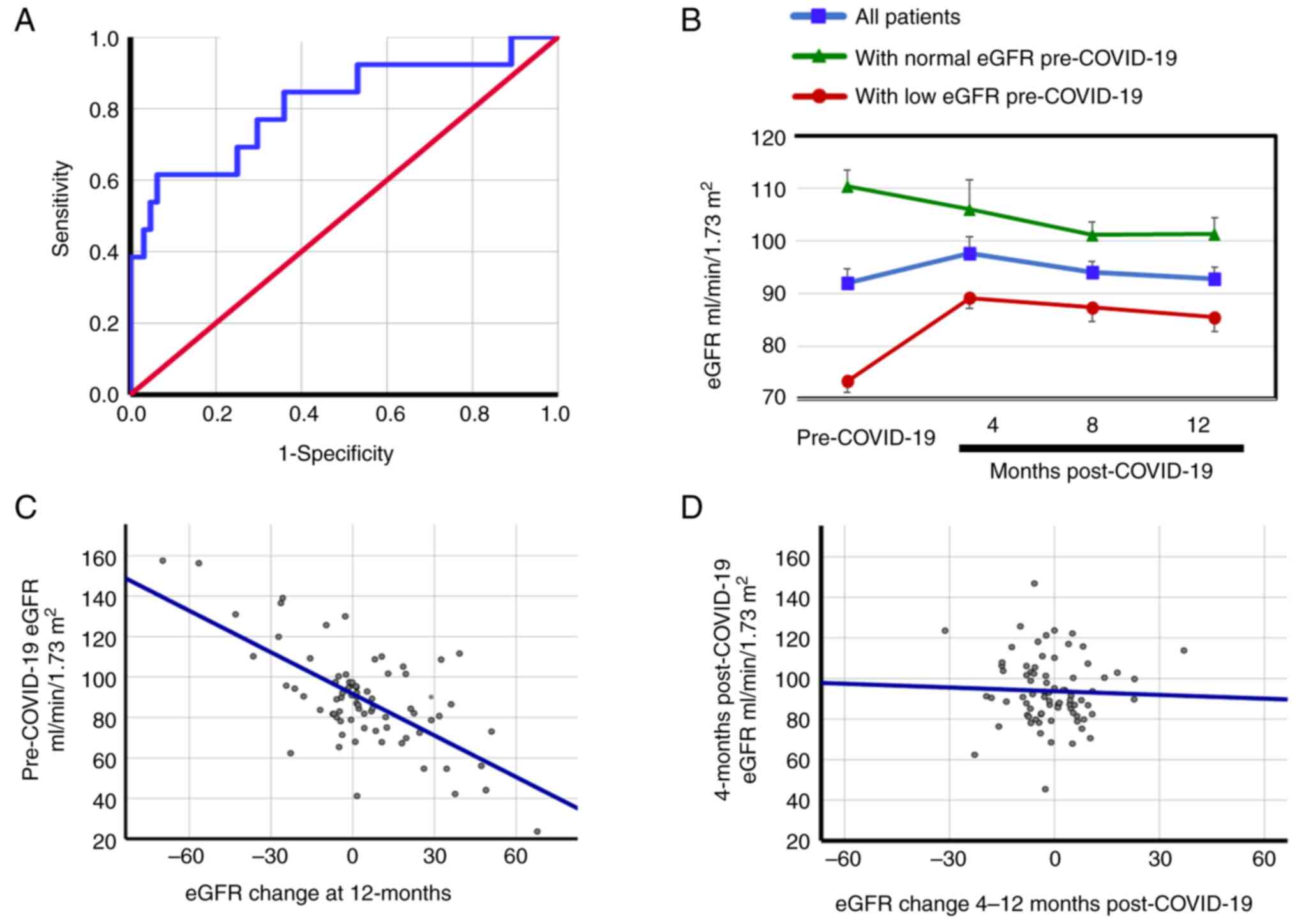
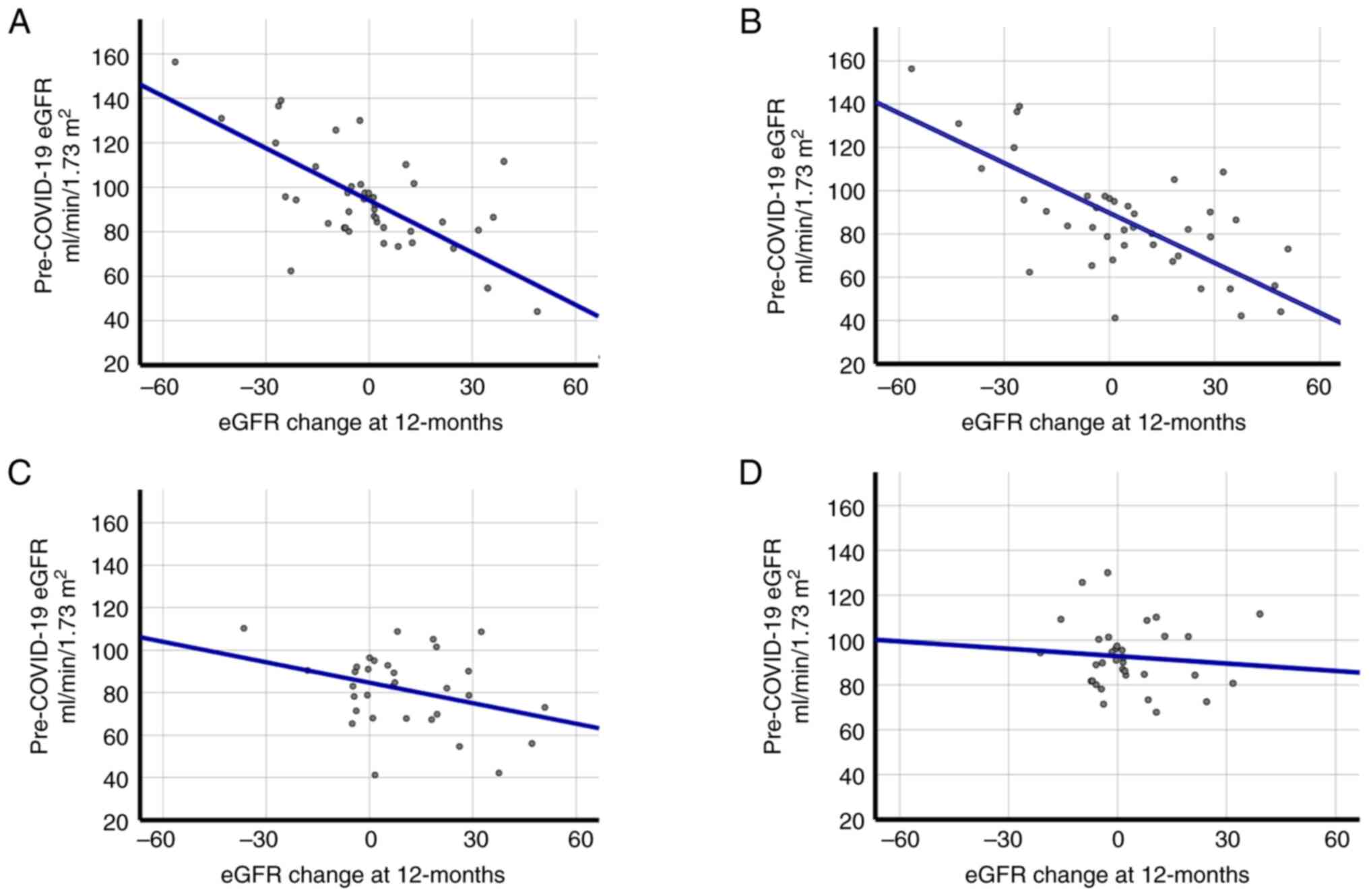
|
1
|
Guzman-Esquivel J, Mendoza-Hernandez MA,
Guzman-Solorzano HP, Sarmiento-Hernandez KA, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP,
Martinez-Fierro ML, Paz-Michel BA, Murillo-Zamora E, Rojas-Larios
F, Lugo-Trampe A, et al: Clinical characteristics in the acute
phase of COVID-19 that predict long COVID: Tachycardia, myalgias,
severity, and use of antibiotics as main risk factors, while
education and blood group B are protective. Healthcare (Basel).
