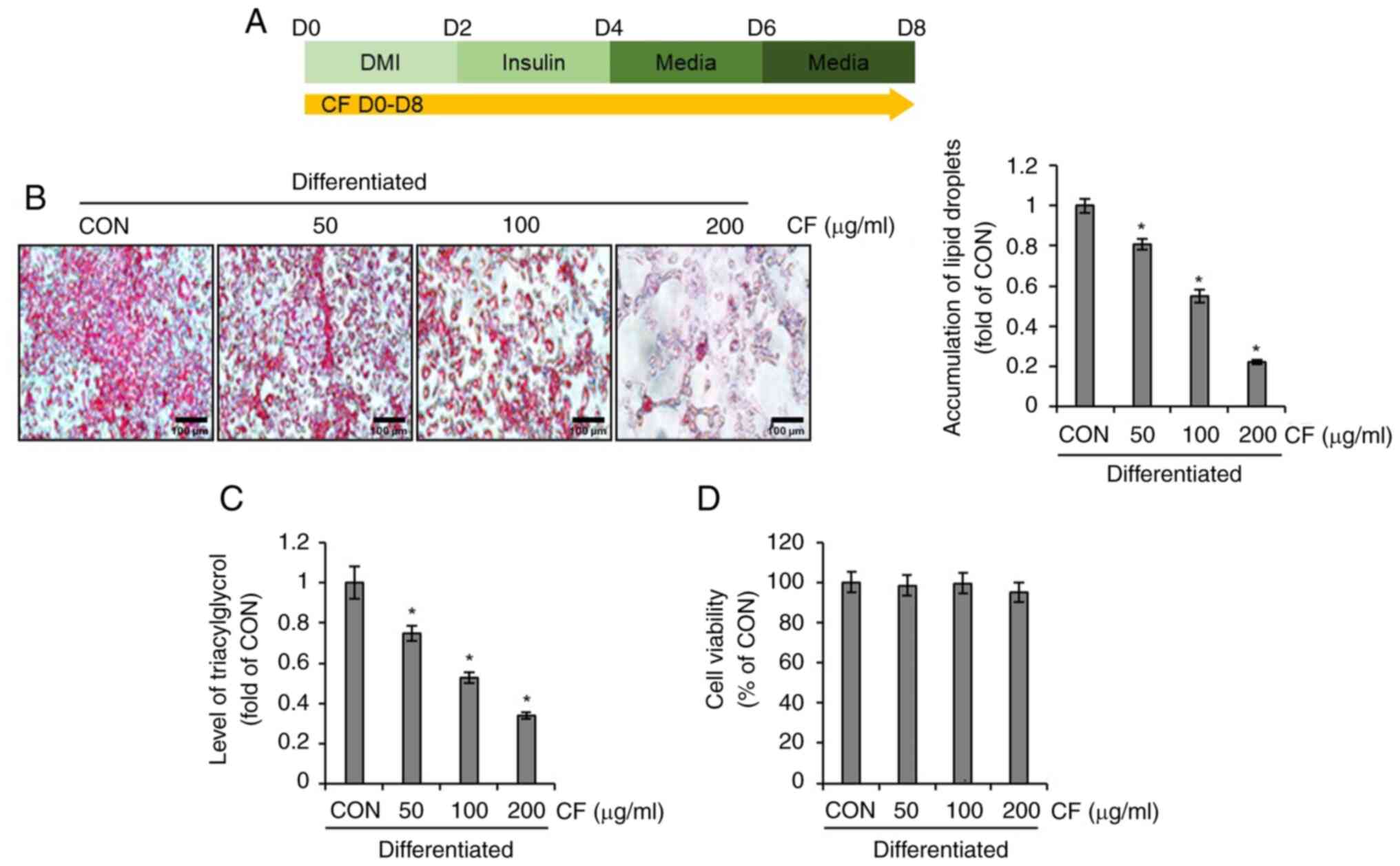
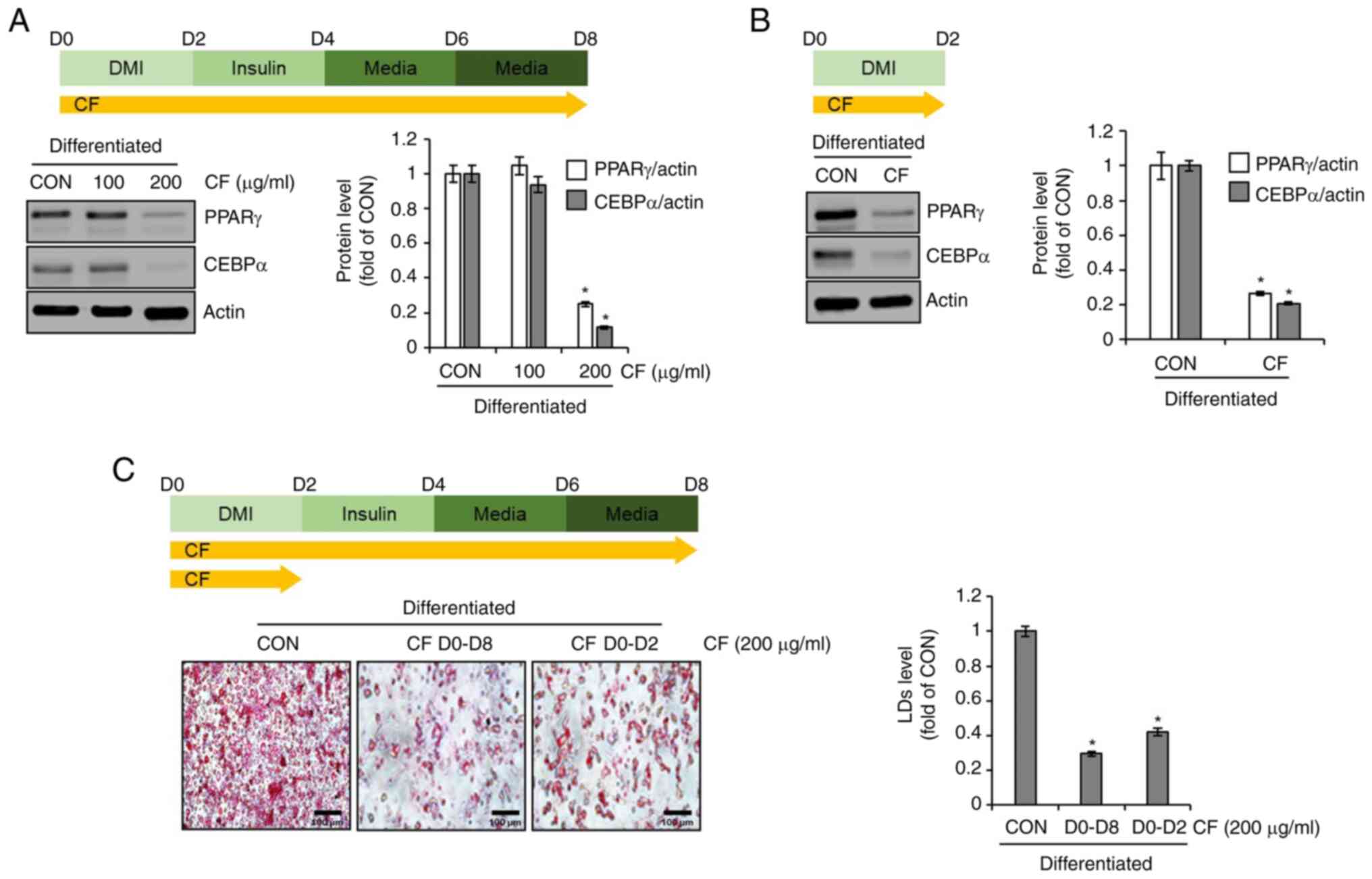
