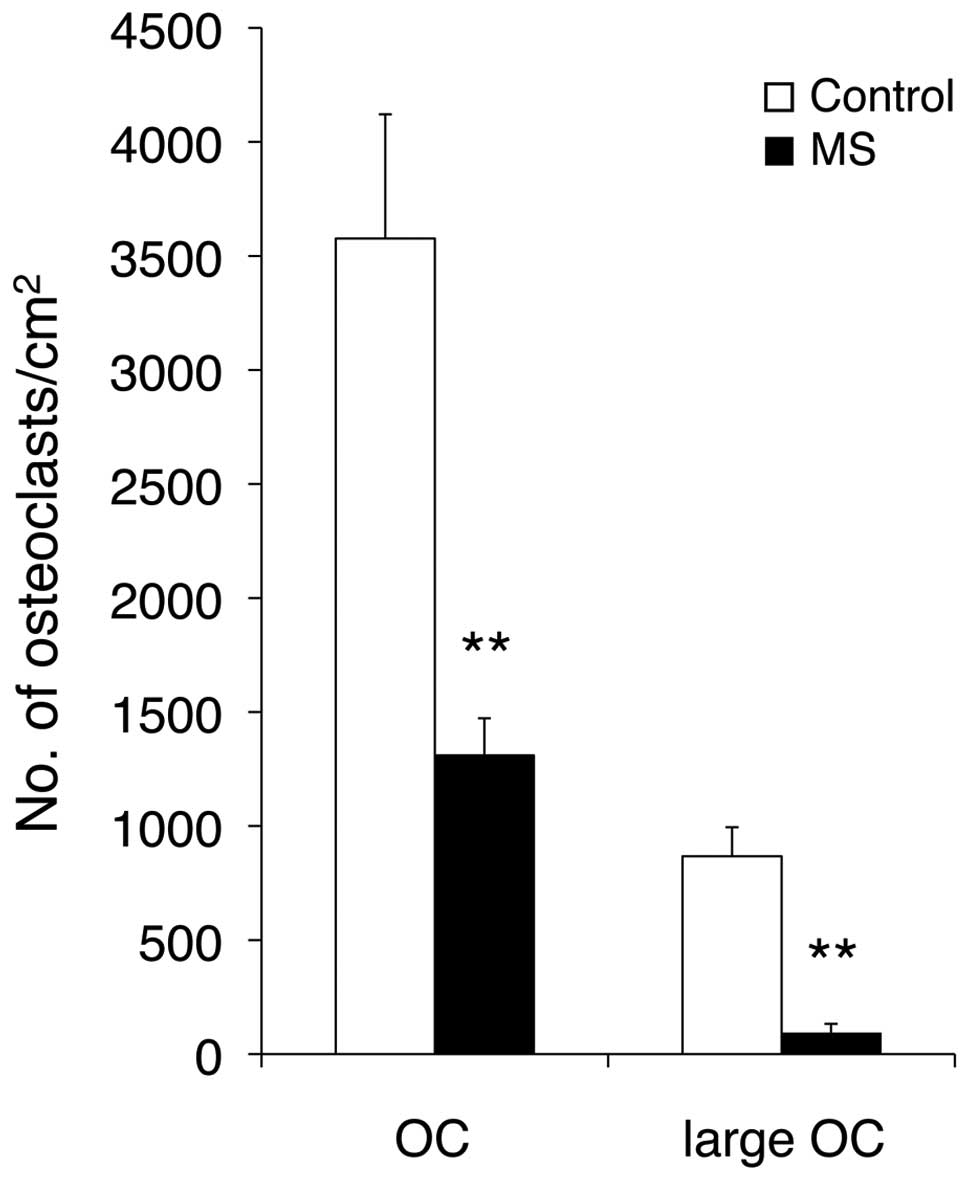
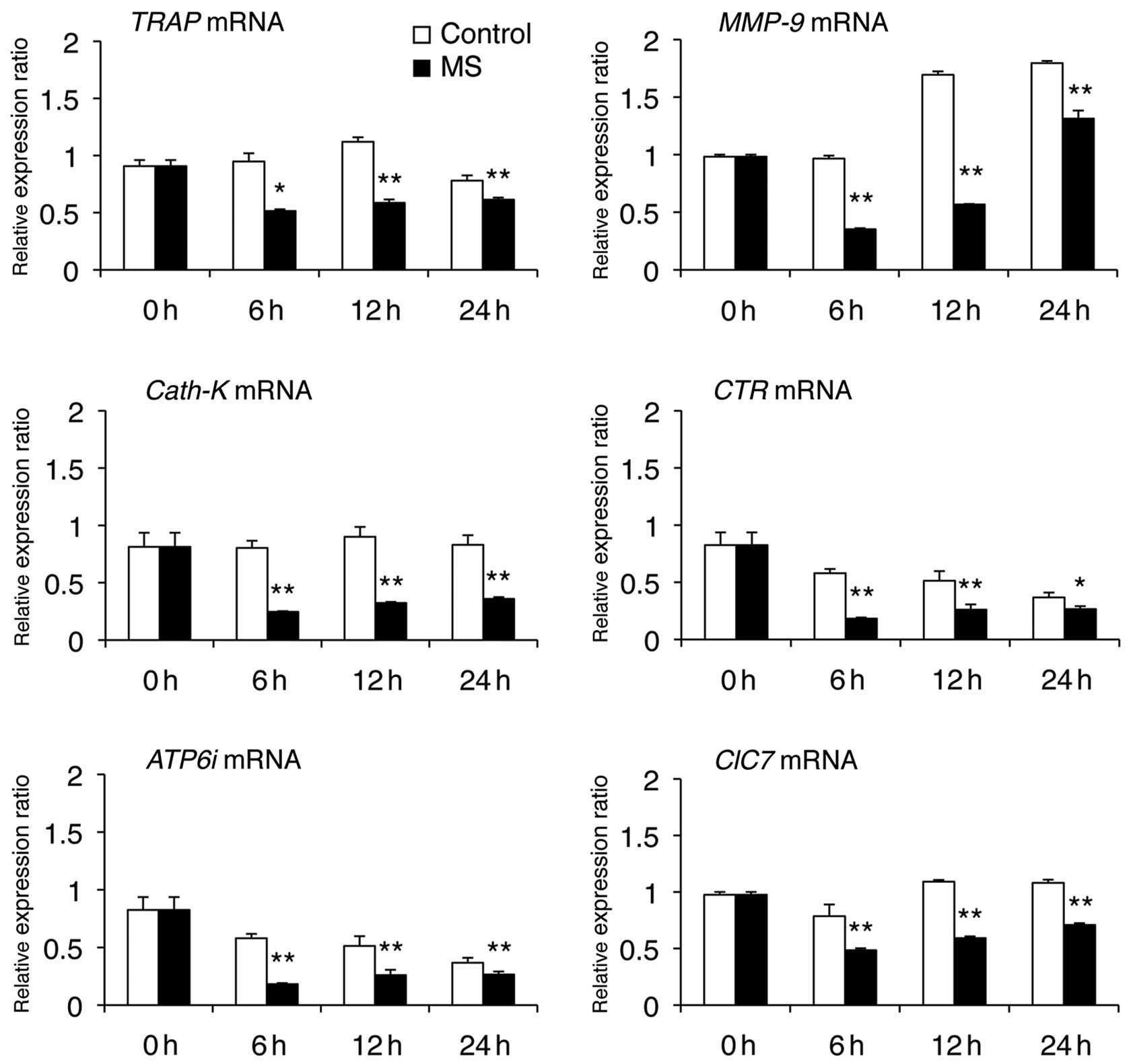
