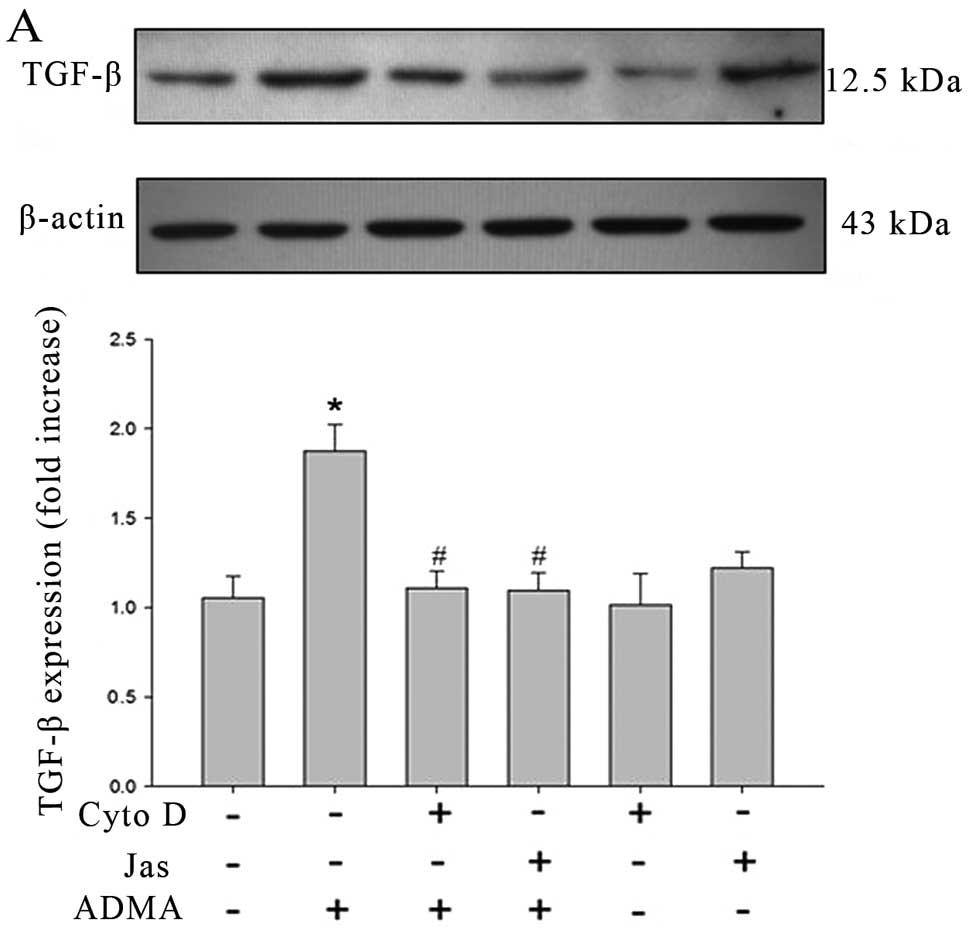
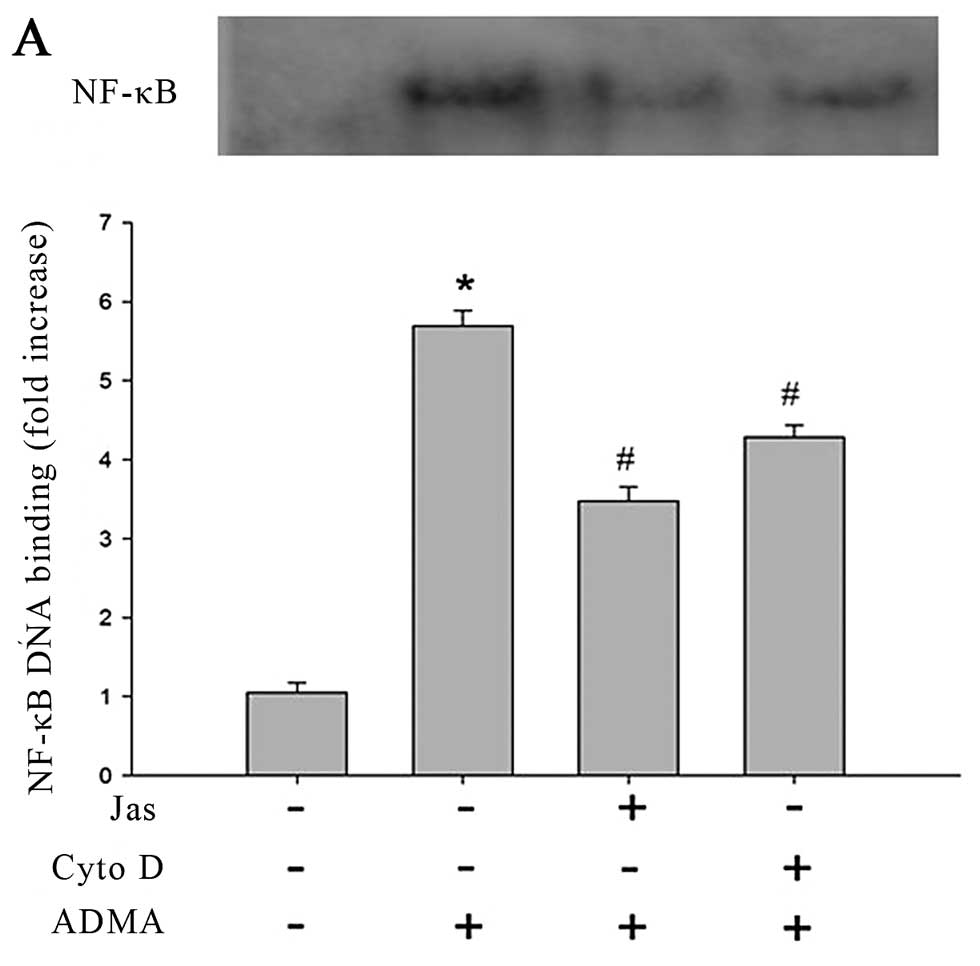
|
1
|
Boger RH: Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an
endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, explains the
‘L-arginine paradox’ and acts as a novel cardiovascular risk
factor. J Nutr. 134(Suppl 10): S2842–S2853. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Cooke JP: Does ADMA cause endothelial
dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2032–2037. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boger RH: Asymmetric dimethylarginine
(ADMA) and cardiovascular disease: insights from prospective
clinical trials. Vasc Med. 10(Suppl 1): S19–S25. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Palm F, Onozato ML, Luo Z and Wilcox CS:
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH): expression,
regulation, and function in the cardiovascular and renal systems.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H3227–H3245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teerlink T, Luo Z, Palm F and Wilcox CS:
Cellular ADMA: regulation and action. Pharmacol Res. 60:448–460.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scalera F, Borlak J, Beckmann B, et al:
Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor asymmetric dimethyl
L-arginine accelerates endothelial cell senescence. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1816–1822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li JC, Chang L, Lu D, Jiang DJ and Tan DM:
Effect of asymmetric dimethylarginine on the activation of hepatic
stellate cells and its mechanism. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue
Ban. 32:427–432. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Guo WK, Zhang DL, Wang XX, Zhang Y, Zhang
QD and Liu WH: Actin cytoskeleton modulates ADMA-induced NF-kappaB
nuclear translocation and ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells.