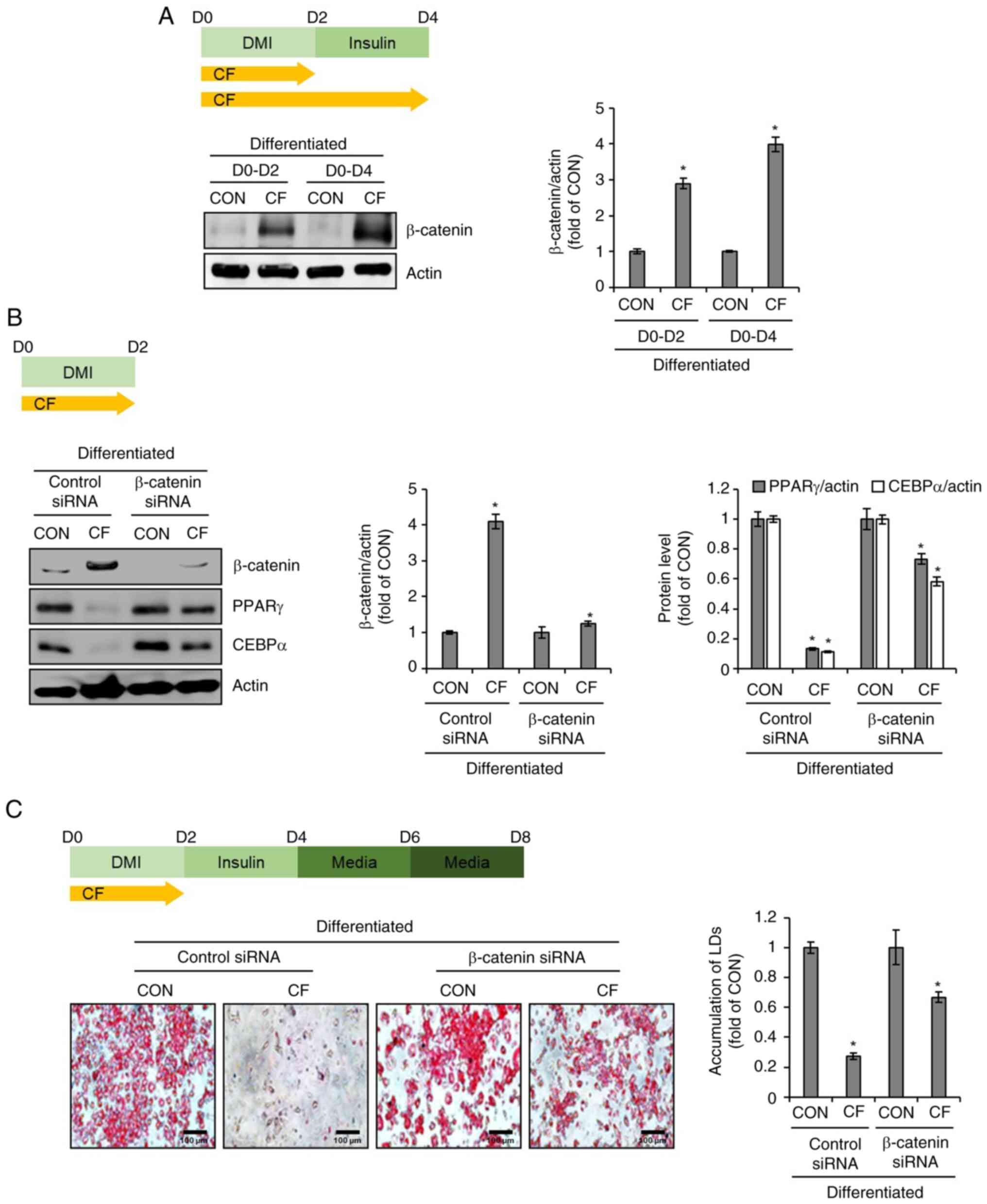
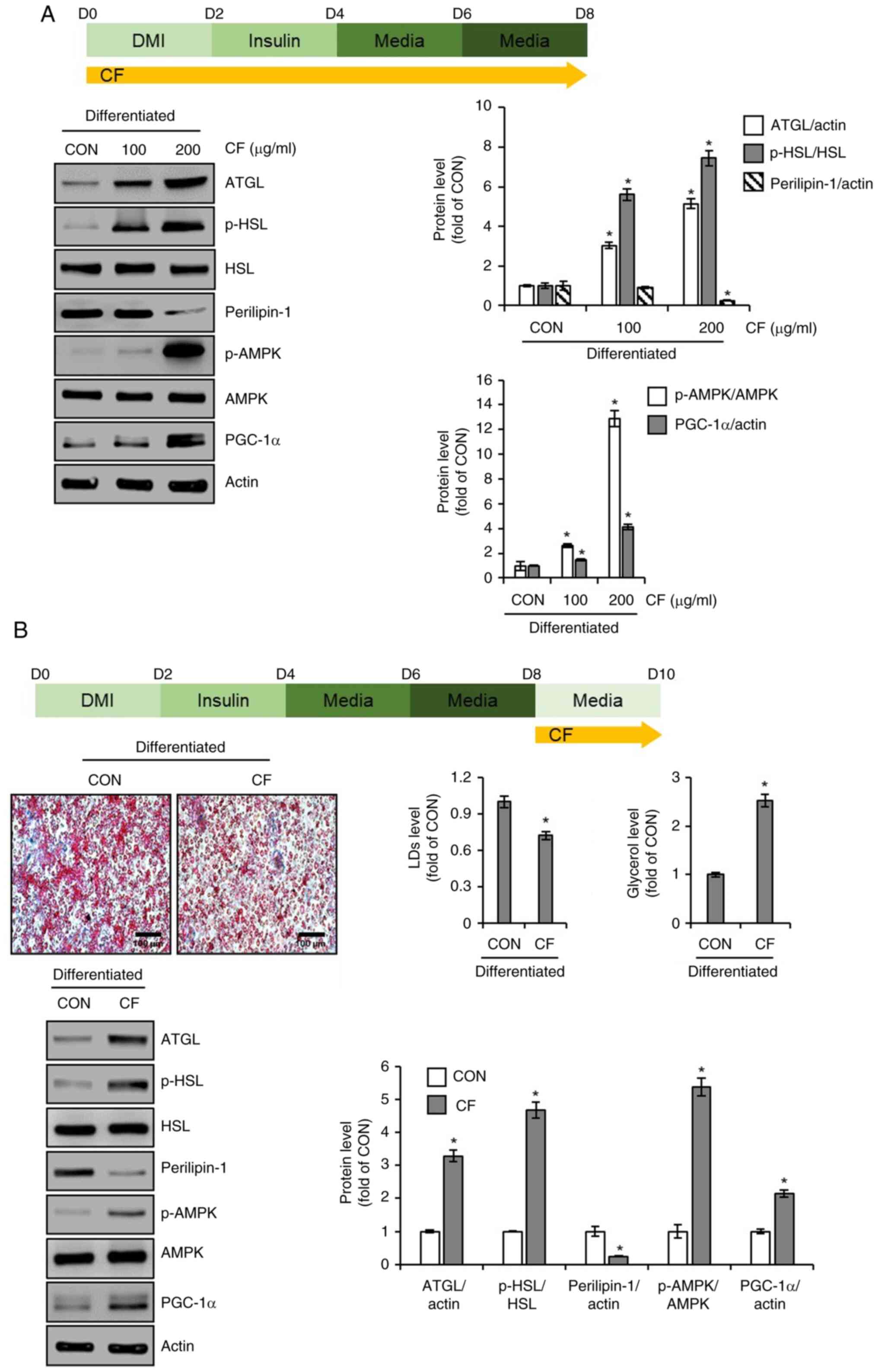
