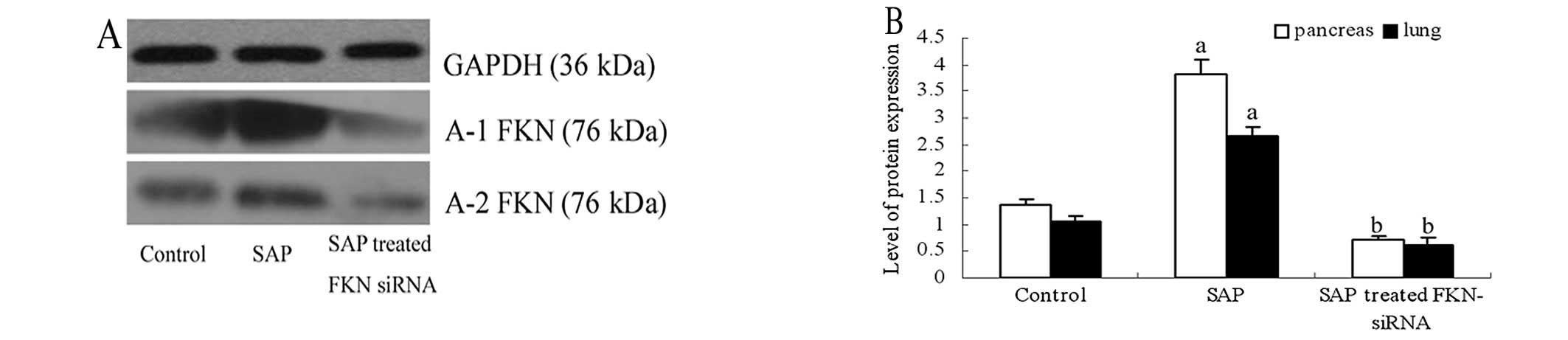
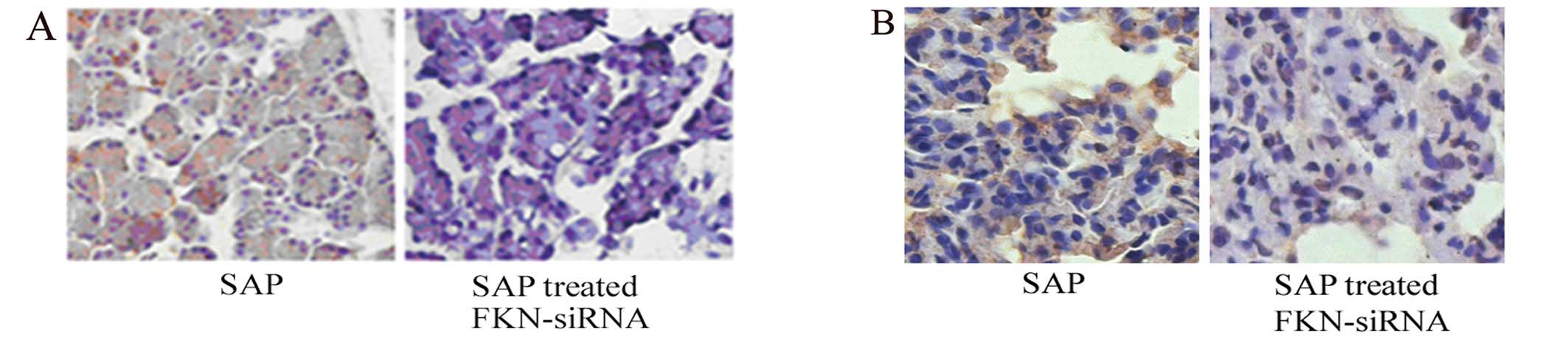
|
1.
|
CD JohnsonM Abu-HilalPersistent organ
failure during the first week as a marker of fatal outcome in acute
pancreatitisGut5313401344200410.1136/gut.2004.03988315306596
|
|
2.
|
Y TakeyamaSignificance of apoptotic cell
death in systemic complications with severe acute pancreatitisJ
Gastroenterol40110200510.1007/s00535-004-1505-815692783
|
|
3.
|
C JohnsonA KingsnorthC ImrieDouble blind,
randomised, placebo controlled study of a platelet activating
factor antagonist, lexipafant, in the treatment and prevention of
organ failure in predicted severe acute
pancreatitisGut486269200110.1136/gut.48.1.62
|
|
4.
