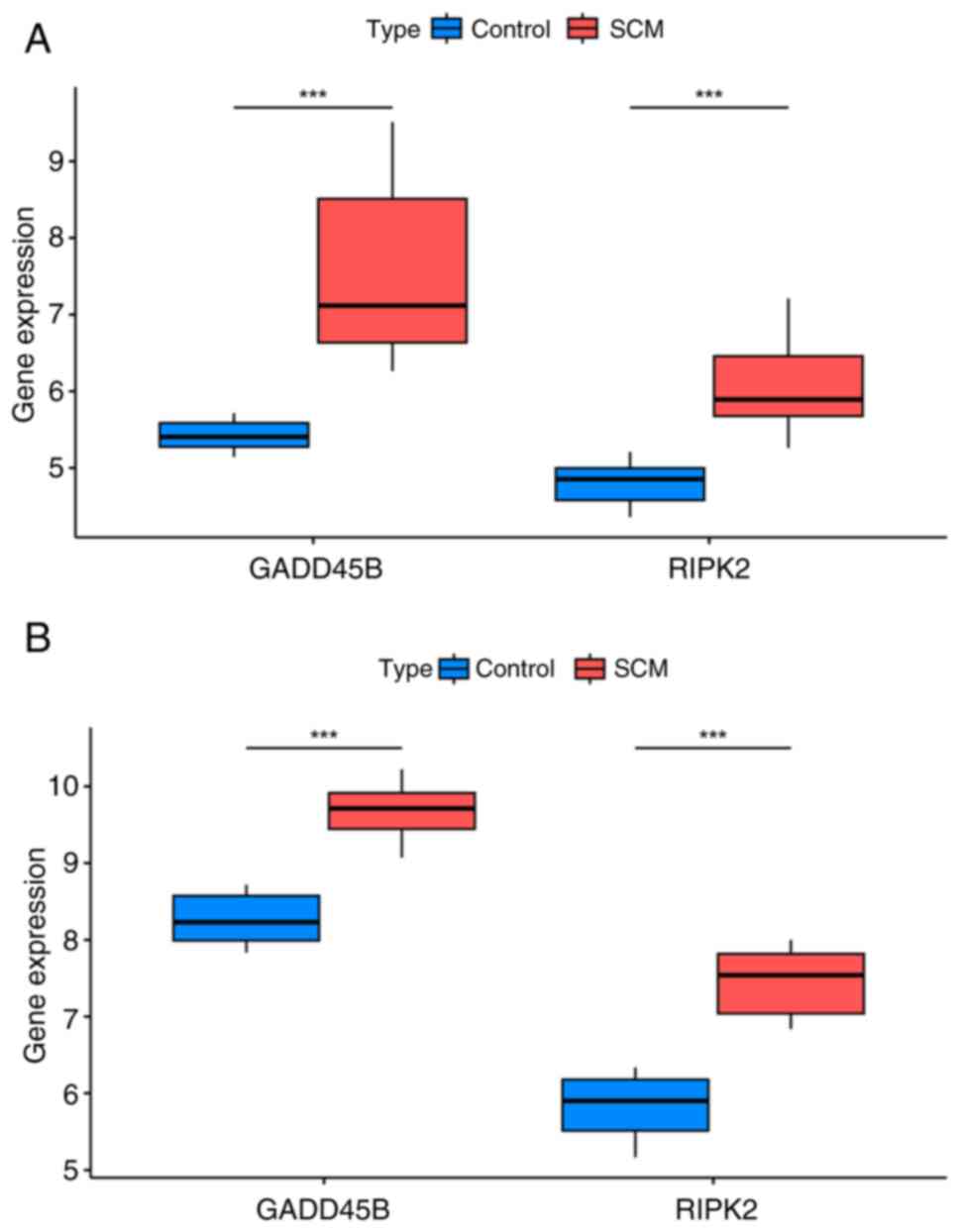
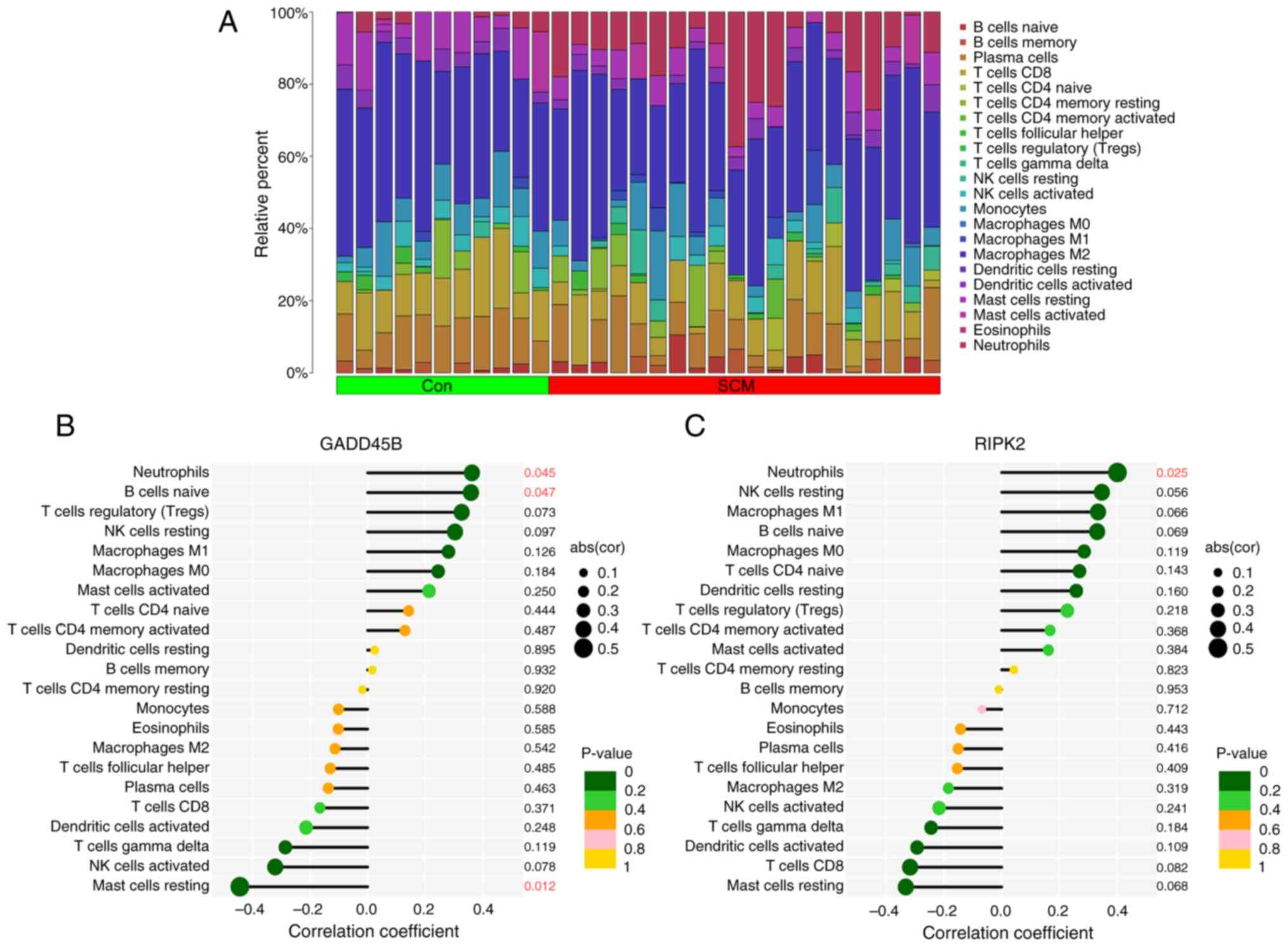
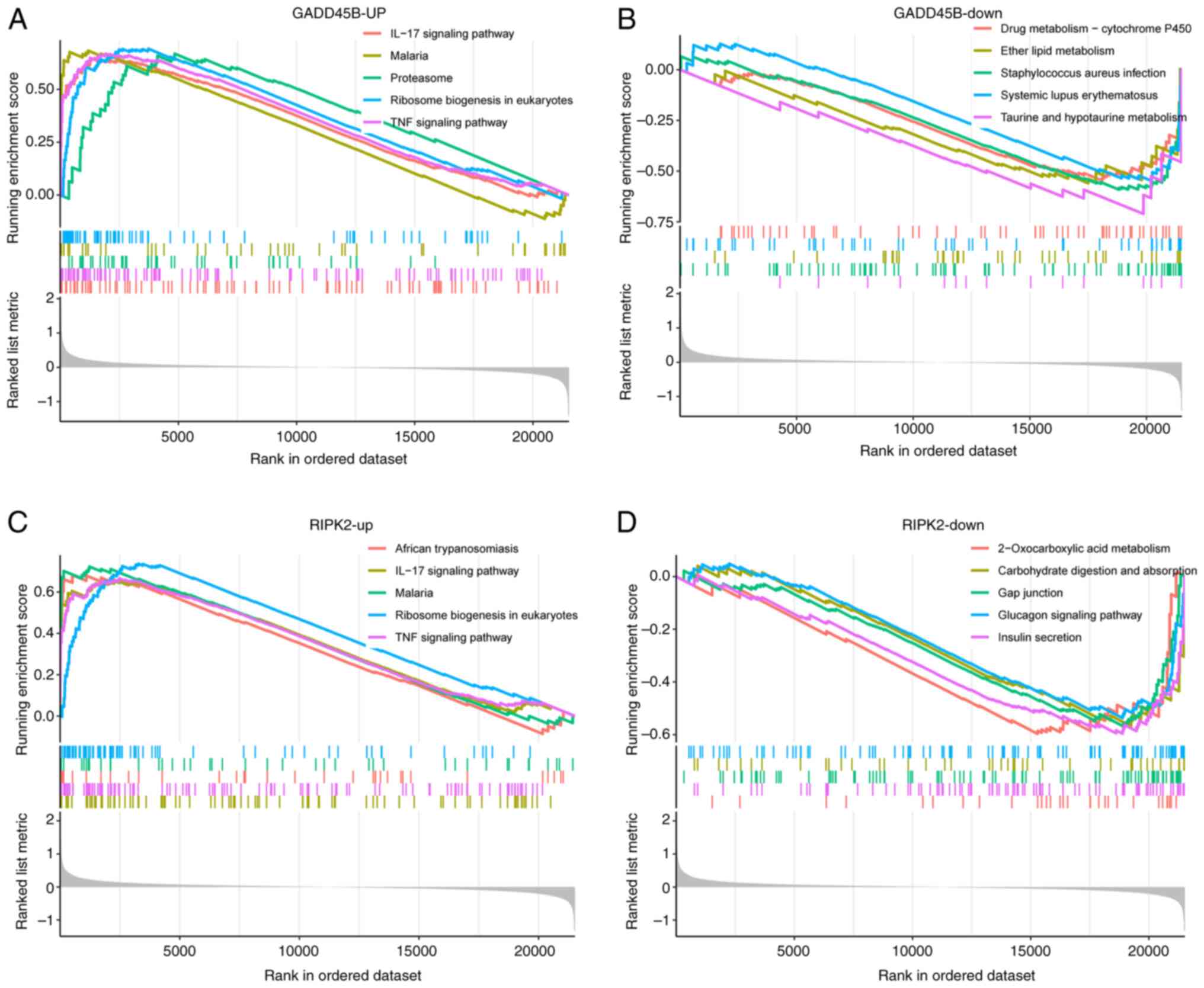
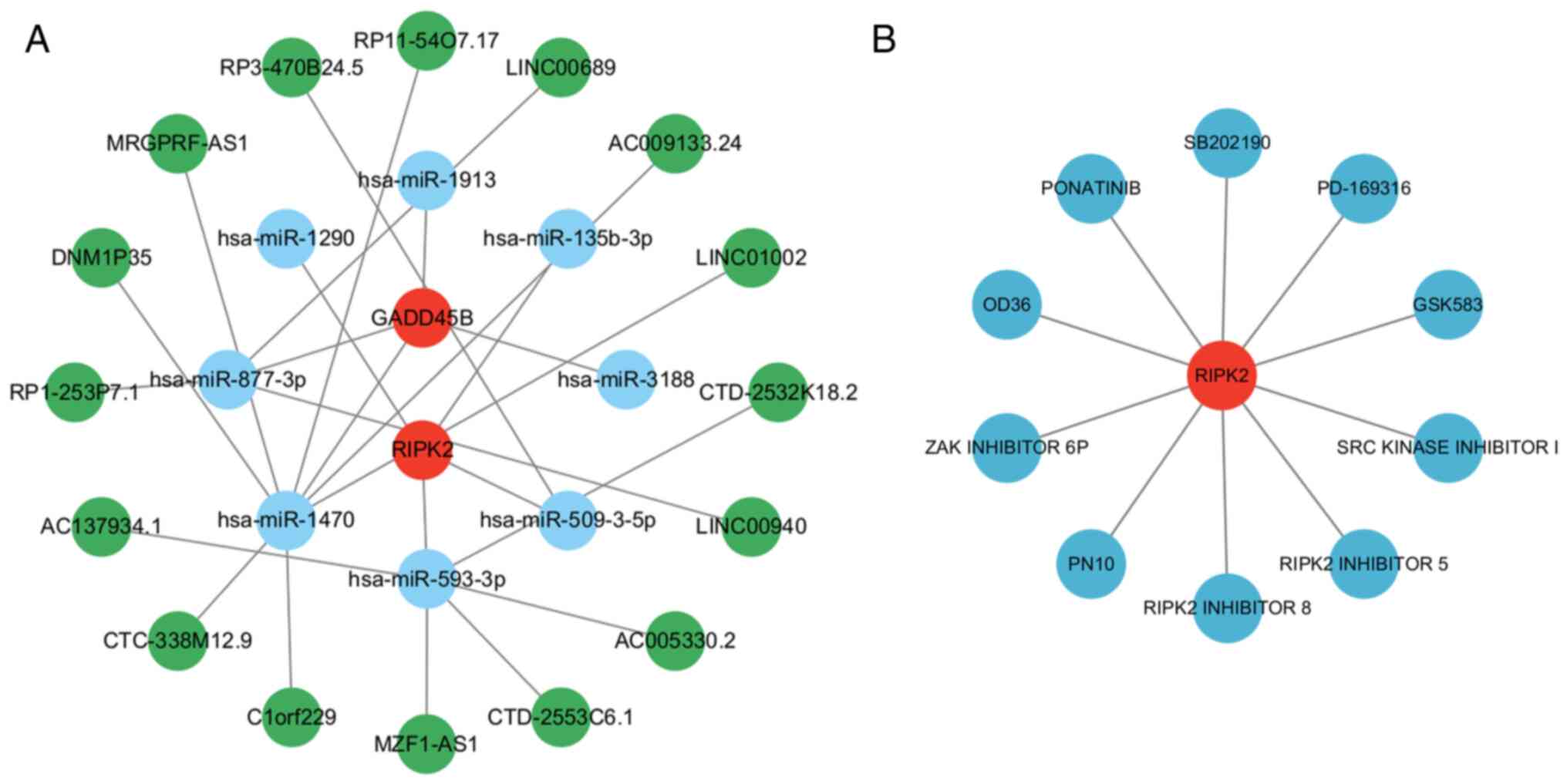
|
1
|
Zhang YY and Ning BT: Signaling pathways
and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6(407)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fleischmann-Struzek C and Rudd K:
Challenges of assessing the burden of sepsis. Med Klin Intensivmed
Notfmed. 118 (Suppl 2):S68–S74. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K and Treggiari
MM: Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: An ongoing
challenge. Shock. 41:12–24. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hollenberg SM: Sepsis-associated
cardiomyopathy: Long-term prognosis, management, and
Guideline-directed medical therapy. Curr Cardiol Rep.
