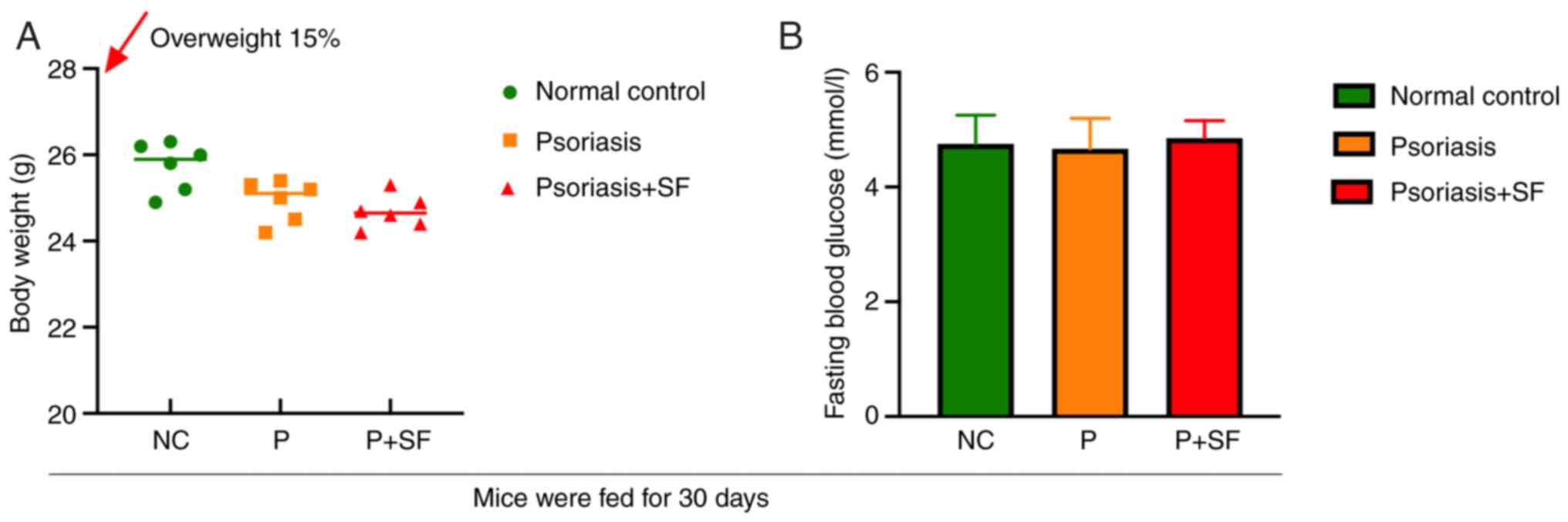
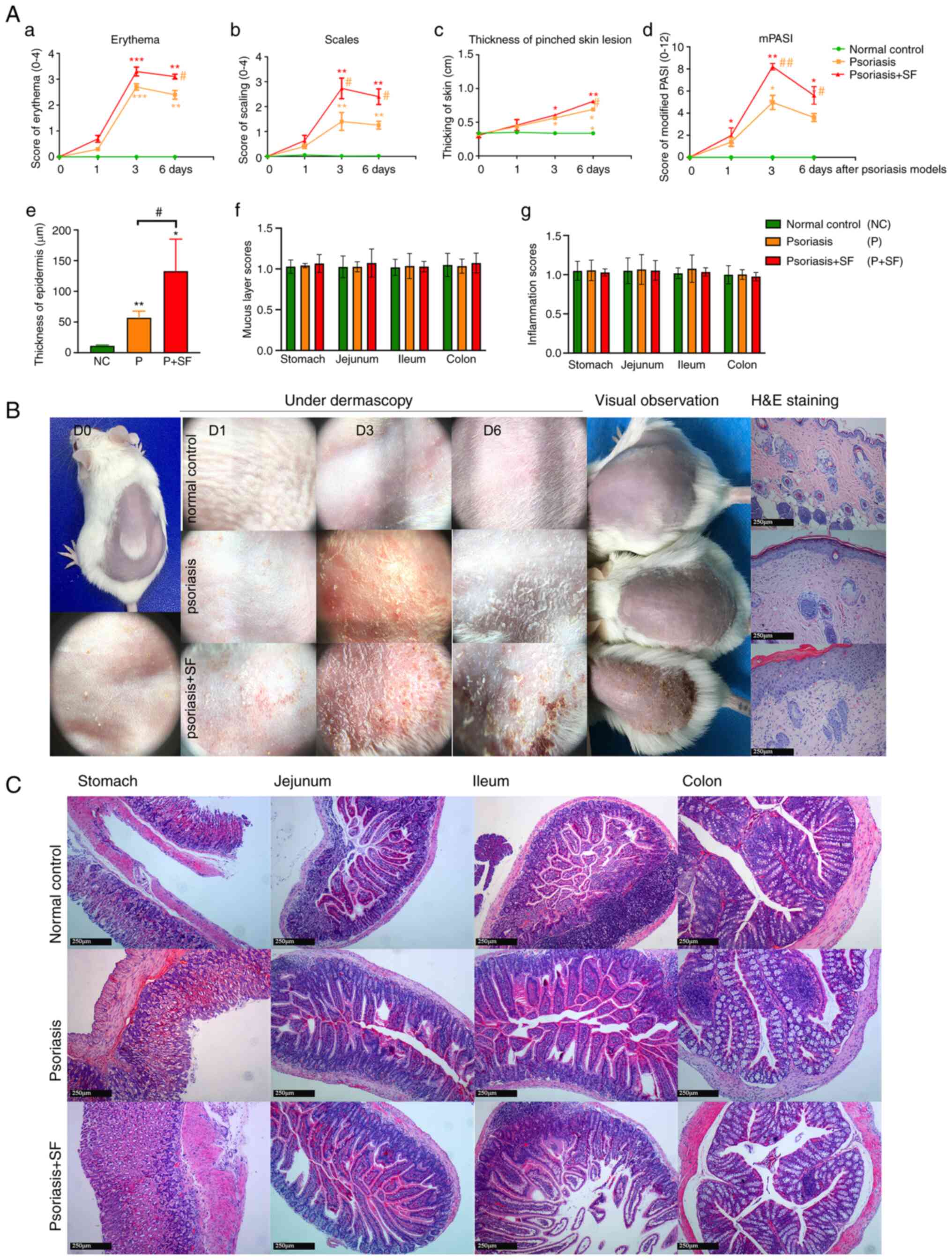
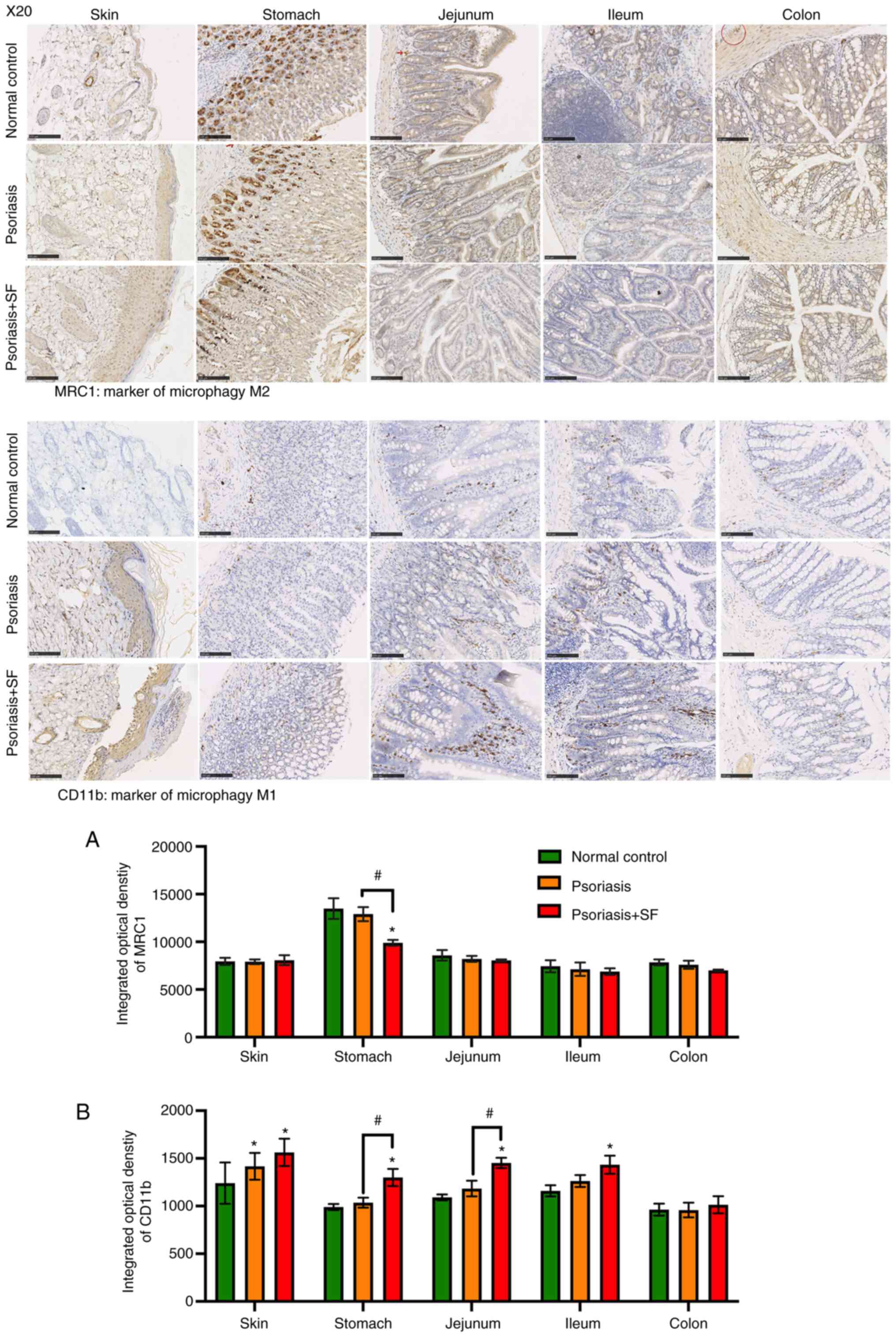
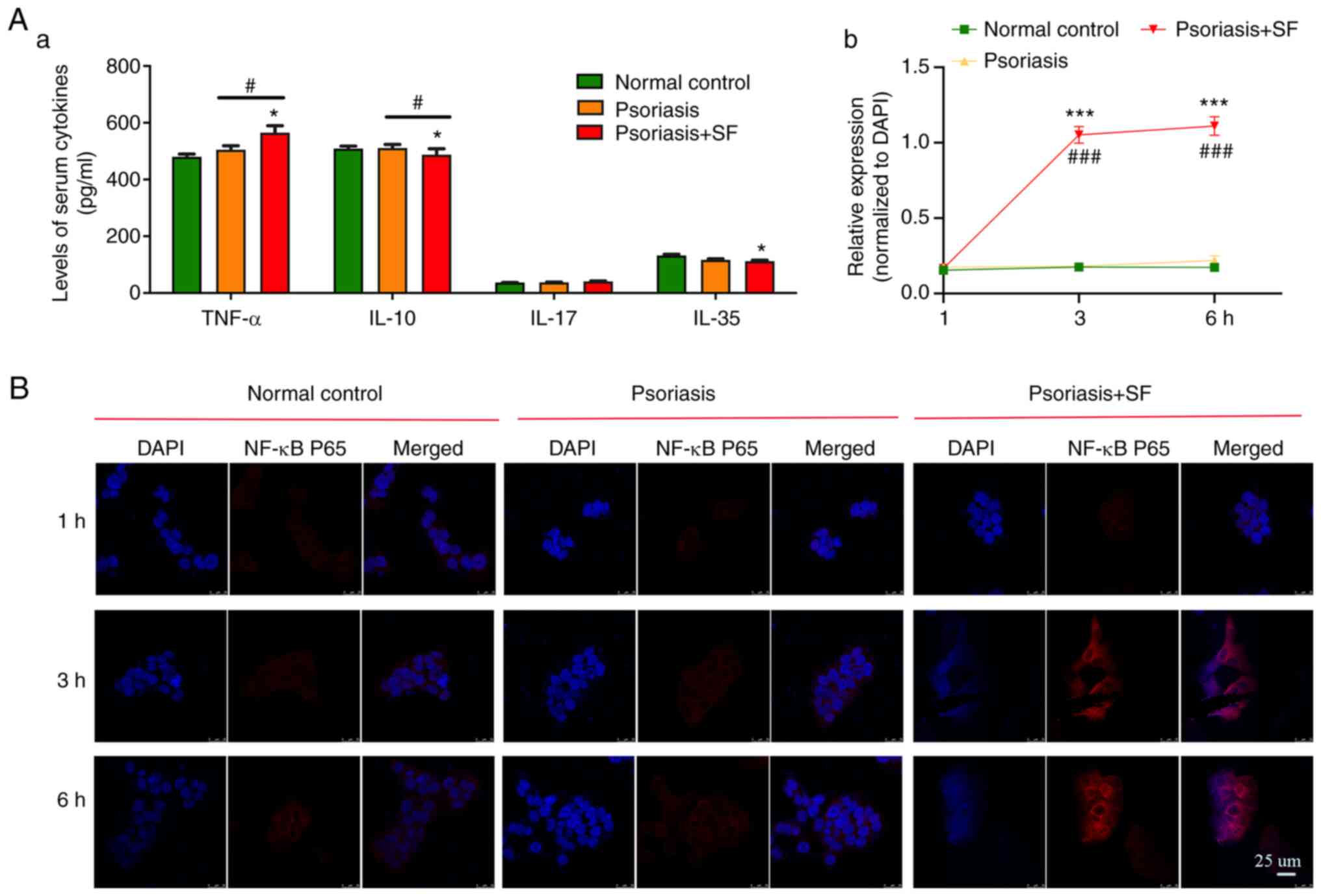
|
1
|
Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE
and Barker JNWN: Psoriasis. Lancet. 397:1301–1315. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, Mehta
NN, Ogdie A, Van Voorhees AS and Gelfand JM: Psoriasis and comorbid
diseases: Epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 76:377–390.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Madden SK, Flanagan KL and Jones G: How
lifestyle factors and their associated pathogenetic mechanisms
impact psoriasis. Clin Nutr. 39:1026–1040. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhu FY and Xie GQ: Discussion on Chinese
Medicine Diet taboo-fawu. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese
Medicine and Pharmacy. 7:3104–3106. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Yu S, Wu X, Zhou Y, Sheng L, Jena PK, Han
D, Wan YJY and Hwang ST: A Western diet, but not a high-fat and
low-sugar diet, predisposes mice to enhanced susceptibility to
imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol.
139:1404–1407. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Boericke H: Critical considerations on a
new treatment for psoriasis. Dtsch Gesundheitsw. 7:919–922.
1952.PubMed/NCBI(In German).
|
|
7
|
Petrozzi JW and Rosenbloom J:
Low-tryptophan diet in treatment of psoriasis. JAMA. 205:345–346.
1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zackheim HS and Farber EM: Low-protein
diet and psoriasis. A hospital study. Arch Dermatol. 99:580–586.
