|
1
|
Sun EW, de Fontgalland D, Rabbitt P,
Hollington P, Sposato L, Due SL, Wattchow DA, Rayner CK, Deane AM,
Young RL and Keating DJ: Mechanisms controlling Glucose-induced
GLP-1 secretion in human small intestine. Diabetes. 66:2144–2149.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Deacon CF: Physiology and pharmacology of
DPP-4 in glucose homeostasis and the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10(80)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Regmi D, Al-Shamsi S, Govender RD and Al
Kaabi J: Incidence and risk factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in
an overweight and obese population: A long-term retrospective
cohort study from a Gulf state. BMJ Open.
10(e035813)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ying Z, van Eenige R, Ge X, van Marwijk C,
Lambooij JM, Guigas B, Giera M, de Boer JF, Coskun T, Qu H, et al:
Combined GIP receptor and GLP1 receptor agonism attenuates NAFLD in
male APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. EBioMedicine.
93(104684)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tomas E and Habener JF: Insulin-like
actions of Glucagon-like peptide-1: A dual receptor hypothesis.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:59–67. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rubio C, Puerto M, García-Rodríquez JJ, Lu
VB, García-Martínez I, Alén R, Sanmartín-Salinas P, Toledo-Lobo MV,
Saiz J, Ruperez J, et al: Impact of global PTP1B deficiency on the
gut barrier permeability during NASH in mice. Mol Metab.
35(100954)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ji W, Chen X, Lv J, Wang M, Ren S, Yuan B,
Wang B and Chen L: Liraglutide exerts antidiabetic effect via PTP1B
and PI3K/Akt2 signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of KKAy Mice.
Int J Endocrinol. 2014(312452)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Cui W and Silverstein RL:
CD36, a signaling receptor and fatty acid transporter that
regulates immune cell metabolism and fate. J Exp Med.
219(e20211314)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Alkhatatbeh MJ, Enjeti AK, Acharya S,
Thorne RF and Lincz LF: The origin of circulating CD36 in type 2
diabetes. Nutr Diabetes. 3(e59)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Handberg A, Norberg M, Stenlund H,
Hallmans G, Attermann J and Eriksson JW: Soluble CD36 (sCD36)
clusters with markers of insulin resistance, and high sCD36 is
associated with increased type 2 diabetes risk. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 95:1939–1946. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Handberg A, Levin K, Højlund K and
Beck-Nielsen H: Identification of the oxidized Low-density
lipoprotein scavenger receptor CD36 in plasma. Circulation.
114:1169–1176. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shibao CA, Celedonio JE, Tamboli R, Sidani
R, Love-Gregory L, Pietka T, Xiong Y, Wei Y, Abumrad NN, Abumrad NA
and Flynn CR: CD36 Modulates fasting and preabsorptive hormone and
bile acid levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 103:1856–1866.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Adam TCM and Westerterp-Plantenga MS:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 release and satiety after a nutrient
challenge in normal-weight and obese subjects. Br J Nutr.
93:845–851. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sell H, Blüher M, Klöting N, Schlich R,
Willems M, Ruppe F, Knoefel WT, Dietrich A, Fielding BA, Arner P,
et al: Adipose Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and Obesity: Correlation with
insulin resistance and depot-specific release from adipose tissue
in vivo and in vitro. Diabetes Care. 36:4083–4090. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bonen A, Tandon NN, Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP
and Heigenhauser GJF: The fatty acid transporter FAT/CD36 is
upregulated in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissues in human
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes (Lond). 30:877–883.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Elchebly M, Payette P, Michaliszyn E,
Cromlish W, Collins S, Loy AL, Normandin D, Cheng A, Himms-Hagen J,
Chan CC, et al: Increased insulin sensitivity and obesity
resistance in mice lacking the protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B
gene. Science. 283:1544–1548. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fang Y, Zhang J, Ji L, Zhu C, Xiao Y, Gao
Q, Song W and Wei L: GLP1R rs3765467 Polymorphism is associated
with the risk of early onset type 2 diabetes. Int J Endocrinol.