27(5)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hasegawa D, Ishisaka Y, Maeda T,
Prasitlumkum N, Nishida K, Dugar S and Sato R: Prevalence and
prognosis of Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: A systematic review and
Meta-analysis. J Intensive Care Med. 38:797–808. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Ge S, Peng Y and Chen X:
Inflammation and cardiac dysfunction during sepsis, muscular
dystrophy, and myocarditis. Burns Trauma. 1:109–121.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dickson K and Lehmann C: Inflammatory
response to different toxins in experimental sepsis models. Int J
Mol Sci. 20(4341)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
van der Slikke EC, Star BS, van Meurs M,
Henning RH, Moser J and Bouma HR: Sepsis is associated with
mitochondrial DNA damage and a reduced mitochondrial mass in the
kidney of patients with sepsis-AKI. Crit Care.
25(36)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Oliveira F, Assreuy J and Sordi R: The
role of nitric oxide in sepsis-associated kidney injury. Biosci
Rep. 42(BSR20220093)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang L, Zhang L, Yang J, Shi H, Zhu H,
Zhai M, Lu L, Wang X, Li XY, Yu S, et al: 1-Deoxynojirimycin
attenuates septic cardiomyopathy by regulating oxidative stress,
apoptosis, and inflammation via the JAK2/STAT6 signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 155(113648)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Malireddi RKS, Kesavardhana S and
Kanneganti TD: ZBP1 and TAK1: Master Regulators of NLRP3
Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PAN-optosis).
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 9(406)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Christgen S, Tweedell RE and Kanneganti
TD: Programming inflammatory cell death for therapy. Pharmacol
Ther. 232(108010)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhu P, Ke ZR, Chen JX, Li SJ, Ma TL and
Fan XL: Advances in mechanism and regulation of PANoptosis:
Prospects in disease treatment. Front Immunol.
14(1120034)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
He YQ, Deng JL, Zhou CC, Jiang SG, Zhang
F, Tao X and Chen WS: Ursodeoxycholic acid alleviates
sepsis-induced lung injury by blocking PANoptosis via STING
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 125(111161)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou R, Ying J, Qiu X, Yu L, Yue Y, Liu Q,
Shi J, Li X, Qu Y and Mu D: A new cell death program regulated by
toll-like receptor 9 through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathway in a neonatal rat model with sepsis associated
encephalopathy. Chin Med J (Engl). 135:1474–1485. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Matkovich SJ, Al Khiami B, Efimov IR,
Evans S, Vader J, Jain A, Brownstein BH, Hotchkiss RS and Mann DL:
Widespread Down-regulation of cardiac mitochondrial and sarcomeric
genes in patients with sepsis. Crit Care Med. 45:407–414.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhu H, Wu J, Li C, Zeng Z, He T, Liu X,
Wang Q, Hu X, Lu Z and Cai H: Transcriptome analysis reveals the
mechanism of pyroptosis-related genes in septic cardiomyopathy.
PeerJ. 11(e16214)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi Y, Zheng X, Zheng M, Wang L, Chen Y
and Shen Y: Identification of mitochondrial function-associated
lncRNAs in septic mice myocardium. J Cell Biochem. 122:53–68.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(e47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gustavsson EK, Zhang D, Reynolds RH,
Garcia-Ruiz S and Ryten M: ggtranscript: An R package for the
visualization and interpretation of transcript isoforms using
ggplot2. Bioinformatics. 38:3844–3846. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Chao P, Zhang L, Xu L, Cui X,
Wang S, Wusiman M, Jiang H and Lu C: Single-cell RNA and
transcriptome sequencing profiles identify immune-associated key
genes in the development of diabetic kidney disease. Front Immunol.
14(1030198)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun W, Li P, Wang M, Xu Y, Shen D, Zhang X
and Liu Y: Molecular characterization of PANoptosis-related genes
with features of immune dysregulation in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 253(109660)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2(100141)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Yu J, Li R, Zhou H and Chang X: New
insights into the role of mitochondrial metabolic dysregulation and
immune infiltration in septic cardiomyopathy by integrated
bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 29(21)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Qi H, Jiang L, Sun S, Zhang J, Yu
J, Liu F, Zhang Y and Du S: Integrating single-cell RNA-Seq and
machine learning to dissect tryptophan metabolism in ulcerative
colitis. J Transl Med. 22(1121)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Engebretsen S and Bohlin J: Statistical
predictions with glmnet. Clin Epigenetics. 11(123)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang Q and Liu X: Screening of feature
genes in distinguishing different types of breast cancer using
support vector machine. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2311–2317.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kuhn M: Building predictive models in R
using the caret package. J Stat Software. 28:1–26. 2008.
