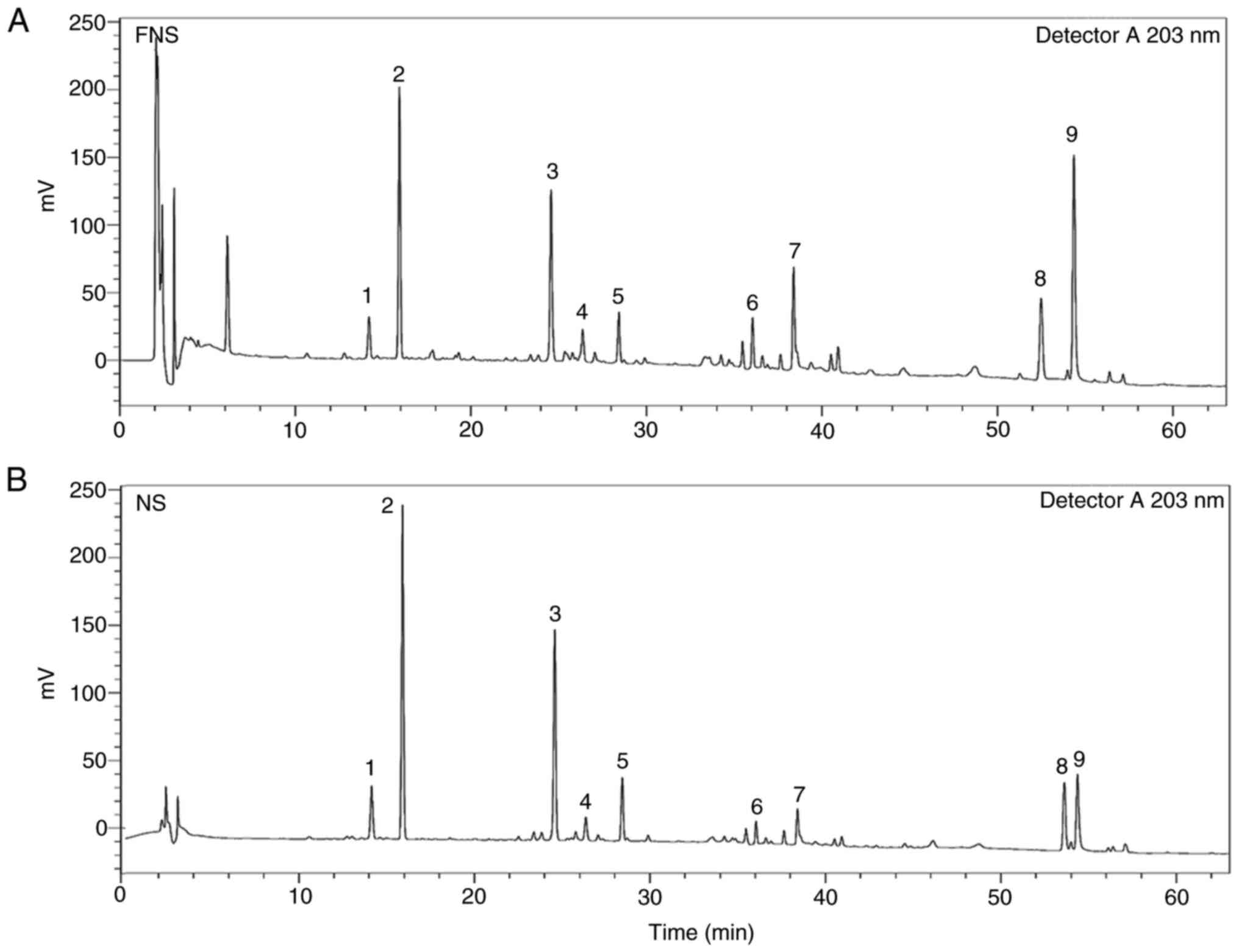
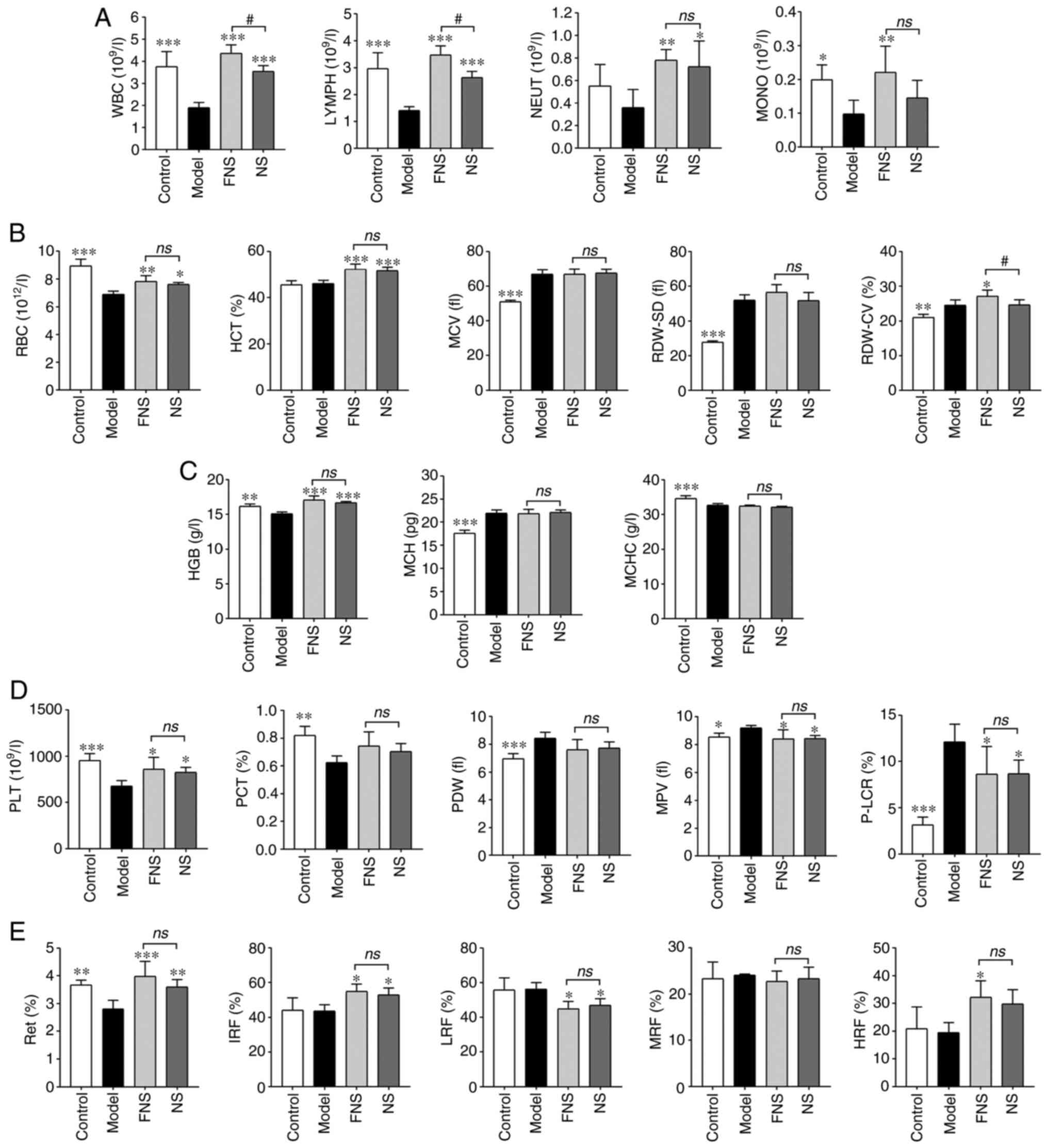
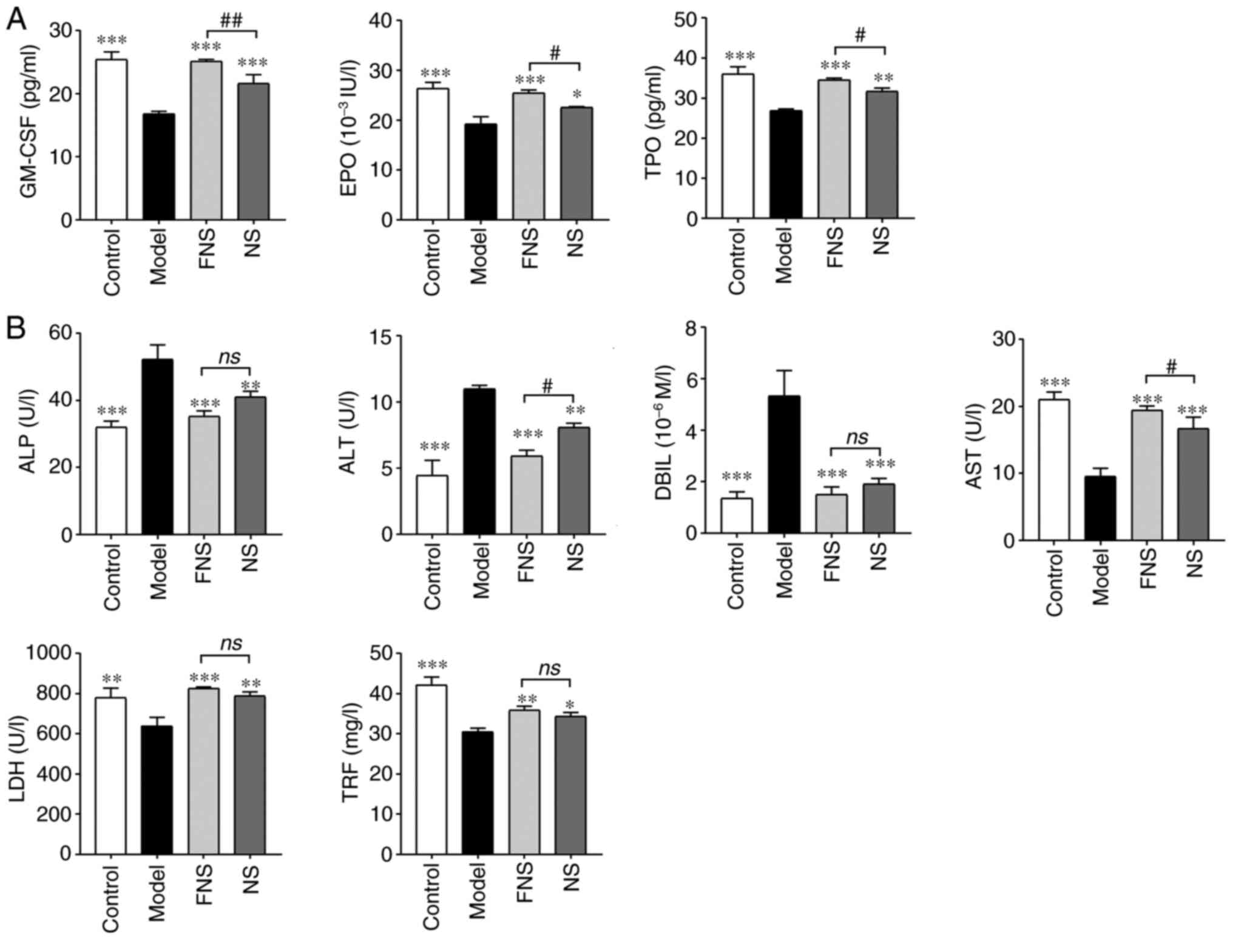
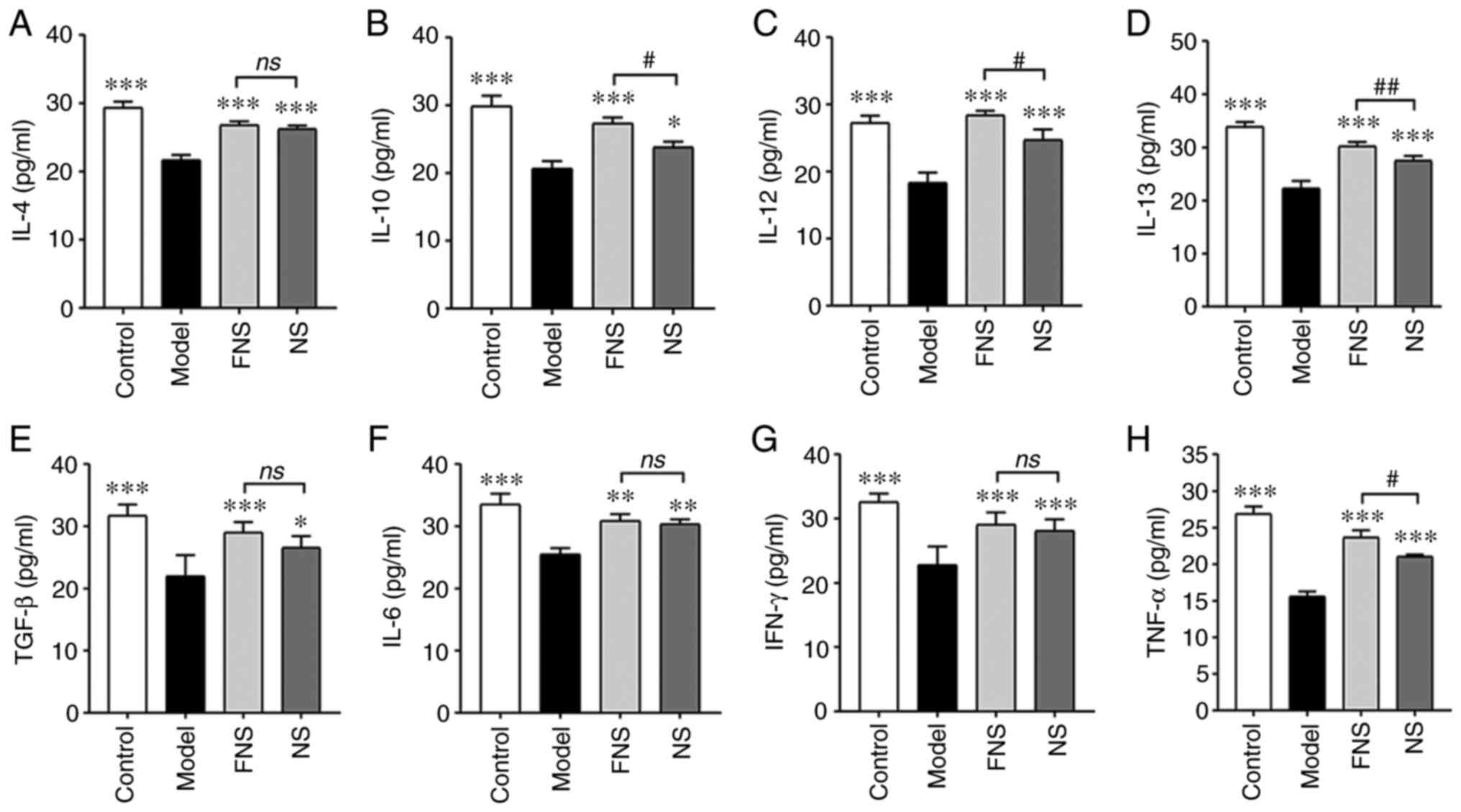
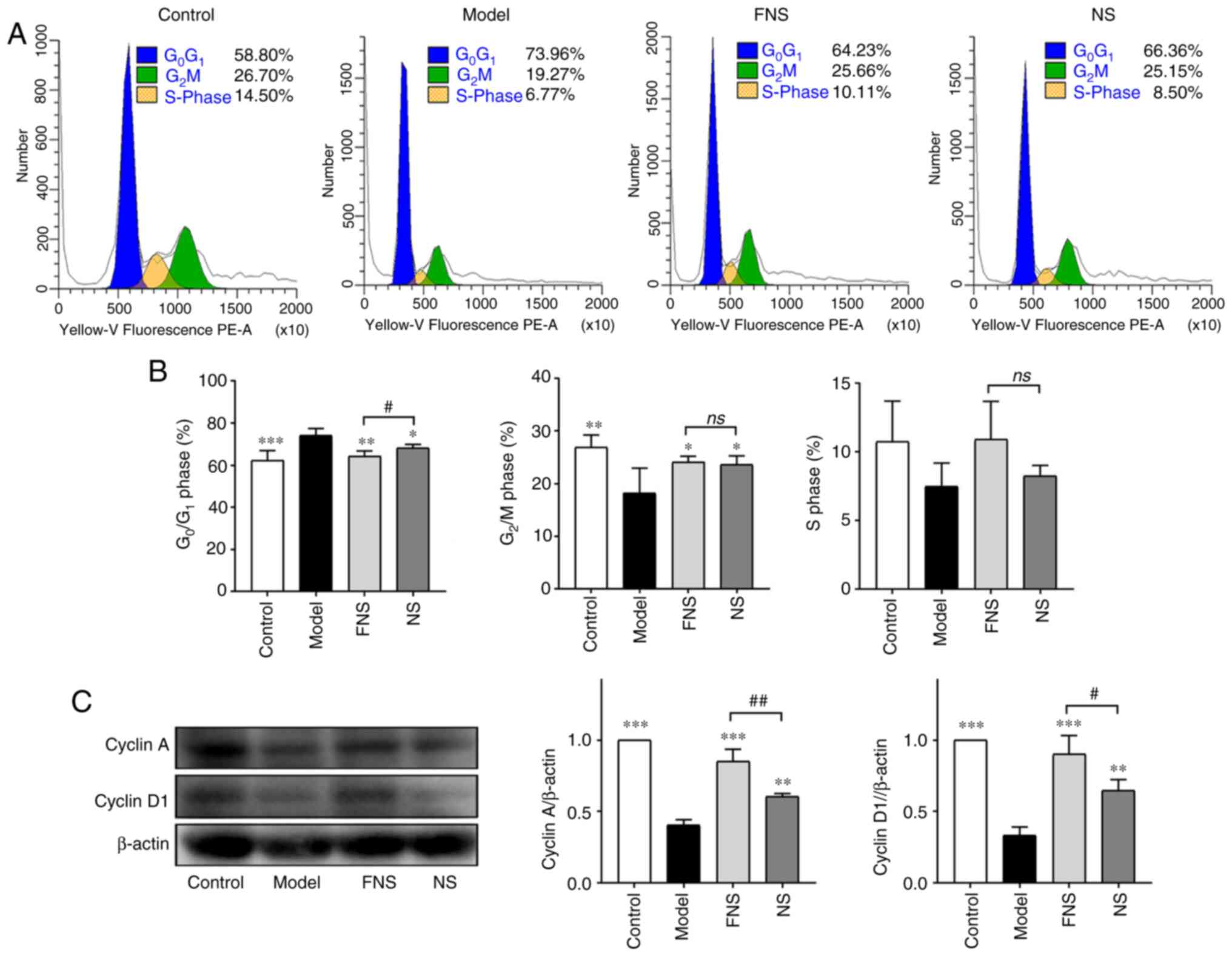
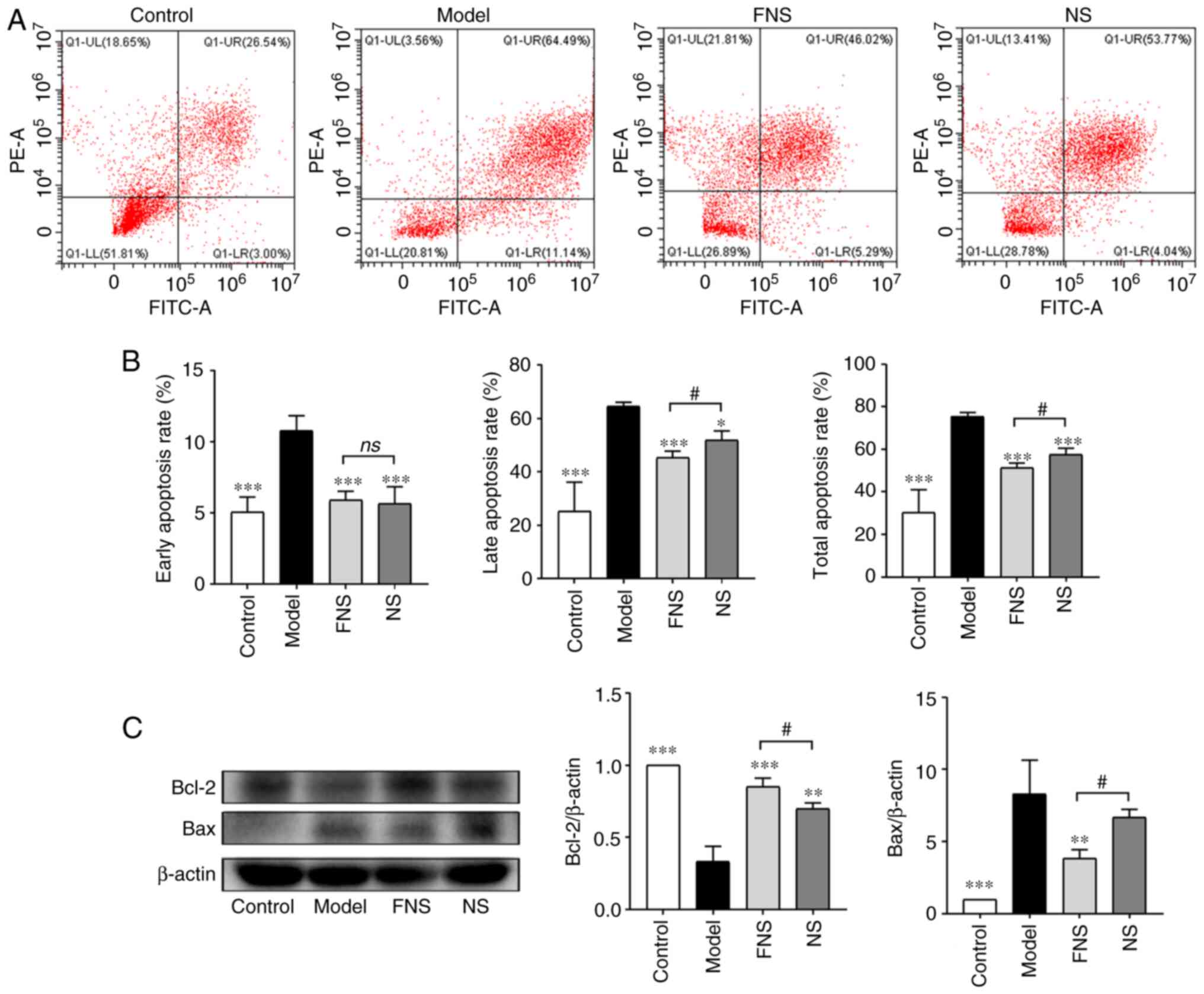
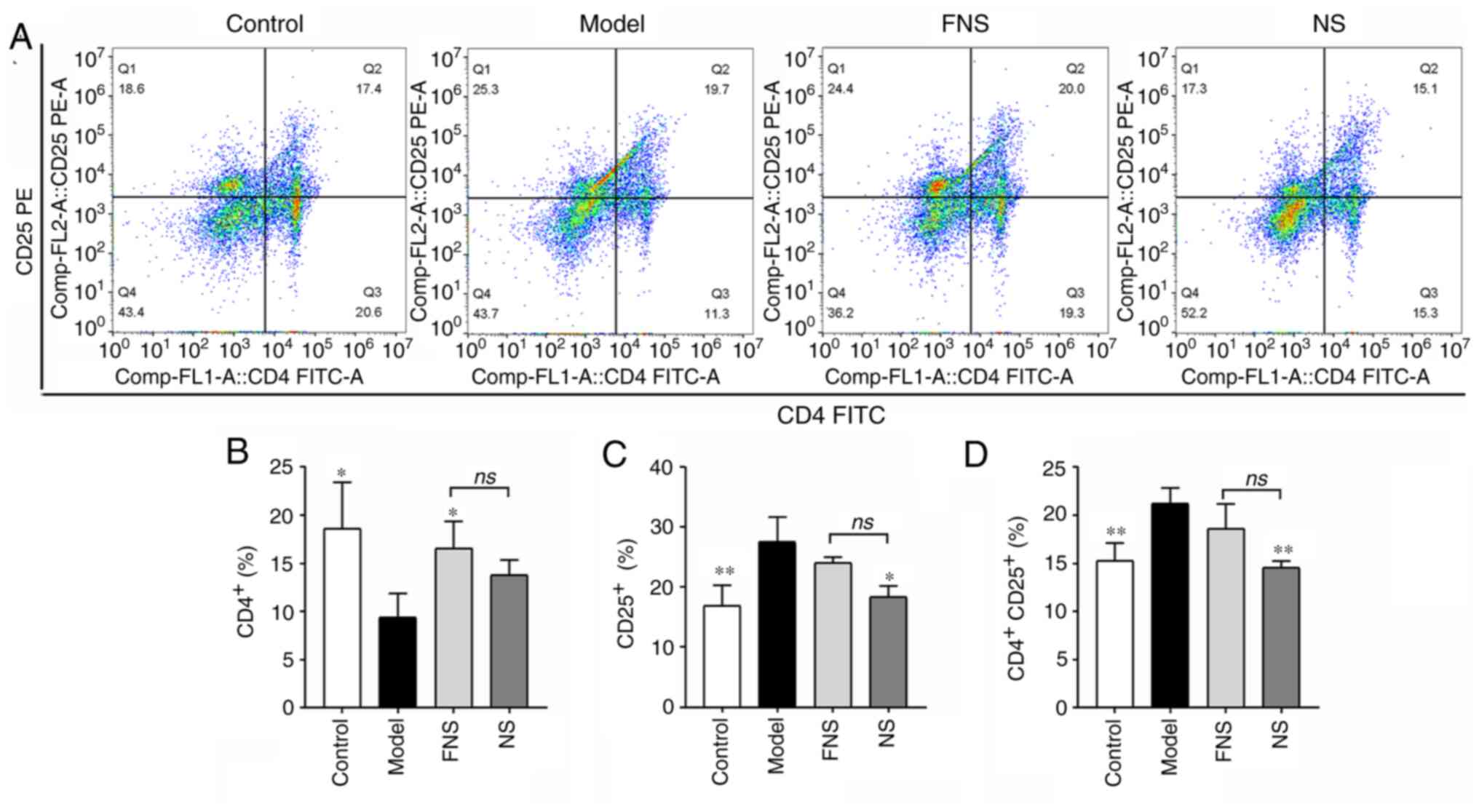
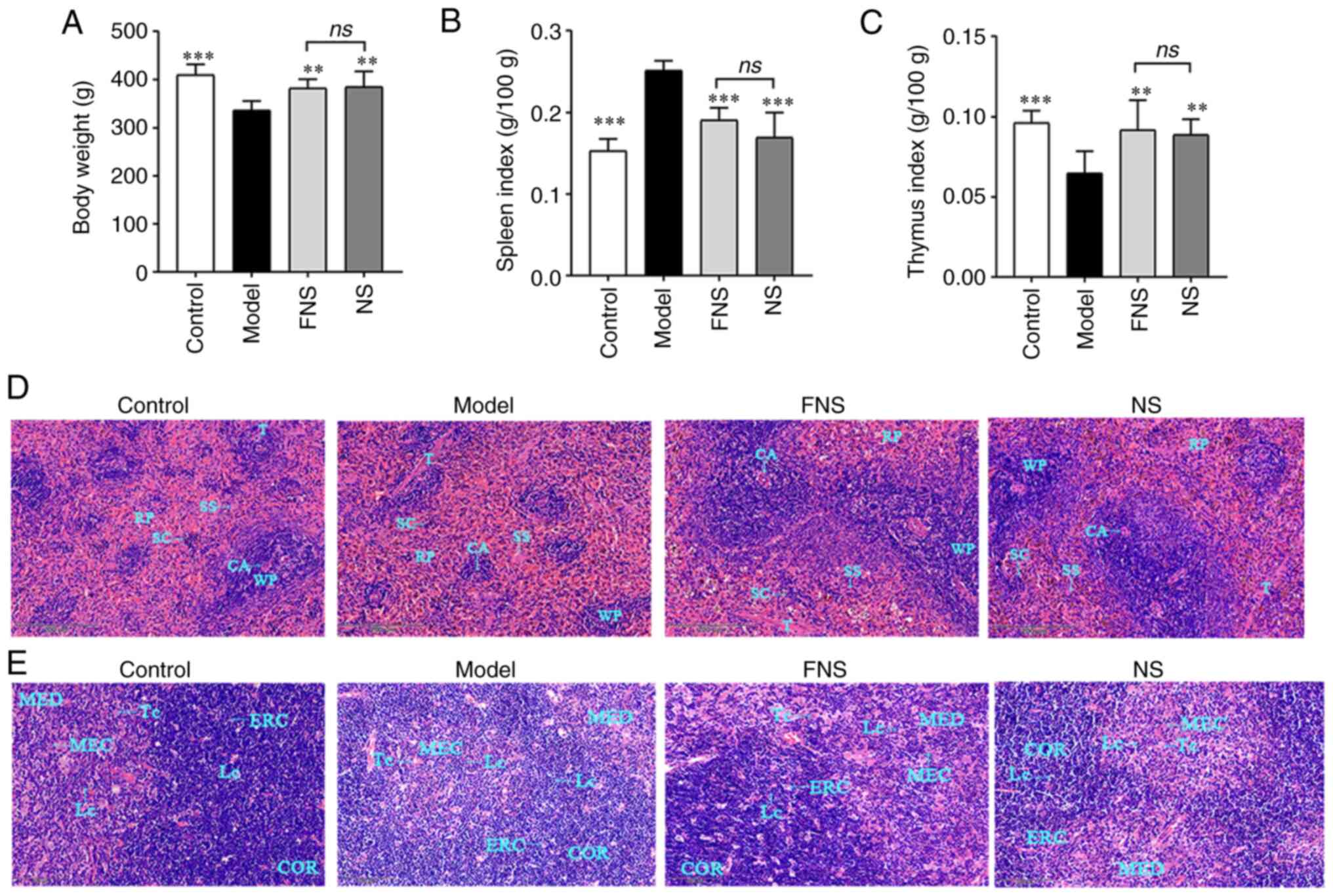
|
1
|
Shi XQ, Yue SJ, Tang YP, Chen YY, Zhou GS,
Zhang J, Zhu ZH, Liu P and Duan JA: A network pharmacology approach