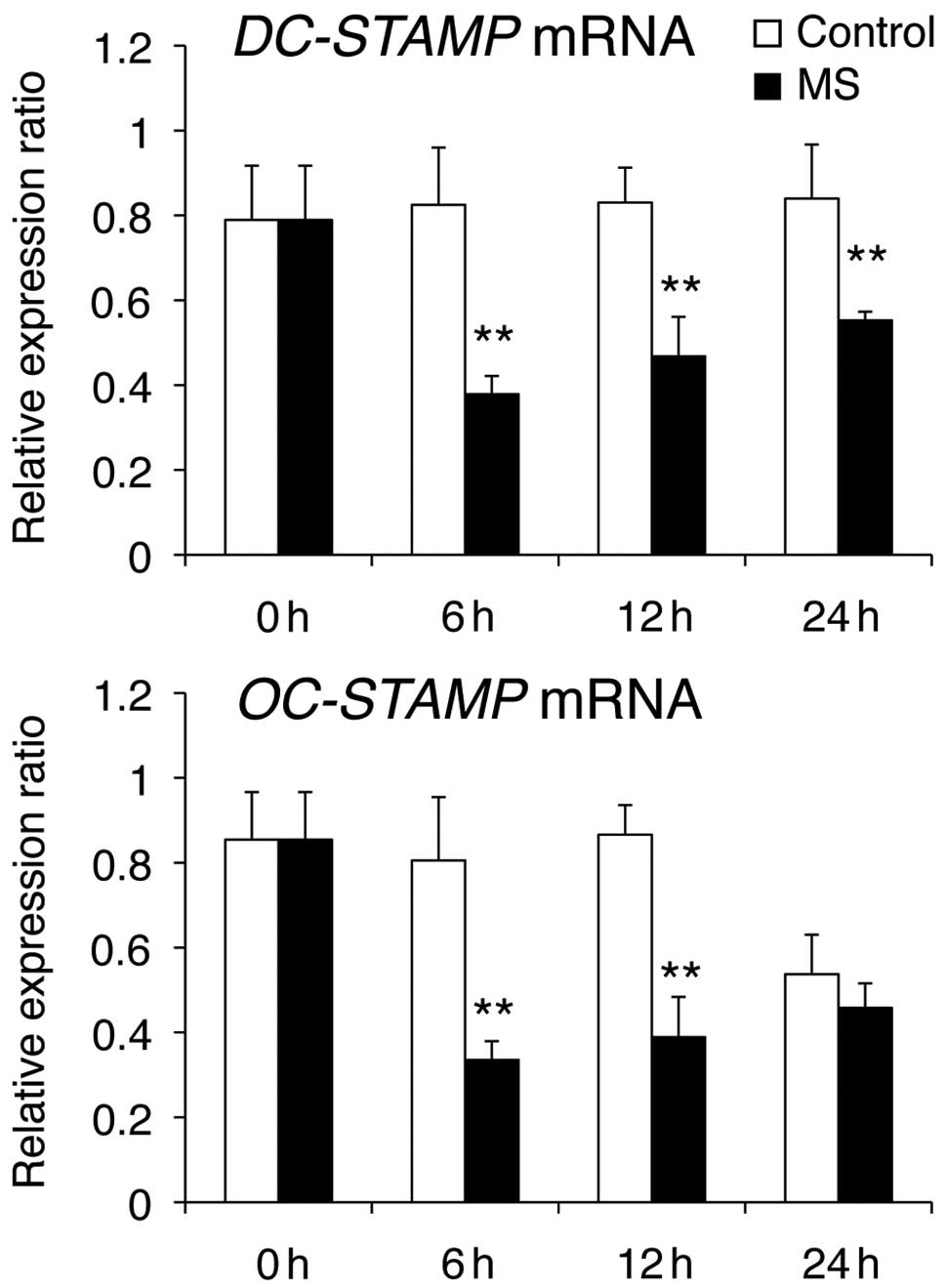