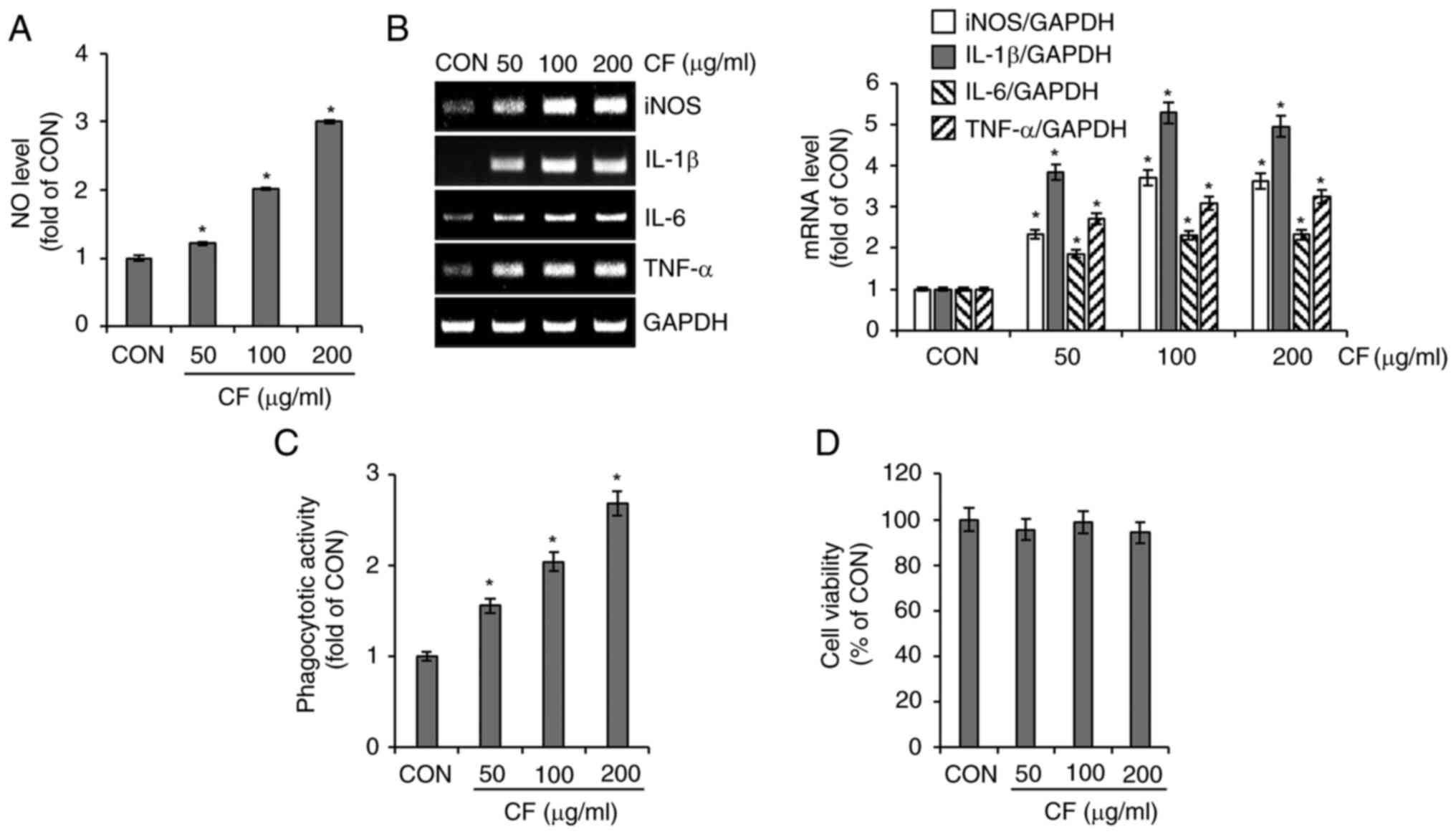
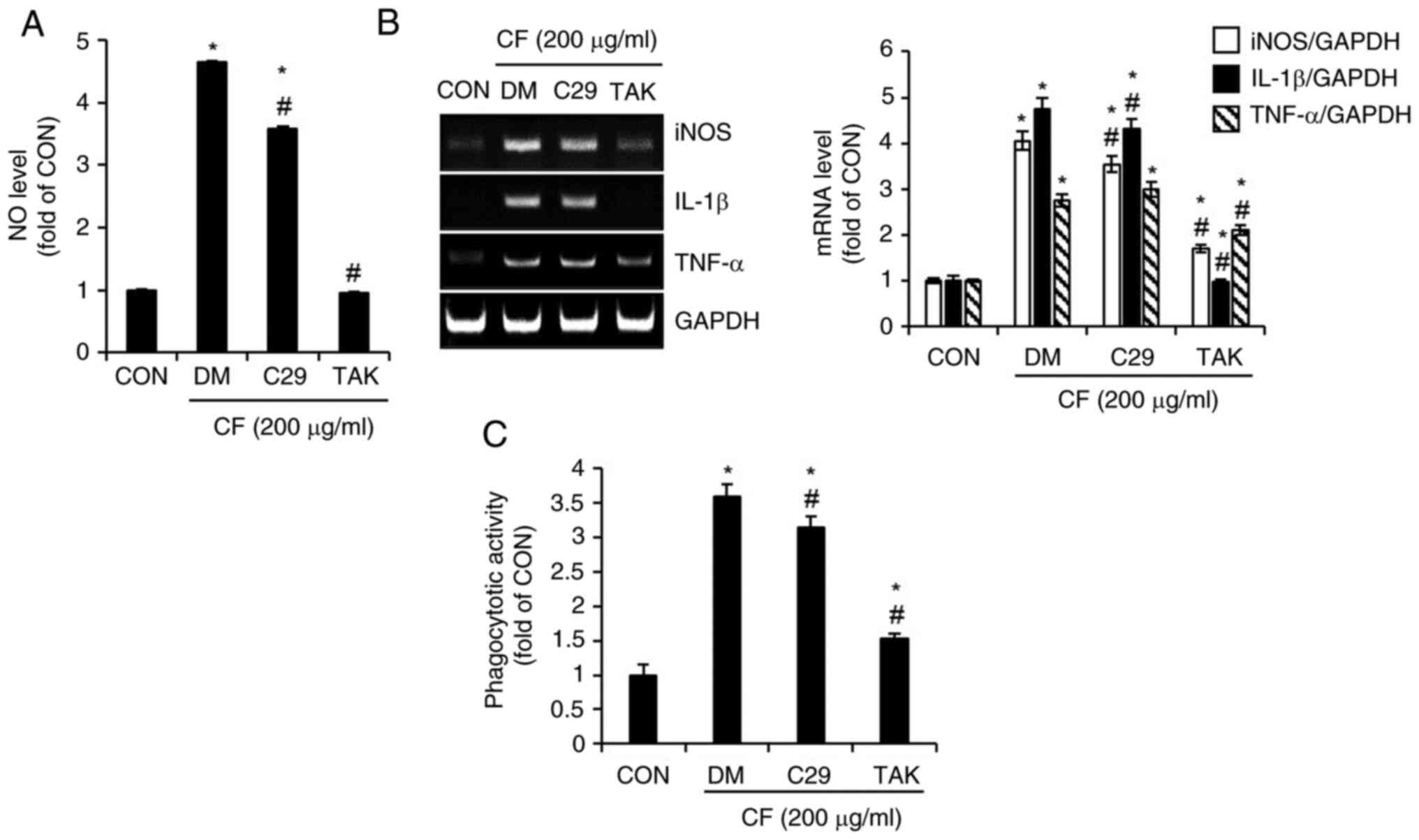