1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kragballe K and Fogh K: A low-fat diet
supplemented with dietary fish oil (Max-EPA) results in improvement
of psoriasis and in formation of leukotriene B5. Acta Derm
Venereol. 69:23–28. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adawi M, Damiani G, Bragazzi NL,
Bridgewood C, Pacifico A, Conic RRZ, Morrone A, Malagoli P, Pigatto
PDM, Amital H, et al: The impact of intermittent fasting (Ramadan
Fasting) on psoriatic arthritis disease activity, enthesitis, and
dactylitis: A multicentre study. Nutrients. 11(601)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Passali M, Josefsen K, Frederiksen JL and
Antvorskov JC: Current evidence on the efficacy of gluten-free
diets in multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, type 1 diabetes and
autoimmune thyroid diseases. Nutrients. 12(2316)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Spiera H and Lefkovits AM: Turkey,
tryptophan, and psoriasis. Lancet. 2(1418)1967.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Phan C, Touvier M, Kesse-Guyot E, Adjibade
M, Hercberg S, Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Ezzedine K and Sbidian E:
Association between mediterranean anti-inflammatory dietary profile
and severity of psoriasis: Results from the NutriNet-Santé cohort.
JAMA Dermatol. 154:1017–1024. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Balić A, Vlašić D, Žužul K, Marinović B
and Mokos ZB: Omega-3 versus omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in
the prevention and treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Int J
Mol Sci. 21(741)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Barrea L, Savanelli MC, Di Somma C,
Napolitano M, Megna M, Colao A and Savastano S: Vitamin D and its
role in psoriasis: An overview of the dermatologist and
nutritionist. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 18:195–205. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Millsop JW, Bhatia BK, Debbaneh M, Koo J
and Liao W: Diet and psoriasis, part III: Role of nutritional
supplements. J Am Acad Dermatol. 71:561–569. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen W, Zhou X and Zhu W: Trace elements
homeostatic imbalance in psoriasis: A meta-analysis. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 191:313–322. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ely PH: Is psoriasis a bowel disease?
Successful treatment with bile acids and bioflavonoids suggests it
is. Clin Dermatol. 36:376–389. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zackheim HS: Taurine and diet in
psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 118(961)1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reich K, Augustin M, Thaçi D, Pinter A,
Leutz A, Henneges C, Schneider E, Schacht A, Dossenbach M and
Mrowietz U: A 24-week multicentre, randomized, open-label,
parallel-group study comparing the efficacy and safety of
ixekizumab vs. fumaric acid esters and methotrexate in patients
with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis naive to systemic
treatment. Br J Dermatol. 182:869–879. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jena PK, Sheng L, McNeil K, Chau TQ, Yu S,
Kiuru M, Fung MA, Hwang ST and Wan YJY: Long-term Western diet
intake leads to dysregulated bile acid signaling and dermatitis
with Th2 and Th17 pathway features in mice. J Dermatol Sci.