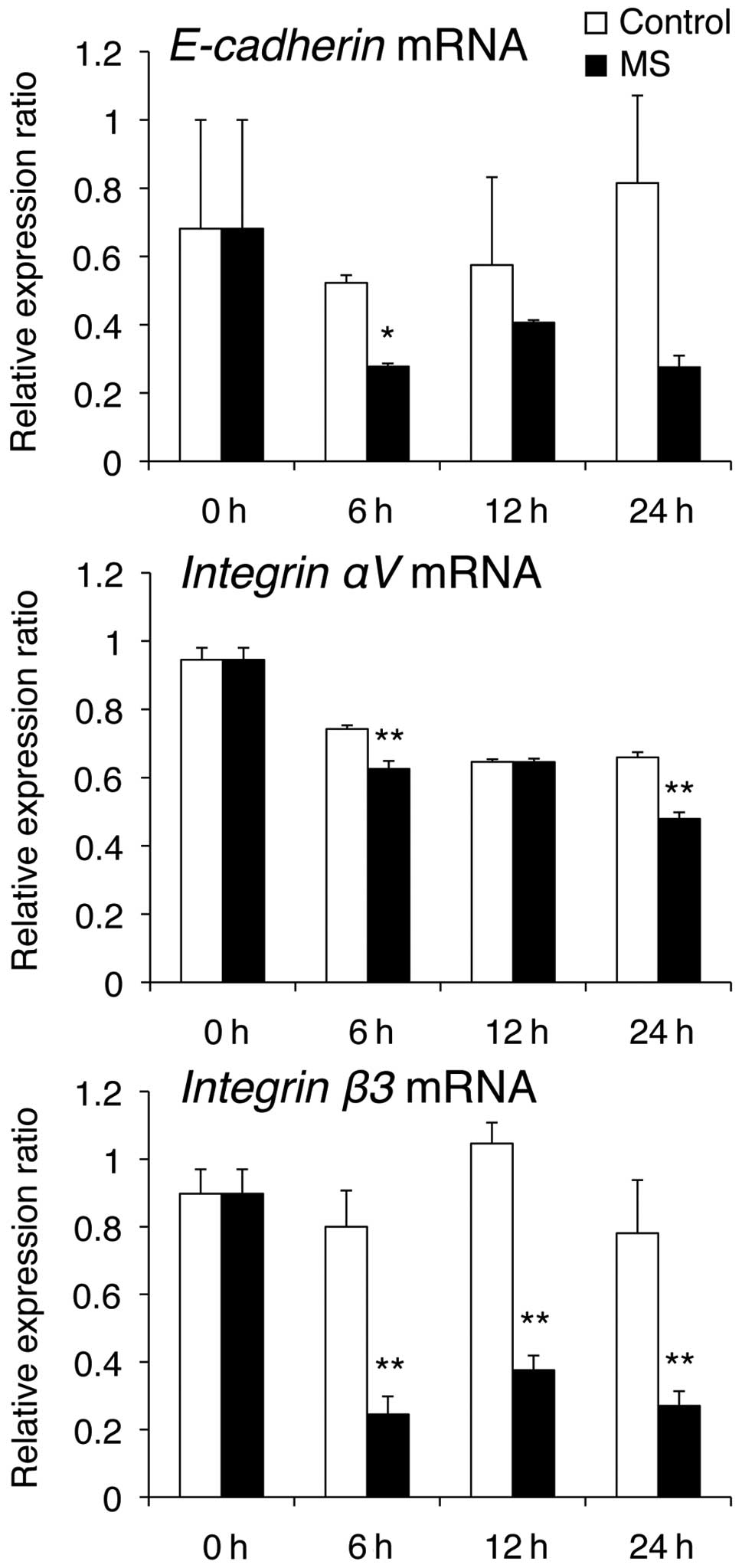
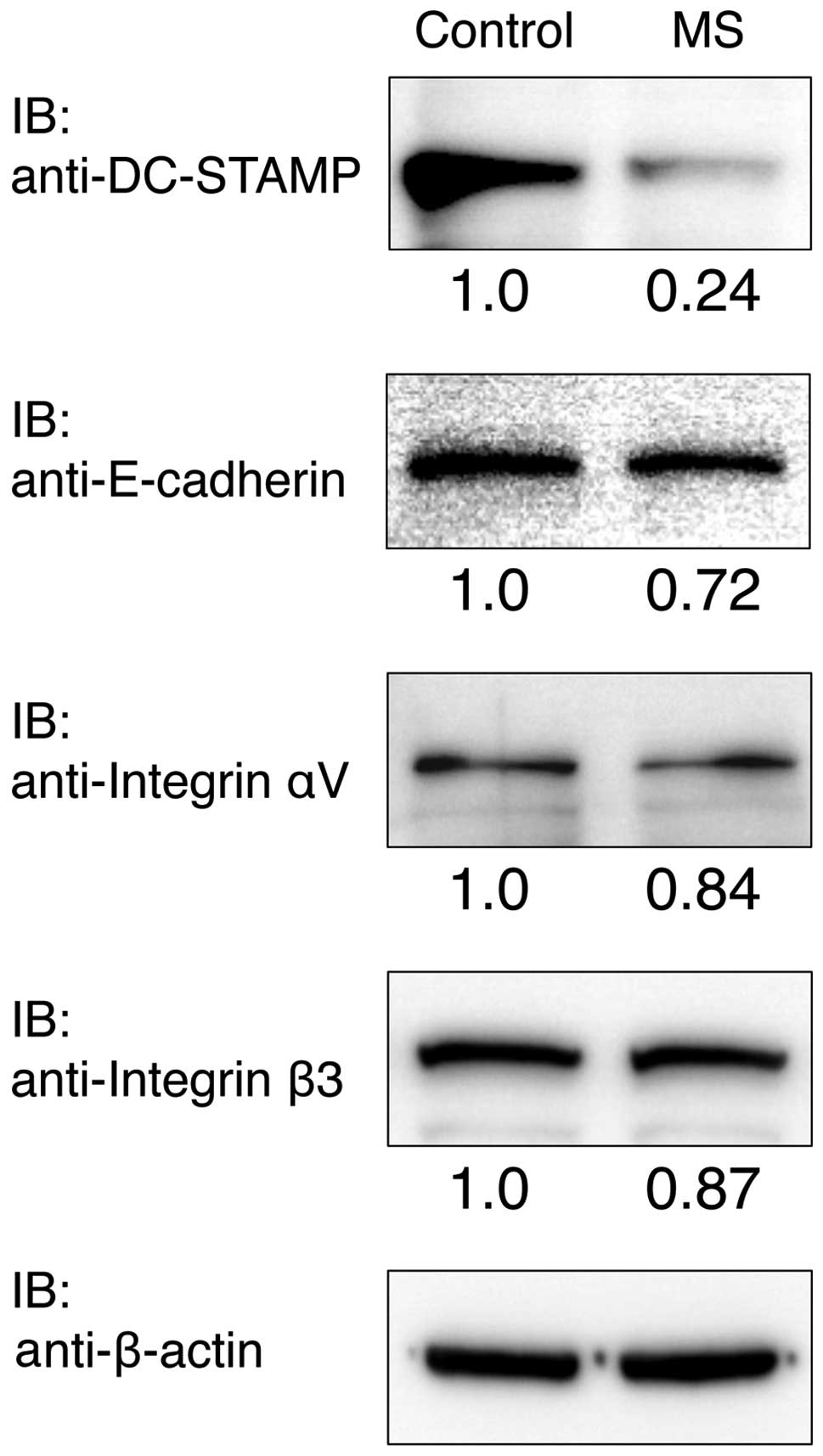
