|
1
|
GBD Spinal Cord Injuries Collaborators.
Global, regional, and national burden of spinal cord injury,
1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 22:1026–1047. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shang FF, Zhao W, Zhao Q, Liu J, Li DW,
Zhang H, Zhou XF, Li CY and Wang TH: Upregulation of eIF-5A1 in the
paralyzed muscle after spinal cord transection associates with
spontaneous hindlimb locomotor recovery in rats by upregulation of
the ErbB, MAPK and neurotrophin signal pathways. J Proteomics.
91:188–199. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu W, Shang FF, Xu Y, Belegu V, Xia L,
Zhao W, Liu R, Wang W, Liu J, Li CY and Wang TH: eIF5A1/RhoGDIα
pathway: A novel therapeutic target for treatment of spinal cord
injury identified by a proteomics approach. Sci Rep.
5(16911)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zheng Q, Lin R, Wang D, Zheng C and Xu W:
Effects of circulating inflammatory proteins on spinal degenerative
diseases: Evidence from genetic correlations and Mendelian
randomization study. JOR Spine. 7(e1346)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shang FF, Xia QJ, Liu W, Xia L, Qian BJ,
You L, He M, Yang JL and Wang TH: miR-434-3p and DNA
hypomethylation co-regulate eIF5A1 to increase AChRs and to improve
plasticity in SCT rat skeletal muscle. Sci Rep.
6(22884)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Varma AK, Das A, Wallace G IV, Barry J,
Vertegel AA, Ray SK and Banik NL: Spinal cord injury: A review of
current therapy, future treatments, and basic science frontiers.
Neurochem Res. 38:895–905. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fujieda Y, Ueno S, Ogino R, Kuroda M,
Jönsson TJ, Guo L, Bamba T and Fukusaki E: Metabolite profiles
correlate closely with neurobehavioral function in experimental
spinal cord injury in rats. PLoS One. 7(e43152)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Peng J, Zeng J, Cai B, Yang H, Cohen MJ,
Chen W, Sun MW, Lu CD and Jiang H: Establishment of quantitative
severity evaluation model for spinal cord injury by metabolomic
fingerprinting. PLoS One. 9(e93736)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Baker SA and Rutter J: Metabolites as
signalling molecules. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:355–374.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gorgey AS, Dolbow DR, Dolbow JD, Khalil
RK, Castillo C and Gater DR: Effects of spinal cord injury on body
composition and metabolic profile - part I. J Spinal Cord Med.
37:693–702. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Alexandrov T: Spatial metabolomics: From a
niche field towards a driver of innovation. Nat Metab. 5:1443–1445.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Arifin WN and Zahiruddin WM: Sample size
calculation in animal studies using resource equation approach.
Malays J Med Sci. 24:101–105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Scheff SW, Saucier DA and Cain ME: A
statistical method for analyzing rating scale data: The BBB
locomotor score. J Neurotrauma. 19:1251–1260. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bemis KA, Föll MC, Guo D, Lakkimsetty SS
and Vitek O: Cardinal v. 3: A versatile open-source software for
mass spectrometry imaging analysis. Nat Methods. 20:1883–1886.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Triba MN, Le Moyec L, Amathieu R, Goossens
C, Bouchemal N, Nahon P, Rutledge DN and Savarin P: PLS/OPLS models
in metabolomics: The impact of permutation of dataset rows on the
K-fold cross-validation quality parameters. Mol Biosyst. 11:13–19.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen X, Shu W, Zhao L and Wan J: Advanced
mass spectrometric and spectroscopic methods coupled with machine
learning for in vitro diagnosis. View. 4(20220038)2023.
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Hu A, Chen X, Shen F, Zhang L,
Lin Y and Shen H: Pan-targeted quantification of deep and
comprehensive cancer serum proteome improves cancer detection.
