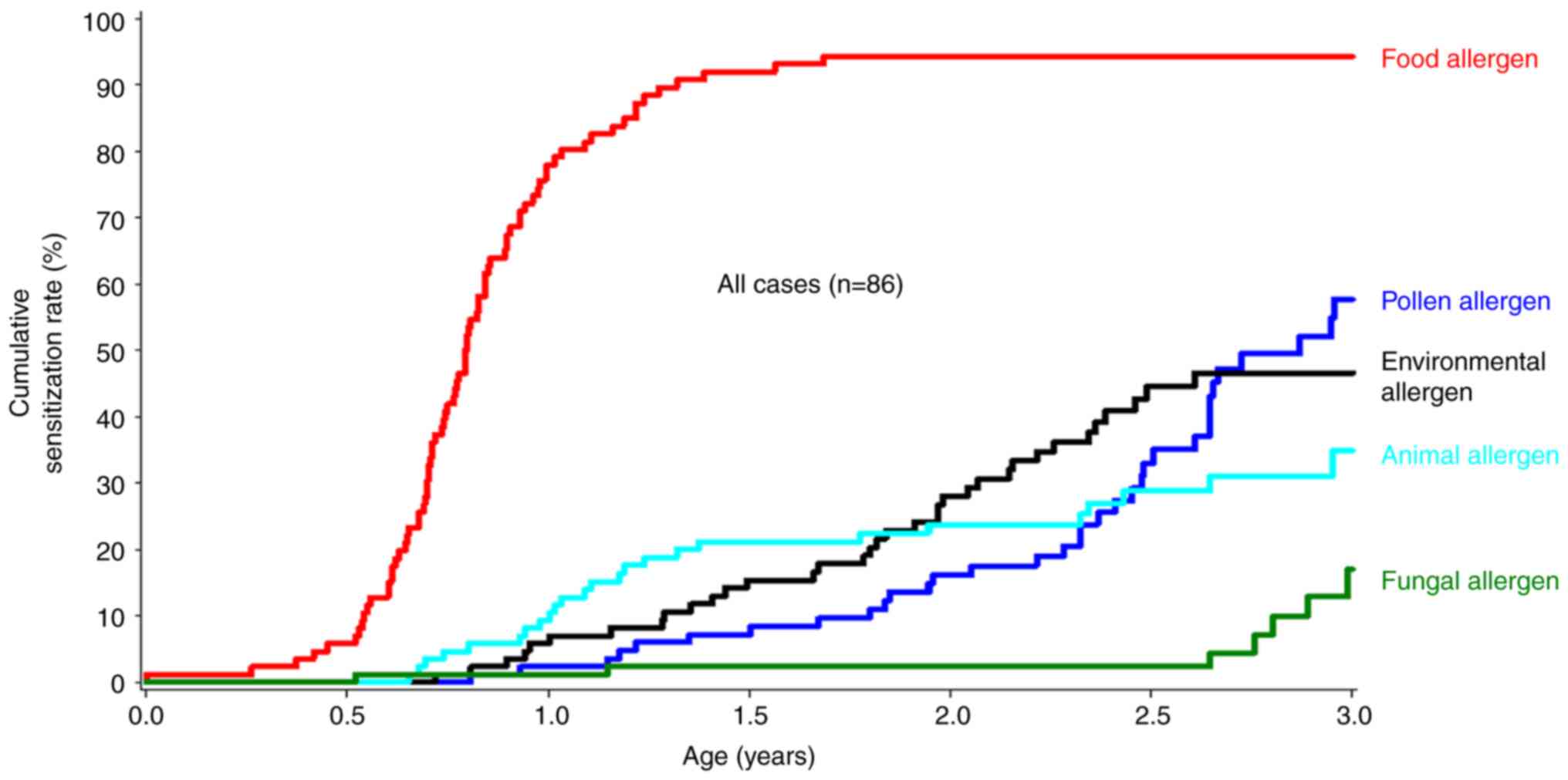
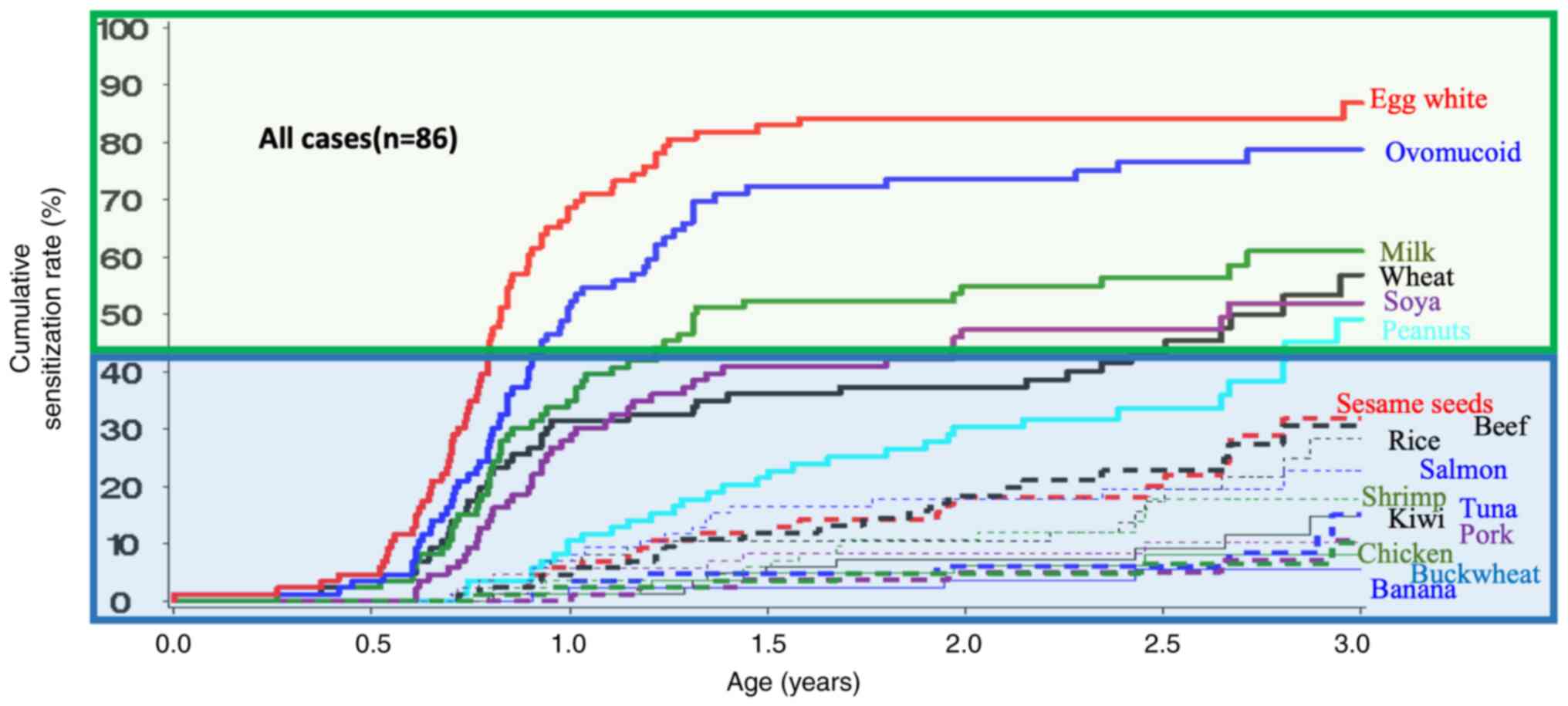
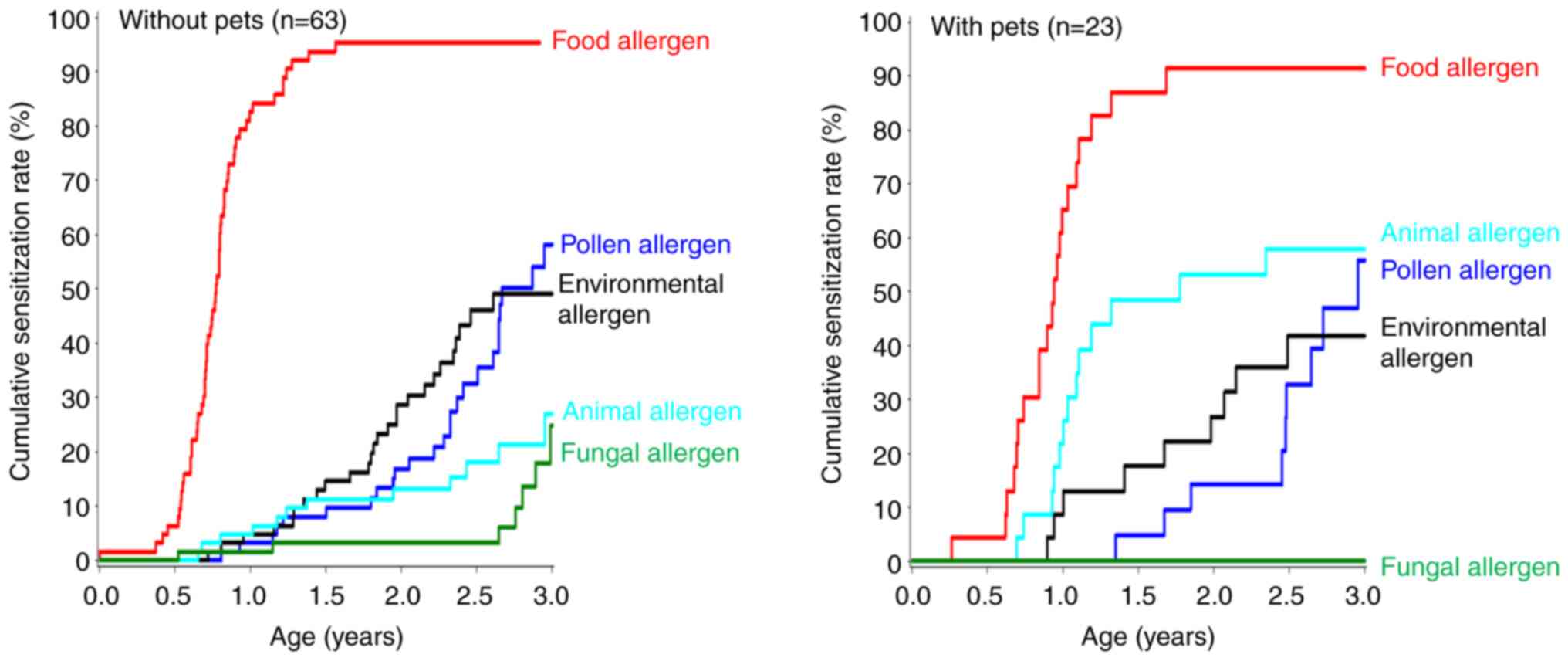
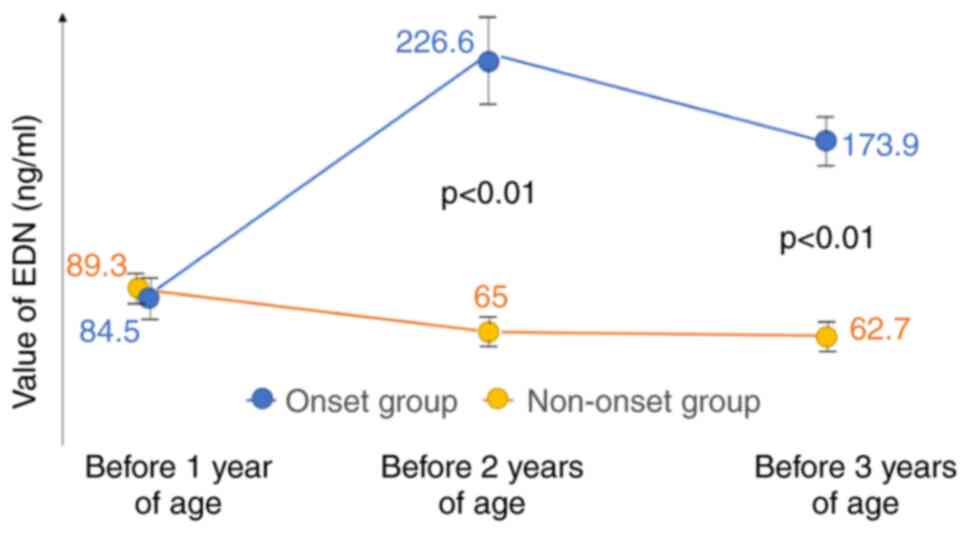
|
1
|
Hill DA and Spergel JM: The atopic march:
Critical evidence and clinical relevance. Ann Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 120:131–137. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hill DA, Grundmeier RW, Ram G and Spergel
JM: The epidemiologic characteristics of healthcare
provider-diagnosed eczema, asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food
allergy in children: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pediatr.