|
J MayerB RauF GansaugeHG BegerInflammatory
mediators in human acute pancreatitis: clinical and
pathophysiological
implicationsGut47546552200010.1136/gut.47.4.54610986216
|
|
5.
|
H UmeharaET BloomT OkazakiY NaganoO
YoshieT ImaiFractalkine in vascular biology: from basic research to
clinical diseaseArterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol243440200410.1161/01.ATV.0000095360.62479.1F12969992
|
|
6.
|
AM FongLA RobinsonDA SteeberFractalkine
and CX3CR1 mediate a novel mechanism of leukocyte capture, firm
adhesion, and activation under physiologic flowJ Exp
Med18814131419199810.1084/jem.188.8.14139782118
|
|
7.
|
T ImaiK HieshimaC HaskellIdentification
and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1,
which mediates both leukocyte migration and
adhesionCell91521530199710.1016/S0092-8674(00)80438-99390561
|
|
8.
|
MV VolinJM WoodsMA AminMA ConnorsLA
HarlowAE KochFractalkine: a novel angiogenic chemokine in
rheumatoid arthritisAm J
Pathol15915211530200110.1016/S0002-9440(10)62537-011583978
|
|
9.
|
SJ LeeS NamkoongYM KimFractalkine
stimulates angiogenesis by activating the Raf-1/MEK/ERK- and
PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent signal pathwaysAm J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol291H2836H2846200610.1152/ajpheart.00113.200616877565
|
|
10.
|
E EfsenC GrapponeRM DeFrancoUp-regulated
expression of fractalkine and its receptor CX3CR1 during liver
injury in humansJ
Hepatol373947200210.1016/S0168-8278(02)00065-X12076860
|
|
11.
|
S SegererE HughesKL HudkinsM MackT
GoodpasterCE AlpersExpression of the fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1)
in human kidney diseaseKidney
Int62488495200210.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00480.x12110009
|
|
12.
|
SM ElbashirJ HarborthW LendeckelA YalcinK
WeberT TuschlDuplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA
interference in cultured mammalian
cellsNature411494498200110.1038/3507810711373684
|
|
13.
|
GJ HannonRNA
interferenceNature418244251200210.1038/418244a12110901
|
|
14.
|
MS DuxburyE MatrosH ItoMJ ZinnerSW
AshleyEE WhangSystemic siRNA-mediated gene silencing: a new
approach to targeted therapy of cancerAnn
Surg240667674200415383794
|
|
15.
|
S FilleurA CourtinS AliSiRNA-mediated
inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor severely limits
tumor resistance to antiangiogenic thrombospondin-1 and slows tumor
vascularization and growthCancer Res63391939222003
|
|
16.
|
E SongSK LeeJ WangRNA interference
targeting Fasprotects mice from fulminant hepatitisNat
Med9347351200310.1038/nm82812579197
|
|
17.
|
M SioudAdvances in RNA sensing by the
immune system: separation of siRNA unwanted effects from RNA
inferenceMethods Mol
Biol6293352201010.1007/978-1-60761-657-3_320387141
|
|
18.
|
RK LeungPA WhittakerRNA interference: from
gene silencing to gene- specific therapeuticsPharmacol
Ther107222239200510.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.03.00415908010
|
|
19.
|
DH KimJJ RossiStrategies for silencing
human disease using RNA interferenceNat Rev
Genet8173184200710.1038/nrg200617304245
|
|
20.
|
L YulongG HongL Shiaw-YihJA GossFC
BrunicardiK LisiRNA-based targeting of cyclin E over-expression
inhibits breast cancer cell growth and suppresses tumor development
in breast cancer mouse modelPLoS
One5e12860201010.1371/journal.pone.001286020877462
|
|
21.
|
S YuberoL RamudoMA MansoI De
DiosMechanisms of dexamethasone-mediated chemokine down-regulation
in mild and severe acute pancreatitisBiochim Biophys
Acta179212051211200910.1016/j.bbadis.2009.10.00119818401
|
|
22.
|
P ChenY YuanS WangL ZhanJ XuCaptopril, an
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, attenuates the severity of
acute pancreatitis in rats by reducing expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 9Tohoku J Exp
Med20999101200610.1620/tjem.209.99
|
|
23.
