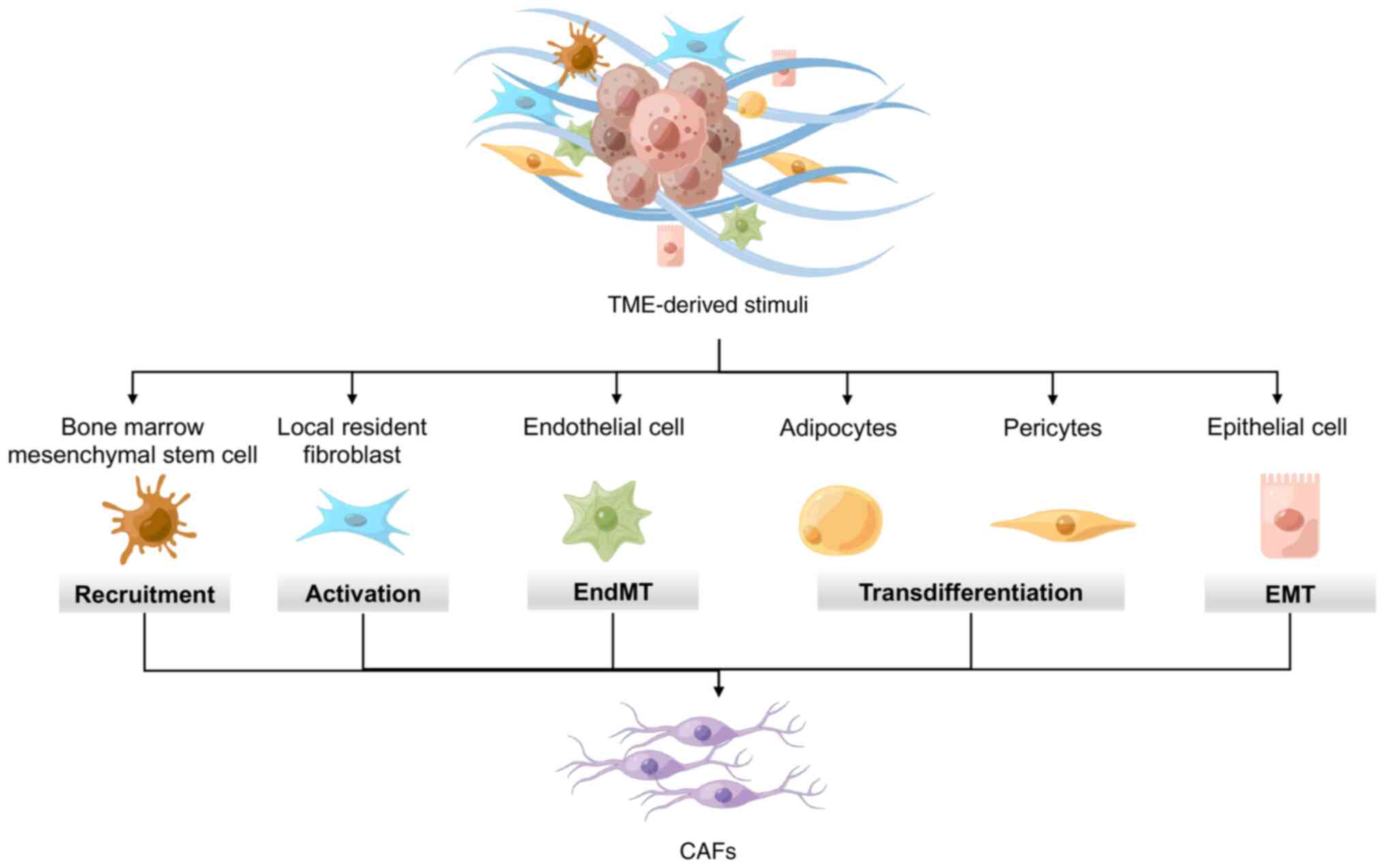
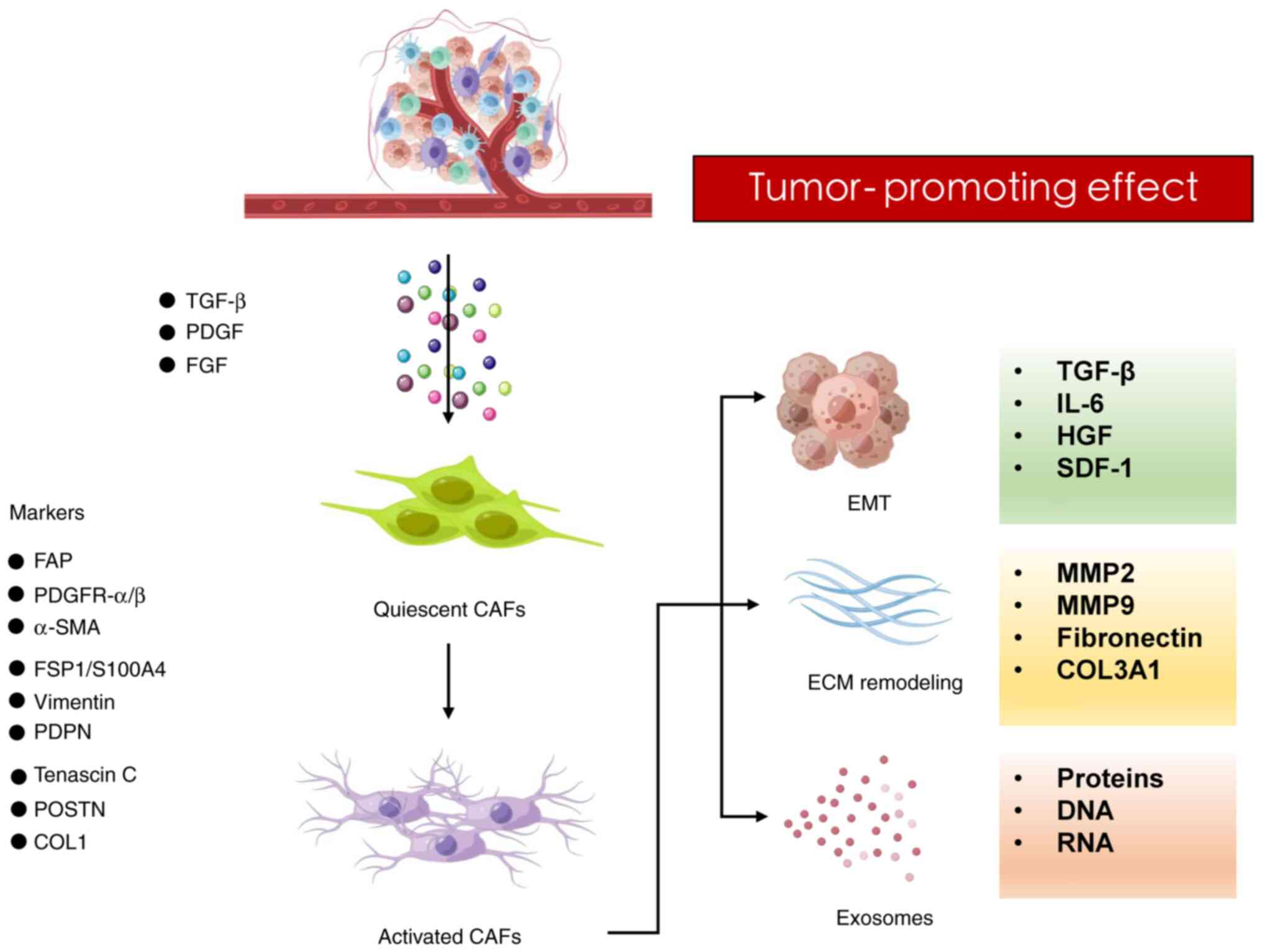