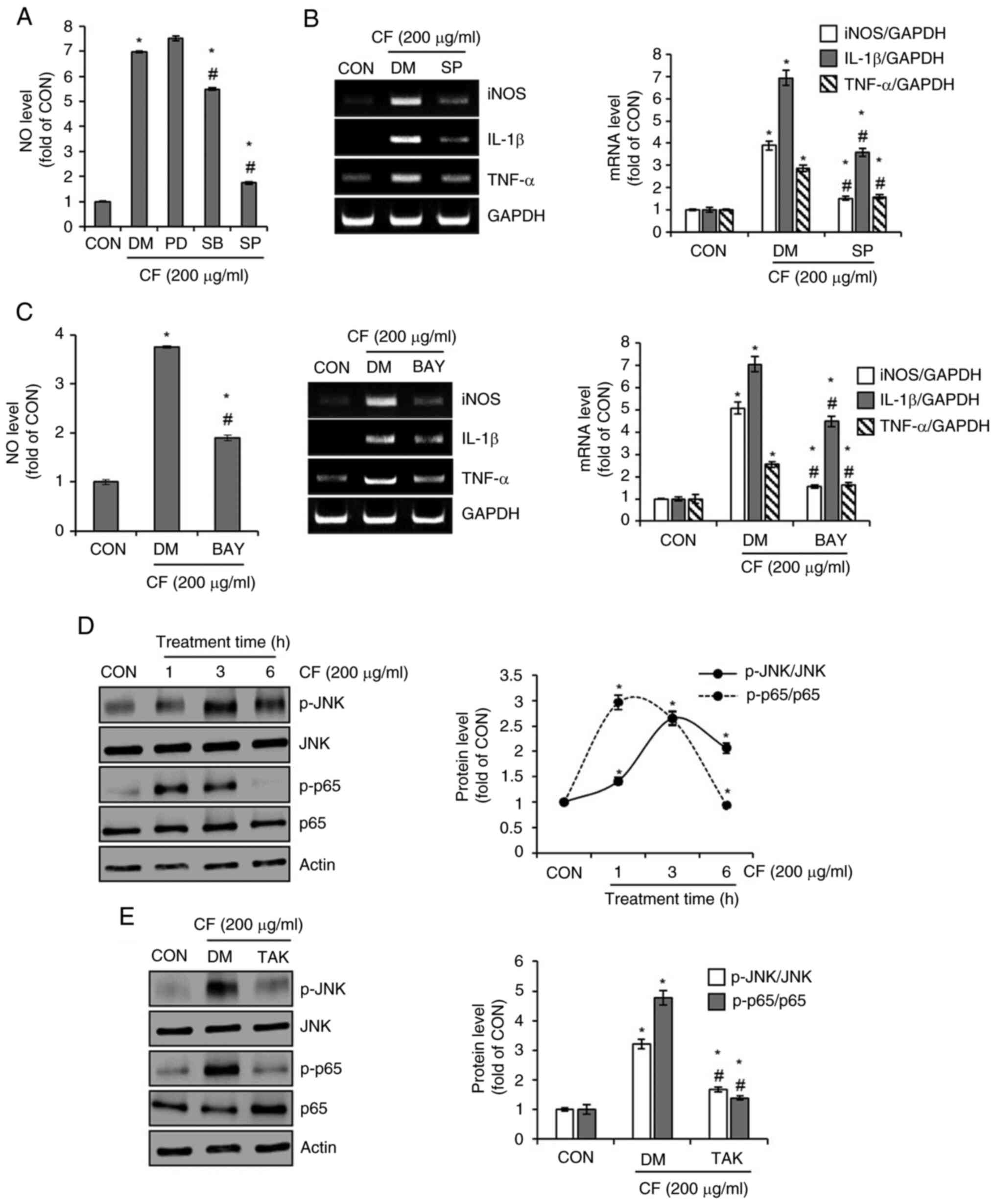
|
1
|
Jin H, Han H, Song G, Oh HJ and Lee BY:
Anti-obesity effects of GABA in C57BL/6J mice with high-fat
diet-induced obesity and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Sci.