|
|
31
|
Scharl T, Grü B and Leisch F: Mixtures of
regression models for time course gene expression data: Evaluation
of initialization and random effects. Bioinformatics. 26:370–377.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Alderden J, Pepper GA, Wilson A, Whitney
JD, Richardson S, Butcher R, Jo Y and Cummins MR: Predicting
pressure injury in critical care patients: A Machine-learning
model. Am J Crit Care. 27:461–468. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Müller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12(77)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Lu T, Liang R, Wu Z, Liu M,
Qin L, Chen H, Yan X, Deng S, et al: Identification of diagnostic
genes for both Alzheimer's disease and Metabolic syndrome by the
machine learning algorithm. Front Immunol.
13(1037318)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang WY, Chen ZH, An XX, Li H, Zhang HL,
Wu SJ, Guo YQ, Zhang K, Zeng CL and Fang XM: Analysis and
validation of diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration
characteristics in pediatric sepsis by integrating bioinformatics
and machine learning. World J Pediatr. 19:1094–1103.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Peng H, Hu Q, Zhang X, Huang J, Luo S,
Zhang Y, Jiang B and Sun D: Identifying therapeutic targets and
potential drugs for diabetic retinopathy: Focus on oxidative stress
and immune infiltration. J Inflamm Res. 18:2205–2227.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zheng Z, Li K, Yang Z, Wang X, Shen C,
Zhang Y, Lu H, Yin Z, Sha M, Ye J and Zhu L: Transcriptomic
analysis reveals molecular characterization and immune landscape of
PANoptosis-related genes in atherosclerosis. Inflamm Res.
73:961–678. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huang X, Liu J and Huang W: Identification
of S100A8 as a common diagnostic biomarkers and exploring potential
pathogenesis for osteoarthritis and metabolic syndrome. Front
Immunol. 14(1185275)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2(e363)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen Y and Wang X: miRDB: An online
database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48:D127–D131. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13(e0206239)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Furió-Tarí P, Tarazona S, Gabaldón T,
Enright AJ and Conesa A: spongeScan: A web for detecting microRNA
binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:W176–W180. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Deutschman CS and Tracey KJ: Sepsis:
Current dogma and new perspectives. Immunity. 40:463–475.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lu JS, Wang JH, Han K and Li N: Nicorandil
regulates ferroptosis and mitigates septic cardiomyopathy via
TLR4/SLC7A11 signaling pathway. Inflammation. 47:975–988.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yuan X, Chen G, Guo D, Xu L and Gu Y:
Polydatin alleviates septic myocardial injury by promoting
SIRT6-Mediated autophagy. Inflammation. 43:785–795. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Han X, Liu X, Zhao X, Wang X, Sun Y, Qu C,
Liang J and Yang B: Dapagliflozin ameliorates sepsis-induced heart
injury by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and electrical
remodeling through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
955(175930)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Salvador JM, Brown-Clay JD and Fornace AJ
Jr: Gadd45 in stress signaling, cell cycle control, and apoptosis.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 793:1–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xu W, Jiang T, Shen K, Zhao D, Zhang M,
Zhu W, Liu Y and Xu C: GADD45B regulates the carcinogenesis process
of chronic atrophic gastritis and the metabolic pathways of gastric
cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14(1224832)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Xie M, Xie R, Huang P, Yap DYH and Wu P:
GADD45A and GADD45B as novel biomarkers associated with chromatin
regulators in renal Ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Sci.
24(11304)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kim MY, Seo EJ, Lee DH, Kim EJ, Kim HS,
Cho HY, Chung EY, Lee SH, Baik EJ, Moon CH and Jung YS: Gadd45beta
is a novel mediator of cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by
ischaemia/hypoxia. Cardiovasc Res. 87:119–126. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sheng M, Huang Z, Pan L, Yu M, Yi C, Teng
L, He L, Gu C, Xu C and Li J: SOCS2 exacerbates myocardial injury
induced by ischemia/reperfusion in diabetic mice and H9c2 cells
through inhibiting the JAK-STAT-IGF-1 pathway. Life Sci.