to investigate the blood enriching mechanism of Danggui Buxue
decoction. J Ethnopharmacol. 235:227–242. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li PL, Sun HG, Hua YL, Ji P, Zhang L, Li
JX and Wei Y: Metabolomics study of hematopoietic function of
Angelica sinensis on blood deficiency mice model. J Ethnopharmacol.
166:261–269. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Huang Q, Feng L, Li H, Zheng L, Qi X, Wang
Y, Feng Q, Liu Z, Liu X and Lu L: Jian-Pi-Bu-Xue-formula alleviates
cyclophosphamide-induced myelosuppression via up-regulating
NRF2/HO1/NQO1 signaling. Front Pharmacol. 11(1302)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Uzayisenga R, Ayeka PA and Wang Y:
Anti-diabetic potential of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS):
A review. Phytother Res. 28:510–516. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li YH, Li YY, Fan GW, Yu JH, Duan ZZ, Wang
LY and Yu B: Cardioprotection of ginsenoside Rb1 against
ischemia/reperfusion injury is associated with mitochondrial
permeability transition pore opening inhibitiz. Chin J Integr Med:
Jan 6, 2016 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
6
|
Li L, Wang Y, Qi B, Yuan D, Dong S, Guo D,
Zhang C and Yu M: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion
and migration by ginsenoside Rg1 via the inhibition of
NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:1779–1786.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Gao M, Cui X, Yang Y,
van Duijn B, Wang M, Hu Y, Wang C and Xiong Y: Steamed Panax
notoginseng attenuates anemia in mice with blood deficiency
syndrome via regulating hematopoietic factors and JAK-STAT pathway.
