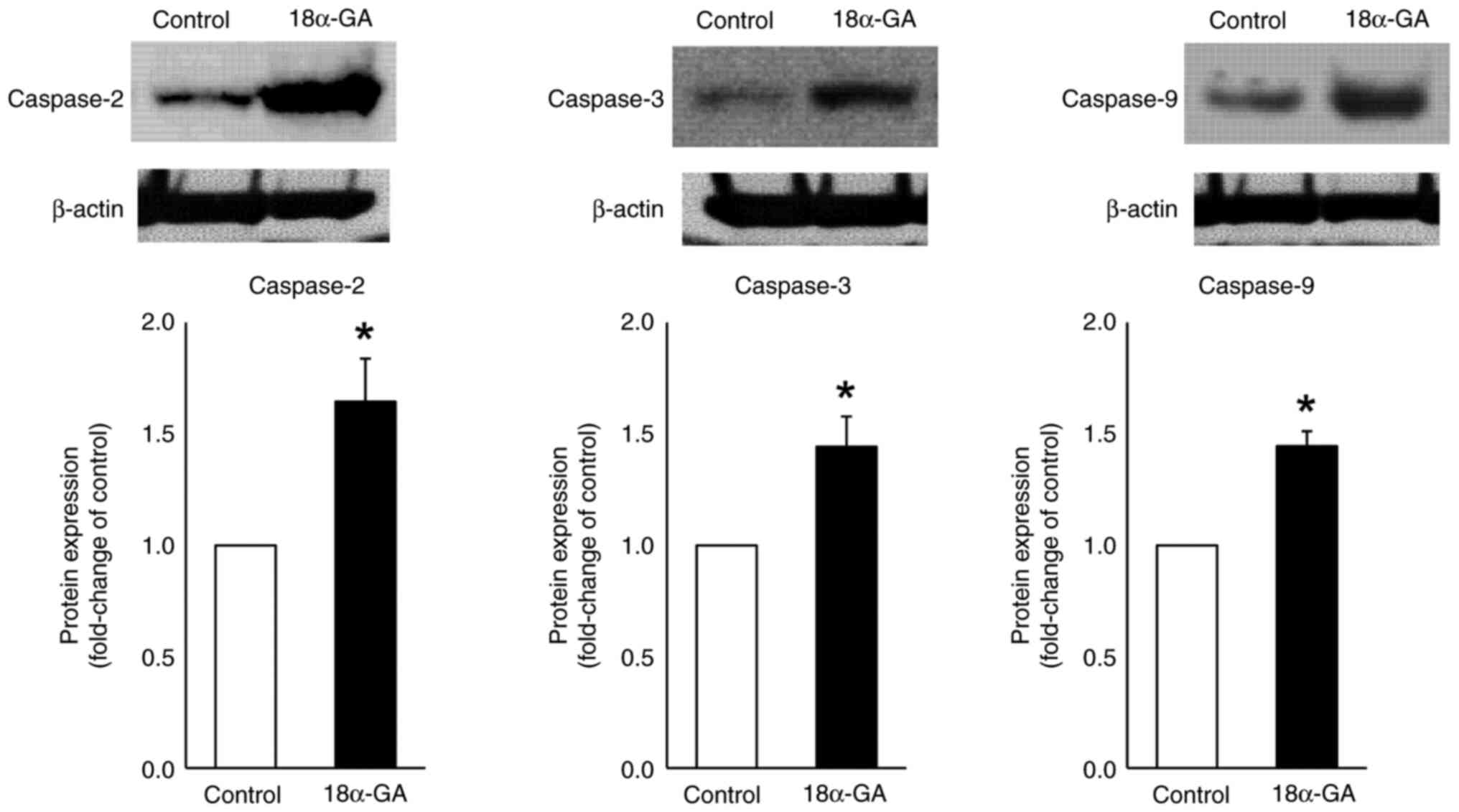
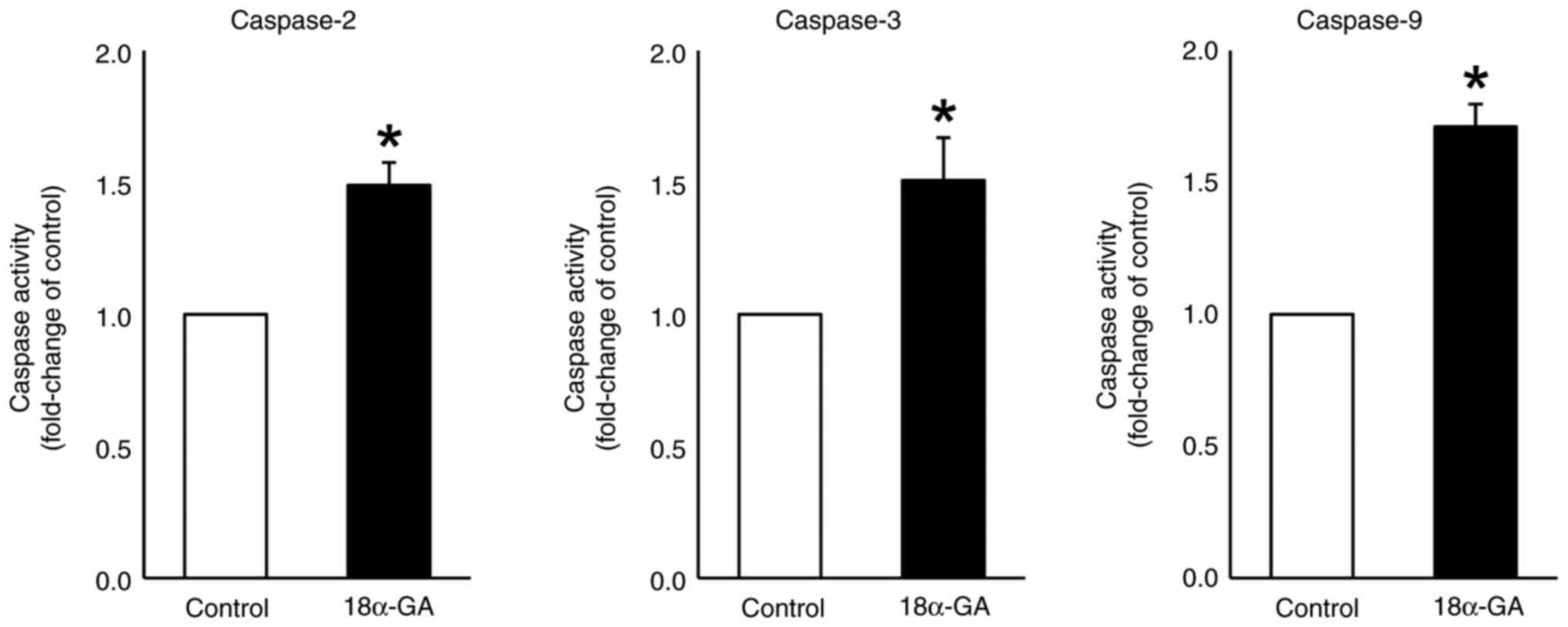
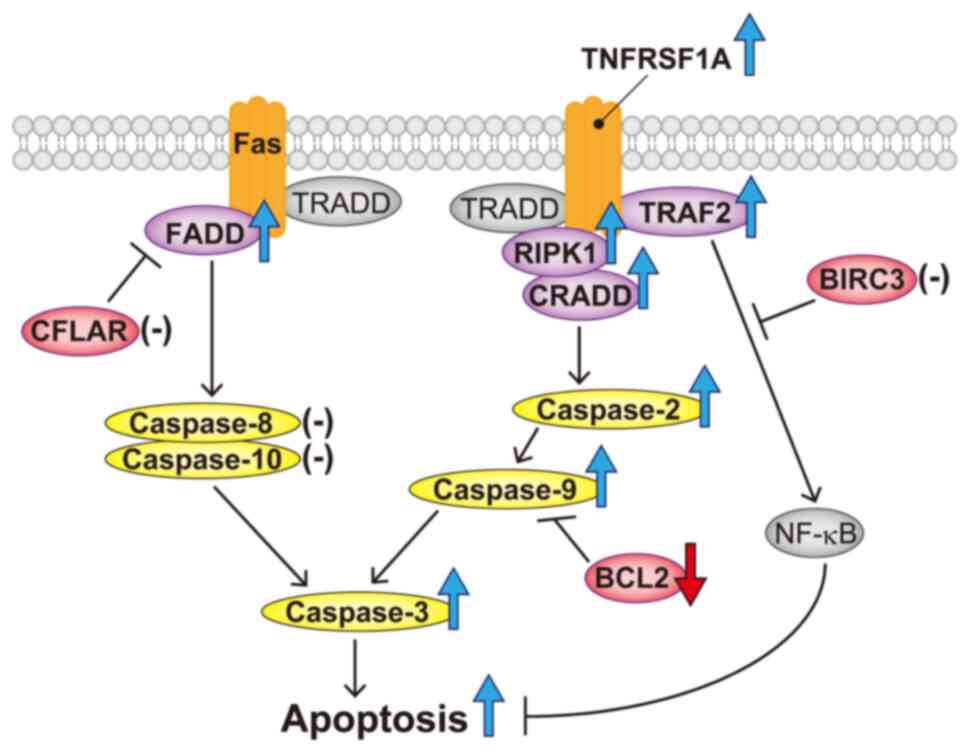
|
1
|
Takeuchi R: The effect of basic fibroblast
growth factor on cell cycle in human gingival fibroblasts from
nifedipine responder and non-responder. J Oral Sci. 46:37–44.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Takeuchi R, Matsumoto H, Okada H, Hori M,
Gunji A, Hakozaki K, Akimoto Y and Fujii A: Differences of cell
growth and cell cycle regulators induced by basic fibroblast growth
factor between nifedipine responders and non-responders. J
Pharmacol Sci. 103:168–174. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takeuchi R, Matsumoto H, Arikawa K,