16(133)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Renz H, Allen KJ, Sicherer SH, Sampson HA,
Lack G, Beyer K and Oettgen HC: Food allergy. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
4(17098)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hogan SP, Rosenberg HF, Moqbel R, Phipps
S, Foster PS, Lacy P, Kay AB and Rothenberg ME: Eosinophils:
Biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin Exp
Allergy. 38:709–750. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Venge P: Monitoring the allergic
inflammation. Allergy. 59:26–32. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kim H, Kwon GE, Kim YH, Callaway Z, Han
YS, Seo JJ, Jiao F and Kim CK: Comparison of serum
eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels between wheezing and
non-wheezing groups in children with respiratory tract infection. J
Asthma. 57:1211–1215. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim CK, Callaway Z, Park JS, Nishimori H,
Ogino T, Nagao M and Fujisawa T: Montelukast reduces serum levels
of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in preschool asthma. Allergy
Asthma Immunol Res. 10:686–697. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim CK, Callaway Z, Park JS and Kwon E:
Utility of serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) measurement by
ELISA in young children with asthma. Allergol Int. 66:70–74.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim CK, Callaway Z, Kim DW and Kita H:
Eosinophil degranulation is more important than eosinophilia in
identifying asthma in chronic cough. J Asthma. 48:994–1000.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim CK, Callaway Z, Fletcher R and Koh YY:
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in childhood asthma: correlation with
disease severity. J Asthma. 47:568–573. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim CK, Seo JK, Ban SH, Fujisawa T, Kim DW
and Callaway Z: Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels at 3 months
post-respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis are a predictive
biomarker of recurrent wheezing. Biomarkers. 18:230–235.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Peterson CG, Enander I, Nystrand J,
Anderson AS, Nilsson L and Venge P: Radioimmunoassay of human
eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) by an improved method.
Establishment of normal levels in serum and turnover in vivo. Clin
Exp Allergy. 21:561–567. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Murphy KP: The detection, measurement, and
characterization of antibodies, and their use as research and
diagnostic tools. Janeway's immunobiology. 8th edition. Garland
Science, New York, NY, 2012.
