, Scherr J, Schinner S, Braun
S, Scherbaum WA and Halle M: Evidence for an exercise induced
increase of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in marathon runners. Scand J Med Sci
Sports. 23:207–214. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mohan S and Gupta D: Crosstalk of
toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of
inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1866–1878. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Asp S, Schjerling P
and Pedersen BK: Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in
strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol. 515:287–291.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Veresh Z, Racz A, Lotz G and Koller A:
ADMA impairs nitric oxide-mediated arteriolar function due to
increased superoxide production by angiotensin II-NAD(P)H oxidase
pathway. Hypertension. 52:960–966. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Simko F and Simko J: The potential role of
nitric oxide in the hypertrophic growth of the left ventricle.
Physiol Res. 49:37–46. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nemeth Z, Cziraki A, Szabados S, Biri B,
Keki S and Koller A: Elevated levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine
(ADMA) in the pericardial fluid of cardiac patients correlate with
cardiac hypertrophy. PLoS One. 10(e0135498)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rolski F and Blyszczuk P: Complexity of
TNF-α signaling in heart disease. J Clin Med.
9(3267)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sun M, Chen M, Dawood F, Zurawska U, Li
JY, Parker T, Kassiri Z, Kirshenbaum LA, Arnold M, Khokha R and Liu
PP: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates cardiac remodeling and
ventricular dysfunction after pressure overload state. Circulation.
115:1398–1407. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sack MN, Smith RM and Opie LH: Tumor
necrosis factor in myocardial hypertrophy and ischaemia-an
anti-apoptotic perspective. Cardiovasc Res. 45:688–695.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Besse S, Nadaud S, Balse E and Pavoine C:
Early protective role of inflammation in cardiac remodeling and
heart failure: Focus on TNFα and resident macrophages. Cells.
11(1249)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
La Gerche A, Inder WJ, Roberts TJ, Brosnan
MJ, Heidbuchel H and Prior DL: Relationship between inflammatory
cytokines and indices of cardiac dysfunction following intense
endurance exercise. PLoS One. 10(e0130031)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eijsvogels TM, Fernandez AB and Thompson
PD: Are there deleterious cardiac effects of acute and chronic
endurance exercise? Physiol Rev. 96:99–125. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vilela EM, Bettencourt-Silva R, Nunes JP
and Ribeiro VG: BNP and NT-proBNP elevation after running-a
systematic review. Acta Cardiol. 70:501–509. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kumar H and Choi DK: Hypoxia inducible
factor pathway and physiological adaptation: A cell survival
pathway? Mediators Inflamm. 2015(584758)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mounier R, Pialoux V, Roels B, Thomas C,
Millet G, Mercier J, Coudert J, Fellmann N and Clottes E: Effect of
intermittent hypoxic training on HIF gene expression in human
skeletal muscle and leukocytes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 105:515–524.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pluim BM, Zwinderman AH, van der Laarse A
and van der Wall EE: The athlete's heart. A meta-analysis of
cardiac structure and function. Circulation. 101:336–344.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pelliccia A, Maron BJ, Di Paolo FM, Biffi
A, Quattrini FM, Pisicchio C, Roselli A, Caselli S and Culasso F:
Prevalence and clinical significance of left atrial remodeling in
competitive athletes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 46:690–696.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rafaqat S, Sharif S, Majeed M, Naz S,
Manzoor F and Rafaqat S: Biomarkers of metabolic syndrome: Role in
pathogenesis and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. J Atr
Fibrillation. 14(20200495)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Psychari SN, Apostolou TS, Sinos L,
Hamodraka E, Liakos G and Kremastinos DT: Relation of elevated
C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels to left atrial size and
duration of episodes in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J
Cardiol. 95:764–767. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kazanski V, Mitrokhin VM, Mladenov MI and
Kamkin AG: Cytokine effects on mechano-induced electrical activity
in atrial myocardium. Immunol Invest. 46:22–37. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
La Gerche A, Burns AT, Mooney DJ, Inder
WJ, Taylor AJ, Bogaert J, Macisaac AI, Heidbüchel H and Prior DL:
Exercise-induced right ventricular dysfunction and structural
remodelling in endurance athletes. Eur Heart J. 33:998–1006.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Oxborough D, Shave R, Warburton D,
Williams K, Oxborough A, Charlesworth S, Foulds H, Hoffman MD,
Birch K and George K: Dilatation and dysfunction of the right
ventricle immediately after ultraendurance exercise: Exploratory
insights from conventional two-dimensional and speckle tracking
echocardiography. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 4:253–263.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Neilan TG, Januzzi JL, Lee-Lewandrowski E,
Ton-Nu TT, Yoerger DM, Jassal DS, Lewandrowski KB, Siegel AJ,
Marshall JE, Douglas PS, et al: Myocardial injury and ventricular
dysfunction related to training levels among nonelite participants
in the Boston marathon. Circulation. 114:2325–2333. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Erol MK and Karakelleoglu S: Assessment of
right heart function in the athlete's heart. Heart Vessels.