Taguchi C, Nakayama R, Nasu I and Hiratsuka K: Phenytoin-induced
gingival overgrowth caused by death receptor pathway malfunction.
Oral Dis. 23:653–659. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nakib N and Ashrafi SS: Drug-induced
gingival overgrowth. Dis Mon. 57:225–230. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Corrêa JD, Queiroz-Junior CM, Costa JE,
Teixeira AL and Silva TA: Phenytoin-induced gingival overgrowth: A
review of the molecular, immune, and inflammatory features. ISRN
Dent. 2011(497850)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hassell TM and Hefti AF: Drug-induced
gingival overgrowth: Old problem, new problem. Crit Rev Oral Biol
Med. 2:103–137. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kato T, Okahashi N, Ohno T, Inaba H, Kawai
S and Amano A: Effect of phenytoin on collagen accumulation by
human gingival fibroblasts exposed to TNF-alpha in vitro. Oral Dis.
12:156–162. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bajkovec L, Mrzljak A, Likic R and Alajbeg
I: Drug-induced gingival overgrowth in cardiovascular patients.
World J Cardiol. 13:68–75. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Morikawa S, Nasu M, Miyashita Y and
Nakagawa T: Treatment of calcium channel blocker-induced gingival
overgrowth without modifying medication. BMJ Case Rep.