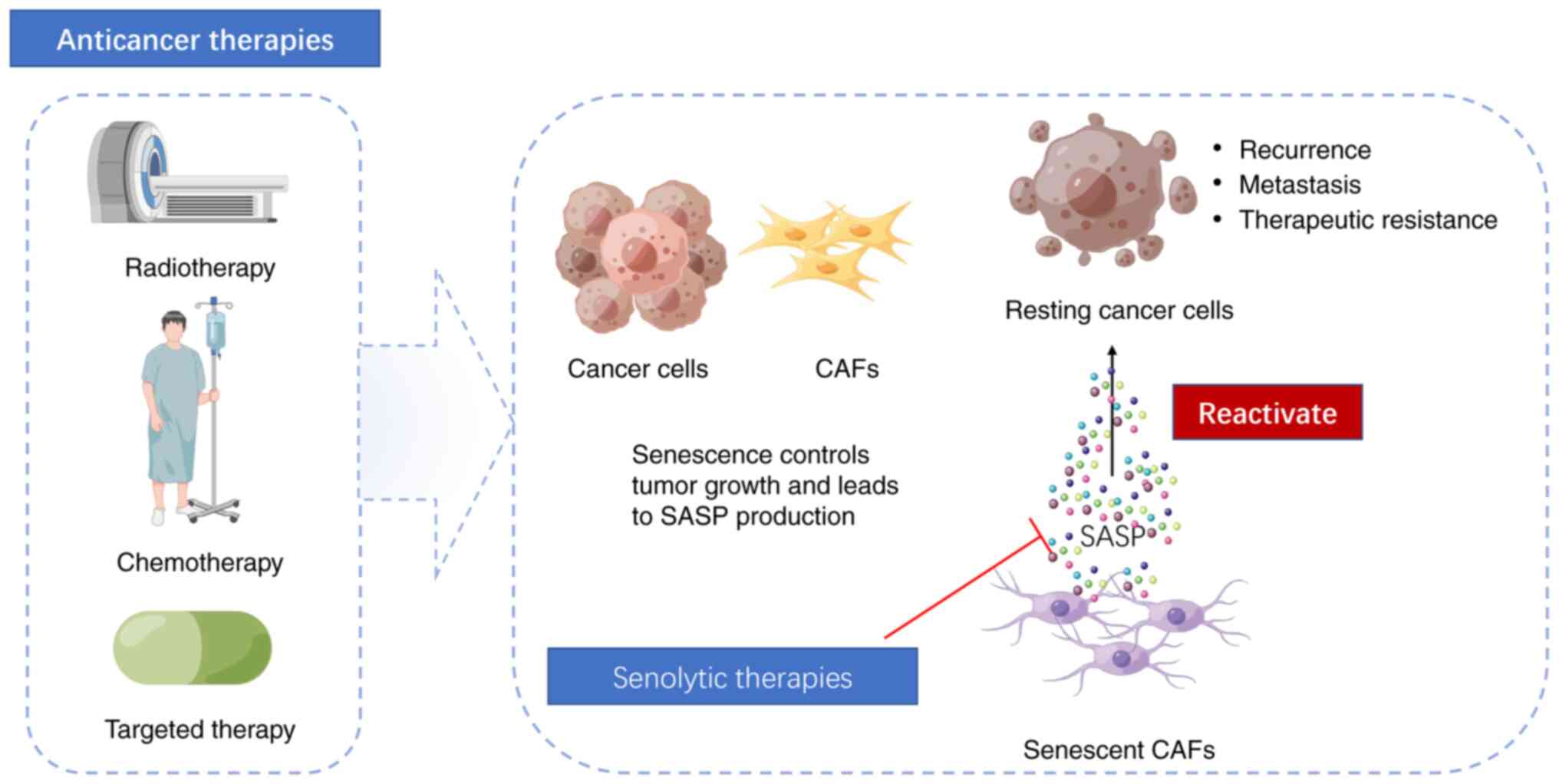
|
1
|
de Visser KE and Joyce JA: The evolving
tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic.