16:175–180. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
D'Andrea A, Riegler L, Golia E, Cocchia R,
Scarafile R, Salerno G, Pezzullo E, Nunziata L, Citro R, Cuomo S,
et al: Range of right heart measurements in top-level athletes: The
training impact. Int J Cardiol. 164:48–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ujka K, Bastiani L, D'Angelo G, Catuzzo B,
Tonacci A, Mrakic-Sposta S, Vezzoli A, Giardini G and Pratali L:
Enhanced right-chamber remodeling in endurance ultra-trail athletes
compared to marathon runners detected by standard and
speckle-tracking echocardiography. Front Physiol.
8(527)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
De Maria B, de Oliveira Gois M, Catai AM,
Marra C, Lucini D, Porta A, Pagani M and Vecchia LAD: Ten-year
follow-up of cardiac function and neural regulation in a group of
amateur half-marathon runners. Open Heart.
8(e001561)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Vitarelli A, Capotosto L, Placanica G,
Caranci F, Pergolini M, Zardo F, Martino F, Chiara SD and Vitarelli
M: Comprehensive assessment of biventricular function and aortic
stiffness in athletes with different forms of training by
three-dimensional echocardiography and strain imaging. Eur Heart J
Cardiovasc Imaging. 14:1010–1020. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Maron BJ, Douglas PS, Graham TP, Nishimura
RA and Thompson PD: Task Force 1: Preparticipation screening and
diagnosis of cardiovascular disease in athletes. J Am Coll Cardiol.
45:1322–1326. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Nassenstein K, Breuckmann F, Lehmann N,
Schmermund A, Hunold P, Broecker-Preuss M, Sandner TA, Halle M,
Mann K, Jöckel KH, et al: Left ventricular volumes and mass in
marathon runners and their association with cardiovascular risk
factors. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 25:71–79. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Stamatopoulos PG, Dangas G, Tsarouhas K,
Ziogas G, Tsitsimpikou C, Stamatopoulos G and Chrousos G: Subtotal
occlusion of left anterior coronary artery in a professional
athlete. Cardiology. 140:71–73. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Mavrogeni SI, Tsarouhas K, Spandidos DA,
Kanaka-Gantenbein C and Bacopoulou F: Sudden cardiac death in
football players: Towards a new pre-participation algorithm. Exp
Ther Med. 17:1143–1148. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Giannakopoulou A,
Andreou N, Papadopoulos G, Vartela V, Kolovou G, Bacopoulou F,
Tsarouhas K, Kanaka-Gantenbein C, Spandidos DA and Mavrogeni SI:
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance clarifies arrhythmogenicity in
asymptomatic young athletes with ventricular arrhythmias undergoing
pre-participation evaluation. Exp Ther Med. 20:561–571.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|