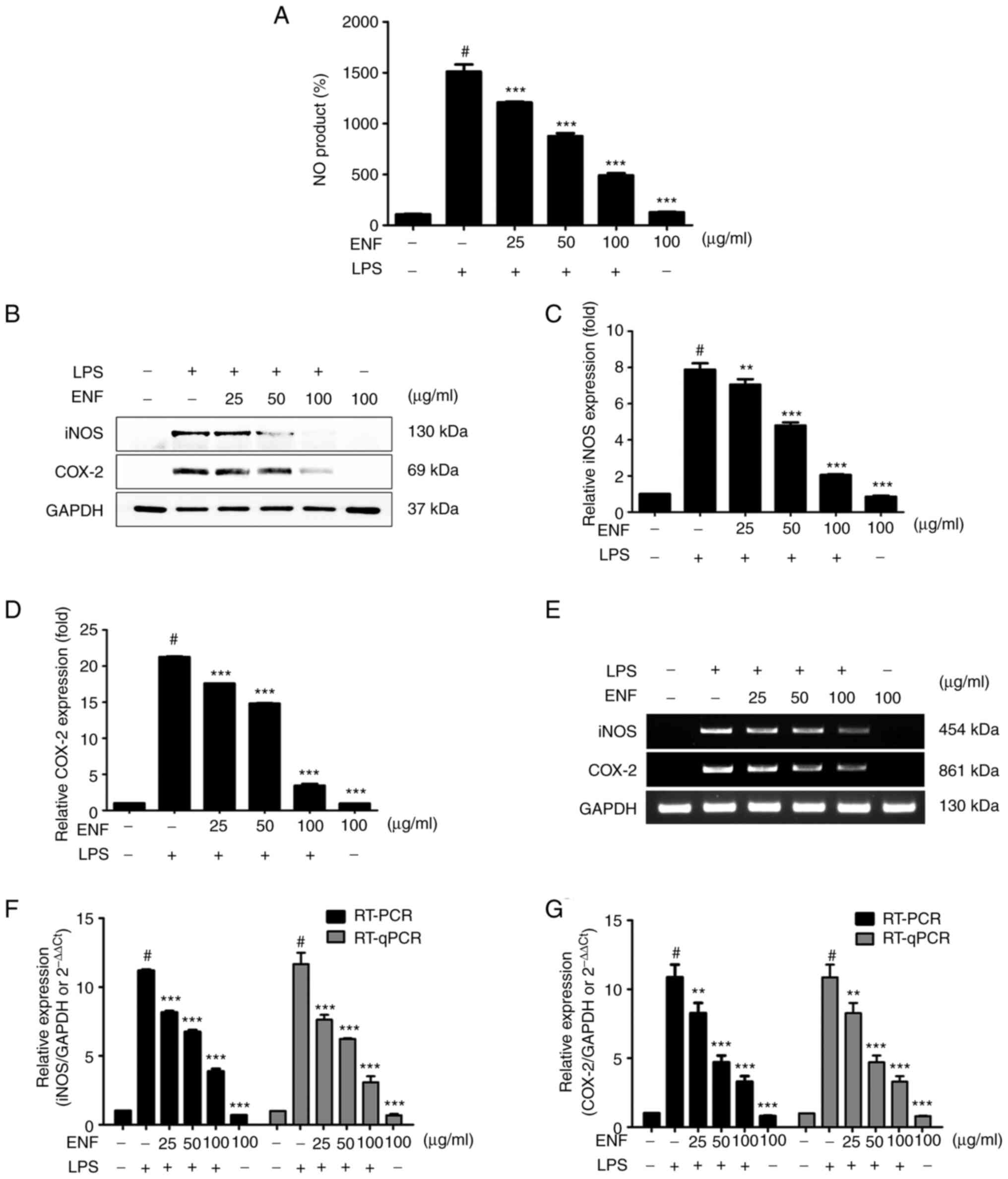
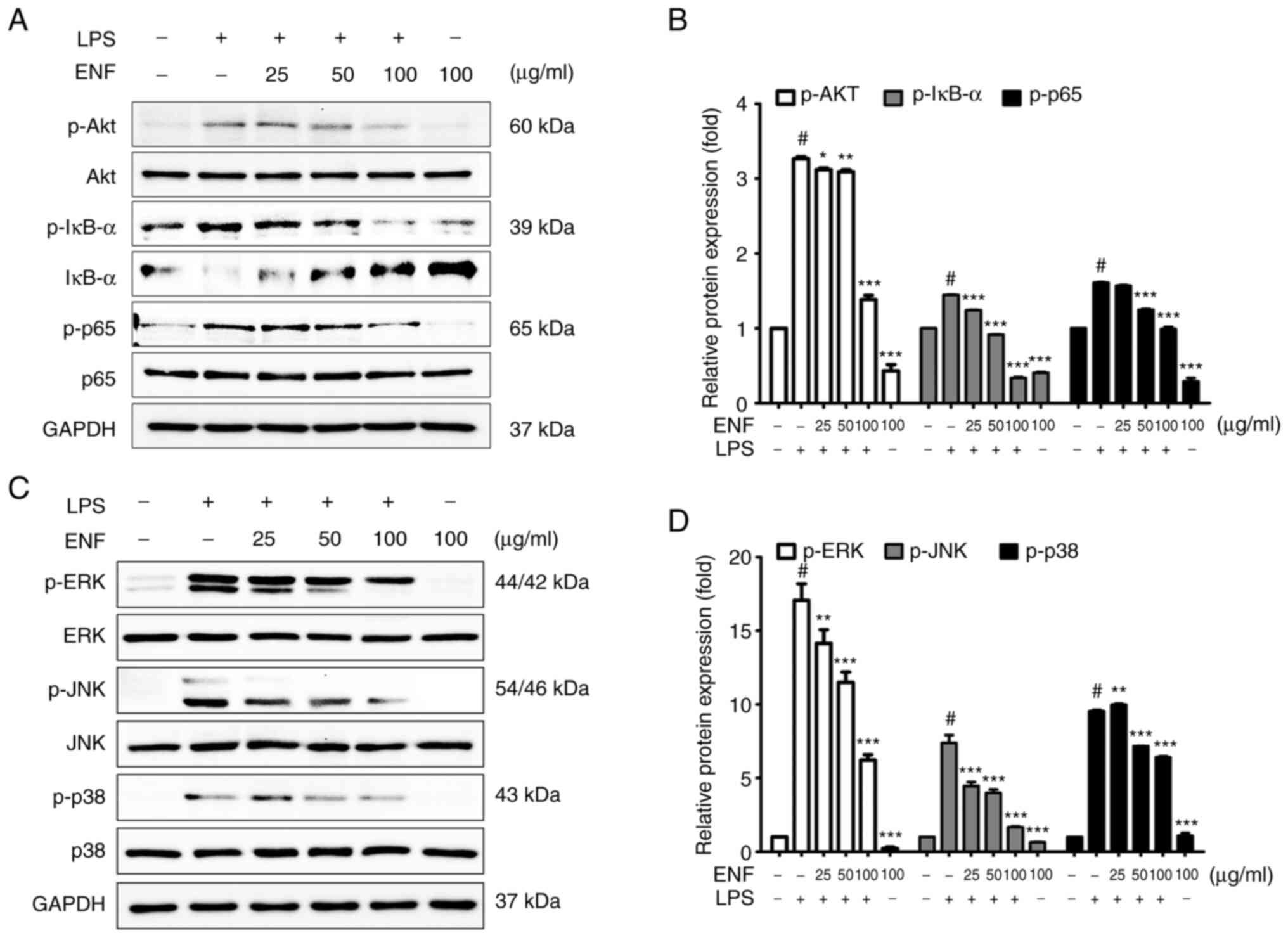
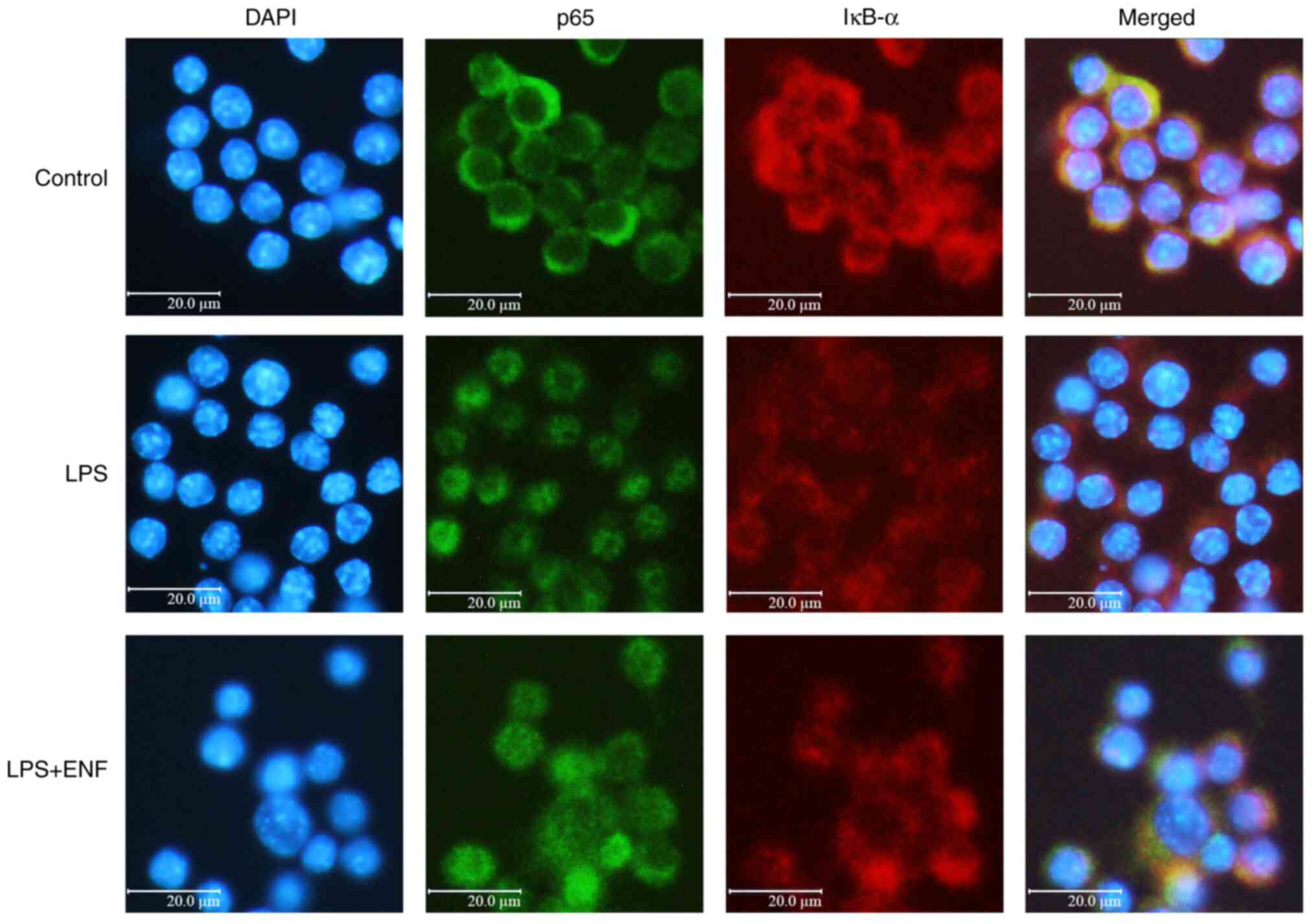
|
1
|
Tamunaidu P and Saka S: Chemical
characterization of various parts of nipa palm (Nypa
fruticans). Ind Crops Prod. 34:1423–1428. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Bandaranayake W: Traditional and medicinal
uses of mangroves. Mangroves and Salt Marshes. 2:133–148. 1998.