Front Pharmacol. 10(1578)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xiong Y, Chen L, Man J, Hu Y and Cui X:
Chemical and bioactive comparison of Panax notoginseng root
and rhizome in raw and steamed forms. J Ginseng Res. 43:385–393.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Quan LH, Piao JY, Min JW, Kim HB, Kim SR,
Yang DU and Yang DC: Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to
prosapogenins, gypenoside XVII, ginsenoside Rd, ginsenoside F2, and
compound K by Leuconostoc mesenteroides DC102. J Ginseng
Res. 35:344–351. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li J, Huang Q, Yao Y, Ji P, Mingyao E,
Chen J, Zhang Z, Qi H, Liu J, Chen Z, et al: Biotransformation,
pharmacokinetics, and pharmacological activities of ginsenoside Rd
against multiple diseases. Front Pharmacol.
13(909363)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang D, Liao PY, Zhu HT, Chen KK, Xu M,
Zhang YJ and Yang CR: The processing of Panax notoginseng
and the transformation of its saponin components. Food Chem.
132:1808–1813. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Zheng F, Zhang MY, Wu YX, Wang YZ, Li FT,
Han MX, Dai YL and Yue H: Biotransformation of Ginsenosides
(Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc) in human
intestinal bacteria and its effect on intestinal flora. Chem
Biodivers. 18(e2100296)2021.
|
|
13
|
Liu Z, Li JX, Wang CZ, Zhang DL, Wen X,
Ruan CC, Li Y and Yuan CS: Microbial conversion of
protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides by the edible and medicinal
mushroom schizophyllum commune: A green biotransformation strategy.
ACS Omega. 4:13114–13123. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim BG, Shin KS, Yoon TJ, Yu KW, Ra KS,
Kim JM, Kim SY and Suh HJ: Fermentation of Korean red ginseng by
Lactobacillus plantarum M-2 and its immunological
activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 165:1107–1119. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park SE, Na CS, Yoo SA, Seo SH and Son HS:
Biotransformation of major ginsenosides in ginsenoside model
culture by lactic acid bacteria. J Ginseng Res. 41:36–42.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Barreda D, Hanington P and Belosevic M:
Regulation of myeloid development and function by colony
stimulating factors. Dev Comp Immunol. 28:509–554. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Sun Y, Fan M, Zhang Y, Liang Z,
Zhang L, Gao X, He X, Li X, Zhao D, et al: Prevention effect of
total ginsenosides and ginseng extract from Panax ginseng on
cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. Phytother Res.
37:3583–3601. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Barone FC and Feuerstein GZ: Inflammatory
mediators and stroke: new opportunities for novel therapeutics. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 19:819–834. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sharir R, Semo J, Shaish A, Landa-Rouben
N, Entin-Meer M, Keren G and George J: Regulatory T cells influence
blood flow recovery in experimental hindlimb ischaemia in an
IL-10-dependent manner. Cardiovasc Res. 103:585–596.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C and Use of Laboratory A: The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. In: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. National Academies Press (US), Copyright ©. 2011, National
Academy of Sciences, Washington (DC), 2011.
|
|
21
|
Li W, Tang Y, Guo J, Shang E, Qian Y, Wang
L, Zhang L, Liu P, Su S, Qian D and Duan JA: Comparative
metabolomics analysis on hematopoietic functions of herb pair
Gui-Xiong by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled
to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and pattern
recognition approach. J Chromatogr A. 1346:49–56. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gao J, Liu J, Yao M, Zhang W, Yang B and
Wang G: Panax notoginseng saponins stimulates neurogenesis
and neurological restoration after microsphere-induced cerebral
embolism in rats partially via mTOR signaling. Front Pharmacol.
13(889404)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Steinbrecht S, Kiebist J, König R,
Thiessen M, Schmidtke KU, Kammerer S, Küpper JH and Scheibner K:
Synthesis of cyclophosphamide metabolites by a peroxygenase from
Marasmius rotula for toxicological studies on human cancer cells.
AMB Express. 10(128)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Wang F, Yuan L, Ruan H, Zhu Z, Fan
X, Zhu L and Peng X: Blood-enriching effects and immune-regulation
mechanism of steam-processed polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide
in blood deficiency syndrome mice. Front Immunol.
13(813676)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu B, Yang Z, Bo L, Zhao Z, Zhou Q and
Sun C: Cytotoxic effects, inflammatory response and apoptosis
induction of cyclophosphamide in the peripheral blood leukocyte of
blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish
Immunol. 93:174–182. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cheng Y, Liu L, Mo S, Gao J, Zhang H,
Zhang H, Zhang C, Song X, Li L and Geng Z: The immunomodulatory
effects of phellodendri cortex polysaccharides on
cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2021(3027708)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Huang S, Ye Q, Zeng X, Yu H, Qi D
and Qiao S: Prevention of cyclophosphamide-induced
immunosuppression in mice with the antimicrobial peptide sublancin.
J Immunol Res. 2018(4353580)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Economopoulou C, Pappa V, Papageorgiou S,
Kontsioti F, Economopoulou P, Charitidou E, Girkas K, Kapsimali V,
Papasteriadi C, Tsirigotis P, et al: Cell cycle and apoptosis
regulatory gene expression in the bone marrow of patients with de
novo myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Ann Hematol. 89:349–358.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN and Van
Bockstaele DR: Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 36:165–175.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Czabotar PE and Garcia-Saez AJ: Mechanisms
of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Bio. 24:732–748. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Westphal D, Dewson G, Czabotar PE and
Kluck RM: Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:521–531. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Raj S and Gothandam K: Immunomodulatory
activity of methanolic extract of Amorphophallus commutatus var.
Wayanadensis under normal and cyclophosphamide induced
immunosuppressive conditions in mice models. Food Chem Toxicol.
81:151–159. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hou F, Yang H, Yu T and Chen W: The
immunosuppressive effects of 10 mg/kg cyclophosphamide in Wistar
rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 24:30–36. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shrief AI, Hamed WHE, Mazroa SA and
Moustafa AM: Histological study of the role of CD34+ stem cells and
mast cells in cyclophosphamide-induced thymic injury in rats and
the possible attenuating role of melatonin. Histochem Cell Biol.