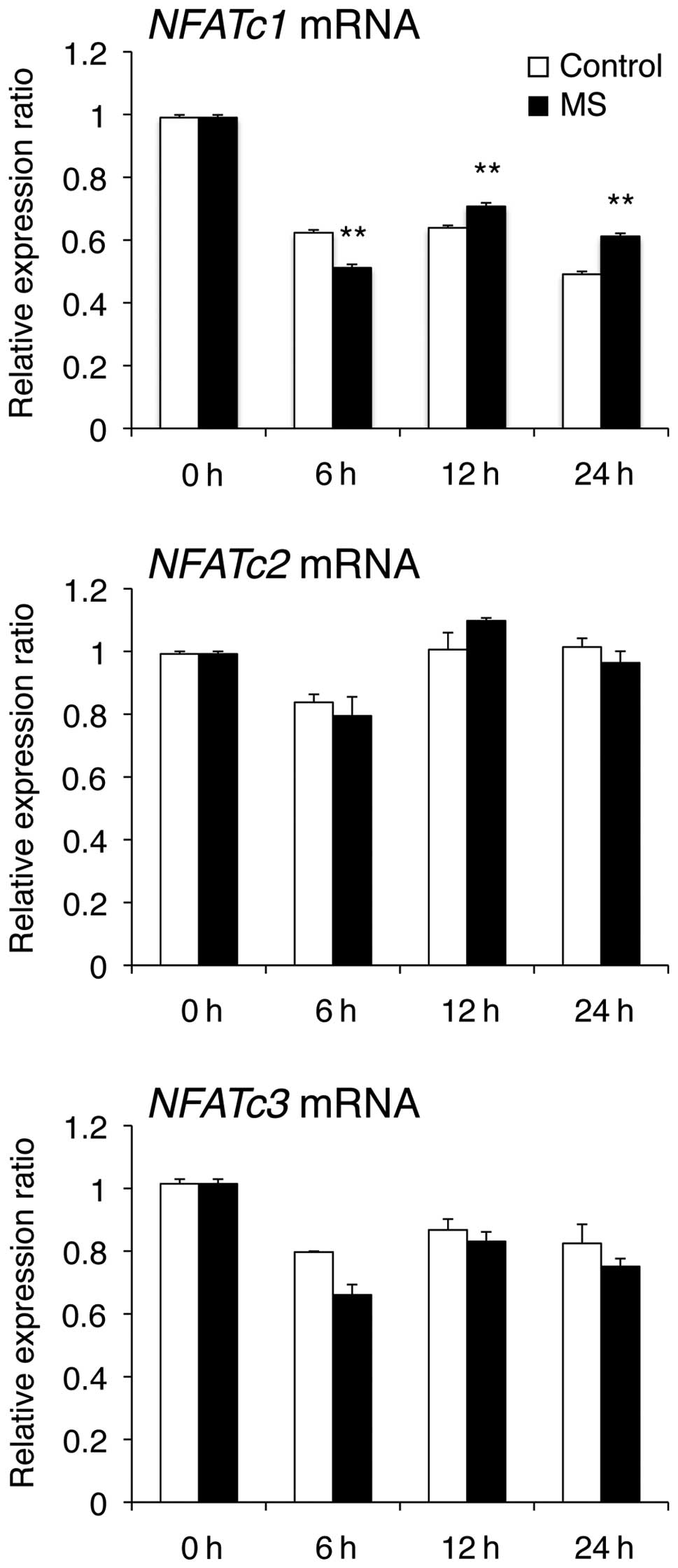