|
|
3
|
Hossain MF and Islam MA: Utilization of
mangrove forest plant: Nipa palm (Nypa fruticans Wurmb.). Am
J Agric Fores. 3:156–160. 2015.
|
|
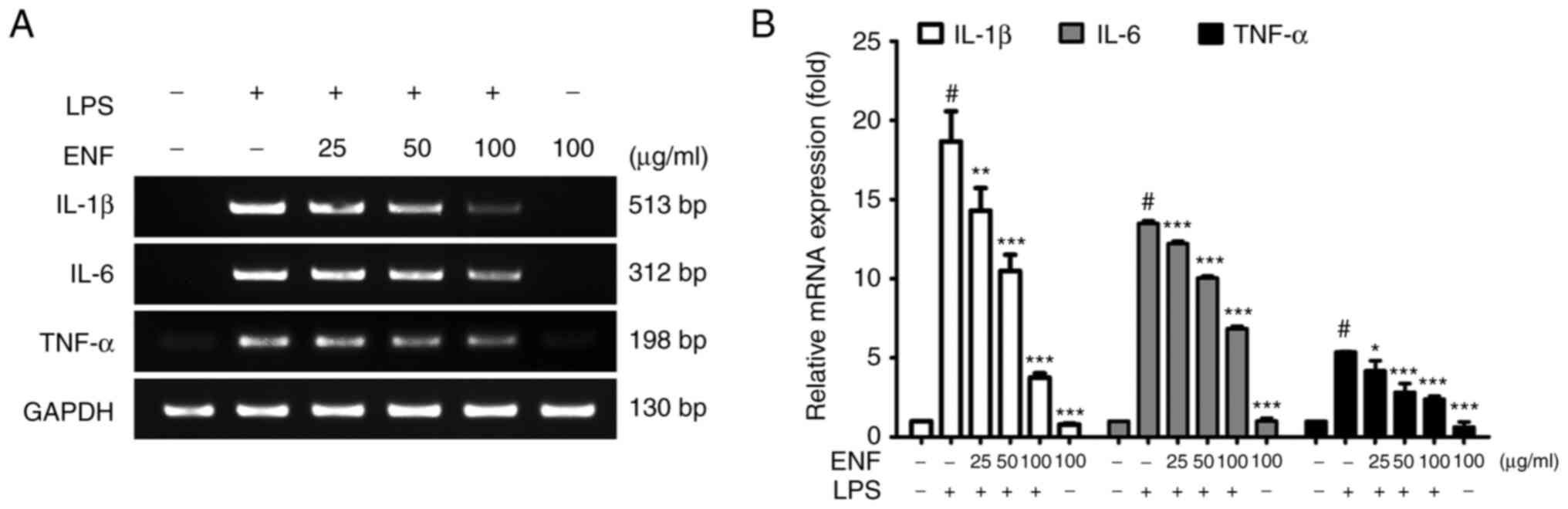
4
|
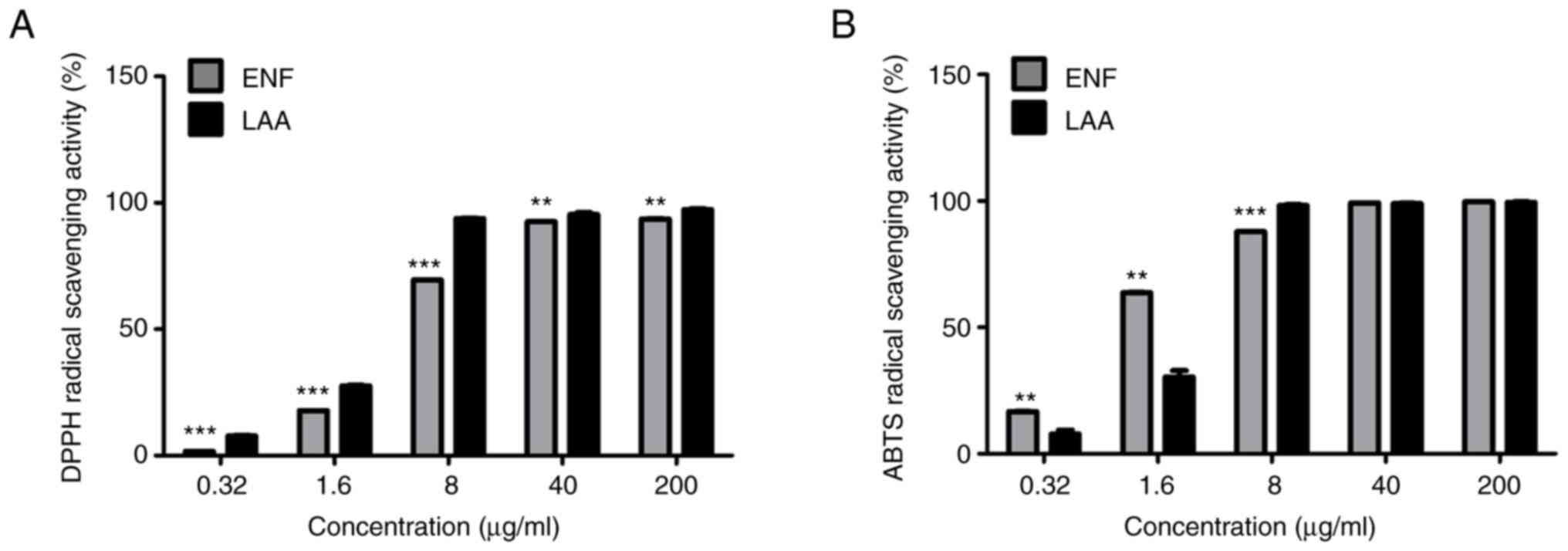
Prasad N, Yang B, Kong KW, Khoo HE, Sun J,
Azlan A, Ismail A and Romli ZB: Phytochemicals and antioxidant
capacity from Nypa fruticans Wurmb. fruit. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013(154606)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yusoff NA, Yam MF, Beh HK, Abdul Razak KN,
Widyawati T, Mahmud R, Ahmad M and Asmawi MZ: Antidiabetic and
antioxidant activities of Nypa fruticans Wurmb. vinegar
sample from Malaysia. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:595–605.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yusoff NA, Lim V, Al-Hindi B, Abdul Razak
KN, Widyawati T, Anggraini DR, Ahmad M and Asmawi MZ: Nypa
fruticans Wurmb. Vinegar's aqueous extract stimulates insulin
secretion and exerts hepatoprotective effect on STZ-induced
diabetic rats. Nutrients. 9(925)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
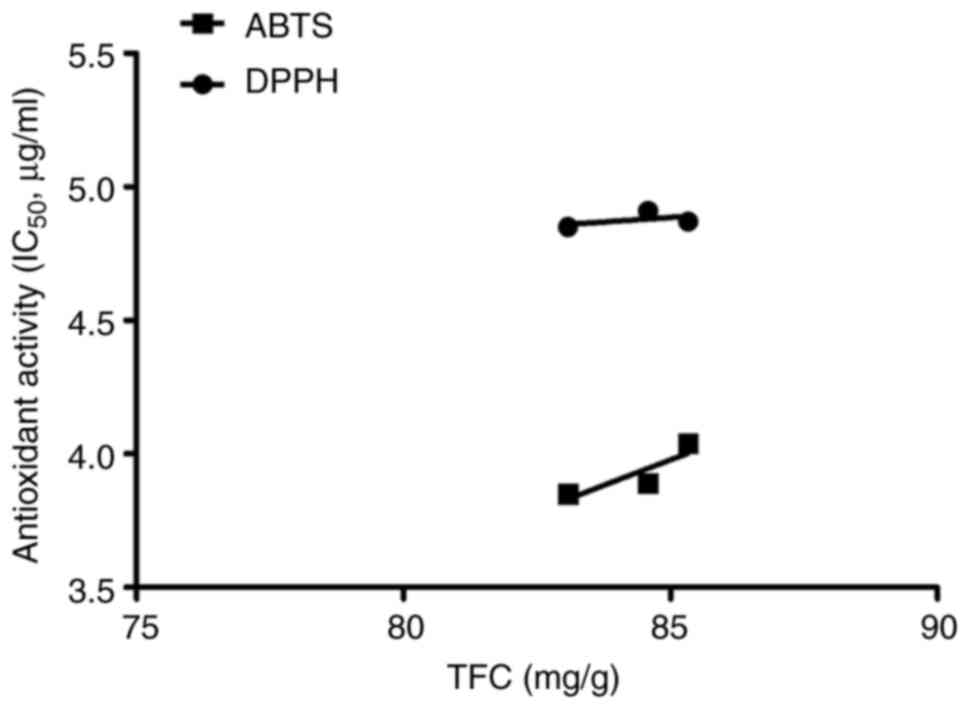
|
7
|