View. 4(20220039)2023.
|
|
18
|
Cao J, Yao QJ, Wu J, Chen X, Huang L, Liu
W, Qian K, Wan JJ and Zhou BO: Deciphering the metabolic
heterogeneity of hematopoietic stem cells with single-cell
resolution. Cell Metab. 36:209–221.e6. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Li Z, Cao G, Tang L, Zhou R, Li C,
Zhang J, Wu H, Li X and Yang H: Targeted energy metabolomics
combined with spatial metabolomics study on the efficacy of guhong
injection against cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Mol Neurobiol.
60:5533–5547. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Santos AA, Delgado TC, Marques V,
Ramirez-Moncayo C, Alonso C, Vidal-Puig A, Hall Z, Martínez-Chantar
ML and Rodrigues CMP: Spatial metabolomics and its application in
the liver. Hepatology. 79:1158–1179. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Young LEA, Conroy LR, Clarke HA, Hawkinson
TR, Bolton KE, Sanders WC, Chang JE, Webb MB, Alilain WJ, Vander
Kooi CW, et al: In situ mass spectrometry imaging reveals
heterogeneous glycogen stores in human normal and cancerous
tissues. EMBO Mol Med. 14(e16029)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zheng Q, Wang D, Lin R, Li Z, Chen Y, Chen
R, Zheng C and Xu W: Effects of circulating inflammatory proteins
on osteoporosis and fractures: Evidence from genetic correlation
and Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
15(1386556)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Afjehi-Sadat L, Brejnikow M, Kang SU,
Vishwanath V, Walder N, Herkner K, Redl H and Lubec G: Differential
protein levels and post-translational modifications in spinal cord
injury of the rat. J Proteome Res. 9:1591–1597. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Di Giulio F, Castellini C, Palazzi S,
Tienforti D, Antolini F, Felzani G, Baroni MG and Barbonetti A:
Correlates of metabolic syndrome in people with chronic spinal cord
injury. J Endocrinol Invest. 47:2097–2105. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim D, Zai L, Liang P, Schaffling C,
Ahlborn D and Benowitz LI: Inosine enhances axon sprouting and
motor recovery after spinal cord injury. PLoS One.
8(e81948)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
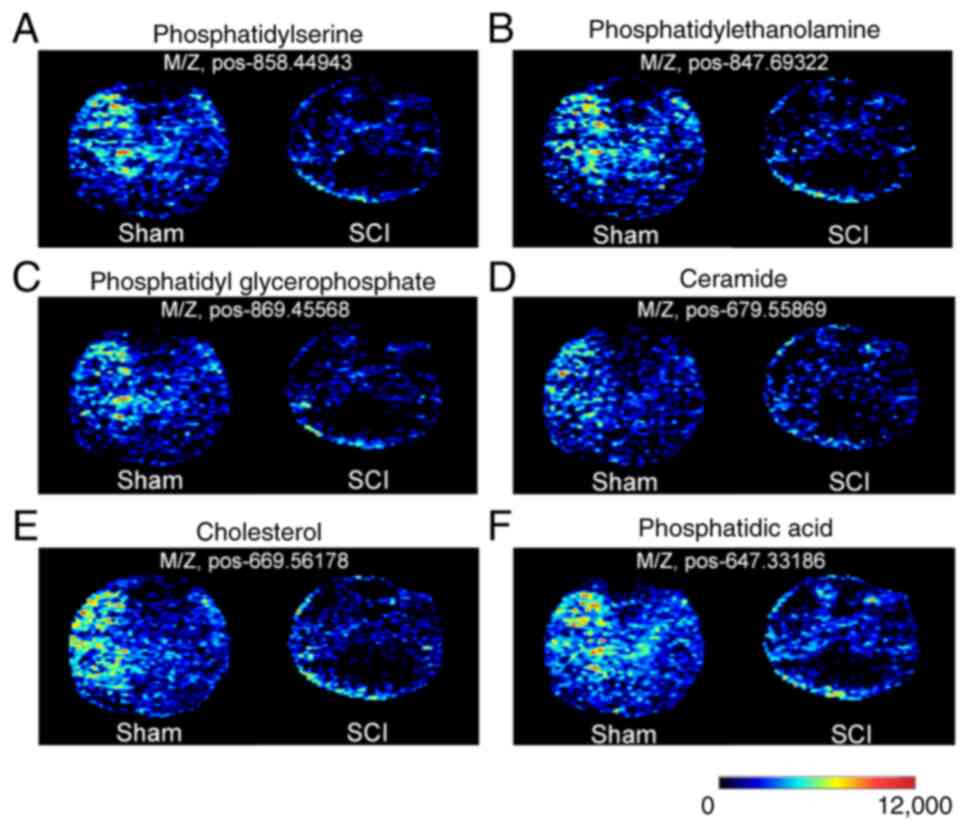
Ma X, Li X, Wang W, Zhang M, Yang B and
Miao Z: Phosphatidylserine, inflammation, and central nervous
system diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 14(975176)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
De SR, Ajmone-Cat MA, Nicolini A and
Minghetti L: Expression of phosphatidylserine receptor and
down-regulation of pro-inflammatory molecule production by its
natural ligand in rat microglial cultures. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 61:237–244. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lukacova N, Halát G, Chavko M and Marsala
J: Ischemia-reperfusion injury in the spinal cord of rabbits
strongly enhances lipid peroxidation and modifies phospholipid
profiles. Neurochem Res. 21:869–873. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Vance JE and Tasseva G: Formation and
function of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in
mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:543–554.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hao T, Fang W, Xu D, Chen Q, Liu Q, Cui K,
Cao X, Li Y, Mai K and Ai Q: Phosphatidylethanolamine alleviates
OX-LDL-induced macrophage inflammation by upregulating autophagy
and inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome activation. Free Radic Biol Med.
208:402–417. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim W, Cho SB, Jung HY, Yoo DY, Oh JK,
Choi GM, Cho TG, Kim DW, Hwang IK, Choi SY and Moon SM:
Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 ameliorates
ischemia-induced inflammation and neuronal damage in the rabbit
spinal cord. Cells. 8(1370)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tall AR and Yvan-Charvet L: Cholesterol,
inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:104–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Syed MUS, Khan Z, Zulfiqar A, Basham MA,
Abdul Haseeb H, Azizullah S, Ismail H, Elbahnasawy M, Nadeem Z and
Karimi S: Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with
spinal cord injury with deranged lipid profile. Cureus.
13(e18246)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Arana L, Gangoiti P, Ouro A, Trueba M and
Gómez-Muñoz A: Ceramide and ceramide 1-phosphate in health and
disease. Lipids Health Dis. 9(15)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cuzzocrea S, Deigner HP, Genovese T,
Mazzon E, Esposito E, Crisafulli C, Di Paola R, Bramanti P,
Matuschak G and Salvemini D: Inhibition of ceramide biosynthesis
ameliorates pathological consequences of spinal cord injury. Shock.
31:634–644. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu F, You SW, Yao LP, Liu HL, Jiao XY,
Shi M, Zhao QB and Ju G: Secondary degeneration reduced by inosine
after spinal cord injury in rats. Spinal Cord. 44:421–426.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hu X, Huang J, Li Z, Li J, Ouyang F, Chen
Z, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang J, Yu S, et al: Lactate promotes microglial
scar formation and facilitates locomotor function recovery by
enhancing histone H4 lysine 12 lactylation after spinal cord
injury. J Neuroinflammation. 21(193)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang J, Zhang H, Zhang J, Yu H, Lin Z and
Cai Y: Spermidine exhibits protective effects against traumatic
brain injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 40:927–937. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Watanabe M, Fujimura Y, Nakamura M, Yato
Y, Ohta K, Okai H and Ogawa Y: Changes of amino acid levels and
aspartate distribution in the cervical spinal cord after traumatic
spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 15:285–293. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Erens C, Van Broeckhoven J, Bronckaers A,
Lemmens S and Hendrix S: The dark side of an essential amino acid:
L-Arginine in spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 40:820–832.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang Y and Qian T:
Inflammatory response to spinal cord injury and its treatment.
World Neurosurg. 155:19–31. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|