Med Sci Monit. 17:BR242–BR247. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fazal F, Minhajuddin M, Bijli KM, McGrath
JL and Rahman A: Evidence for actin cytoskeleton-dependent and
-independent pathways for RelA/p65 nuclear translocation in
endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 282:3940–3950. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang LY, Zhang DL, Zheng JF, Zhang Y,
Zhang QD and Li WH: Apelin-13 passes through the ADMA-damaged
endothelial barrier and acts on vascular smooth muscle cells.
Peptides. 32:2436–2443. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fliser D, Kronenberg F, Kielstein JT, et
al: Asymmetric dimethylarginine and progression of chronic kidney
disease: the mild to moderate kidney disease study. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 16:2456–2461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zoccali C, Bode-Boger S, Mallamaci F, et
al: Plasma concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and
mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease: a prospective
study. Lancet. 358:2113–2117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zoccali C: Traditional and emerging
cardiovascular and renal risk factors: an epidemiologic
perspective. Kidney Int. 70:26–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsumoto Y, Ueda S, Yamagishi S, et al:
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase prevents progression of
renal dysfunction by inhibiting loss of peritubular capillaries and
tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney
disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:1525–1533. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wagner L, Riggleman A, Erdely A, Couser W
and Baylis C: Reduced nitric oxide synthase activity in rats with
chronic renal disease due to glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int.