Tsai SJ and Yin MC: Anti-glycative and
anti-inflammatory effects of protocatechuic acid in brain of mice
treated by D-galactose. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3198–3205.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ahn SK, Goo YM, Ko KH, Lee SJ, Moon YH and
Lee SS, Kim JW and Lee SS: Study on the evaluation of nutritional
values and antioxidant activities for herbal medicine by-products.
J Agric Life Sci. 48:101–110. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Kim EY, Baik IH, Kim JH, Kim SR and Rhyu
MR: Screening of the antioxidant activity of some medicinal plants.
KOREAN J FOOD SCI. TECHNOL. 36:333–338. 2004.
|
|
10
|
Nirmala MJ, Samundeeswari A and Sankar PD:
Natural plant resources in anti-cancer therapy-A review. Res Plant
Biol. 1:01–14. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Wang Q, Kuang H, Su Y, Sun Y, Feng J, Guo
R and Chan K: Naturally derived anti-inflammatory compounds from
Chinese medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:9–39.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lawrence T, Willoughby DA and Gilroy DW:
Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution
of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:787–795. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Neumann J, Schaale K, Farhat K, Endermann
T, Ulmer AJ, Ehlers S and Reiling N: Frizzled1 is a marker of
inflammatory macrophages, and its ligand Wnt3a is involved in
reprogramming Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages.
FASEB J. 24:4599–4612. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sweet MJ and Hume DA: Endotoxin signal
transduction in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 60:8–26.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang R, Wang X, Zhou Y and Xiao Y:
RANKL-induced M1 macrophages are involved in bone formation. Bone
Res. 5(17019)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
So MS, Lee JS and Yi SY: Induction of
nitric oxide and cytokines in macrophages by Codonopsis lanceolata.
Korean J Food Sci Technol. 36:986–990. 2004.
|
|
17
|
Bjorkbacka H, Fitzgerald KA, Huet F, Li X,
Gregory JA, Lee MA, Ordija CM, Dowley NE, Golenbock DT and Freeman
MW: The induction of macrophage gene expression by LPS
predominantly utilizes Myd88-independent signaling cascades.