2023(8729242)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dorsey-Trevino EG, Kaur V, Mercader JM,
Florez JC and Leong A: Association of GLP1R polymorphisms with the
incretin response. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 107:2580–2588.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bhargave A, Devi K, Ahmad I, Yadav A and
Gupta R: Genetic variation in DPP-IV gene linked to predisposition
of T2DM: A case control study. J Diabetes Metab Disord.
21:1709–1716. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
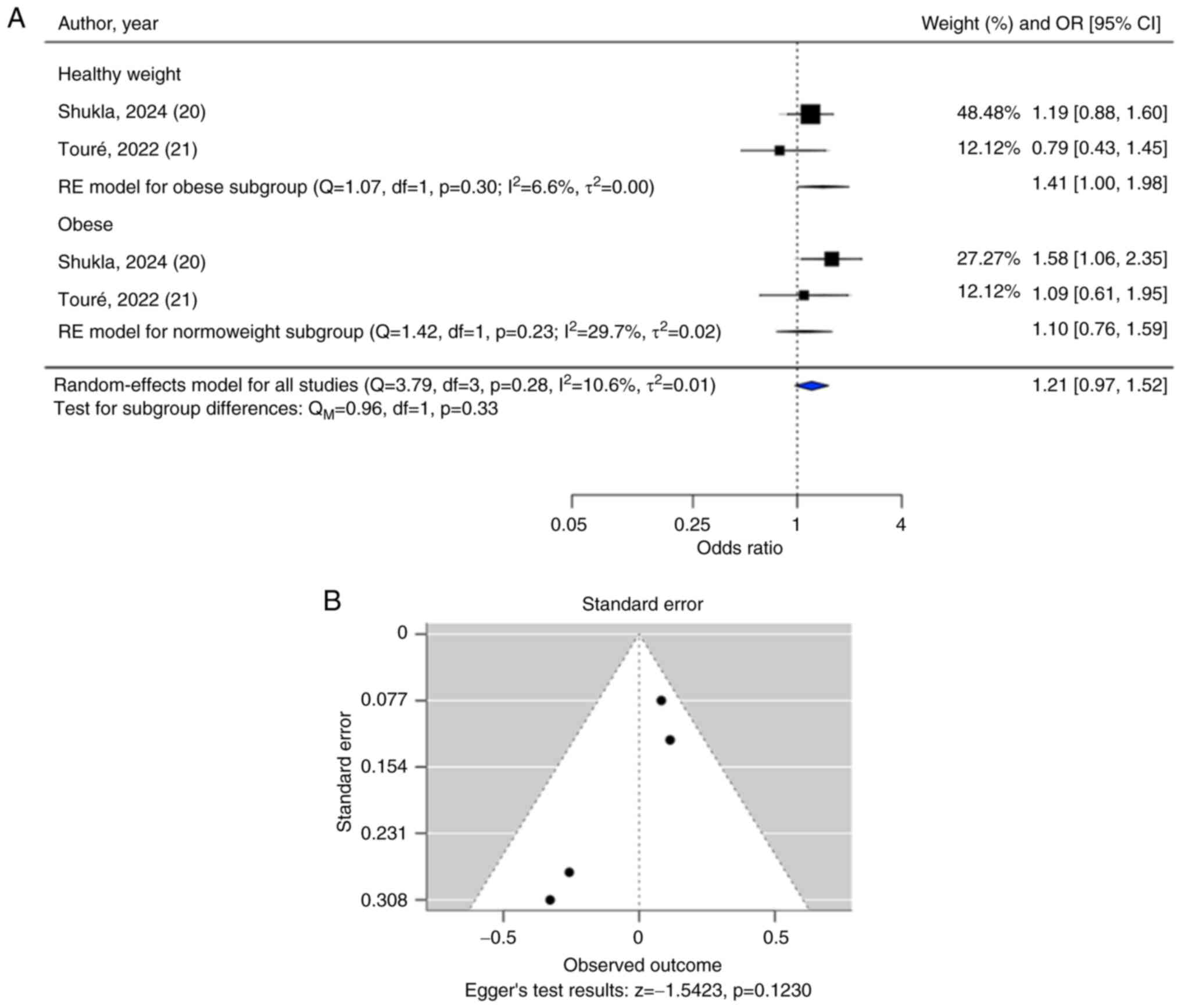
20
|
Shukla AK, Shamsad A, Kushwah AS, Singh S,
Usman K and Banerjee M: CD36 gene variant rs1761667(G/A) as a
biomarker in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus cases. Egypt J Med Hum
Genet. 25(9)2024.