Cancer Cell. 41:374–403. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV
and Fernandes AR: Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer
therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20(840)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Zhang X, Yang H, Liang T and Bai
X: The ‘Self-eating’ of cancer-associated fibroblast: A potential
target for cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 163(114762)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Saw PE, Chen J and Song E: Targeting CAFs
to overcome anticancer therapeutic resistance. Trends Cancer.
8:527–555. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Prasanna PG, Citrin DE, Hildesheim J,
Ahmed MM, Venkatachalam S, Riscuta G, Xi D, Zheng G, Deursen JV,
Goronzy J, et al: Therapy-Induced senescence: Opportunities to
improve anticancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 113:1285–1298.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kumari R and Jat P: Mechanisms of cellular
senescence: Cell cycle arrest and senescence associated Secretory
Phenotype. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9(645593)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hwang HJ, Lee YR, Kang D, Lee HC, Seo HR,
Ryu JK, Kim YN, Ko YG, Park HJ and Lee JS: Endothelial cells under
therapy-induced senescence secrete CXCL11, which increases
aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 490:100–110.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen X and Song E: Turning foes to
friends: Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 18:99–115. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G,
Elyada E, Almeida AS, Ponz-Sarvise M, Corbo V, Oni TE, Hearn SA,
Lee EJ, et al: Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and
myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. 214:579–596.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Filliol A, Saito Y, Nair A, Dapito DH, Yu
LX, Ravichandra A, Bhattacharjee S, Affo S, Fujiwara N, Su H, et
al: Opposing roles of hepatic stellate cell subpopulations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Nature. 610:356–365. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Quante M, Tu SP, Tomita H, Gonda T, Wang
SS, Takashi S, Baik GH, Shibata W, Diprete B, Betz KS, et al: Bone
marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem
cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 19:257–272.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A,
Bailey JM, McAllister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK,
Vonderheide RH, et al: EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic
tumor formation. Cell. 48:349–361. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Park D, Sahai E and Rullan A: SnapShot:
Cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Cell. 181:486–486.e1.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Glabman RA, Choyke PL and Sato N:
Cancer-Associated fibroblasts: Tumorigenicity and targeting for
cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 14(3906)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fiori ME, Di Franco S, Villanova L, Bianca
P, Stassi G and De Maria R: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as
abettors of tumor progression at the crossroads of EMT and therapy
resistance. Mol Cancer. 18(70)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y, Shen M, Wu L, Yang H, Yao Y, Yang
Q, Du J, Liu L, Li Y and Bai Y: Stromal cells in the tumor
microenvironment: Accomplices of tumor progression? Cell Death Dis.
14(587)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Biffi G and Tuveson DA: Diversity and
biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Physiol Rev. 101:147–176.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fiaschi T, Marini A, Giannoni E, Taddei
ML, Gandellini P, De Donatis A, Lanciotti M, Serni S, Cirri P and
Chiarugi P: Reciprocal metabolic reprogramming through lactate
shuttle coordinately influences tumor-stroma interplay. Cancer Res.
72:5130–5140. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Singh S, Singh AP and Mitra R:
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Major co-conspirators in tumor
development. Cancers (Basel). 16(211)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kuzet SE and Gaggioli C: Fibroblast
activation in cancer: When seed fertilizes soil. Cell Tissue Res.
365:607–619. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Caja L, Dituri F, Mancarella S,
Caballero-Diaz D, Moustakas A, Giannelli G and Fabregat I: TGF-β
and the tissue microenvironment: Relevance in fibrosis and cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 19(1294)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Derynck R, Turley SJ and Akhurst RJ: TGFβ
biology in cancer progression and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 18:9–34. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chandra Jena B, Sarkar S, Rout L and
Mandal M: The transformation of cancer-associated fibroblasts:
Current perspectives on the role of TGF-β in CAF mediated tumor
progression and therapeutic resistance. Cancer Lett. 520:222–232.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Neri S, Miyashita T, Hashimoto H, Suda Y,
Ishibashi M, Kii H, Watanabe H, Kuwata T, Tsuboi M, Goto K, et al:
Fibroblast-led cancer cell invasion is activated by
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through platelet-derived growth
factor BB secretion of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 395:20–30.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bronzert DA, Pantazis P, Antoniades HN,
Kasid A, Davidson N, Dickson RB and Lippman ME: Synthesis and
secretion of platelet-derived growth factor by human breast cancer
cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:5763–5767. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shao ZM, Nguyen M and Barsky SH: Human
breast carcinoma desmoplasia is PDGF initiated. Oncogene.