Physiol Genomics. 19:319–330. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kanarek N, London N, Schueler-Furman O and
Ben-Neriah Y: Ubiquitination and degradation of the inhibitors of
NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
2(a000166)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rajaram MV, Ganesan LP, Parsa KV, Butchar
JP, Gunn JS and Tridandapani S: Akt/Protein kinase B modulates
macrophage inflammatory response to Francisella infection and
confers a survival advantage in mice. J Immunol. 177:6317–6324.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Haque MA, Jantan I and Harikrishnan H:
Zerumbone suppresses the activation of inflammatory mediators in
LPS-stimulated U937 macrophages through MyD88-dependent
NF-κB/MAPK/PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.
55:312–322. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bae GS and Park SJ: The anti-inflammatory
effect of Nypa fruticans Wurmb fruit on
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response on RAW 264.7
cells. Korea J Herbol. 31:79–84. 2016.
|
|
22
|
Kang MS and Hyun KY: Antinociceptive and
anti-inflammatory effects of Nypa fruticans wurmb by
suppressing TRPV1 in the sciatic neuropathies. Nutrients.
12(135)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bondet V, Brand-Williams W and Berset C:
Kinetics and mechanisms of antioxidant activity using the DPPH.
free radical method. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 30:609–615. 1997.
|
|
24
|
van den Berg R, Haenen GRMM, van den Berg
H and Bast A: Applicability of an improved Trolox equivalent
antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay for evaluation of antioxidant
capacity measurements of mixtures. Food Chem. 66:511–517. 1999.
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jang TW and Park JH: Anti-Inflammatory
Effects of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Cultivar Okhwang 1)
Callus through Inhibition of PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling
Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Macrophages. Processes.
9(1071)2021.
|
|
27
|
Kim EA, Kim SY, Ye BR, Kim J, Ko SC, Lee
WW, Kim KN, Choi IW, Jung WK and Heo SJ: Anti-inflammatory effect
of Apo-9'-fucoxanthinone via inhibition of MAPKs and NF-kB
signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and
zebrafish model. Int Immunopharmacol. 59:339–346. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Adcock IM, Ford PA, Bhavsar P, Ahmad T and
Chung KF: Steroid resistance in asthma: Mechanisms and treatment
options. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 8:171–178. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Caban M, Chojnacka K, Owczarek K,
Laskowska J, Fichna J, Podsedek A, Sosnowska D and Lewandowska U:
Spent hops (Humulus lupulus L.) extract as modulator of the
inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide stimulated raw 264.7
macrophages. J Physiol Pharmacol: Apr 27, 2020 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
30
|
Biswas SK and Lewis CE: NF-κB as a central
regulator of macrophage function in tumors. J Leukoc Biol.
88:877–884. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ngabire D, Seong Y, Patil MP, Niyonizigiye
I, Seo YB and Kim GD: Anti-inflammatory effects of aster incisus
through the inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK, and akt pathways in
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mediators Inflamm.
2018(4675204)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Riehemann K
and Wesselborg S: Regulation of NF-kappaB activation by MAP kinase
cascades. Immunobiology. 198:35–49. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim NY, Cheong SH, Lee KJ, Sok DE and Kim
MR: Anti-inflammatory effects of Ribes diacanthum Pall mediated via
regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and a TPA-induced dermatitis
animal model. Antioxidants (Basel). 9(622)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
El-Desouky SK, Kim KH, Ryu SY, Eweas AF,
Gamal-Eldeen AM and Kim YK: A new pyrrole alkaloid isolated
fromArum palaestinum Boiss. and its biological activities. Arch
Pharm Res. 30:927–931. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Koes RE, Quattrocchio F and Mol JNM: The
flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in plants: Function and evolution.
BioEssays. 16:123–132. 1994.
|
|
36
|
Leiherer A, Mündlein A and Drexel H:
Phytochemicals and their impact on adipose tissue inflammation and
diabetes. Vascul Pharmacol. 58:3–20. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Johnson IT: Phytochemicals and cancer.