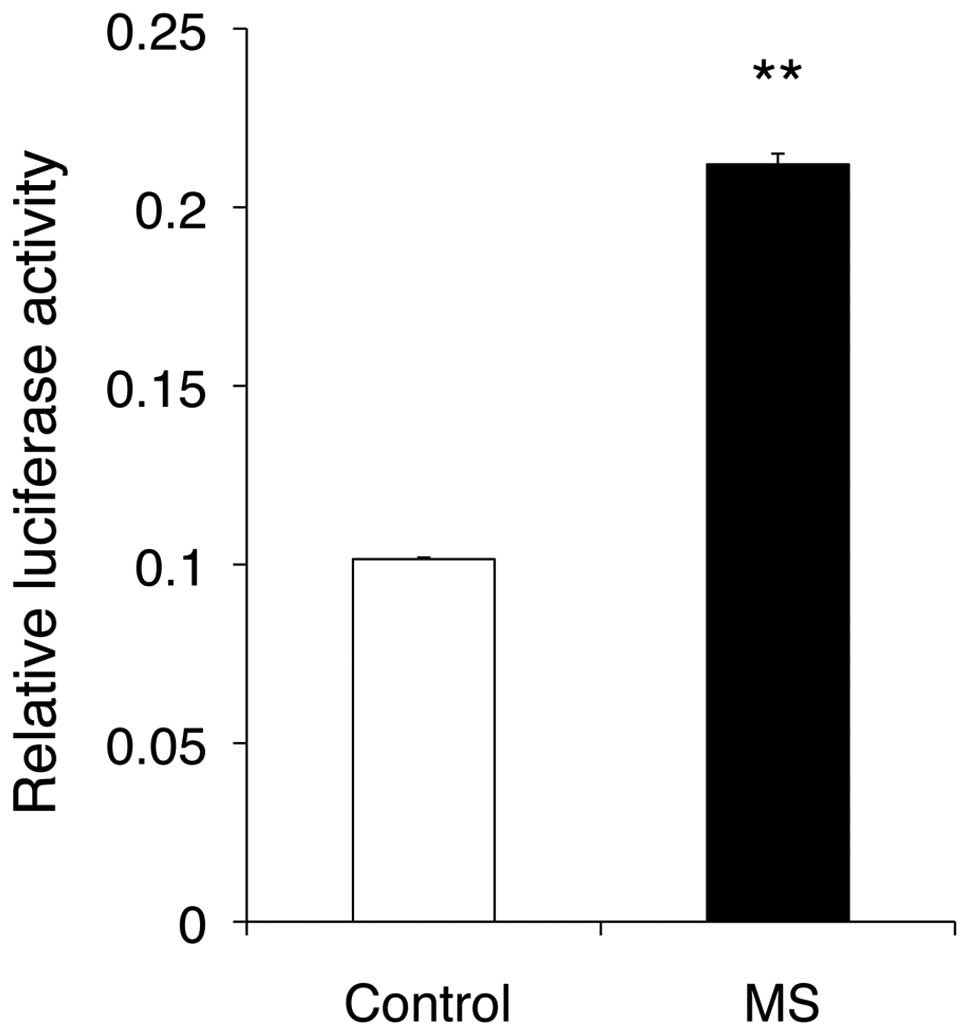
|
1.
|
Teitelbaum SL and Ross FP: Genetic
regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet.