19:4337–4345. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Montori M, Scorzoni C, Argenziano ME,
Balducci D, De Blasio F, Martini F, Buono T, Benedetti A, Marzioni
M and Maroni L: Cancer-Associated fibroblasts in
cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and possible implications for
therapy. J Clin Med. 11(6498)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, Lim S, Hosaka K, Yang Y,
Pavlova T, Alkasalias T, Hartman J, Jensen L, Xing X, et al: A
zebrafish model discovers a novel mechanism of stromal
fibroblast-mediated. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4769–4779. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nissen LJ, Cao R, Hedlund EM, Wang Z, Zhao
X, Wetterskog D, Funa K, Bråkenhielm E and Cao Y: Angiogenic
factors FGF2 and PDGF-BB synergistically promote murine tumor
neovascularization and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 117:2766–2777.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nurmik M, Ullmann P, Rodriguez F, Haan S
and Letellier E: In search of definitions: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts and their markers. Int J Cancer. 146:895–905.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yamamoto Y, Kasashima H, Fukui Y, Tsujio
G, Yashiro M and Maeda K: The heterogeneity of cancer-associated
fibroblast subpopulations: Their origins, biomarkers, and roles in
the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Sci. 114:16–24. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Arnold JN, Magiera L, Kraman M and Fearon
DT: Tumoral immune suppression by macrophages expressing fibroblast
activation protein-α and heme oxygenase-1. Cancer Immunol Res.
2:121–126. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tchou J, Zhang PJ, Bi Y, Satija C,
Marjumdar R, Stephen TL, Lo A, Chen H, Mies C, June CH, et al:
Fibroblast activation protein expression by stromal cells and
tumor-associated macrophages in human breast cancer. Hum Pathol.
44:2549–2557. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jin J, Zhu SJ, Zhu ZM, Yang YJ and Ding G:
Relationship between proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells
and PDGF-AA and PDGFR-alpha expression in SHRs. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
54:145–148. 2002.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Smyth LCD, Rustenhoven J, Scotter EL,
Schweder P, Faull RLM, Park TIH and Dragunow M: Markers for human
brain pericytes and smooth muscle cells. J Chem Neuroanat.
92:48–60. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shamsi F, Piper M, Ho LL, Huang TL, Gupta
A, Streets A, Lynes MD and Tseng YH: Vascular smooth muscle-derived
Trpv1(+) progenitors are a source of cold-induced thermogenic
adipocytes. Nat Metab. 3:485–495. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sá da Bandeira D, Casamitjana J and Crisan
M: Pericytes, integral components of adult hematopoietic stem cell
niches. Pharmacol Ther. 171:104–113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Koliaraki V, Pallangyo CK, Greten FR and
Kollias G: Mesenchymal cells in colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
152:964–979. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Togarrati PP, Dinglasan N, Desai S, Ryan
WR and Muench MO: CD29 is highly expressed on epithelial,
myoepithelial, and mesenchymal stromal cells of human salivary
glands. Oral Dis. 24:561–572. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Delangre E, Oppliger E, Berkcan S,
Gjorgjieva M, Correia de Sousa M and Foti M: S100 proteins in fatty
liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
23(11030)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Martin M, Zhang J, Miao Y, He M, Kang J,
Huang HY, Chou CH, Huang TS, Hong HC, Su SH, et al: Role of
endothelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis via SREBP2 activation. JCI
Insight. 6(e125635)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kamphuis W, Kooijman L, Orre M, Stassen O,
Pekny M and Hol EM: GFAP and vimentin deficiency alters gene
expression in astrocytes and microglia in wild-type mice and
changes the transcriptional response of reactive glia in mouse
model for Alzheimer's disease. Glia. 63:1036–1056. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Suzuki-Inoue K: Platelets and
cancer-associated thrombosis: Focusing on the platelet activation
receptor CLEC-2 and podoplanin. Blood. 134:1912–1918.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Krishnan H, Rayes J, Miyashita T, Ishii G,
Retzbach EP, Sheehan SA, Takemoto A, Chang YW, Yoneda K, Asai J, et
al: Podoplanin: An emerging cancer biomarker and therapeutic
target. Cancer Sci. 109:1292–1299. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lowy CM and Oskarsson T: Tenascin C in
metastasis: A view from the invasive front. Cell Adh Migr.
