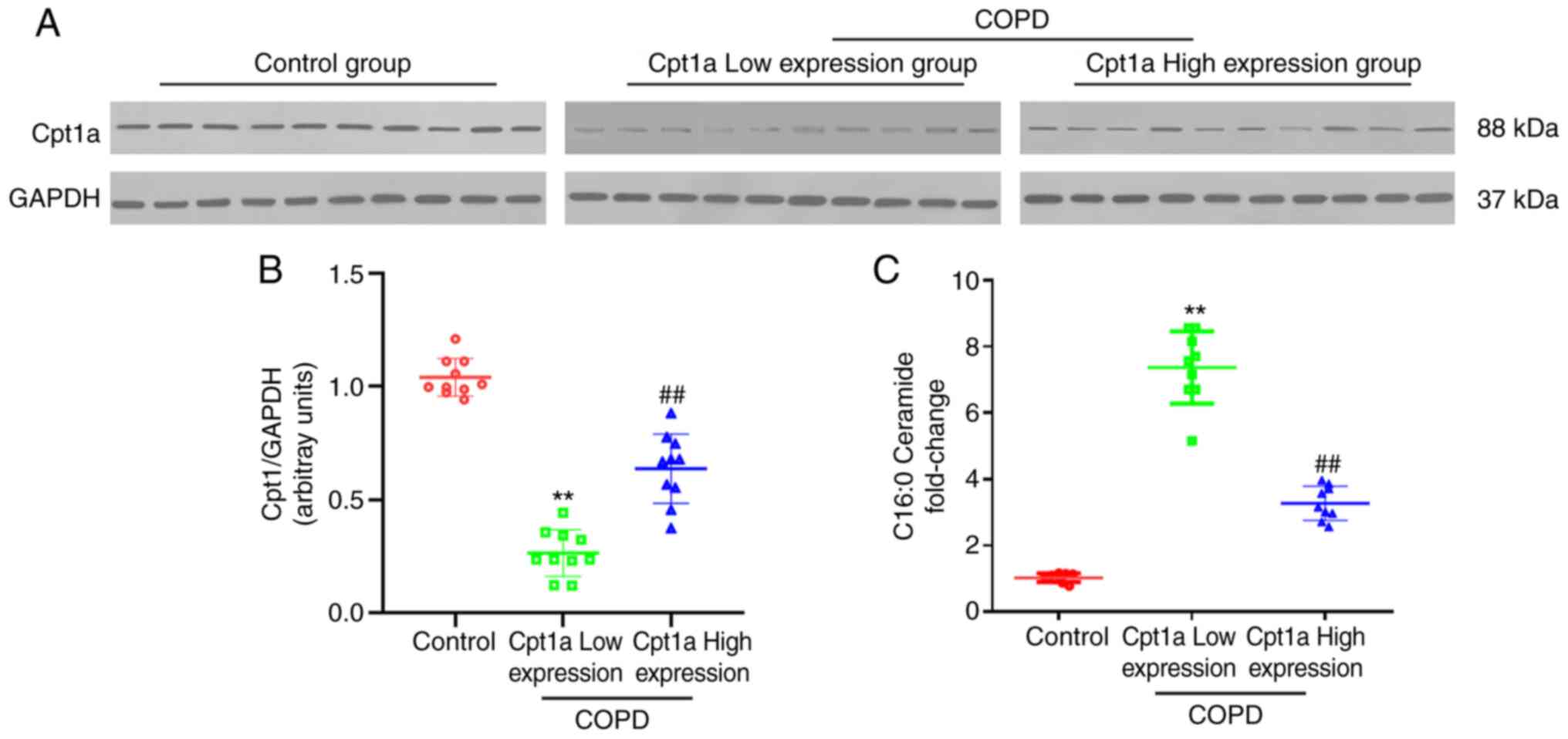
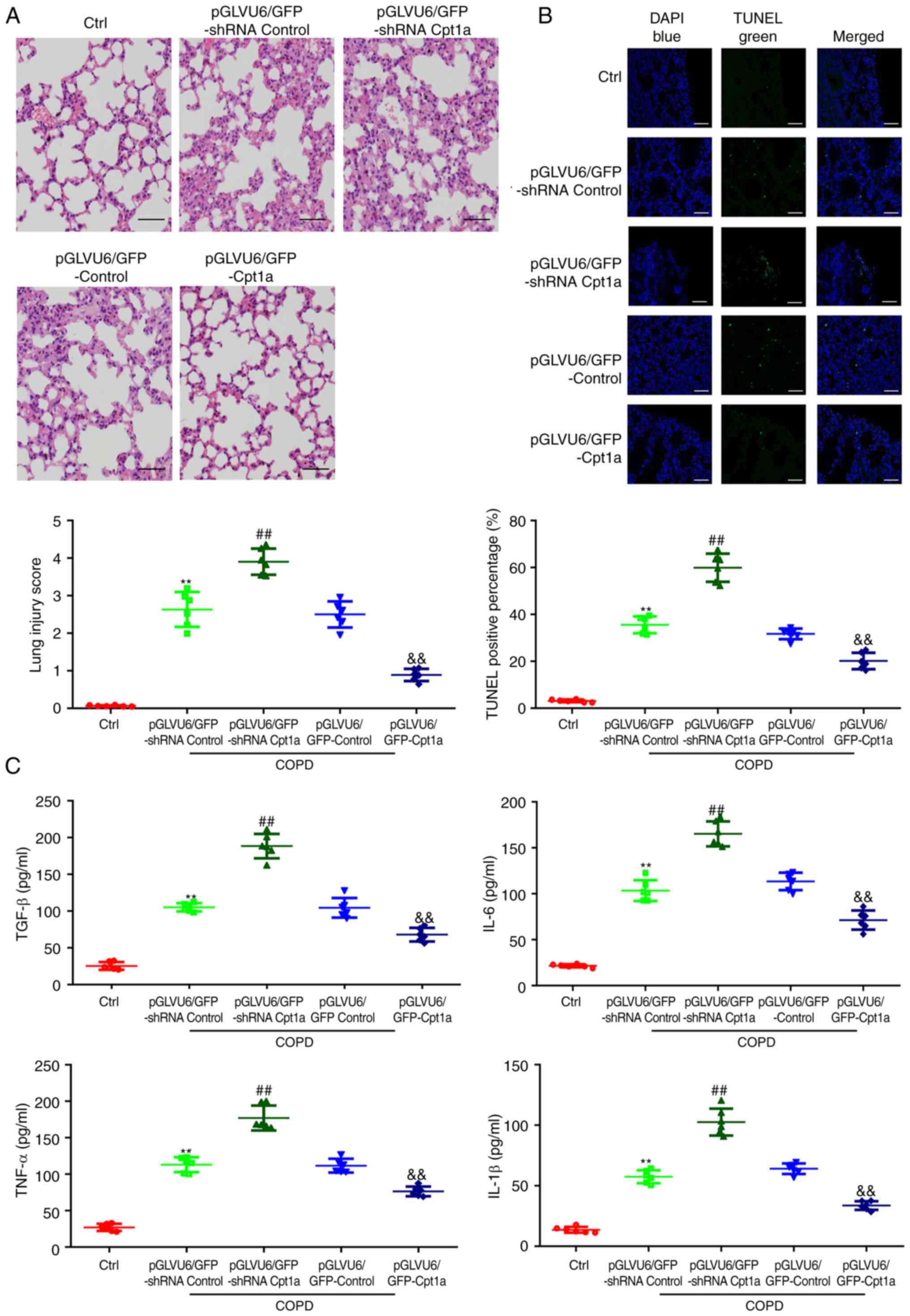
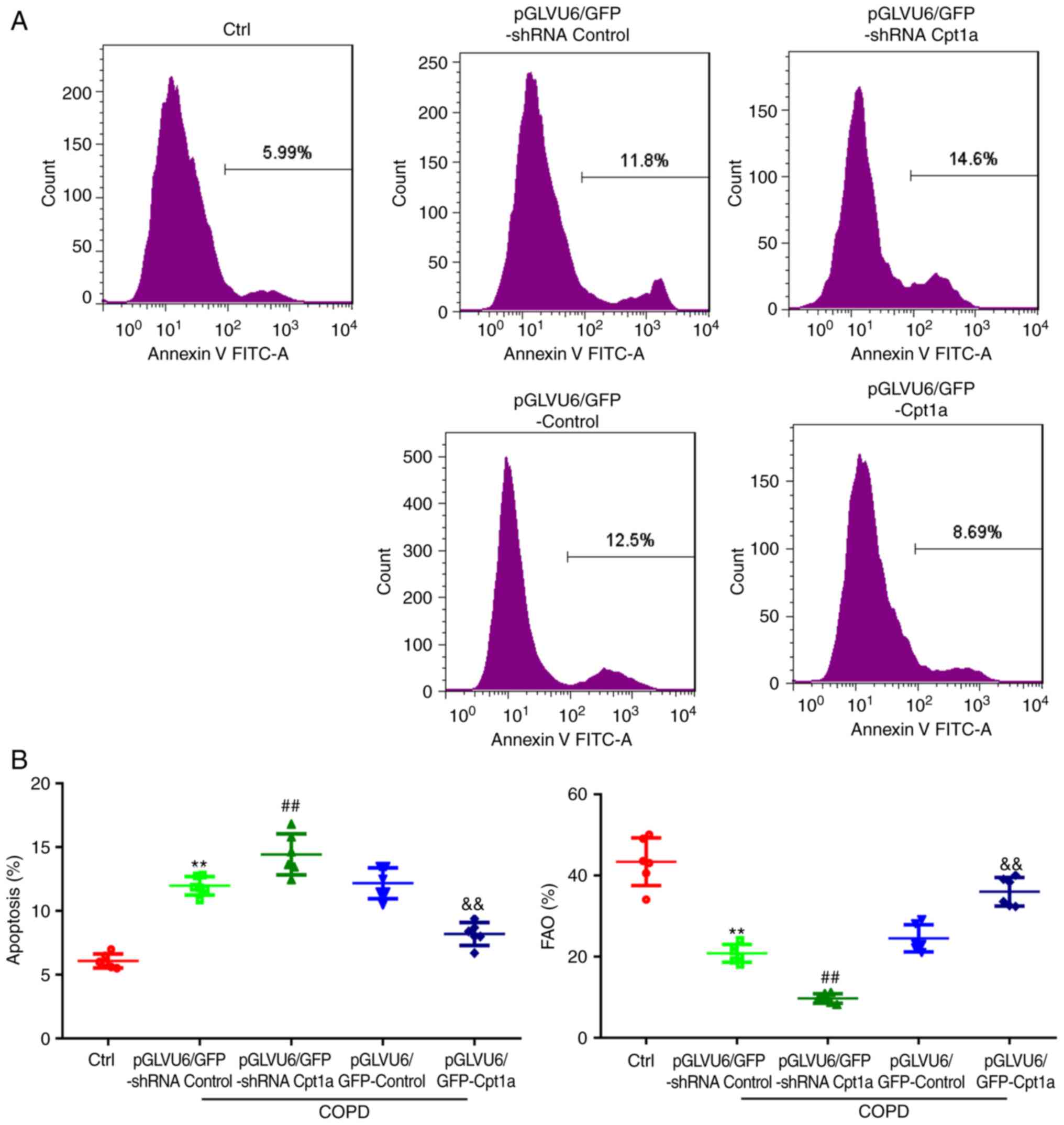