159:501–512. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Khazaei F, Ghanbari E and Khazaei M:
Protective effect of royal jelly against cyclophosphamide-induced
thrombocytopenia and spleen and bone marrow damages in rats. Cell
J. 22:302–309. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen H, Luo Z, Shen H, Ren C, Li Z, Tang
J, Wang J and Wu T: Research on the roles of transcription factors
T-bet and GATA-3 in aplastic anemia. Clin Lab. 60:291–295.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Wang H, Liu Y, Huang L, Wang Z
and Li Y: The haematopoietic effect of Panax japonicus on blood
deficiency model mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 154:818–824.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Fei QQ, Wang J, Zhu FX, Chen Y,
Tang DQ and Chen B: Study on blood enrichment mechanism of steamed
notoginseng based on metabolomics method. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 44:2139–2148. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Zhang Z, Chen L, Cui X, Zhang Y, Hu Y,
Wang C and Xiong Y: Identification of anti-inflammatory components
of raw and steamed Panax notoginseng root by analyses of
spectrum-effect relationship. RSC Adv. 9:17950–17958.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shin NR, Bose S, Choi Y, Kim YM, Chin YW,
Song EJ, Nam YD and Kim H: Anti-obesity effect of fermented
Panax notoginseng is mediated via modulation of appetite and
gut microbial population. Front Pharmacol.
12(665881)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bai Y and Gänzle MG: Conversion of
ginsenosides by Lactobacillus plantarum studied by liquid
chromatography coupled to quadrupole trap mass spectrometry. Food
Res Int. 76:709–718. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen MY, Shao L, Zhang W, Wang CZ, Zhou
HH, Huang WH and Yuan CS: Metabolic analysis of Panax
notoginseng saponins with gut microbiota-mediated
biotransformation by HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS/MS. J Pharmaceut Biomed.
150:199–207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang L, Yang X, Yu X, Yao Y and Ren G:
Evaluation of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities of
less polar ginsenosides produced from polar ginsenosides by
heat-transformation. J Agric Food Chem. 61:12274–12282.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bae Ea, Han MJ, Kim EJ and Kim DH:
Transformation of ginseng saponins to ginsenoside Rh2 by acids and
human intestinal bacteria and biological activities of their
transformants. Arch Pharm Res. 27:61–67. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Akao T, Kanaoka M and Kobashi K:
Appearance of compound K, a major metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 by
intestinal bacteria, in rat plasma after oral
administration-measurement of compound K by enzyme immunoassay.
Biol Pharm Bull. 21:245–249. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Choi HS, Kim SY, Park Y, Jung EY and Suh
HJ: Enzymatic transformation of ginsenosides in Korean Red Ginseng
(Panax ginseng Meyer) extract prepared by Spezyme and Optidex. J
Ginseng Res. 38:264–269. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lee SY, Jeong JJ, Eun SH and Kim DH:
Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and its metabolites
ginsenoside Rh1 and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in mice with
TNBS-induced colitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 762:333–343. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu Z, Wen X, Wang CZ, Li W, Huang WH, Xia
J, Ruan CC and Yuan CS: Remarkable impact of amino acids on
ginsenoside transformation from fresh ginseng to red ginseng. J
Ginseng Res. 44:424–434. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang HY, Hua HY, Liu XY, Liu JH and Yu BY:
In vitro biotransformation of red ginseng extract by human
intestinal microflora: Metabolites identification and metabolic
profile elucidation using LC-Q-TOF/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
98:296–306. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lee BH, You HJ, Park MS, Kwon B and Ji GE:
Transformation of the glycosides from food materials by probiotics
and food microorganisms. J Microbiol Biotechn. 16:497–504.
2006.
|
|
52
|
Li W, Tang Y, Guo J, Huang M, Li W, Qian D
and Duan J: Enriching blood effect comparison in three kinds of
blood deficiency model after oral administration of drug pair of
Angelicae Sinensis Radix and Chuanxiong Rhizoma and each single
herb. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 36:1808–1814. 2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
53
|
Hua YL, Ma Q, Yuan ZW, Zhang XS, Yao WL,
Ji P, Hu JJ and Wei YM: A novel approach based on metabolomics
coupled with network pharmacology to explain the effect mechanisms
of Danggui Buxue Tang in anaemia. Chin J Nat Med. 17:275–290.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li S, Lin H, Qu C, Tang Y, Shen J, Li W,
Yue S, Kai J, Shang G, Zhu Z, et al: Urine and plasma metabonomics
coupled with UHPLC-QTOF/MS and multivariate data analysis on
potential biomarkers in anemia and hematinic effects of herb pair
Gui-Hong. J Ethnopharmacol. 170:175–183. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hua Y, Yao W, Ji P and Wei Y: Integrated
metabonomic-proteomic studies on blood enrichment effects of
Angelica sinensis on a blood deficiency mice model. Pharm Biol.
55:853–863. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu H, Pan J, Yang Y, Cui X and Qu Y:
Production of minor ginenosides from Panax notoginseng by
microwave processing method and evaluation of their blood-enriching
and hemostatic activity. Molecules. 23(1243)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhao E, Xu H, Wang L, Kryczek I, Wu K, Hu
Y, Wang G and Zou W: Bone marrow and the control of immunity. Cell
Mol Immunol. 9:11–19. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sieff C: Hematopoietic growth factors. J
Clin Invest. 79:1549–1557. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hokom MM, Lacey D, Kinstler OB, Choi E,
Kaufman S, Faust J, Rowan C, Dwyer E, Nichol JL, Grasel T, et al:
Pegylated megakaryocyte growth and development factor abrogates the
lethal thrombocytopenia associated with carboplatin and irradiation
in mice. Blood. 86:4486–4492. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kumar A, Taghi Khani A, Sanchez Ortiz A
and Swaminathan S: GM-CSF: A double-edged sword in cancer
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 13(901277)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Liu H, Yan Y, Zhang F and Wu Q: The
immuno-enhancement effects of tubiechong (eupolyphaga sinensis)
lyophilized powder in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed
mice. Immunol Invest. 48:844–859. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chen QQ, Han X, Wang WM, Zhao L and Chen
A: Danggui sini decoction ameliorates myelosuppression in animal
model by upregulating thrombopoietin expression. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 71:945–950. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wang LF, Xu ZY, Jin CJ, Sha HF, Wang ZQ,
Zhou WD, Zhang M, Wu J and Bai B: Dual regulation of cell cycles by
Shuanghuang Shengbai Granule in Lewis-bearing mice with
chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression and its mechanism. Zhong Xi
Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 7:453–457. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
64
|
Qiang H, Wang KZ, Shi ZB and Fan LH:
Panax notoginseng saponins protect rabbit bone marrow
stromal cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He Xue Bao. 8:131–137. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Qiang H, Zhang C, Shi ZB, Yang HQ and Wang
KZ: Protective effects and mechanism of Panax notoginseng
saponins on oxidative stress-induced damage and apoptosis of rabbit
bone marrow stromal cells. Chin J Integr Med. 16:525–530.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Han J, Wang Y, Cai E, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Sun
N, Zheng X and Wang S: Study of the effects and mechanisms of
ginsenoside compound K on myelosuppression. J Agric Food Chem.