Proc Nutr Soc. 66:207–215. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rajendran P, Ho E, Williams DE and
Dashwood RH: Dietary phytochemicals, HDAC inhibition, and DNA
damage/repair defects in cancer cells. Clin Epigenetics.
3(4)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nishino H, Satomi Y, Tokuda H and Masuda
M: Cancer control by phytochemicals. Curr Pharm Des. 13:3394–3399.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roshan R, Ahmed S and Hasan MM: Arisaema
jacquemontii Blume (Araceae): A review of medicinal uses,
phytochemistry and pharmacology. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 6:429–432.
2017.
|
|
41
|
Dong H, Geng Y, Wang X, Song X, Wang X and
Yu J: Chemical constituents from scindapsus officinalis (Roxb.)
Schott. and their anti-inflammatory activities. Molecules.
23(2577)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yusoff NA, Ahmad M, Al Hindi B, Widyawati
T, Yam MF, Mahmud R, Razak KN and Asmawi MZ: Aqueous extract of
Nypa fruticans Wurmb. vinegar alleviates postprandial
hyperglycemia in normoglycemic rats. Nutrients. 7:7012–7026.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sahoo S, Ghosh G, Das D and Nayak S:
Phytochemical investigation and in vitro antioxidant activity of an
indigenous medicinal plant Alpinia nigra BL Burtt. Asian Pac J Trop
Biomed. 3:871–876. 2013.
|
|
44
|
Xu XH, Li T, Fong CM, Chen X, Chen XJ,
Wang YT, Huang MQ and Lu JJ: Saponins from Chinese medicines as
anticancer agents. Molecules. 21(1326)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Souto AL, Tavares JF, Da Silva MS, Diniz
Mde F, de Athayde-Filho PF and Barbosa Filho JM: Anti-inflammatory
activity of alkaloids: An update from 2000 to 2010. Molecules.
16:8515–8534. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Choi JH, Hwang JW, Lee SG, Heo SH and Kang
H: Antioxidant effect of hot water extracts from 3 types Indonesia
plants (Hibiscus petals, Moringa Oleifera gymnosperm, and Nipa
Fruticans Wurmb). Journal of Naturopathy. 10:42–47. 2021.
|
|
47
|
Reza H, Haq WM, Das AK, Rahman S, Jahan R
and Rahmatullah M: Anti-hyperglycemic and antinociceptive activity
of methanol leaf and stem extract of Nypa fruticans Wurmb.
Pak J Pharm Sci. 24:485–488. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maleki SJ, Crespo JF and Cabanillas B:
Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem.
299(125124)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Forman HJ and Zhang H: Targeting oxidative
stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:689–709. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Dang Y, Mu Y, Wang K, Xu K, Yang J, Zhu Y
and Luo B: Papaverine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
microglial activation by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 10:851–859. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet
S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre JV and Woolf CJ:
Interleukin-1beta-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS
contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature.
410:471–475. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zeilhofer HU and Brune K: Analgesic
strategies beyond the inhibition of cyclooxygenases. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 27:467–474. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kröncke KD, Fehsel K and Kolb-Bachofen V:
Nitric oxide: Cytotoxicity versus cytoprotection-how, why, when,
and where? Nitric Oxide. 1:107–120. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hofseth LJ, Hussain SP, Wogan GN and
Harris CC: Nitric oxide in cancer and chemoprevention. Free Radic
Biol Med. 34:955–968. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Liew FY: Regulation of nitric oxide
synthesis in infectious and autoimmune diseases. Immunol Lett.
43:95–98. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Grandage VL, Gale RE, Linch DC and Khwaja
A: PI3-kinase/Akt is constitutively active in primary acute myeloid
leukaemia cells and regulates survival and chemoresistance via
NF-kB, MAPkinase and p53 pathways. Leukemia. 19:586–594.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bode JG, Ehlting C and Häussinger D: The
macrophage response towards LPS and its control through the
p38(MAPK)-STAT3 axis. Cell Signal. 24:1185–1194. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|