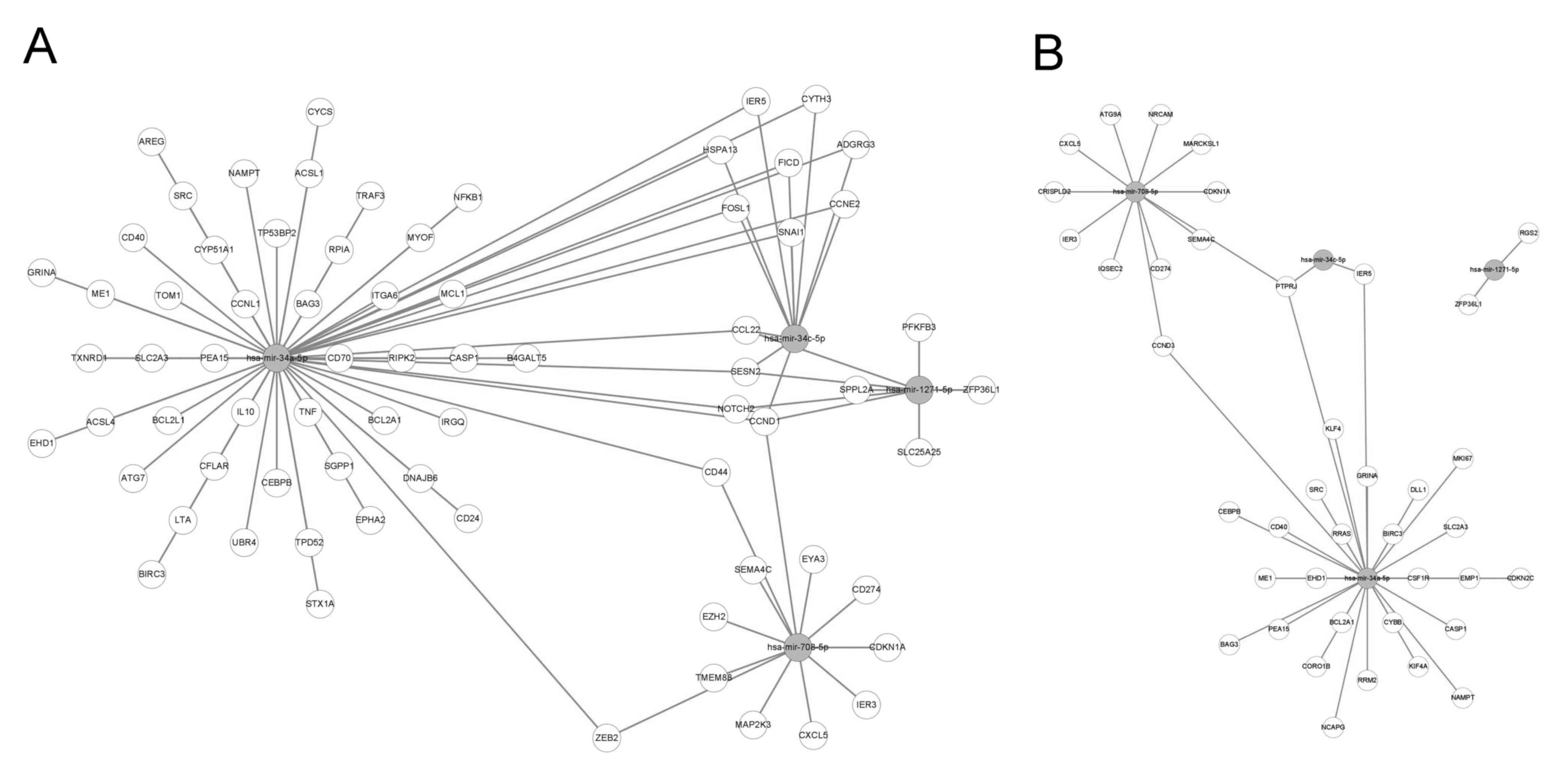
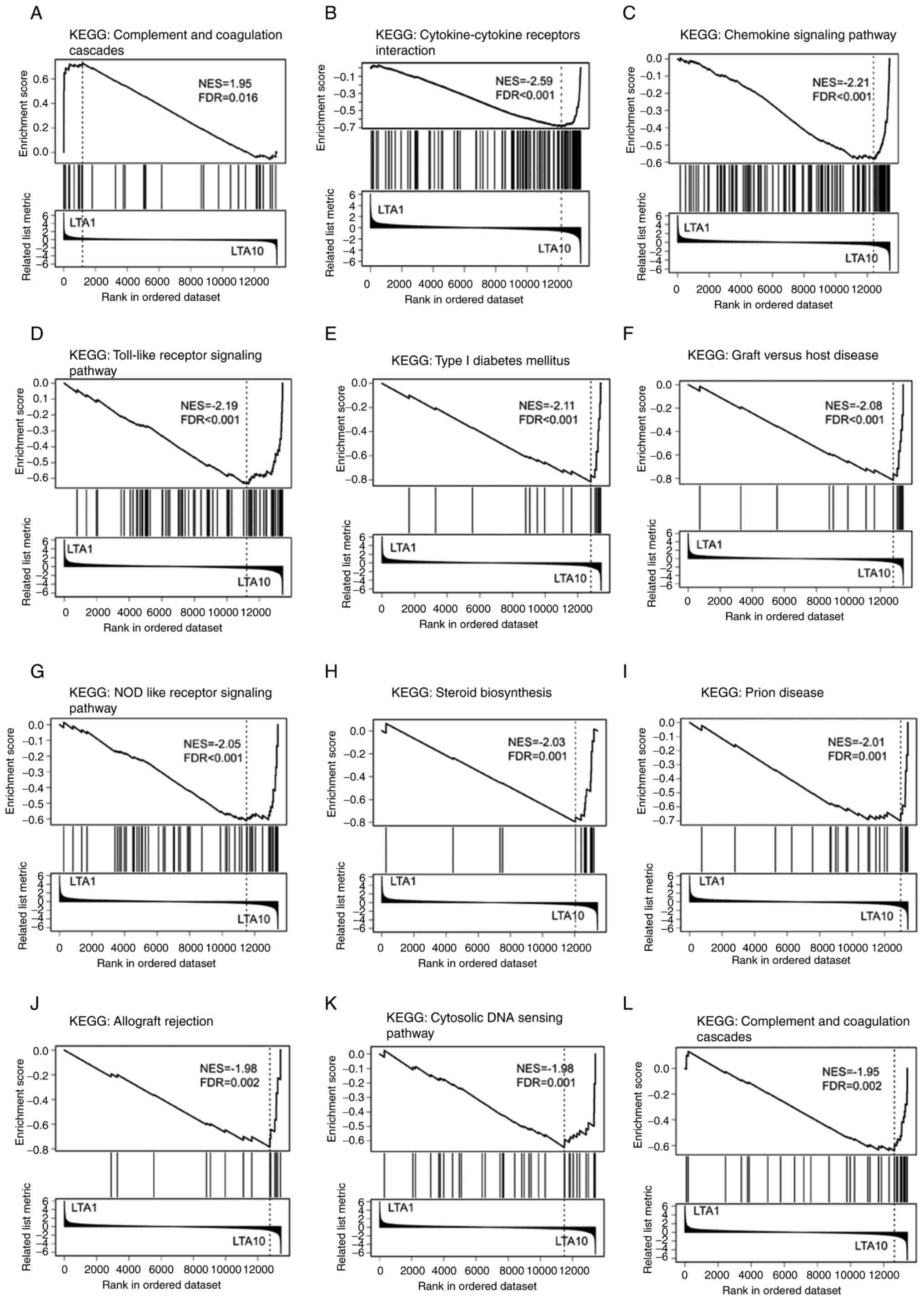
|
1
|
Sagiv JY, Michaeli J, Assi S, Mishalian I,
Kisos H, Levy L, Damti P, Lumbroso D, Polyansky L, Sionov RV, et
al: Phenotypic diversity and plasticity in circulating neutrophil
subpopulations in cancer. Cell Rep. 10:562–573. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C
and Jaillon S: Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of
innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:519–531.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Brubaker SW, Bonham KS, Zanoni I and Kagan
JC: Innate immune pattern recognition: A cell biological
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 33:257–290. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mogensen TH: Pathogen recognition and
inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 22:240–273, table of Contents. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Borregaard N: Neutrophils, from marrow to
microbes. Immunity. 33:657–670. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kawasaki T and Kawai T: Toll-like receptor
signaling pathways. Front Immunol. 5(461)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hayashi F, Means TK and Luster AD:
Toll-like receptors stimulate human neutrophil function. Blood.
102:2660–2669. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cook DN, Pisetsky DS and Schwartz DA:
Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of human disease. Nat
Immunol. 5:975–979. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Seo HS, Michalek SM and Nahm MH:
Lipoteichoic acid is important in innate immune responses to
gram-positive bacteria. Infect Immun. 76:206–213. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe
M and Kirschning CJ: Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced
cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem.