|
|
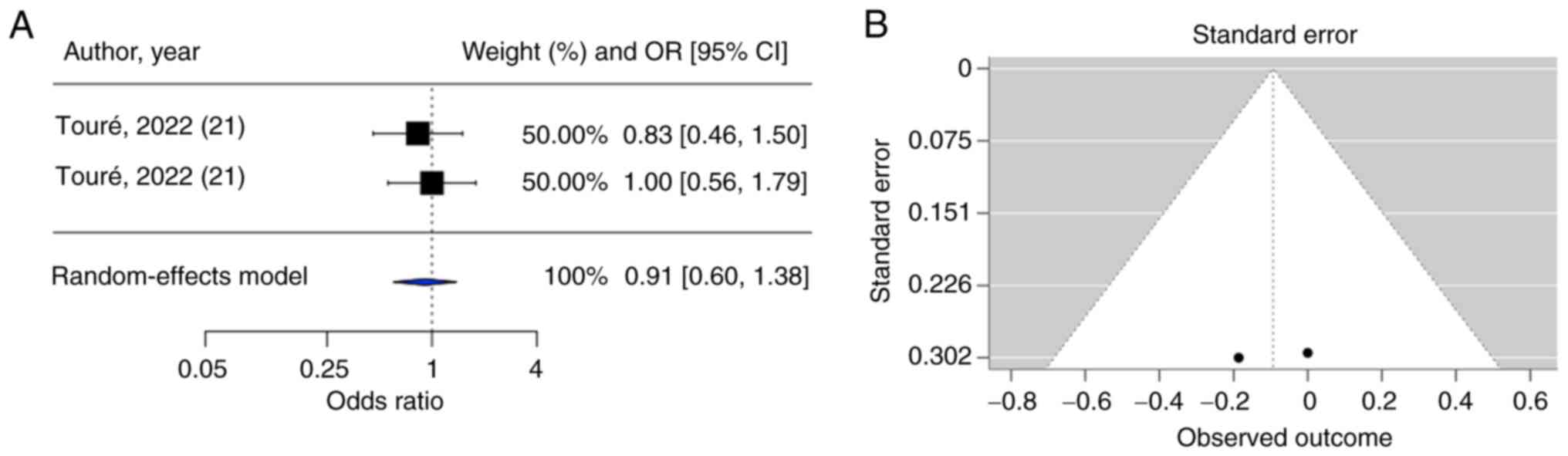
21
|
Touré M, Hichami A, Sayed A, Suliman M,
Samb A and Khan NA: Association between polymorphisms and
hypermethylation of CD36 gene in obese and obese diabetic
Senegalese females. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 14(117)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bento JL, Palmer ND, Mychaleckyj JC, Lange
LA, Langefeld CD, Rich SS, Freedman BI and Bowden DW: Association
of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B gene polymorphisms with type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 53:3007–3012. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Meshkani R, Taghikhani M, Al-Kateb H,
Larijani B, Khatami S, Sidiropoulos GK, Hegele RA and Adeli K:
Polymorphisms within the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTPN1)
gene promoter: Functional characterization and association with
type 2 diabetes and related metabolic traits. Clin Chem.