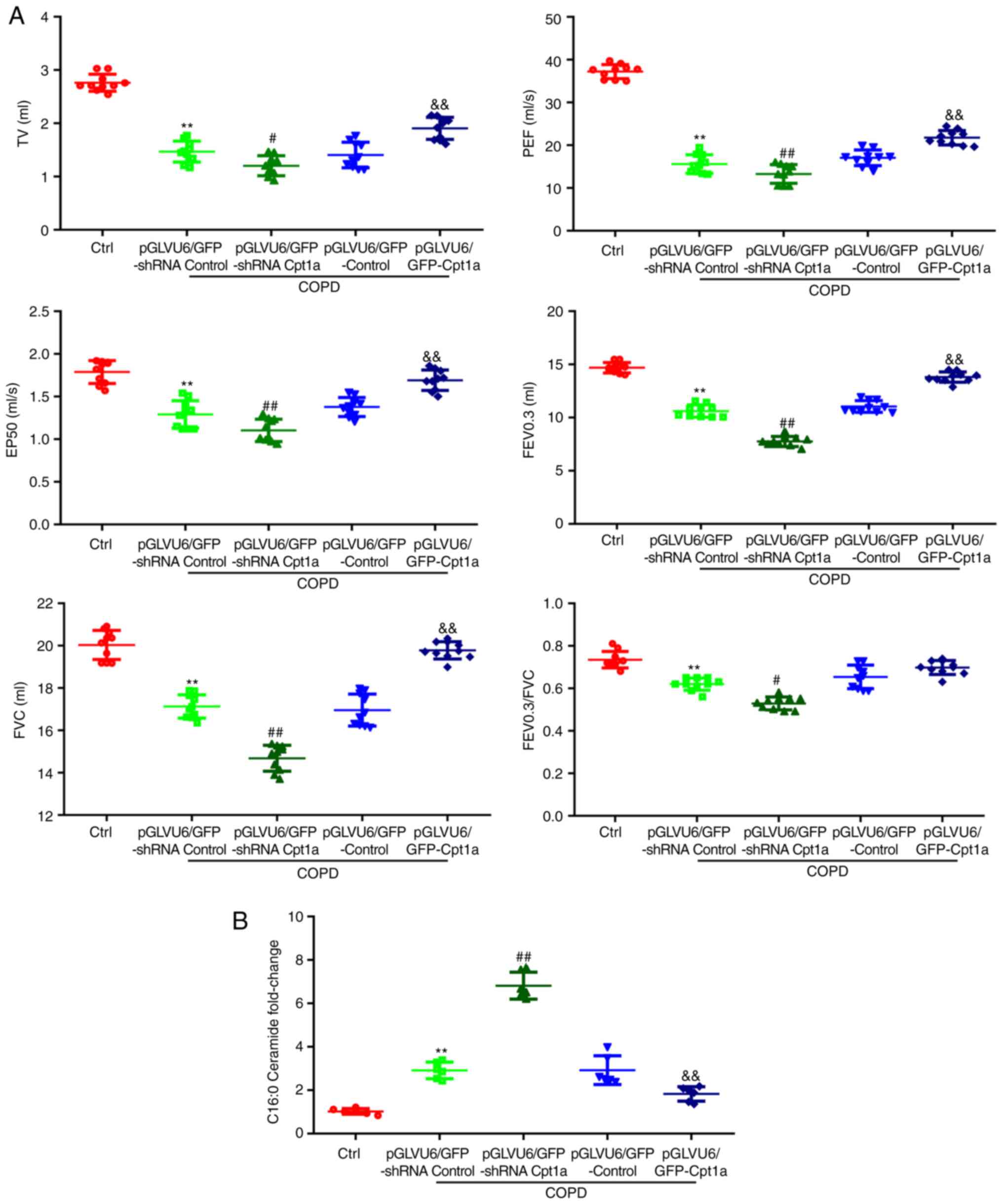
|
1
|
Lareau SC, Fahy B, Meek P and Wang A:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 199:P1–P2. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mannino DM and Buist AS: Global burden of
COPD: Risk factors, prevalence, and future trends. Lancet.