95:13–20. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yu S, Wu X, Shi Z, Huynh M, Jena PK, Sheng
L, Zhou Y, Han D, Wan YJY and Hwang ST: Diet-induced obesity
exacerbates imiquimod-mediated psoriasiform dermatitis in anti-PD-1
antibody-treated mice: Implications for patients being treated with
checkpoint inhibitors for cancer. J Dermatol Sci. 97:194–200.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fernández-Armenteros JM, Gómez-Arbonés X,
Buti-Soler M, Betriu-Bars A, Sanmartin-Novell V, Ortega-Bravo M,
Martínez-Alonso M, Garí E, Portero-Otín M, Santamaria-Babi L and
Casanova-Seuma JM: Psoriasis, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular
risk factors. A population-based study. J Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 33:128–135. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mahil SK, McSweeney SM, Kloczko E, McGowan
B, Barker JN and Smith CH: Does weight loss reduce the severity and
incidence of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis? A critically
appraised topic. Br J Dermatol. 181:946–953. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
De Angelis M, Garruti G, Minervini F,
Bonfrate L, Portincasa P and Gobbetti M: The food-gut human axis:
The effects of diet on gut microbiota and metabolome. Curr Med
Chem. 26:3567–3583. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gentile CL and Weir TL: The gut microbiota
at the intersection of diet and human health. Science. 362:776–780.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tran HQ, Bretin A, Adeshirlarijaney A,
Yeoh BS, Vijay-Kumar M, Zou J, Denning TL, Chassaing B and Gewirtz
AT: ‘Western Diet’-induced adipose inflammation requires a complex
gut microbiota. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:313–333.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ye C, Yano H, Workman CJ and Vignali DAA:
Interleukin-35: Structure, function and its impact on
immune-related diseases. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 41:391–406.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang BY, Cheng YG, Liu Y, Liu Y, Tan JY,
Guan W, Guo S and Kuang HX: Datura Metel L. Ameliorates
imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis and inhibits
inflammatory cytokines production through TLR7/8-MyD88-NF-κB-NLRP3
inflammasome pathway. Molecules. 24(2157)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Marasca C, Scala E, Di Caprio R, Raimondo
A, Cacciapuoti S, Balato A and Fabbrocini G: Notch dysregulation
and hidradenitis suppurativa, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and
lichen planus: Let's talk about Numb. Br J Dermatol. 180:950–951.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kashem SW, Haniffa M and Kaplan DH:
Antigen-presenting cells in the skin. Annu Rev Immunol. 35:469–499.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim ES, Han K, Kim MK, Park YM, Baek KH,
Moon SD, Han JH, Song KH and Kwon HS: Impact of metabolic status on
the incidence of psoriasis: A Korean nationwide cohort study. Sci
Rep. 7(1989)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Semenov YR, Herbosa CM, Rogers AT, Huang
A, Kwatra SG, Cohen B, Anadkat MJ and Silverberg JI: Psoriasis and
mortality in the United States: Data from the national health and
nutrition examination survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 85:396–403.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mohammadi A, Blesso CN, Barreto GE, Banach
M, Majeed M and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization and
function in response to curcumin, a diet-derived polyphenol, as an
immunomodulatory agent. J Nutr Biochem. 66:1–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Brembilla NC, Senra L and Boehncke WH: The
IL-17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: IL-17A and beyond. Front
Immunol. 9(1682)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yilmaz SB, Cicek N, Coskun M, Yegin O and
Alpsoy E: Serum and tissue levels of IL-17 in different clinical
subtypes of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res. 304:465–469.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
De Simone C, Dapavo P, Malagoli P,
Martella A, Campanati A, Campione E, Errichetti E, Franchi C,
Gambardella A, Megna M, et al: Long-term proactive management of
psoriasis with calcipotriol and betamethasone dipropionate foam: An
Italian consensus through a combined nominal group technique and
Delphi approach. Int J Dermatol. 61:1543–1551. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Benhadou F, Mintoff D and Del Marmol V:
Psoriasis: Keratinocytes or immune cells-which is the trigger?
Dermatology. 235:91–100. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Thatikonda S, Pooladanda V, Sigalapalli DK
and Godugu C: Piperlongumine regulates epigenetic modulation and
alleviates psoriasis-like skin inflammation via inhibition of
hyperproliferation and inflammation. Cell Death Dis.
11(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Siebel C and Lendahl U: Notch signaling in
development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. Physiol Rev.
97:1235–1294. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
National Psoriasis Epidemic Survey Group.
Distribution of psoriasis in China: A nation-wide screening in
1984. J Dermatol Venereol. 11:66–78. 1989.
|
|
42
|
Qiao J, Jia QN, Li F, He CX, Wu C, Yu XL,
et al: Epidemic Analysis of Dietary Risk Factors for Psoriasis
Vulgaris. The Chinese Journal of Dermatovenereology,. 31:1301–1305.
2017.
|
|
43
|
Xu Y, Yang J and Yang L: Research on
social phenomenon of Chinese dining tables. Sci Technol
Information. 10:241–242. 2011.
|