9:112–124. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yoshida T, Akatsuka T and Imanaka-Yoshida
K: Tenascin-C and integrins in cancer. Cell Adh Migr. 9:96–104.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yue H, Li W, Chen R, Wang J, Lu X and Li
J: Stromal POSTN induced by TGF-β1 facilitates the migration and
invasion of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 160:530–538.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu C, Feng X, Wang B, Wang X, Wang C, Yu
M, Cao G and Wang H: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote
head and neck cancer progression through Periostin-mediated
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin. Cancer
Sci. 109:688–698. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Soikkeli J, Podlasz P, Yin M, Nummela P,
Jahkola T, Virolainen S, Krogerus L, Heikkilä P, von Smitten K,
Saksela O and Hölttä E: Metastatic outgrowth encompasses COL-I,
FN1, and POSTN up-regulation and assembly to fibrillar networks
regulating cell adhesion, migration, and growth. Am J Pathol.
177:387–403. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Walcher L, Kistenmacher AK, Suo H, Kitte
R, Dluczek S, Strauß A, Blaudszun AR, Yevsa T, Fricke S and
Kossatz-Boehlert U: Cancer stem cells-origins and biomarkers:
Perspectives for targeted personalized therapies. Front Immunol.
11(1280)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Bonnans C, Chou J and Werb Z: Remodelling
the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 15:786–801. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Winkler J, Abisoye-Ogunniyan A, Metcalf KJ
and Werb Z: Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour
progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 11(5120)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Asif PJ, Longobardi C, Hahne M and Medema
JP: The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in cancer invasion
and metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 13(4720)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Eiró N, Fernandez-Garcia B, Vázquez J, Del
Casar JM, González LO and Vizoso FJ: A phenotype from tumor stroma
based on the expression of metalloproteases and their inhibitors,
associated with prognosis in breast cancer. Oncoimmunology.
4(e992222)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Neri S, Ishii G, Hashimoto H, Kuwata T,
Nagai K, Date H and Ochiai A: Podoplanin-expressing
cancer-associated fibroblasts lead and enhance the local invasion
of cancer cells in lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 137:784–796.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C,
Grosse R, Marshall JF, Harrington K and Sahai E: Fibroblast-led
collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for
RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol.
9:1392–1400. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Pastushenko I, Mauri F, Song Y, de Cock F,
Meeusen B, Swedlund B, Impens F, Van Haver D, Opitz M, Thery M, et
al: Fat1 deletion promotes hybrid EMT state, tumour stemness and
metastasis. Nature. 589:448–455. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lüönd F, Sugiyama N, Bill R, Bornes L,
Hager C, Tang F, Santacroce N, Beisel C, Ivanek R, Bürglin T, et
al: Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer
malignancy. Dev Cell. 56:3203–3221.e11. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Fares J, Fares MY, Khachfe HH, Salhab HA
and Fares Y: Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of
cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5(28)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ren Y, Jia HH, Xu YQ, Zhou X, Zhao XH,
Wang YF, Song X, Zhu ZY, Sun T, Dou Y, et al: Paracrine and
epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: The role of HOTAIR
stimulated by TGF-ß1 secretion. Mol Cancer. 17(5)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Nicolas AM, Pesic M, Engel E, Ziegler PK,
Diefenhardt M, Kennel KB, Buettner F, Conche C, Petrocelli V,
Elwakeel E, et al: Inflammatory fibroblasts mediate resistance to
neoadjuvant therapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 40:168–184.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Jia C, Wang G, Wang T, Fu B, Zhang Y,
Huang L, Deng Y, Chen G, Wu X, Chen J, et al: Cancer-associated
Fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the
transglutaminase 2-dependent IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 16:2542–2558. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wang Y, Lan W, Xu M, Song J, Mao J, Li C,
Du X, Jiang Y, Li E, Zhang R and Wang Q: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-derived SDF-1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of lung adenocarcinoma via CXCR4/β-catenin/PPARδ signalling. Cell
Death Dis. 12(214)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Dai J, Su Y, Zhong S, Cong L, Liu B, Yang
J, Tao Y, He Z, Chen C and Jiang Y: Exosomes: Key players in cancer
and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5(145)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Richards KE, Zeleniak AE, Fishel ML, Wu J,
Littlepage LE and Hill R: Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes
regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells.