25(995)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kang SA and Yu HS: Anti-obesity effects by
parasitic nematode (Trichinella spiralis) total lysates.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 13(1285584)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shi Q, Wang Y, Hao Q, Vandvik PO, Guyatt
G, Li J, Chen Z, Xu S, Shen Y, Ge L, et al: Pharmacotherapy for
adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 399:259–269.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huttunen R and Syrjänen J: Obesity and the
outcome of infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 10:442–443.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Muscogiuri G, Pugliese G, Laudisio D,
Castellucci B, Barrea L, Savastano S and Colao A: The impact of
obesity on immune response to infection: Plausible mechanisms and
outcomes. Obes Rev. 22(e13216)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nour TY and Altintaş KH: Effect of the
COVID-19 pandemic on obesity and its risk factors: A systematic
review. BMC Public Health. 23(1018)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tak YJ and Lee SY: Anti-obesity drugs:
Long-term efficacy and safety: An updated review. World J Mens
Health. 39:208–221. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sun NN, Wu TY and Chau CF: Natural dietary
and herbal products in anti-obesity treatment. Molecules.
21(1351)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yan WJ, Yang TG, Liao R, Wu ZH, Qin R and
Liu H: Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Chrysosplenium
macrophyllum and Chrysosplenium flagelliferum
(Saxifragaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 5:2040–2041.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Choi HA, Ahn SO, Lim HD and Kim GJ: Growth
suppression of a gingivitis and skin pathogen Cutibacterium
(Propionibacterium) acnes by medicinal plant extracts.
Antibiotics (Basel). 10(1092)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jakab J, Miškić B, Mikšić S, Juranić B,
Ćosić V, Schwarz D and Včev A: Adipogenesis as a potential
anti-obesity target: A review of pharmacological treatment and
natural products. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 14:67–83.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Madsen MS, Siersbaek R, Boergesen M,
Nielsen R and Mandrup S: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
γ and C/EBPα synergistically activate key metabolic adipocyte genes
by assisted loading. Mol Cell Biol. 34:939–954. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Barak Y, Nelson M, Ong E, Jones Y,
Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien K, Koder A and Evans R: PPAR gamma is required
for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell.
4:585–595. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rosen E, Sarraf P, Troy A, Bradwin G,
Moore K, Milstone D, Spiegelman B and Mortensen R: PPAR gamma is
required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in
vitro. Mol Cell. 4:611–617. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Duan SZ, Ivashchenko CY, Whitesall SE,
D'Alecy LG, Duquaine DC, Brosius FC III, Gonzalez F, Vinson C,
Pierre MA, Milstone DS and Mortensen RM: Hypotension,
lipodystrophy, and insulin resistance in generalized
PPARgamma-deficient mice rescued from embryonic lethality. J Clin
Invest. 117:812–822. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Imai T, Takakuwa R, Marchand S, Dentz E,
Bornert JM, Messaddeq N, Wendling O, Mark M, Desvergne B, Wahli W,
et al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is required
in mature white and brown adipocytes for their survival in the
mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4543–4547. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Linhart HG, Ishimura-Oka K, DeMayo F, Kibe
T, Repka D, Poindexter B, Bick RJ and Darlington GJ: C/EBPalpha is
required for differentiation of white, but not brown, adipose
tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:12532–12537. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang N, Finegold M, Bradley A, Ou C,
Abdelsayed S, Wilde M, Taylor L, Wilson D and Darlington G:
Impaired energy homeostasis in C/EBP alpha knockout mice. Science.