|
|
14
|
Morioka J, Kurosawa M, Inamura H, Nakagami
R, Mizushima Y, Chihara J, Yokoseki T, Kitamura S, Omura Y and
Shibata M: Development of a novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
for blood and urinary eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: A preliminary
study in patients with bronchial asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
122:49–57. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tran MM, Lefebvre DL, Dharma C, Dai D, Lou
WYW, Subbarao P, Becker AB, Mandhane PJ, Turvey SE and Sears MR:
Canadian Healthy Infant Longitudinal Development Study
Investigators. Predicting the atopic march: Results from the
Canadian health infant longitudinal development study. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 141:601–607. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Schenider L, Hanifin J, Boguniewicz M,
Eichenfield LF, Spergel JM, Dakovic R and Paller AS: Study of the
atopic march: development of atopic comorbidities. Pediatr
Dermatol. 33:388–398. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim NY, Kim GR, Kim JH, Baek JH, Yoon JW,
Jee HM, Baek HS, Jung YH, Choi SH, Kim KE, et al: Food allergen
sensitization in young children with typical signs and symptoms of
immediate-type food allergies: A comparison between monosensitized
and polysensitized children. Korean J Pediatr. 58:330–335.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
de Moira AP, Strandberg-Larsen K, Bishop
T, Pedersen M, Avraam D, Cadman T, Calas L, Casas M, Guillain BL,
et al: Associations of early-life pet ownership with asthma and
allergic sensitization: A meta-analysis of more than 77,000
children from the EU Chil Cohort Network. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
150:82–92. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Anyo G, Brunekreef de Meer G, Aarts F,
Janssen NA and van Vliet P: Early, current and past pet ownership:
Associations with sensitization, bronchial responsiveness and
allergic symtpoms in school children. Clin Exp Allergy. 32:361–366.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lødrop Carlsen KC, Roll S, Carlsen KH,
Mowinckel P, Wijga AH, Brunekreef B, Torrent M, Roberts G, Arshad
SH, Kull I, et al: Does pet ownership in infancy lead to asthma or
allergy at school age? Poole analysis of individual participant
data from 11 European birth cohorts. PLoS One.
7(e43214)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fall T, Lundholm C, Ortquvist AK, Fall K,
Fang F, Hedhammar A, Kämpe O, Ilgelsson E and Almqvist C: Early
exposure to dogs and farm animals and the risk of childhood asthma.
JAMA Pediatr. 169(e153219)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hesselmar B, Hicke-Roberts A, Lundell AC,
Adlerberth I, Rudin A, Saalman R, Wennergren G and Wold AE:
Pet-keeping in early life reduces the risk of allergy in a
dose-dependent fashion. PLoS One. 13(e0208472)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ownby DR, Johnson CC and Peterson EL:
Exposure to dogs and cats in the first year of life and risk of
allergic sensitization at 6 to 7 years of age. JAMA. 288:963–972.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jatakanon A, Lim S and Barnes PJ: Changes
in sputum eosinophils predict loss of asthma control. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 161:64–72. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Agache I and Rogozea L: Asthma biomarkers:
Do they bring precision medicine closer to the clinic? Allergy
Asthma Immunol Res. 9:466–476. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Diamant Z, Vijverberg S, Alving K,
Bakirtas A, Bjermer L, Custovic A, Dahlen SE, Gaga M, van Wijk RG,
Del Giacco S, et al: Toward clinically applicable biomarkers for
asthma: an EAACI position paper. Allergy. 74:1835–1851.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim KW, Lee KE, Kim ES, Song TW, Sohn MH
and Kim KE: Serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) in diagnosis
and evaluation of severity and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in
childhood asthma. Lung. 185:97–103. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Taniuchi S, Chihara J, Kojima T, Yamamoto
A, Sasai M and Kobayashi Y: Serum eosinohil derived neurotoxin may
reflect more strongly disease severity in childhood atopic
dermatitis than eosinophil cationic protein. J Dermatol Sci.
26:79–82. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Goto T, Morioka J, Inamura H, Yano M,
Kodaira K, Igarashi Y, Abe S and Kurosawa M: Urinary
eosinophil-derived neurotoxin concentrations in patients with
atopic dermatitis: A useful clinical marker for disease activity.
Allergol Int. 56:433–438. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim CK, Kita H, Callaway Z, Kim HB, Choi
J, Fujisawa T, Shin BM and Koh YY: The roles of a Th2 cytokine and
CC chemokine in children with stable asthma: Potential implication
in eosinphil degranulation. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 21:e697–e704.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Amer OT, Naguib MS, Allam AA and Fouad
EMI: Evaluation of serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin level in
children with bronchial asthma and its relation to disease
severity. Egypt J Hosp Med. 80:951–957. 2020.
|
|
32
|
Malinovschi A, Rydell N, Fujisawa T,
Borres MP and Kim CK: Clinical potential of eosinophil-derived
neurotoxin in asthma management. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract.
11:750–761. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|