274:17406–17409. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oliveira-Nascimento L, Massari P and
Wetzler LM: The role of TLR2 in infection and immunity. Front
Immunol. 3(79)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Park BS and Lee JO: Recognition of
lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp Mol Med.
45(e66)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Miller SI, Ernst RK and Bader MW: LPS,
TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:36–46.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Weidenmaier C and Peschel A: Teichoic
acids and related cell-wall glycopolymers in gram-positive
physiology and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 6:276–287.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Percy MG and Gründling A: Lipoteichoic
acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 68:81–100. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lotz S, Aga E, Wilde I, van Zandbergen G,
Hartung T, Solbach W and Laskay T: Highly purified lipoteichoic
acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous
apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2. J Leukoc Biol. 75:467–477.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hattar K, Grandel U, Moeller A, Fink L,
Iglhaut J, Hartung T, Morath S, Seeger W, Grimminger F and Sibelius
U: Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) from Staphylococcus aureus stimulates
human neutrophil cytokine release by a CD14-dependent,
Toll-like-receptor-independent mechanism: Autocrine role of tumor
necrosis factor-[alpha] in mediating LTA-induced interleukin-8
generation. Crit Care Med. 34:835–841. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
van Kessel KP, Bestebroer J and van Strijp
JA: Neutrophil-mediated phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus.
Front Immunol. 5(467)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Schröder NW, Morath S, Alexander C, Hamann
L, Hartung T, Zähringer U, Göbel UB, Weber JR and Schumann RR:
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae and
Staphylococcus aureus activates immune cells via Toll-like receptor
(TLR)-2, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), and CD14,
whereas TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. J Biol Chem.
278:15587–15594. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh
N, Peters AM and Chilvers ER: Neutrophil kinetics in health and
disease. Trends Immunol. 31:318–324. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kolaczkowska E and Kubes P: Neutrophil
recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 13:159–175. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Collins SJ, Ruscetti FW, Gallagher RE and
Gallo RC: Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia
cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 75:2458–2462. 1978.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang D, Sennari Y, Shen M, Morita K,
Kanazawa T and Yoshida Y: ERK is involved in the differentiation
and function of dimethyl sulfoxide-induced HL-60 neutrophil-like
cells, which mimic inflammatory neutrophils. Int Immunopharmacol.
84(106510)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Poplutz MK, Wessels I, Rink L and
Uciechowski P: Regulation of the interleukin-6 gene expression
during monocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells by chromatin
remodeling and methylation. Immunobiology. 219:619–626.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shuto T, Furuta T, Cheung J, Gruenert DC,
Ohira Y, Shimasaki S, Suico MA, Sato K and Kai H: Increased
responsiveness to TLR2 and TLR4 ligands during
dimethylsulfoxide-induced neutrophil-like differentiation of HL-60
myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 31:1721–1728. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wen SH, Hong ZW, Chen CC, Chang HW and Fu
HW: Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein directly
interacts with and activates Toll-like receptor 2 to induce the
secretion of interleukin-8 from neutrophils and ATRA-induced
differentiated HL-60 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22(11560)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Graziano RF, Ball ED and Fanger MW: The
expression and modulation of human myeloid-specific antigens during
differentiation of the HL-60 cell line. Blood. 61:1215–1221.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Atkinson JP and Jones EA: Biosynthesis of
the human C3b/C4b receptor during differentiation of the HL-60 cell
line. Identification and characterization of a precursor molecule.
J Clin Invest. 74:1649–1657. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Manda-Handzlik A, Bystrzycka W, Wachowska
M, Sieczkowska S, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A, Demkow U and Ciepiela O:
The influence of agents differentiating HL-60 cells toward
granulocyte-like cells on their ability to release neutrophil
extracellular traps. Immunol Cell Biol. 96:413–425. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Babatunde KA, Wang X, Hopke A, Lannes N,
Mantel PY and Irimia D: Chemotaxis and swarming in differentiated
HL-60 neutrophil-like cells. Sci Rep. 11(778)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang L, Zhou G, Soufan O and Xia J:
miRNet 2.0: Network-based visual analytics for miRNA functional
analysis and systems biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (W1):W244–W251.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liao Y, Wang J, Jaehnig EJ, Shi Z and
Zhang B: WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped
UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (W1):W199–W205. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kuwabara WMT, Zhang L, Schuiki I, Curi R,
Volchuk A and Alba-Loureiro TC: NADPH oxidase-dependent production
of reactive oxygen species induces endoplasmatic reticulum stress
in neutrophil-like HL60 cells. PLoS One.