62:532–536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ravani P, Tripepi G, Malberti F, Testa S,
Mallamaci F and Zoccali C: Asymmetrical dimethylarginine predicts
progression to dialysis and death in patients with chronic kidney
disease: a competing risks modeling approach. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:2449–2455. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mihout F, Shweke N, Bige N, et al:
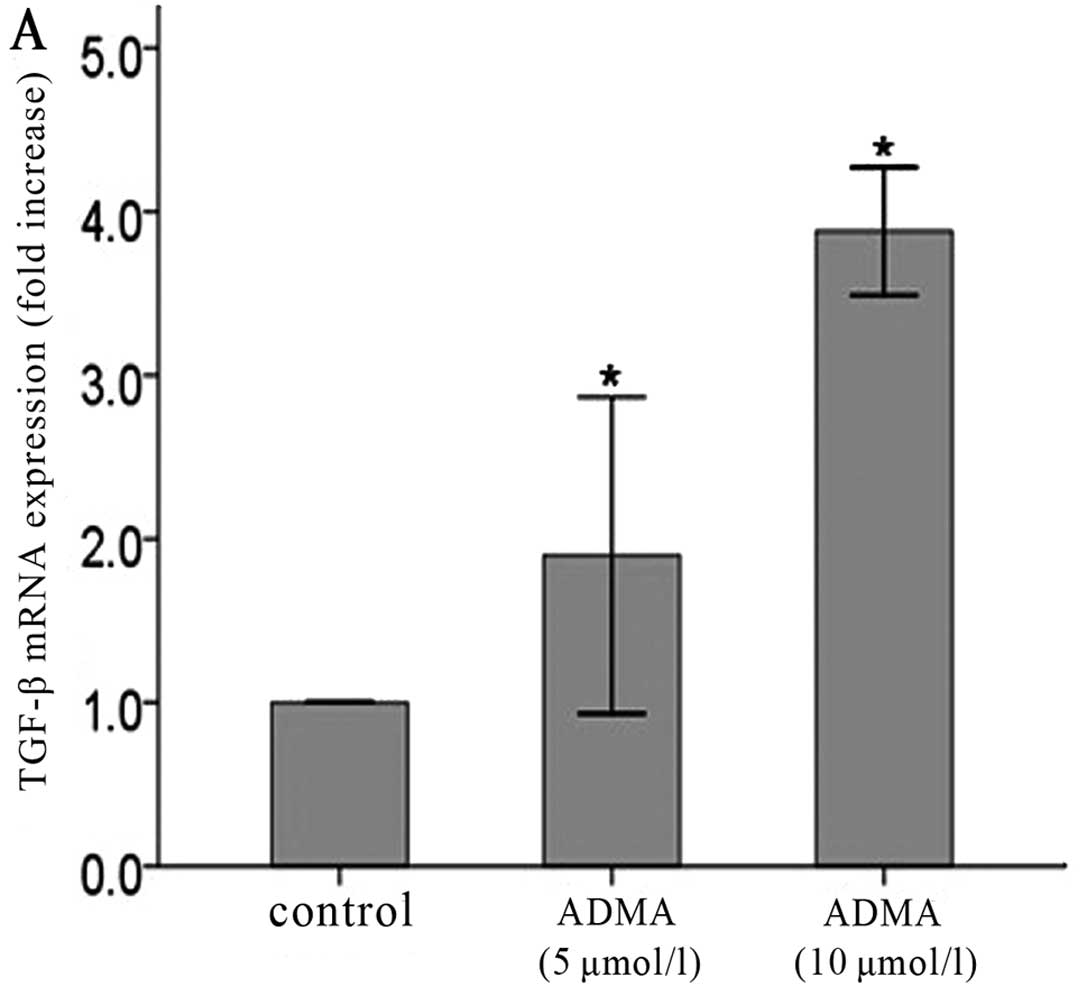
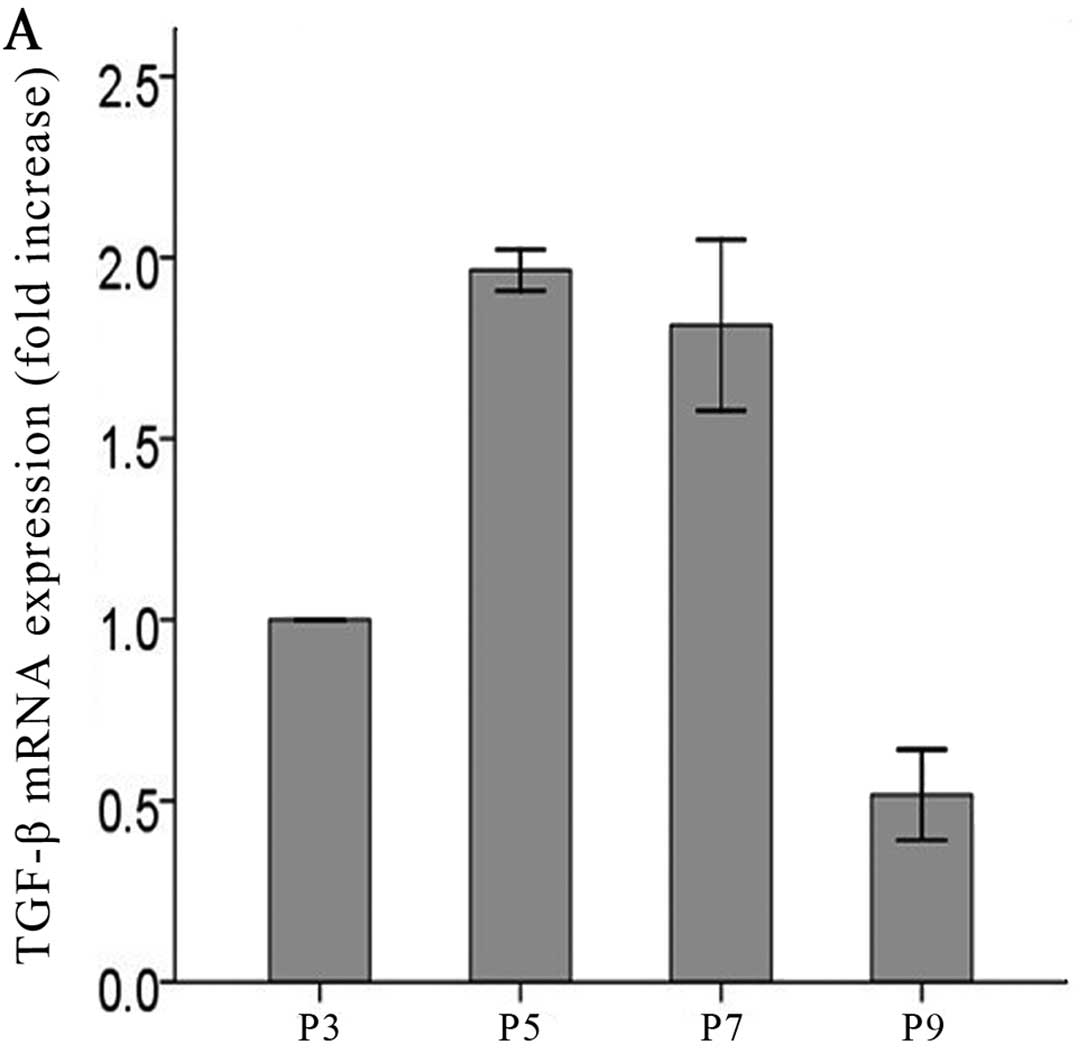
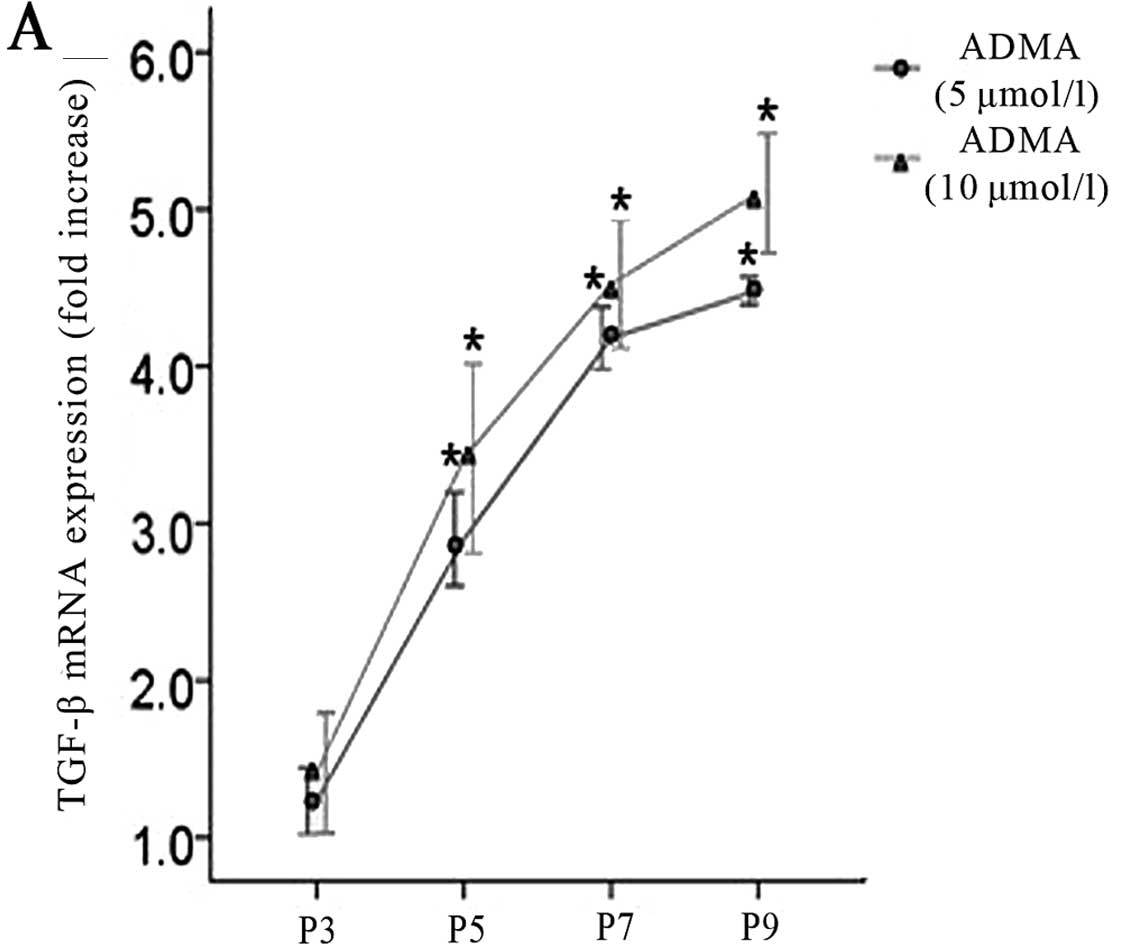
Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) induces chronic kidney disease
through a mechanism involving collagen and TGF-beta1 synthesis. J
Pathol. 223:37–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappa B: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappa B at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
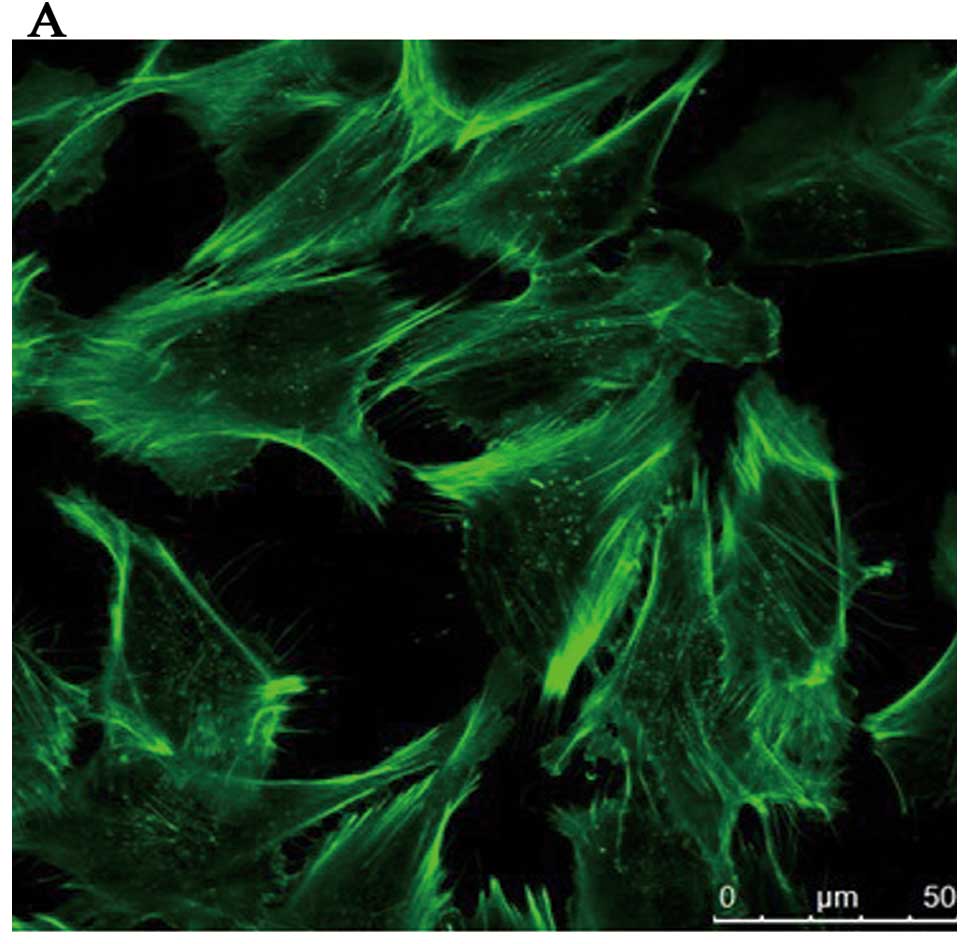
Wojciak-Stothard B, Torondel B, Tsang LY,
et al: The ADMA/DDAH pathway is a critical regulator of endothelial
cell motility. J Cell Sci. 120:929–942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moldovan L, Mythreye K,
Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ and Satterwhite LL: Reactive oxygen species
in vascular endothelial cell motility. Roles of NAD(P)H oxidase and
Rac1. Cardiovasc Res. 71:236–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li JM and Shah AM: Intracellular
localization and preassembly of the NADPH oxidase complex in
cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 277:19952–19960. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tamura M, Kai T, Tsunawaki S, Lambeth JD
and Kameda K: Direct interaction of actin with p47(phox) of
neutrophil NADPH oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
276:1186–1190. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wientjes FB, Reeves EP, Soskic V,
Furthmayr H and Segal AW: The NADPH oxidase components p47(phox)
and p40(phox) bind to moesin through their PX domain. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 289:382–388. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gerthoffer WT and Gunst SJ: Invited
review: focal adhesion and small heat shock proteins in the
regulation of actin remodeling and contractility in smooth muscle.
J Appl Physiol. 91:963–972. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McMullen ME, Bryant PW, Glembotski CC,
Vincent PA and Pumiglia KM: Activation of p38 has opposing effects
on the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 280:20995–21003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lamalice L, Houle F, Jourdan G and Huot J:
Phosphorylation of tyrosine 1214 on VEGFR2 is required for
VEGF-induced activation of Cdc42 upstream of SAPK2/p38. Oncogene.
23:434–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garcia JG, Wang P, Schaphorst KL, et al:
Critical involvement of p38 MAP kinase in pertussis toxin-induced
cytoskeletal reorganization and lung permeability. FASEB J.
16:1064–1076. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song C, Perides G, Wang D and Liu YF:
beta-Amyloid peptide induces formation of actin stress fibers
through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurochem.
83:828–836. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Okuda S, Languino LR, Ruoslahti E and
Border WA: Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta
and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis.
Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J
Clin Invest. 86:453–462. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tamaki K, Okuda S, Ando T, Iwamoto T,
Nakayama M and Fujishima M: TGF-beta 1 in glomerulosclerosis and
interstitial fibrosis of adriamycin nephropathy. Kidney Int.
45:525–536. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boffa JJ, Lu Y, Placier S, Stefanski A,
Dussaule JC and Chatziantoniou C: Regression of renal vascular and
glomerular fibrosis: role of angiotensin II receptor antagonism and
matrix metalloproteinases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1132–1144. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tomita H, Egashira K, Ohara Y, et al:
Early induction of transforming growth factor-beta via angiotensin
II type 1 receptors contributes to cardiac fibrosis induced by
long-term blockade of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. Hypertension.
32:273–279. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|