14(e238872)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hallmon WW and Rossmann JA: The role of
drugs in the pathogenesis of gingival overgrowth. A collective
review of current concepts. Periodontol 2000. 21:176–196.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Naruishi K: Biological roles of
fibroblasts in periodontal diseases. Cells. 11(3345)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Alikhani M, Alikhani Z and Graves DT:
Apoptotic effects of LPS on fibroblasts are indirectly mediated
through TNFR1. J Dent Res. 83:671–676. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shafer WG: Effect of dilantin sodium
analogues on cell proliferation in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp
Biol Med. 106:205–207. 1961.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Smith QT and Hinrichs JE: Phenytoin and
5-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenylhydantoin do not alter the effects of
bacterial and amplified plaque extracts on cultures of fibroblasts
from normal and overgrown gingivae. J Dent Res. 66:1393–1398.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Vernillo AT and Schwartz NB: The effects
of phenytoin (5,5-diphenylhydantoin) on human gingival fibroblasts
in culture. J Periodontal Res. 22:307–312. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vijayasingham SM, Dykes PJ and Marks R:
Phenytoin has little effect on in-vitro models of wound healing. Br
J Dermatol. 125:136–139. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Takeuchi R, Matsumoto H, Akimoto Y and
Fujii A: Inhibition of G1 cell cycle arrest in human gingival
fibroblasts exposed to phenytoin. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
28:114–119. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kantarci A, Augustin P, Firatli E, Sheff
MC, Hasturk H, Graves DT and Trackman PC: Apoptosis in gingival
overgrowth tissues. J Dent Res. 86:888–892. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jung JY, Jeong YJ, Jeong TS, Chung HJ and
Kim WJ: Inhibition of apoptotic signals in overgrowth of human
gingival fibroblasts by cyclosporin A treatment. Arch Oral Biol.
53:1042–1049. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Takeuchi R, Hiratsuka K, Arikawa K, Ono M,
Komiya M, Akimoto Y, Fujii A and Matsumoto H: Possible
pharmacotherapy for nifedipine-induced gingival overgrowth:
18a-glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits human gingival fibroblast growth.
Br J Pharmacol. 173:913–924. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ding Y, Brand E, Wang W and Zhao Z:
Licorice: Resources, applications in ancient and modern times. J
Ethnopharmacol. 298(115594)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Moustafa GO, Shalaby A, Naglah AM, Mounier
MM, El-Sayed H, Anwar MM and Nossier ES: Synthesis,
characterization, in vitro anticancer potentiality, and
antimicrobial activities of novel peptide-glycyrrhetinic-acid-based
derivatives. Molecules. 26(4573)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chu XT, de la Cruz J, Hwang SG and Hong H:
Tumorigenic effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals are
alleviated by licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) root extract through
suppression of AhR expression in mammalian cells. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:4809–4813. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Haku K, Muramatsu T, Hara A, Kikuchi A,
Hashimoto S, Inoue T and Shimono M: Epithelial cell rests of
Malassez modulate cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis
via gap junctional communication under mechanical stretching in
vitro. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 52:173–182. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tiboni M, Benedetti S, Skouras A, Curzi G,
Perinelli DR, Palmieri GF and Casettari L: 3D-printed microfluidic
chip for the preparation of glycyrrhetinic acid-loaded ethanolic
liposomes. Int J Pharm. 584(119436)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pirzadeh S, Fakhari S, Jalili A, Mirzai S,
Ghaderi B and Haghshenas V: Glycyrrhetinic acid induces apoptosis
in Leukemic HL60 cells through upregulating of CD95/CD178. Int J
Mol Cell Med. 3:272–278. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haghshenas V, Fakhari S, Mirzaie S,
Rahmani M, Farhadifar F, Pirzadeh S and Jalili A: Glycyrrhetinic
acid inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer
a2780 cells. Adv Pharm Bull. 4 (Suppl 1):S437–S441. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Takeuchi R, Matsumoto H, Akimoto Y and
Fujii A: Reduction in lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of
fibroblasts obtained from a patient with gingival overgrowth during
nifedipine-treatment. Arch Oral Biol. 56:1073–1080. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sano M, Ohuchi N, Inoue T, Tono K,