4:638–649. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Helming L and Gordon S: Molecular
mediators of macrophage fusion. Trends Cell Biol. 19:514–522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Negishi-Koga T and Takayanagi H:
Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast
differentiation. Immunol Rev. 231:241–256. 2009.
|
|
6.
|
Nakashima T and Takayanagi H: New
regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1240:E13–E18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Thompson WR, Rubin CT and Rubin J:
Mechanical regulation of signaling pathways in bone. Gene.
503:179–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Al Nazer R, Lanovaz J, Kawalilak C,
Johnston JD and Kontulainen S: Direct in vivo strain measurements
in human bone-a systematic literature review. J Biomech. 45:27–40.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Mehrotra M, Saegusa M, Wadhwa S,
Voznesensky O, Peterson D and Pilbeam C: Fluid flow induces Rankl
expression in primary murine calvarial osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem.
98:1271–1283. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Tan SD, de Vries TJ, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM,
Semeins CM, Everts V and Klein-Nulend J: Osteocytes subjected to
fluid flow inhibit osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Bone.
41:745–751. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kulkarni RN, Bakker AD, Everts V and
Klein-Nulend J: Mechanical loading prevents the stimulating effect
of IL-1β on osteocyte-modulated osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 420:11–16. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ichimiya H, Takahashi T, Ariyoshi W,
Takano H, Matayoshi T and Nishihara T: Compressive mechanical
stress promotes osteoclast formation through RANKL expression on
synovial cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
103:334–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhang F, Wang CL, Koyama Y, Mitsui N,
Shionome C, Sanuki R, Suzuki N, Mayahara K, Shimizu N and Maeno M:
Compressive force stimulates the gene expression of IL-17s and
their receptors in MC3T3-E1 cells. Connect Tissue Res. 51:359–369.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Cho ES, Lee KS, Son YO, Jang YS, Lee SY,
Kwak SY, Yang YM, Park SM and Lee JC: Compressive mechanical force
augments osteoclastogenesis by bone marrow macrophages through
activation of c-Fms-mediated signaling. J Cell Biochem.
111:1260–1269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kaneuji T, Ariyoshi W, Okinaga T,
Toshinaga A, Takahashi T and Nishihara T: Mechanisms involved in
regulation of osteoclastic differentiation by mechanical
stress-loaded osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:103–109.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Rubin J, Murphy TC, Fan X, Goldschmidt M
and Taylor WR: Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase
is involved in mechanical strain inhibition of RANKL expression in
bone stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res. 17:1452–1460. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Koike M, Shimokawa H, Kanno Z, Ohya K and
Soma K: Effects of mechanical strain on proliferation and
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cell line ST2. J Bone Miner
Metab. 23:219–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kanzaki H, Chiba M, Sato A, Miyagawa A,
Arai K, Nukatsuka S and Mitani H: Cyclical tensile force on
periodontal ligament cells inhibits osteoclastogenesis through OPG
induction. J Dent Res. 85:457–462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Rubin J, Biskobing D, Fan X, Rubin C,
McLeod K and Taylor WR: Pressure regulates osteoclast formation and
MCSF expression in marrow culture. J Cell Physiol. 170:81–87. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Makihira S, Kawahara Y, Yuge L, Mine Y and
Nikawa H: Impact of the microgravity environment in a 3-dimensional
clinostat on osteoblast- and osteoclast-like cells. Cell Biol Int.
32:1176–1181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kadow-Romacker A, Hoffmann JE, Duda G,
Wildemann B and Schmidmaier G: Effect of mechanical stimulation on
osteoblastand osteoclast-like cells in vitro. Cells Tissues Organs.
190:61–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kurata K, Uemura T, Nemoto A, Tateishi T,
Murakami T, Higaki H, Miura H and Iwamoto Y: Mechanical strain
effect on bone-resorbing activity and messenger RNA expressions of
marker enzymes in isolated osteoclast culture. J Bone Miner Res.
16:722–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Yan YX, Gong YW, Guo Y, Lv Q, Guo C,
Zhuang Y, Zhang Y, Li R and Zhang XZ: Mechanical strain regulates
osteoblast proliferation through Integrin-mediated ERK activation.