67:1402–1408. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Senior J: Alanine aminotransferase: A
clinical and regulatory tool for detecting liver injury-past,
present, and future. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 92:332–339.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lee CH and Kim IH: Direct
hyperbilirubinemia as a predictor of mortality in patients with
liver cirrhosis. Gut Liver. 15:490–491. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Vimalraj S: Alkaline phosphatase:
Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization.
Gene. 754(144855)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Gkouvatsos K, Papanikolaou G and
Pantopoulos K: Regulation of iron transport and the role of
transferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:188–202. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Boshuizen M, van der Ploeg K, von
Bonsdorff L, Biemond BJ, Zeerleder SS, van Bruggen R and Juffermans
NP: Therapeutic use of transferrin to modulate anemia and
conditions of iron toxicity. Blood Rev. 31:400–405. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Ding RB, Tian K, Cao YW, Bao JL, Wang M,
He C, Hu Y, Su H and Wan JB: Protective effect of Panax
notoginseng saponins on acute ethanol-induced liver injury is
associated with ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation and
reducing ethanol-mediated oxidative stress. J Agric Food Chem.
63:2413–2422. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Xu Y, Wang N, Tan HY, Li S, Zhang C and
Feng Y: Gut-liver axis modulation of Panax notoginseng
saponins in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int.
15:350–365. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Zhong H, Wu H, Bai H, Wang M, Wen J, Gong
J, Miao M and Yuan F: Panax notoginseng saponins promote
liver regeneration through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR cell
proliferation pathway and upregulation of the AKT/Bad cell survival
pathway in mice. BMC Complem Altern Med. 19(122)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Ahlmann M and Hempel G: The effect of
cyclophosphamide on the immune system: Implications for clinical
cancer therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 78:661–671.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Travlos GS: Normal structure, function,
and histology of the bone marrow. Toxicol Pathol. 34:548–565.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kar UK and Joosten LAB: Training the
trainable cells of the immune system and beyond. Nat Immunol.
21:115–119. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Dong C: Cytokine regulation and function
in T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 39:51–76. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Oestreich KJ and Weinmann AS: T-bet
employs diverse regulatory mechanisms to repress transcription.
Trends Immunol. 33:78–83. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Elenkov IJ and Chrousos GP: Stress
hormones, proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, and
autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 966:290–303. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Mei YX, Chen HX, Zhang J, Zhang XD and
Liang YX: Protective effect of chitooligosaccharides against
cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. Int J Biol
Macromol. 62:330–335. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhu G, Luo J, Du H, Jiang Y, Tu Y, Yao Y
and Xu M: Ovotransferrin enhances intestinal immune response in
cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Int J Biol
Macromol. 120:1–9. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Zhao Y, Sun X, Yu X, Gao R and Yin L:
Saponins from Panax notoginseng leaves improve the symptoms
of aplastic anemia and aberrant immunity in mice. Biomed
Pharmacother. 102:959–965. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Yang Z, Chen A, Sun H, Ye Y and Fang W:
Ginsenoside Rd elicits Th1 and Th2 immune responses to ovalbumin in
mice. Vaccine. 25:161–169. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Won HJ, Kim HI, Park T, Kim H, Jo K, Jeon
H, Ha SJ, Hyun JM, Jeong A, Kim JS, et al: Non-clinical
pharmacokinetic behavior of ginsenosides. J Ginseng Res.
43:354–360. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Han M and Fang XL: Difference in oral
absorption of ginsenoside Rg1 between in vitro and in vivo models.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:499–505. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Paek IB, Moon Y, Kim J, Ji HY, Kim SA,
Sohn DH, Kim JB and Lee HS: Pharmacokinetics of a ginseng saponin
metabolite compound K in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 27:39–45.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Xu QF, Fang XL and Chen DF:
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1
from Panax notoginseng in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
84:187–192. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Peng Y, Wu Z, Huo Y, Chen Y, Lu F, Peng Q
and Liang Y: Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides Rg1, Re,
and Rb1 and notoginsenoside R1 by solid phase extraction followed
by UHPLC-MS/MS and investigation of their concentrations in various
kinds of cosmetics. Anal Methods. 9:5441–5448. 2017.
|
|
90
|
Li W, Wu Y, Wan M, Chu Y, Wang X, Li S,
Liu Z, Chen X, Polachi N, Zhou S and Sun H: Simultaneous
determination of three saponins in human plasma after oral
administration of compound danshen dripping pills by LC-MS/MS and
its application in a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
169:254–259. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhu D, Zhou Q, Li H, Li S, Dong Z, Li D
and Zhang W: Pharmacokinetic characteristics of steamed notoginseng
by an efficient LC-MS/MS method for simultaneously quantifying
twenty-three triterpenoids. J Agric Food Chem. 66:8187–8198.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Sharma A and Lee HJ: Ginsenoside compound
K: Insights into recent studies on pharmacokinetics and
health-promoting activities. Biomolecules. 10(1028)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Kim HK: Pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside
Rb1 and its metabolite compound K after oral administration of
Korean Red Ginseng extract. J Ginseng Res. 37:451–456.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Fukami H, Ueda T and Matsuoka N:
Pharmacokinetic study of compound K in Japanese subjects after
ingestion of Panax ginseng fermented by Lactobacillus
paracasei A221 reveals significant increase of absorption into
blood. J Med Food. 22:257–263. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Choi ID, Ryu JH, Lee DE, Lee MH, Shim JJ,
Ahn YT, Sim JH, Huh CS, Shim WS, Yim SV, et al: Enhanced absorption
study of ginsenoside compound K
(20-O-β-(D-Glucopyranosyl)-20(S)-protopanaxadiol) after oral
administration of fermented red ginseng extract (HYFRG™)
in healthy Korean volunteers and rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2016(3908142)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|