53:1585–1592. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lefebvre C, Manheimer E and Glanville J:
Searching for Studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews
of Interventions (eds J.P. Higgins and S. Green), 2008. Available
from: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.ch6.
|
|
25
|
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z and
Elmagarmid A: Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews.
Syst Rev. 5(210)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li T, Higgins JPT and Deeks JJ: Chapter 5:
Collecting data. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of
Interventions version 6.5. Cochrane, 2024. Higgins JPT, Thomas J,
Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA (eds). Available
from https://cochrane.org/handbook.
|
|
27
|
Sohani ZN, Sarma S, Alyass A, de Souza RJ,
Robiou-du-Pont S, Li A, Mayhew A, Yazdi F, Reddon H, Lamri A, et
al: Empirical evaluation of the Q-Genie tool: A protocol for
assessment of effectiveness. BMJ Open. 6(e010403)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Page MJ, Sterne JAC, Boutron I,
Hróbjartsson A, Kirkham JJ, Li T, Lundh A, Mayo-Wilson E, McKenzie
JE, Stewart LA, et al: ROB-ME: A tool for assessing risk of bias
due to missing evidence in systematic reviews with meta-analysis.
BMJ. 383(e076754)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Little J, Higgins JPT, Ioannidis JPA,
Moher D, Gagnon F, von Elm E, Khoury MJ, Cohen B, Davey-Smith G,
Grimshaw J, et al: STrengthening the REporting of Genetic
Association Studies (STREGA)-an extension of the STROBE statement.
Genet Epidemiol. 33:581–598. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mahanani M, Susilawati T, Wibowo Y and
Indarto D: The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus and
metabolic-related gene polymorphism. Available from: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024531067,
PROSPERO 2024.
|
|
31
|
Jackson D, Law M, Stijnen T, Viechtbauer W
and White IR: A comparison of seven Random-effects models for
meta-analyses that estimate the summary odds Ratio. In: Statistics
in Medicine. Wiley Online Library, 2018.
|
|
32
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Willis BH and Riley RD: Measuring the
statistical validity of summary meta-analysis and meta-regression
results for use in clinical practice. Stat Med. 36:3283–3301.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Viechtbauer W: Conducting Meta-analyses in
R with the metafor package. J Stati Software. 36:1–48. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ahmed RH, Huri HZ, Al-Hamodi Z, Salem SD,
Al-Absi B and Muniandy S: Association of DPP4 gene polymorphisms
with type 2 diabetes mellitus in malaysian subjects. PLoS One.
11(e0154369)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Alves ES, Tonet-Furioso AC, Alves VP,
Moraes CF, Pérez DIV, Bastos IMD, Córdova C and Nóbrega OT: A
haplotype in the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 gene impacts
glycemic-related traits of Brazilian older adults. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 55(e12148)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wanic K, Malecki MT, Klupa T, Warram JH,
Sieradzki J and Krolewski AS: Lack of association between
polymorphisms in the gene encoding protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
(PTPN1) and risk of Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 24:650–655.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bodhini D, Radha V, Ghosh S, Majumder PP
and Mohan V: Lack of association of PTPN1 gene polymorphisms with
type 2 diabetes in south Indians. J Genet. 90:323–326.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Corpeleijn E, Van Der Kallen CJH,
Kruijshoop M, Magagnin MG, de Bruin TW, Feskens EJ, Saris WH and
Blaak EE: Direct association of a promoter polymorphism in the
CD36/FAT fatty acid transporter gene with Type 2 diabetes mellitus
and insulin resistance. Diabet Med. 23:907–911. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Echwald SM, Bach H, Vestergaard H,
Richelsen B, Kristensen K, Drivsholm T, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T
and Pedersen O: A P387L variant in protein tyrosine Phosphatase-1B
(PTP-1B) is associated with type 2 diabetes and impaired serine
phosphorylation of PTP-1B in vitro. Diabetes. 51:1–6.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Florez JC, Agapakis CM, Burtt NP, Sun M,
Almgren P, Råstam L, Tuomi T, Gaudet D, Hudson TJ, Daly MJ, et al:
Association testing of the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B gene
(PTPN1) with type 2 diabetes in 7,883 people. Diabetes.