11(197)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Delgado-Enciso I, Paz-Garcia J,
Barajas-Saucedo CE, Mokay-Ramírez KA, Meza-Robles C, Lopez-Flores
R, Delgado-Machuca M, Murillo-Zamora E, Toscano-Velazquez JA,
Delgado-Enciso J, et al: Safety and efficacy of a COVID-19
treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed
saline combined with usual medical care vs usual medical care
alone: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial. Exp Ther Med.
22(915)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Diao B, Wang C, Wang R, Feng Z, Zhang J,
Yang H, Tan Y, Wang H, Wang C, Liu L, et al: Human kidney is a
target for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
infection. Nat Commun. 12(2506)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yende S and Parikh CR: Long COVID and
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:792–793. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Faour WH, Choaib A, Issa E, Choueiry FE,
Shbaklo K, Alhajj M, Sawaya RT, Harhous Z, Alefishat E and Nader M:
Mechanisms of COVID-19-induced kidney injury and current
pharmacotherapies. Inflamm Res. 71:39–56. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Spruill WJ, Wade WE and Cobb HH III:
Comparison of estimated glomerular filtration rate with estimated
creatinine clearance in the dosing of drugs requiring adjustments
in elderly patients with declining renal function. Am J Geriatr
Pharmacother. 6:153–160. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tong M, Yan X, Jiang Y, Jin Z, Zhu S, Zou
L, Liu Y, Zheng Q, Chen G, Gu R, et al: Endothelial biomarkers in
patients recovered from COVID-19 one year after hospital discharge:
A cross-sectional study. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis.
14(e2022033)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nugent J, Aklilu A, Yamamoto Y, Simonov M,
Li F, Biswas A, Ghazi L, Greenberg H, Mansour G, Moledina G and
Wilson FP: Assessment of acute kidney injury and longitudinal
kidney function after hospital discharge among patients with and
without COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open. 4(e211095)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhou M, Tan X, Luo P, Xu J, Yin Z, Liao T,
Wang S, Wang Z and Jin Y: Changes in glomerular filtration rate and
metabolomic differences in severely ill coronavirus disease
survivors 3 months after discharge. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1868(166289)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T,
Rogers N and Roth D: A more accurate method to estimate glomerular
filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation.
Modification of diet in renal disease study group. Ann Intern Med.
130:461–470. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ruggenenti P, Cortinovis M, Trillini M,
Parvanova A, Abbate M, Satriano C, Salvetti F, Bossi AC, Trevisan
R, Perna A, et al: Long-term kidney and systemic effects of calorie
restriction in overweight or obese type 2 diabetic patients
(C.Re.S.O. 2 randomized controlled trial). Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
185(109804)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
McDonald JH: Biological statistics. 1st
edition. California State, 2023.
|
|
13
|
Jaffa MA, Gebregziabher M, Luttrell DK,
Luttrell LM and Jaffa AA: Multivariate generalized linear mixed
models with random intercepts to analyze cardiovascular risk
markers in type-1 diabetic patients. J Appl Stat. 43:1447–1464.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Baum MK, Tamargo JA, Diaz-Martinez J,
Delgado-Enciso I, Meade CS, Kirk GD, Mehta SH, Moore R, Kipke MD,
Shoptaw SJ, et al: HIV, psychological resilience, and substance
misuse during the COVID-19 pandemic: A multi-cohort study. Drug
Alcohol Depend. 231(109230)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rosner B: Fundamentals of biostatistics.