Tachikawa T, Kizawa Y and Murakami H: Proliferative response to
phenytoin and nifedipine in gingival fibroblasts cultured from
humans with gingival fibromatosis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
18:465–470. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mitic K, Popovska M, Pandilova M,
Jovanovic R, Spasovski G and Nikolov V: The role of inflammation
and apoptosis in cyclosporine A-induced gingival overgrowth. Bosn J
Basic Med Sci. 13:14–20. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ma Y, Cao W, Wang L, Jiang J, Nie H, Wang
B, Wei X and Ying W: Basal CD38/cyclic ADP-ribose-dependent
signaling mediates ATP release and survival of microglia by
modulating connexin 43 hemichannels. Glia. 62:943–955.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gottlieb TM and Oren M: p53 in growth
control and neoplasia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1287:77–102.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bulut S, Ozdemir BH, Alaaddinoĝlu EE,
Oduncuoĝlu FB, Bulut OE and Demirhan B: Effect of cyclosporin A on
apoptosis and expression of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in the gingiva
of renal transplant patients. J Periodontol. 76:691–695.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bulut S and Ozdemir BH: Apoptosis and
expression of caspase-3 in cyclosporin-induced gingival overgrowth.
J Periodontol. 78:2364–2368. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Das S, Shukla N, Singh SS, Kushwaha S and
Shrivastava R: Mechanism of interaction between autophagy and
apoptosis in cancer. Apoptosis. 26:512–533. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Feng S, Zha Z, Wang Z, Yang P, Wu J, Li X,
Xu Q and Liu Y: Anticancer activity of oleiferoside B involving
autophagy and apoptosis through increasing ROS release in MCF-7
cells and SMMC-7721 cells. Nat Prod Res. 35:4865–4869.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Peña-Blanco A and García-Sáez AJ: Bax, Bak
and beyond-mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J.
285:416–431. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Füllsack S, Rosenthal A, Wajant H and
Siegmund D: Redundant and receptor-specific activities of TRADD,
RIPK1 and FADD in death receptor signaling. Cell Death Dis.
10(122)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Green DR: The death receptor pathway of
apoptosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
14(a041053)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hsu H, Xiong J and Goeddel DV: The TNF
receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa
B activation. Cell. 81:495–504. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Grimm S, Stanger BZ and Leder P: RIP and
FADD: Two ‘death domain’-containing proteins can induce apoptosis
by convergent, but dissociable, pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:10923–10927. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wajant H: The Fas signaling pathway: More
than a paradigm. Science. 296:1635–1636. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Nikoletopoulou V, Markaki M, Palikaras K
and Tavernarakis N: Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and
autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3448–3459. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P,
Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C,
et al: Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP.
Nature. 388:190–195. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Palladino MA, Bahjat FR, Theodorakis EA
and Moldawer LL: Anti-TNF-alpha therapies: The next generation. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 2:736–46. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Maas C, Tromp JM, van Laar J, Thijssen R,
Elias JA, Malara A, Krippner-Heidenreich A, Silke J, van Oers MH
and Eldering E: CLL cells are resistant to smac mimetics because of
an inability to form a ripoptosome complex. Cell Death Dis.
4(e782)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gray CM, McCorkell KA, Chunduru SK,
McKinlay MA and May MJ: Negative feedback regulation of
NF-κB-inducing kinase is proteasome-dependent but does not require
cellular inhibitors of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
450:341–346. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Krumschnabel G, Sohm B, Bock F, Manzl C
and Villunger A: The enigma of caspase-2: The laymen's view. Cell
Death Differ. 16:195–207. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Werner AB, de Vries E, Tait SW, Bontjer I
and Borst J: Bcl-2 family member Bfl-1/A1 sequesters truncated bid
to inhibit its collaboration with pro-apoptotic Bak or Bax. J Biol
Chem. 277:22781–22788. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|