188:101–109. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Tigno-Aranjuez JT, Asara JM and Abbott DW:
Inhibition of RIP2's tyrosine kinase activity limits NOD2-driven
cytokine responses. Genes Dev. 24:2666–2677. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tian E, Zhou C, Quan S, Su C, Zhang G, Yu
Q, Li J and Zhang J: RIPK2 inhibitors for disease therapy: Current
status and perspectives. Eur J Med Chem. 259(115683)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhao W, Leng RX and Ye DQ: RIPK2 as a
promising druggable target for autoimmune diseases. Int
Immunopharmacol. 118(110128)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Pham AT, Ghilardi AF and Sun L: Recent
advances in the development of RIPK2 modulators for the treatment
of inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol.
14(1127722)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
You J, Wang Y, Chen H and Jin F: RIPK2: A
promising target for cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol.
14(1192970)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhao CH, Ma X, Guo HY, Li P and Liu HY:
RIP2 deficiency attenuates cardiac hypertrophy, inflammation and
fibrosis in pressure overload induced mice. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 493:1151–1158. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Andersson L, Scharin Täng M, Lundqvist A,
Lindbom M, Mardani I, Fogelstrand P, Shahrouki P, Redfors B,
Omerovic E, Levin M, et al: Rip2 modifies VEGF-induced signalling
and vascular permeability in myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res.
107:478–486. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhang J, Wang M, Ye J, Liu J, Xu Y, Wang
Z, Ye D, Zhao M and Wan J: The Anti-inflammatory mediator resolvin
E1 protects mice against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced heart injury.
Front Pharmacol. 11(203)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Brown KA, Brain SD, Pearson JD, Edgeworth
JD, Lewis SM and Treacher DF: Neutrophils in development of
multiple organ failure in sepsis. Lancet. 368:157–169.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li J, Xiao F, Lin B, Huang Z, Wu M, Ma H,
Dou R, Song X, Wang Z, Cai C, et al: Ferrostatin-1 improves acute
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via inhibiting neutrophil
infiltration through impaired chemokine axis. Front Cell Dev Biol.
12(1510232)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhou S, Xu Y, Tu J and Zhang M: Inhibiting
NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis: A new role of GADD45B's
role in hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis. Discov
Med. 37:1105–1116. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Goh FY, Cook KL, Upton N, Tao L, Lah LC,
Leung BP and Wong WS: Receptor-interacting protein 2 gene silencing
attenuates allergic airway inflammation. J of Immunol.
191:2691–2699. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Chen XS, Wang SH, Liu CY, Gao YL, Meng XL,
Wei W, Shou ST, Liu YC and Chai YF: Losartan attenuates
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating macrophage polarization
via TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Pharmacol Res.
185(106473)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Yang Y, Li XY, Li LC, Xiao J, Zhu YM, Tian
Y, Sheng YM, Chen Y, Wang JG and Jin SW: γδ T/Interleukin-17A
contributes to the effect of maresin conjugates in tissue
regeneration 1 on Lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac injury. Front
Immunol. 12(674542)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Csiszar A and Ungvari Z: Synergistic
effects of vascular IL-17 and TNFalpha may promote coronary artery
disease. Med Hypotheses. 63:696–698. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ahmad S, Ahmed MM, Hasan PMZ, Sharma A,
Bilgrami AL, Manda K, Ishrat R and Syed MA: Identification and
validation of Potential miRNAs, as biomarkers for sepsis and
associated lung injury: A Network-based approach. Genes (Basel).
11(1327)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wu K, Hu M, Chen Z, Xiang F, Chen G, Yan
W, Peng Q and Chen X: Asiatic acid enhances survival of human AC16
cardiomyocytes under hypoxia by upregulating miR-1290. IUBMB Life.
69:660–667. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Tigno-Aranjuez JT, Benderitter P, Rombouts
F, Deroose F, Bai X, Mattioli B, Cominelli F, Pizarro TT, Hoflack J
and Abbott DW: In vivo inhibition of RIPK2 kinase alleviates
inflammatory disease. J Biol Chem. 289:29651–2964. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|