PLoS One. 7:e357092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Suzuki N, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y, Suzuki K
and Kitagawa Y: Mechanical stress directly suppresses osteoclast
differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:291–296.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Shibata K, Yoshimura Y, Kikuiri T,
Hasegawa T, Taniguchi Y, Deyama Y, Suzuki K and Iida J: Effect of
the release from mechanical stress on osteoclastogenesis in
RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 28:73–79. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Oursler MJ: Recent advances in
understanding the mechanisms of osteoclast precursor fusion. J Cell
Biochem. 110:1058–1062. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hartgers FC, Vissers JL, Looman MW, van
Zoelen C, Huffine C, Figdor CG and Adema GJ: DC-STAMP, a novel
multimembrane-spanning molecule preferentially expressed by
dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 30:3585–3590. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Sawatani Y, Iwamoto K,
Hosogane N, Fujita N, Morita K, Ninomiya K, Suzuki T, Miyamoto K,
Oike Y, Takeya M, Toyama Y and Suda T: DC-STAMP is essential for
cell-cell fusion in osteoclasts and foreign body giant cells. J Exp
Med. 202:345–351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kukita T, Wada N, Kukita A, Kakimoto T,
Sandra F, Toh K, Nagata K, Iijima T, Horiuchi M, Matsusaki H,
Hieshima K, Yoshie O and Nomiyama H: RANKL-induced DC-STAMP is
essential for osteoclastogenesis. J Exp Med. 200:941–946. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Toyama Y and Suda T:
Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage
giant cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 24:355–358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Yagi M, Ninomiya K, Fujita N, Suzuki T,
Iwasaki R, Morita K, Hosogane N, Matsuo K, Toyama Y, Suda T and
Miyamoto T: Induction of DC-STAMP by alternative activation and
downstream signaling mechanisms. J Bone Miner Res. 22:992–1001.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Iwasaki R, Ninomiya K, Miyamoto K, Suzuki
T, Sato Y, Kawana H, Nakagawa T, Suda T and Miyamoto T: Cell fusion
in osteoclasts plays a critical role in controlling bone mass and
osteoblastic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:899–904.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kim K, Lee SH, Ha Kim J, Choi Y and Kim N:
NFATc1 induces osteoclast fusion via up-regulation of Atp6v0d2 and
the dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). Mol
Endocrinol. 22:176–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yang M, Birnbaum MJ, MacKay CA,
Mason-Savas A, Thompson B and Odgren PR: Osteoclast stimulatory
trans-membrane protein (OC-STAMP), a novel protein induced by RANKL
that promotes osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Physiol.
215:497–505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Miyamoto H, Suzuki T, Miyauchi Y, Iwasaki
R, Kobayashi T, Sato Y, Miyamoto K, Hoshi H, Hashimoto K, Yoshida
S, Hao W, Mori T, Kanagawa H, Katsuyama E, Fujie A, Morioka H,
Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Takeya M, Toyama Y and Miyamoto T: Osteoclast
stimulatory transmembrane protein and dendritic cell-specific
transmembrane protein cooperatively modulate cell-cell fusion to
form osteoclasts and foreign body giant cells. J Bone Miner Res.
27:1289–1297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Mbalaviele G, Chen H, Boyce BF, Mundy GR
and Yoneda T: The role of cadherin in the generation of
multinucleated osteoclasts from mononuclear precursors in murine
marrow. J Clin Invest. 95:2757–2765. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Miyamoto T, Arai F, Ohneda O, Takagi K,
Anderson DM and Suda T: An adherent condition is required for
formation of multinuclear osteoclasts in the presence of macrophage
colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator of nuclear factor
kappa B ligand. Blood. 96:4335–4343. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Asagiri M, Sato K, Usami T, Ochi S,
Nishina H, Yoshida H, Morita I, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Serfling E and
Takayanagi H: Autoamplification of NFATc1 expression determines its
essential role in bone homeostasis. J Exp Med. 202:1261–1269. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Yasui T, Hirose J, Tsutsumi S, Nakamura K,
Aburatani H and Tanaka S: Epigenetic regulation of osteoclast
differentiation: possible involvement of Jmjd3 in the histone
demethylation of Nfatc1. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2665–2671. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Youn MY, Yokoyama A, Fujiyama-Nakamura S,
Ohtake F, Minehata K, Yasuda H, Suzuki T, Kato S and Imai Y: JMJD5,
a Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing protein, negatively regulates
osteoclastogenesis by facilitating NFATc1 protein degradation. J
Biol Chem. 287:12994–13004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Ilizarov GA: The tension-stress effect on
the genesis and growth of tissues. Part I. The influence of
stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 238:249–281. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Ilizarov GA: The tension-stress effect on
the genesis and growth of tissues: Part II. The influence of the
rate and frequency of distraction. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
239:263–285. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Ilizarov GA: Clinical application of the
tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
250:8–26. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|