Oncogene. 36:1770–1778. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H,
Liu D, Zhang Q, Lin D, Ge S, Bai M, et al: CAF secreted miR-522
suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in
gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 19(43)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Martínez-Zamudio RI, Robinson L, Roux PF
and Bischof O: SnapShot: Cellular senescence pathways. Cell.
170:816–816.e11. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang L, Lankhorst L and Bernards R:
Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
22:340–355. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Bahcecioglu G, Yue X, Howe E, Guldner I,
Stack MS, Nakshatri H, Zhang S and Zorlutuna P: Aged breast
extracellular matrix drives mammary epithelial cells to an
invasive. Adv Sci (Weinh). 8(e2100128)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Bancaro N, Calì B, Troiani M, Elia AR,
Arzola RA, Attanasio G, Lai P, Crespo M, Gurel B, Pereira R, et al:
Apolipoprotein E induces pathogenic senescent-like myeloid cells in
prostate. Cancer Cell. 41:602–619.e11. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Nguyen PT, Kanno K, Pham QT, Kikuchi Y,
Kakimoto M, Kobayashi T, Otani Y, Kishikawa N, Miyauchi M, Arihiro
K, et al: Senescent hepatic stellate cells caused by deoxycholic
acid modulates malignant. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:3255–3268.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yoshimoto S, Loo TM, Atarashi K, Kanda H,
Sato S, Oyadomari S, Iwakura Y, Oshima K, Morita H, Hattori M, et
al: Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer
through senescence secretome. Nature. 499:97–101. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Loo TM, Kamachi F, Watanabe Y, Yoshimoto
S, Kanda H, Arai Y, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Iwama A, Koga T, Sugimoto Y,
et al: Gut Microbiota Promotes Obesity-Associated Liver Cancer
through PGE(2)-Mediated. Cancer Discov. 7:522–538. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Chambers CR, Ritchie S, Pereira BA and
Timpson P: Overcoming the senescence-associated secretory phenotype
(SASP): A complex mechanism of resistance in the treatment of
cancer. Mol Oncol. 15:3242–3255. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Groelly FJ, Fawkes M, Dagg RA, Blackford
AN and Tarsounas M: Targeting DNA damage response pathways in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 23:78–94. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Shiloh Y: ATM and related protein kinases:
Safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:155–168.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Buzun K, Bielawska A, Bielawski K and
Gornowicz A: DNA topoisomerases as molecular targets for anticancer
drugs. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 35:1781–1799. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Aasland D, Götzinger L, Hauck L, Berte N,
Meyer J, Effenberger M, Schneider S, Reuber EE, Roos WP, Tomicic
MT, et al: Temozolomide induces senescence and repression of DNA
repair pathways in glioblastoma cells via activation of ATR-CHK1,
p21, and NF-κB. Cancer Res. 79:99–113. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Mikuła-Pietrasik J, Witucka A, Pakuła M,
Uruski P, Begier-Krasińska B, Niklas A, Tykarski A and Książek K:
Comprehensive review on how platinum- and taxane-based chemotherapy
of ovarian cancer affects biology of normal cells. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 76:681–697. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Burdelya LG, Komarova EA, Hill JE, Browder
T, Tararova ND, Mavrakis L, DiCorleto PE, Folkman J and Gudkov AV:
Inhibition of p53 response in tumor stroma improves efficacy of
anticancer treatment by increasing antiangiogenic effects of
chemotherapy and radiotherapy in mice. Cancer Res. 66:9356–9361.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Pardella E, Pranzini E, Nesi I, Parri M,
Spatafora P, Torre E, Muccilli A, Castiglione F, Fambrini M, Sorbi
F, et al: Therapy-Induced stromal senescence promoting
aggressiveness of prostate and ovarian cancer. Cells.