370:765–773. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rao W, Wang S, Duleba M, Niroula S, Goller
K, Xie J, Mahalingam R, Neupane R, Liew AA, Vincent M, et al:
Regenerative metaplastic clones in COPD lung drive inflammation and
fibrosis. Cell. 181:848–864. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hisata S, Racanelli AC, Kermani P,
Schreiner R, Houghton S, Palikuqi B, Kunar B, Zhou A, McConn K,
Capili A, et al: Reversal of emphysema by restoration of pulmonary
endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 218(e20200938)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Raud B, Roy DG, Divakaruni AS, Tarasenko
TN, Franke R, Ma EH, Samborska B, Hsieh WY, Wong AH, Stüve P, et
al: Etomoxir actions on regulatory and memory T cells are
independent of Cpt1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation. Cell Metab.
28:504–515. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yao H, Gong J, Peterson AL, Lu X, Zhang P
and Dennery PA: Fatty acid oxidation protects against
hyperoxia-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and lung injury in
neonatal mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 60:667–677.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gong J, Zhao H, Liu T, Li L, Cheng E, Zhi
S, Kong L, Yao W and Li J: Cigarette smoke reduces fatty acid
catabolism, leading to apoptosis in lung endothelial cells:
Implication for pathogenesis of COPD. Front Pharmacol.
10(941)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schoors S, Bruning U, Missiaen R, Queiroz
KC, Borgers G, Elia I, Zecchin A, Cantelmo AR, Christen S, Goveia
J, et al: Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in
endothelial cells. Nature. 520:192–197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yao RQ, Ren C, Xia ZF and Yao YM:
Organelle-specific autophagy in inflammatory diseases: A potential
therapeutic target underlying the quality control of multiple
organelles. Autophagy. 17:385–401. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Çolak Y, Afzal S, Nordestgaard BG, Lange P
and Vestbo J: Importance of early COPD in young adults for
development of clinical COPD: Findings from the copenhagen general
population study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 203:1245–1256.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wong J, Magun BE and Wood LJ: Lung
inflammation caused by inhaled toxicants: A review. Int J Chron
Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 11:1391–401. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li F, Jiang T, Li Q and Ling X:
Camptothecin (CPT) and its derivatives are known to target
topoisomerase I (Top1) as their mechanism of action: Did we miss
something in CPT analogue molecular targets for treating human
disease such as cancer? Am J Cancer Res. 7:2350–2394.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bonnefont JP, Djouadi F, Prip-Buus C,
Gobin S, Munnich A and Bastin J: Carnitine palmitoyltransferases 1
and 2: Biochemical, molecular and medical aspects. Mol Aspects Med.
25:495–520. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Casals N, Zammit V, Herrero L, Fadó R,
Rodríguez-Rodríguez R and Serra D: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase
1C: From cognition to cancer. Prog Lipid Res. 61:134–148.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wolfgang MJ, Kurama T, Dai Y, Suwa A,
Asaumi M, Matsumoto SI, Cha SH, Shimokawa T and Lane MD: The
brain-specific carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1c regulates energy
homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7282–7287. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gao XF, Chen W, Kong XP, Xu AM, Wang ZG,
Sweeney G and Wu D: Enhanced susceptibility of Cpt1c knockout mice
to glucose intolerance induced by a high-fat diet involves elevated
hepatic gluconeogenesis and decreased skeletal muscle glucose
uptake. Diabetologia. 52:912–920. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jiang Z, Knudsen NH, Wang G, Qiu W, Naing
ZZC, Bai Y, Ai X, Lee CH and Zhou X: Genetic control of fatty acid
β-oxidation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 56:738–748. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xiong X, Wen YA, Fairchild R, Zaytseva YY,
Weiss HL, Evers BM and Gao T: Upregulation of CPT1A is essential
for the tumor-promoting effect of adipocytes in colon cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 11(736)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tan Z, Xiao L, Tang M, Bai F, Li J, Li L,
Shi F, Li N, Li Y, Du Q, et al: Targeting CPT1A-mediated fatty acid
oxidation sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiation therapy.