|
HP GrewalA Mohey el DinL GaberM KotbAO
GaberAmelioration of the physiologic and biochemical changes of
acute pancreatitis using an anti-TNF-alpha polyclonal antibodyAm J
Sug167214218199410.1016/0002-9610(94)90076-08311136
|
|
24.
|
XP ZhangJ ZhangML MaPathological changes
at early stage of multiple organ injury in a rat model of severe
acute pancreatitisHepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int98387201020133235
|
|
25.
|
PM MurphyThe molecular biology of
leukocyte chemoattractant receptorsAnnu Rev
Immunol12593633199410.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.0031138011292
|
|
26.
|
M BrueckmannM BorggrefeTherapeutic
potential of fractalkine: a novel approach to metastatic colon
cancerGut56314316200710.1136/gut.2006.10331717339240
|
|
27.
|
A InoueH HasegawaM KohnoAntagonist of
fractalkine (CX3CL1) delays the initiation and ameliorates the
progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr miceArthritis
Rheum5215221533200510.1002/art.2100715880599
|
|
28.
|
P CockwellSJ ChakravortyJ GirdlestoneCO
SavageFractalkine expression in human renal inflammationJ
Pathol1968589200210.1002/path.101011748646
|
|
29.
|
V BjerkeliJK DamaB FevangJC HolterP
AukrustSS FrolandIncreased expression of fractalkine (CX3CL1) and
its receptor CX3CR1, in Wegener’s granulomatosis-possible role in
vascular inflammationRheumatology46142214272007
|
|
30.
|
JF BazanKB BaconG HardimanA new class of
membrane bound chemokine with a CX3C
motifNature385640644199710.1038/385640a09024663
|
|
31.
|
C HundhausenD MisztelaTA BerkhoutThe
disintegrin-like metalloproteinase ADAM10 is involved in
constitutive cleavage of CX3CL1 (fractalkine) and regulates
CX3CL1-mediated cell-cell
adhesionBlood10211861195200310.1182/blood-2002-12-377512714508
|
|
32.
|
XP ZhangL WangYF ZhouThe pathogenic
mechanism of severe acute pancreatitis complicated with renal
injury: a review of current knowledgeDig Dis
Sci53297306200810.1007/s10620-007-9866-517597411
|
|
33.
|
A KingsnorthRole of cytokines and their
inhibitors in acute
pancreatitisGut4014199710.1136/gut.40.1.19155566
|
|
34.
|
IA Al MoflehSevere acute pancreatitis:
pathogenetic aspects and prognostic factorsWorld J
Gastroenterol14675684200818205255
|
|
35.
|
TR BrummelkampR BernardsR AgamiStable
suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA
interferenceCancer
Cell2243247200210.1016/S1535-6108(02)00122-812242156
|
|
36.
|
C ChettyP BhoopathiP JosephS ChittiveluJS
RaoS LakkaAdenovirus-mediated siRNA against MMP-2 suppresses tumor
growth and lung metastasis in miceMol Cancer
Ther522892299200610.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-016916985063
|
|
37.
|
AA SandbergA BorgstromEarly prediction of
severity in acute pancreatitis: is this
possible?JOP3116125200212221326
|
|
38.
|
J SoutschekA AkincB BramlageTherapeutic
silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of
siRNAsNature432173178200410.1038/nature0312115538359
|
|
39.
|
BR GoyalMM PatelMK SoniSV
BhadadaTherapeutic opportunities of small interfering RNAFundam
Clin
Pharmacol23367386200910.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00694.x19709318
|
|
40.
|
M SochorS RichterA SchmidtS HempelUT HoptT
KeckInhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 with doxycycline
reduces pancreatitis-associated lung
injuryDigestion806573200910.1159/00021208019494493
|
|
41.
|
C ChenS XuWX WangRosiglitazone attenuates
the severity of sodium taurocholate induced acute pancreatitis and
pancreatitis-associated lung injuryArch Med
Res407988200910.1016/j.arcmed.2008.11.00419237016
|
|
42.
|
F PerrosP DrofmullerR
SouzaFractalkine-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation in
pulmonary hypertensionEur Respir
J29937943200710.1183/09031936.0010470617182651
|