11(4026)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Li M, You L, Xue J and Lu Y: Ionizing
radiation-induced cellular senescence in normal, non-transformed
cells and the involved DNA damage response: A mini review. Front
Pharmacol. 9(522)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Meng J, Li Y, Wan C, Sun Y, Dai X, Huang
J, Hu Y, Gao Y, Wu B, Zhang Z, et al: Targeting senescence-like
fibroblasts radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer and reduces
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. JCI Insight.
6(e146334)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Wagner V and Gil J: Senescence as a
therapeutically relevant response to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Oncogene.
39:5165–5176. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Coppé JP, Rodier F, Patil CK, Freund A,
Desprez PY and Campisi J: Tumor suppressor and aging biomarker
p16(INK4a) induces cellular senescence without the associated
inflammatory secretory phenotype. J Biol Chem. 286:36396–36403.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Capparelli C, Chiavarina B,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Pestell TG, Pestell RG, Hulit J, Andò S, Howell
A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: CDK inhibitors
(p16/p19/p21) induce senescence and autophagy in cancer-associated
fibroblasts, ‘fueling’ tumor growth via paracrine interactions,
without an increase in neo-angiogenesis. Cell Cycle. 11:3599–3610.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Guan X, LaPak KM, Hennessey RC, Yu CY,
Shakya R, Zhang J and Burd CE: Stromal senescence by prolonged
CDK4/6 inhibition potentiates tumor growth. Mol Cancer Res.
15:237–249. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Campisi J, Kapahi P, Lithgow GJ, Melov S,
Newman JC and Verdin E: From discoveries in ageing research to
therapeutics for healthy ageing. Nature. 571:183–192.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Chaib S, Tchkonia T and Kirkland JL:
Cellular senescence and senolytics: The path to the clinic. Nat
Med. 28:1556–1568. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Yosef R, Pilpel N, Tokarsky-Amiel R, Biran
A, Ovadya Y, Cohen S, Vadai E, Dassa L, Shahar E, Condiotti R, et
al: Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W
and BCL-XL. Nat Commun. 7(11190)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Jochems F, Thijssen B, De Conti G, Jansen
R, Pogacar Z, Groot K, Wang L, Schepers A, Wang C, Jin H, et al:
The Cancer SENESCopedia: A delineation of cancer cell senescence.
Cell Rep. 36(109441)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Fletcher-Sananikone E, Kanji S, Tomimatsu
N, Di Cristofaro LFM, Kollipara RK, Saha D, Floyd JR, Sung P,
Hromas R, Burns TC, et al: Elimination of radiation-induced
senescence in the brain tumor microenvironment attenuates
glioblastoma recurrence. Cancer Res. 81:5935–5947. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Li F, Huangyang P, Burrows M, Guo K,
Riscal R, Godfrey J, Lee KE, Lin N, Lee P, Blair IA, et al: FBP1
loss disrupts liver metabolism and promotes tumorigenesis through a
hepatic stellate cell senescence secretome. Nat Cell Biol.
22:728–739. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Baar MP, Brandt RMC, Putavet DA, Klein
JDD, Derks KWJ, Bourgeois BRM, Stryeck S, Rijksen Y, van
Willigenburg H, Feijtel DA, et al: Targeted apoptosis of senescent
cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and
aging. Cell. 169:132–147.e16. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|