54:1884–1891. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gautam S, Agrawal CG and Banerjee M: CD36
gene variants in early prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 19:144–149. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gautam S, Pirabu L, Agrawal CG and
Banerjee M: CD36 gene variants and their association with type 2
diabetes in an Indian population. Diabetes Technol Ther.
15:680–687. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gautam S, Agrawal CG, Bid HK and Banerjee
M: Preliminary studies on CD36 gene in type 2 diabetic patients
from north India. Indian J Med Res. 134:107–112. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gouni-Berthold I, Giannakidou E,
Müller-Wieland D, Faust M, Kotzka J, Berthold HK and Krone W: The
Pro387Leu variant of protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B is not
associated with diabetes mellitus type 2 in a German population. J
Intern Med. 257:272–280. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hatmal MM, Alshaer W, Mahmoud IS,
Al-Hatamleh MAI, Al-Ameer HJ, Abuyaman O, Zihlif M, Mohamud R,
Darras M, Al Shhab M, et al: Investigating the association of CD36
gene polymorphisms (rs1761667 and rs1527483) with T2DM and
dyslipidemia: Statistical analysis, machine learning based
prediction, and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
16(e0257857)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kwak SH, Chae J, Lee S, Choi S, Koo BK,
Yoon JW, Park JH, Cho B, Moon MK, Lim S, et al: Nonsynonymous
Variants in PAX4 and GLP1R are associated with type 2 diabetes in
an East Asian population. Diabetes. 67:1892–1902. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Malodobra M, Pilecka A, Gworys B and
Adamiec R: Single nucleotide polymorphisms within functional
regions of genes implicated in insulin action and association with
the insulin resistant phenotype. Mol Cell Biochem. 349:187–193.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Malodobra-Mazur M, Lebioda A, Majda F,
Skoczyńska A and Dobosz T: Correlation of SNP polymorphism in GAD2
and PTPN1 genes with type 2 diabetes in obese people. Diabetologia
Doswiadczalna i Kliniczna. (7)2007.
|
|
51
|
Leprêtre F, Vasseur F, Vaxillaire M,
Scherer PE, Ali S, Linton K, Aitman T and Froguel P: A CD36
nonsense mutation associated with insulin resistance and familial
type 2 diabetes. Hum Mutat. 24(104)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Martín-Márquez BT, Sandoval-Garcia F,
Vazquez-Del Mercado M, Martínez-García EA, Corona-Meraz FI,
Fletes-Rayas AL and Zavaleta-Muñiz SA: Contribution of rs3211938
polymorphism at CD36 to glucose levels, oxidized low-density
lipoproteins, insulin resistance, and body mass index in Mexican
mestizos with type-2 diabetes from western Mexico. Nutr Hosp.
38:742–748. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mok A, Cao H, Zinman B, Hanley AJG, Harris
SB, Kennedy BP and Hegele RA: A single nucleotide polymorphism in
protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-1B is associated with protection
from diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance in Oji-Cree. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 87:724–727. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Santaniemi M, Ukkola O and Kesäniemi YA:
Tyrosine phosphatase 1B and leptin receptor genes and their
interaction in type 2 diabetes. J Intern Med. 256:48–55.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Traurig M, Hanson RL, Kobes S, Bogardus C
and Baier LJ: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B is not a major
susceptibility gene for type 2 diabetes mellitus or obesity among
Pima Indians. Diabetologia. 50:985–989. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Meyre D, Andress EJ, Sharma T, Snippe M,
Asif H, Maharaj A, Vatin V, Gaget S, Besnard P, Choquet H, et al:
Contribution of rare coding mutations in CD36 to type 2 diabetes
and cardio-metabolic complications. Sci Rep.