10(e0116410)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo Y, Gao F, Wang Q, Wang K, Pan S, Pan
Z, Xu S, Li L and Zhao D: Differentiation of HL-60 cells in
serum-free hematopoietic cell media enhances the production of
neutrophil extracellular traps. Exp Ther Med.
21(353)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yen MC, Yeh IJ, Liu KT, Jian SF, Lin CJ,
Tsai MJ and Kuo PL: Next-generation sequencing predicts interaction
network between miRNA and target genes in lipoteichoic
acid-stimulated human neutrophils. Int J Mol Med. 44:1436–1446.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Coady TH and Lorson CL: SMN in spinal
muscular atrophy and snRNP biogenesis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
2:546–564. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Pennamen P, Le L, Tingaud-Sequeira A,
Fiore M, Bauters A, Van Duong Béatrice N, Coste V, Bordet JC,
Plaisant C, Diallo M, et al: BLOC1S5 pathogenic variants cause a
new type of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Genet Med. 22:1613–1622.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Blanter M, Gouwy M and Struyf S: Studying
neutrophil function in vitro: Cell models and environmental
factors. J Inflamm Res. 14:141–162. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
von Aulock S, Morath S, Hareng L, Knapp S,
van Kessel KP, van Strijp JA and Hartung T: Lipoteichoic acid from
Staphylococcus aureus is a potent stimulus for neutrophil
recruitment. Immunobiology. 208:413–422. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Askarian F, Wagner T, Johannessen M and
Nizet V: Staphylococcus aureus modulation of innate immune
responses through Toll-like (TLR), (NOD)-like (NLR) and C-type
lectin (CLR) receptors. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 42:656–671.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Damsker JM, Hansen AM and Caspi RR: Th1
and Th17 cells: Adversaries and collaborators. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1183:211–221. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bradley LM, Dalton DK and Croft M: A
direct role for IFN-gamma in regulation of Th1 cell development. J
Immunol. 157:1350–1358. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yoshimura T and Takahashi M:
IFN-gamma-mediated survival enables human neutrophils to produce
MCP-1/CCL2 in response to activation by TLR ligands. J Immunol.
179:1942–1949. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Donath MY, Dinarello CA and
Mandrup-Poulsen T: Targeting innate immune mediators in type 1 and
type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol. 19:734–746. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Penack O, Holler E and van den Brink MRM:
Graft-versus-host disease: Regulation by microbe-associated
molecules and innate immune receptors. Blood. 115:1865–1872.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Aguzzi A, Nuvolone M and Zhu C: The
immunobiology of prion diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:888–902.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Murphy SP, Porrett PM and Turka LA: Innate
immunity in transplant tolerance and rejection. Immunol Rev.
241:39–48. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ito Y and Amagai M: Controlling skin
microbiome as a new bacteriotherapy for inflammatory skin diseases.
Inflamm Regen. 42(26)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
de Bont CM, Boelens WC and Pruijn GJM:
NETosis, complement, and coagulation: A triangular relationship.
Cell Mol Immunol. 16:19–27. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ko YP, Kuipers A, Freitag CM, Jongerius I,
Medina E, van Rooijen WJ, Spaan AN, van Kessel KP, Höök M and
Rooijakkers SH: Phagocytosis escape by a Staphylococcus aureus
protein that connects complement and coagulation proteins at the
bacterial surface. PLoS Pathog. 9(e1003816)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Mori R, Tanaka K and Shimokawa I:
Identification and functional analysis of inflammation-related
miRNAs in skin wound repair. Dev Growth Differ. 60:306–315.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tanaka K, Kim SE, Yano H, Matsumoto G,
Ohuchida R, Ishikura Y, Araki M, Araki K, Park S, Komatsu T, et al:
MiR-142 is required for Staphylococcus aureus clearance at skin
wound sites via small GTPase-mediated regulation of the neutrophil
actin cytoskeleton. J Invest Dermatol. 137:931–940. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhang W, Qu X, Zhu Z, Wang L, Qi Q, Zhou
P, Wang X and Li W: Inhibition of miR-139-5p by topical JTXK gel
promotes healing of Staphylococcus aureus-infected skin wounds.
Cells Dev. 166(203658)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
de Kerckhove M, Tanaka K, Umehara T,
Okamoto M, Kanematsu S, Hayashi H, Yano H, Nishiura S, Tooyama S,
Matsubayashi Y, et al: Targeting miR-223 in neutrophils enhances
the clearance of Staphylococcus aureus in infected wounds. EMBO Mol
Med. 10(e9024)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|