Theranostics. 8:2329–2347. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hecht SS: Tobacco carcinogens, their
biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:733–744.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rabe KF and Watz H: Chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Lancet. 389:1931–1940. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hogg JC and Timens W: The pathology of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Rev Pathol. 4:435–459.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Brandsma CA, Van den Berge M, Hackett TL,
Brusselle G and Timens W: Recent advances in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease pathogenesis: From disease mechanisms to
precision medicine. J Pathol. 250:624–635. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Taylor JD: COPD and the response of the
lung to tobacco smoke exposure. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 23:376–383.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schupp JC, Adams TS, Cosme C Jr, Raredon
MSB, Yuan Y, Omote N, Poli S, Chioccioli M, Rose KA, Manning EP, et
al: Integrated single-cell atlas of endothelial cells of the human
lung. Circulation. 144:286–302. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Castro BM, Prieto M and Silva LC:
Ceramide: A simple sphingolipid with unique biophysical properties.
Prog Lipid Res. 54:53–67. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Choi Y, Kim M, Kim SJ, Yoo HJ, Kim SH and
Park HS: Metabolic shift favoring C18:0 ceramide accumulation in
obese asthma. Allergy. 75:2858–2866. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ekroos K, Lavrynenko O, Titz B, Pater C,
Hoeng J and Ivanov NV: Lipid-based biomarkers for CVD, COPD, and
aging-A translational perspective. Prog Lipid Res.
78(101030)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
McVey MJ, Weidenfeld S, Maishan M, Spring
C, Kim M, Tabuchi A, Srbely V, Takabe-French A, Simmons S, Arenz C,
et al: Platelet extracellular vesicles mediate transfusion-related
acute lung injury by imbalancing the sphingolipid rheostat. Blood.
137:690–701. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tsurumaki H, Katano H, Sato K, Imai R,
Niino S, Hirabayashi Y and Ichikawa S: WP1066, a small molecule
inhibitor of the JAK/STAT3 pathway, inhibits ceramide
glucosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
491:265–270. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kurinna SM, Tsao CC, Nica AF, Jiffar T and
Ruvolo PP: Ceramide promotes apoptosis in lung cancer-derived A549
cells by a mechanism involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Cancer
Res. 64:7852–7856. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yeganeh B, Lee J, Bilodeau C, Lok I,
Ermini L, Ackerley C, Caniggia I, Tibboel J, Kroon A and Post M:
Acid sphingomyelinase inhibition attenuates cell death in
mechanically ventilated newborn rat lung. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 199:760–772. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim SH, Singh MP, Sharma C and Kang SC:
Fumonisin B1 actuates oxidative stress-associated colonic damage
via apoptosis and autophagy activation in murine model. J Biochem
Mol Toxicol. 22(e22161)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rosenthal MD: Fatty acid metabolism of
isolated mammalian cells. Prog Lipid Res. 26:87–124.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Houten SM, Violante S, Ventura FV and
Wanders RJA: The biochemistry and physiology of mitochondrial fatty
acid β-oxidation and its genetic disorders. Ann Rev Physiol.
78:23–44. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Han J, Qu H, Han M, Ding Y, Xie M, Hu J,
Chen Y and Dong H: MSC-induced lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 promotes stemness
and trastuzumab resistance through regulating CPT1 expression and
fatty acid oxidation in breast cancer. Oncogene. 40:833–847.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dai J, Liang K, Zhao S, Jia W, Liu Y, Wu
H, Lv J, Cao C, Chen T, Zhuang S, et al: Chemoproteomics reveals
baicalin activates hepatic CPT1 to ameliorate diet-induced obesity
and hepatic steatosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E5896–E5905.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|