9(17123)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tokuyama Y, Matsui K, Egashira T, Nozaki
O, Ishizuka T and Kanatsuka A: Five missense mutations in
glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene in Japanese population.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 66:63–69. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang Y, Zhou XO, Zhang Y, Gao PJ and Zhu
DL: Association of the CD36 gene with impaired glucose tolerance,
impaired fasting glucose, type-2 diabetes, and lipid metabolism in
essential hypertensive patients. Genet Mol Res. 11:2163–2170.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang D, Zhang R, Liu Y, Sun X, Yin Z, Li
H, Zhao Y, Wang B, Ren Y, Cheng C, et al: CD36 gene variants is
associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus through the interaction of
obesity in rural Chinese adults. Gene. 659:155–159. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wessel J, Chu AY, Willems SM, Wang S,
Yaghootkar H, Brody JA, Dauriz M, Hivert MF, Raghavan S, Lipovich
L, et al: Low-frequency and rare exome chip variants associate with
fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat Commun.
6(5897)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Nishiya Y, Daimon M, Mizushiri S, Murakami
H, Tanabe J, Matsuhashi Y, Yanagimachi M, Tokuda I, Sawada K and
Ihara K: Nutrient consumption-dependent association of a
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism with insulin
secretion. Sci Rep. 10(16382)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Rać ME, Suchy J, Kurzawski G, Kurlapska A,
Safranow K, Rać M, Sagasz-Tysiewicz D, Krzystolik A, Poncyljusz W,
Jakubowska K, et al: Polymorphism of the CD36 gene and
cardiovascular risk factors in patients with coronary artery
disease manifested at a young age. Biochem Genet. 50:103–111.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cheyssac C, Lecoeur C, Dechaume A, Bibi A,
Charpentier G, Balkau B, Marre M, Froguel P, Gibson F and
Vaxillaire M: Analysis of common PTPN1 gene variants in type 2
diabetes, obesity and associated phenotypes in the French
population. BMC Med Genet. 7(44)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Touré M, Samb A, Sène M, Thiam S, Mané
CAB, Sow AK, Ba-Diop A, Kane MO, Sarr M, Ba A and Gueye L: Impact
of the interaction between the polymorphisms and hypermethylation
of the CD36 gene on a new biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Circulating soluble CD36 (sCD36) in Senegalese females. BMC Med
Genomics. 15(186)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Meshkani R, Taghikhani M, Mosapour A,
Larijani B, Khatami S, Khoshbin E, Ahmadvand D, Saeidi P, Maleki A,
Yavari K, et al: 1484insG polymorphism of the PTPN1 gene is
associated with insulin resistance in an Iranian population. Arch
Med Res. 38:556–562. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ali O: Genetics of type 2 diabetes. World
J Diabetes. 4:114–123. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Groop L and Pociot F: Genetics of
diabetes-are we missing the genes or the disease? Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 382:726–739. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Szczerbinski L, Mandla R, Schroeder P,
Porneala BC, Li JH, Florez JC, Mercader JM, Manning AK and Udler
MS: Algorithms for the identification of prevalent diabetes in the
All of Us Research Program validated using polygenic scores. Sci
Rep. 14(26895)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhang JS, Gui ZH, Zou ZY, Yang BY, Ma J,
Jing J, Wang HJ, Luo JY, Zhang X, Luo CY, et al: Long-term exposure
to ambient air pollution and metabolic syndrome in children and
adolescents: A national cross-sectional study in China. Environ
Int. 148(106383)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kapellou A, Salata E, Vrachnos DM,
Papailia S and Vittas S: Gene-diet interactions in diabetes
mellitus: Current insights and the potential of personalized
nutrition. Genes (Basel). 16(578)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S,
Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I, McGowan BM, Rosenstock J, Tran
MTD, Wadden TA, et al: Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with
overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 384:989–1002. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|