3rd edition. PWS-Kent Pub. Co, Boston, Mass, 1990.
|
|
16
|
Pewsner D, Battaglia M, Minder C, Marx A,
Bucher HC and Egger M: Ruling a diagnosis in or out with ‘SpPIn’
and ‘SnNOut’: A note of caution. BMJ. 329:209–213. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hardenberg JHB and Luft FC: Covid-19, ACE2
and the kidney. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 230(e13539)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rodrigues R and Costa De Oliveira S: The
impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression levels
in patients with comorbidities on COVID-19 severity: A
comprehensive review. Microorganisms. 9(1692)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zavori L, Molnar T, Varnai R, Kanizsai A,
Nagy L, Vadkerti B, Szirmay B, Schwarcz A and Csecsei P: Cystatin-c
may indicate subclinical renal involvement, while orosomucoid is
associated with fatigue in patients with long-COVID syndrome. J
Pers Med. 13(371)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Torjesen I: Covid-19: Infection increases
the risk of kidney disease even in mild cases, finds study. BMJ.
374(n2189)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Reis S, Popp M, Schießer S, Metzendorf MI,
Kranke P, Meybohm P and Weibel S: Anticoagulation in COVID-19
patients-an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb
Res. 219:40–48. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Reis G, Silva EASM, Silva DCM, Thabane L,
Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, Dos Santos CVQ, Campos VHS, Nogueira AMR,
de Almeida APFG, et al: Effect of early treatment with Ivermectin
among patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 386:1721–1731.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Furlan L: Ivermectin treatment for
COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 387(e66)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Barus R, Gautier S and Wabont G:
Ivermectin treatment for COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 387(e66)2022.
|
|
25
|
Arise RO and Malomo SO: Effects of
ivermectin and albendazole on some liver and kidney function
indices in rats. Afr J Biochem Res. 3:190–197. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Nunes LLA and Lima TDM: Use of medicines
for COVID-19 treatment in patients with loss of kidney function: A
narrative review. J Bras Nefrol. 43:254–262. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
27
|
Tawfeek SE, Domouky AM and Abdel-Kareem
RH: Protective effect of vitamin C against ivermectin induced
nephrotoxicity in different age groups of male wistar rats:
Bio-histopathological study. Anat Cell Biol. 54:501–517.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Niki E: Action of ascorbic acid as a
scavenger of active and stable oxygen radicals. Am J Clin Nutr. 54
(6 Suppl):1119S–1124S. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
GabAllh MS, El-mashad ABE, Amin AA and
Darweish MM: Pathological studies on effects of ivermectin on male
and female rabbits. Benha Vet Med J. 32:104–112. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Khawla B, Al-Deen A and Al-Masoudi EA,
Majeed SK and Al-Masoudi EA: Histopathological and biochemical
effects of ivermectin on kidney functions, lung, and the
ameliorative effects of vitamin C in rabbits (lupus cuniculus).
Basrah J Vet Res. 14:110–124. 2016.
|
|
31
|
Xu F, Wen Y, Hu X, Wang T and Chen G: The
potential use of vitamin C to prevent kidney injury in patients
with COVID-19. Diseases. 9(46)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hazan S, Dave S, Gunaratne AW, Dolai S,
Clancy RL, McCullough PA and Borody TJ: Effectiveness of
ivermectin-based multidrug therapy in severely hypoxic, ambulatory
COVID-19 patients. Future Microbiol. 17:339–350. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
May JM and Harrison FE: Role of vitamin C
in the function of the vascular endothelium. Antioxid Redox Signal.
19:2068–2083. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rana R, Ranjan V and Kumar N: Association
of ABO and Rh blood group in susceptibility, severity, and
mortality of coronavirus disease 2019: A hospital-based study from
Delhi, India. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
11(767771)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim Y, Latz CA, DeCarlo CS, Lee S, Png
CYM, Kibrik P, Sung E, Alabi O and Dua A: Relationship between
blood type and outcomes following COVID-19 infection. Semin Vasc
Surg. 34:125–131. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang M, Xie J, Ouyang Y, Zhang X, Shi M,
Li X, Wang Z, Shen P, Ren H, Zhang W, et al: ABO blood type is
associated with renal outcomes in patients with IgA nephropathy.
Oncotarget. 8:73603–73612. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|