269:1108–1112. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Croniger C, Lekstrom-Himes J,
Zhang P, Fenyus M, Tenen D, Darlington G and Hanson R: Metabolic
response of mice to a postnatal ablation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein alpha. J Biol Chem. 280:38689–38699. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rosen E, Hsu CH, Wang X, Sakai S, Freeman
M, Gonzalez F and Spiegelman B: C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis
through PPARgamma: A unified pathway. Genes Dev. 16:22–26.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rosen ED and MacDougald OA: Adipocyte
differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
7:885–896. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chang E and Kim CY: Natural products and
obesity: A focus on the regulation of mitotic clonal expansion
during adipogenesis. Molecules. 24(1157)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang XD, Ge XC, Jiang SY and Yang YY:
Potential lipolytic regulators derived from natural products as
effective approaches to treat obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13(1000739)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Saponaro C, Gaggini M, Carli F and
Gastaldelli A: The subtle balance between lipolysis and
lipogenesis: A critical point in metabolic homeostasis. Nutrients.
7:9453–9474. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Song Z, Xiaoli AM and Yang F: Regulation
and metabolic significance of de novo lipogenesis in adipose
tissues. Nutrients. 10(1383)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Brejchova K, Radner FPW, Balas L,
Paluchova V, Cajka T, Chodounska H, Kudova E, Schratter M,
Schreiber R, Durand T, et al: Distinct roles of adipose
triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase in the catabolism
of triacylglycerol estolides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118(e2020999118)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mottillo EP and Granneman JG:
Intracellular fatty acids suppress β-adrenergic induction of
PKA-targeted gene expression in white adipocytes. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 301:E122–E131. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chakrabarti P, English T, Karki S, Qiang
L, Tao R, Kim J, Luo Z, Farmer SR and Kandror KV: SIRT1 controls
lipolysis in adipocytes via FOXO1-mediated expression of ATGL. J
Lipid Res. 52:1693–1701. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Barbato DL, Aquilano K, Baldelli S,
Cannata SM, Bernardini S, Rotilio G and Ciriolo MR: Proline
oxidase-adipose triglyceride lipase pathway restrains adipose cell
death and tissue inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 21:113–123.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Granneman JG, Moore HP, Krishnamoorthy R
and Rathod M: Perilipin controls lipolysis by regulating the
interactions of AB-hydrolase containing 5 (Abhd5) and adipose
triglyceride lipase (Atgl). J Biol Chem. 284:34538–34544.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Contreras GA, Strieder-Barboza C and
Raphael W: Adipose tissue lipolysis and remodeling during the
transition period of dairy cows. J Anim Sci Biotechnol.
8(41)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Straub BK, Stoeffel P, Heid H, Zimbelmann
R and Schirmacher P: Differential pattern of lipid
droplet-associated proteins and de novo perilipin expression in
hepatocyte teratogenesis. Hepatology. 47:1936–1946. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Temprano A, Sembongi H, Han GS, Sebastián
D, Capellades J, Moreno C, Guardiola J, Wabitsch M, Richart C,
Yanes O, et al: Redundant roles of the phosphatidate phosphatase
family in triacylglycerol synthesis in human adipocytes.
Diabetologia. 59:1985–1994. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shin H, Shi H, Xue B and Yu L: What
activates thermogenesis when lipid droplet lipolysis is absent in
brown adipocytes? Adipocyte. 7:143–147. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nguyen VTT, Vu VV and Pham PV: Brown
adipocyte and browning thermogenesis: Metabolic crosstalk beyond
mitochondrial limits and physiological impacts. Adipocytes.
12(2237164)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Van der Vaart JI, Boon MR and Houtkooper
RH: The role of AMPK signaling in brown adipose tissue activation.
Cells. 10(1122)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gulyaeva O, Dempersmier J and Sul HS:
Genetic and epigenetic control of adipose development. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1864:3–12. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hirayama D, Iida T and Nakase H: The
phagocytic function of macrophage-enforcing innate immunity and
tissue homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 19(92)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Navegantes KC, de Souza Gomes R, Pereira
PAT, Czaikoski PG, Azevedo CHM and Monteiro MC: Immune modulation
of some autoimmune diseases: The critical role of macrophages and
neutrophils in the innate and adaptive immunity. J Transl Med.
15(36)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lagos LS, Luu TV, De Haan B, Faas M and De
Vos P: TLR2 and TLR4 activity in monocytes and macrophages after
exposure to amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline and
erythromycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 77:2972–2983. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu J, Mo J, Xiang W, Shi X, Guo L, Li Y,
Bao Y and Zheng L: Immunoregulatory effects of Tetrastigma
hemsleyanum polysaccharide via TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK
signaling pathways in Raw264.7 macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother.
161(114471)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|