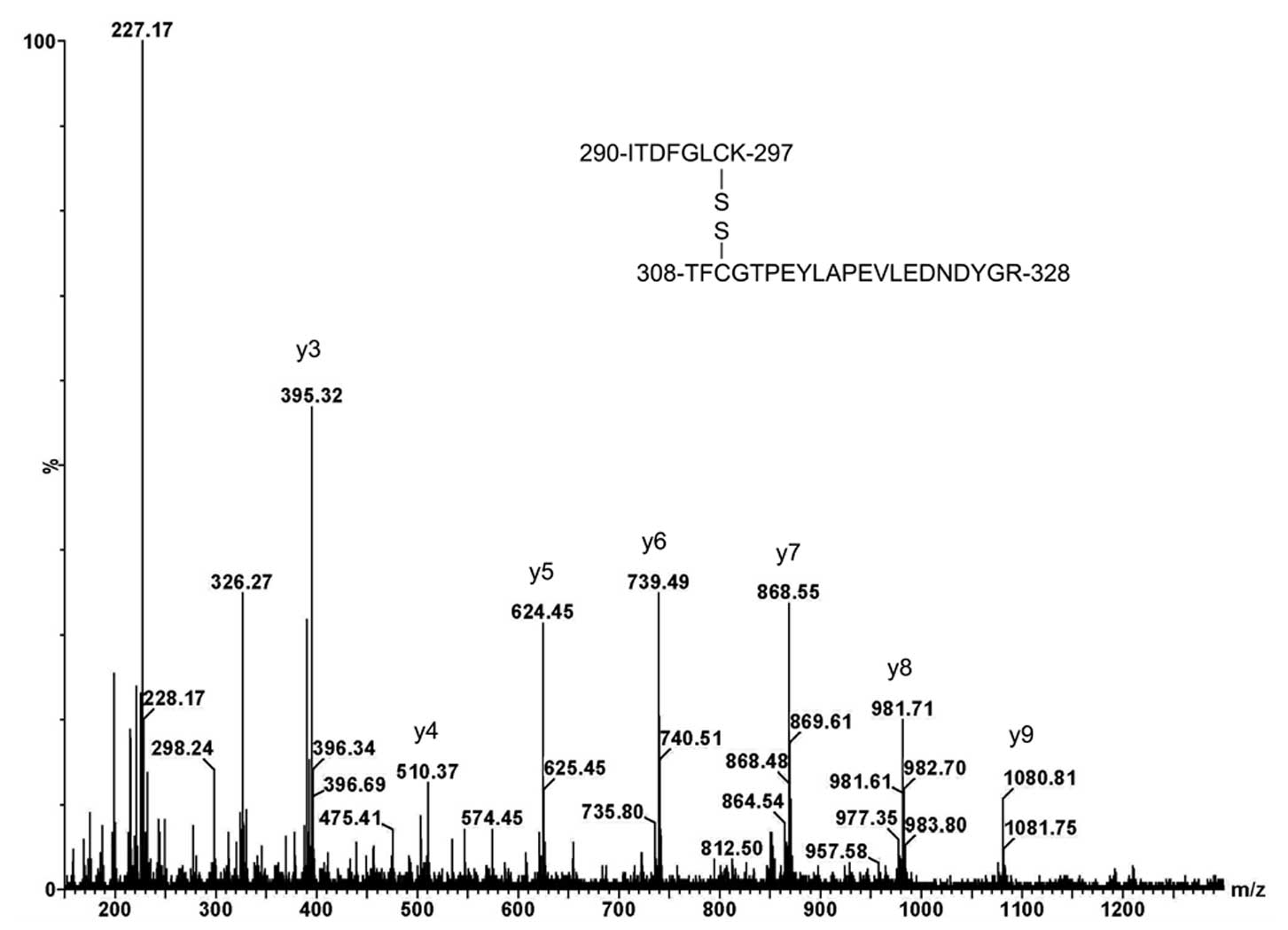
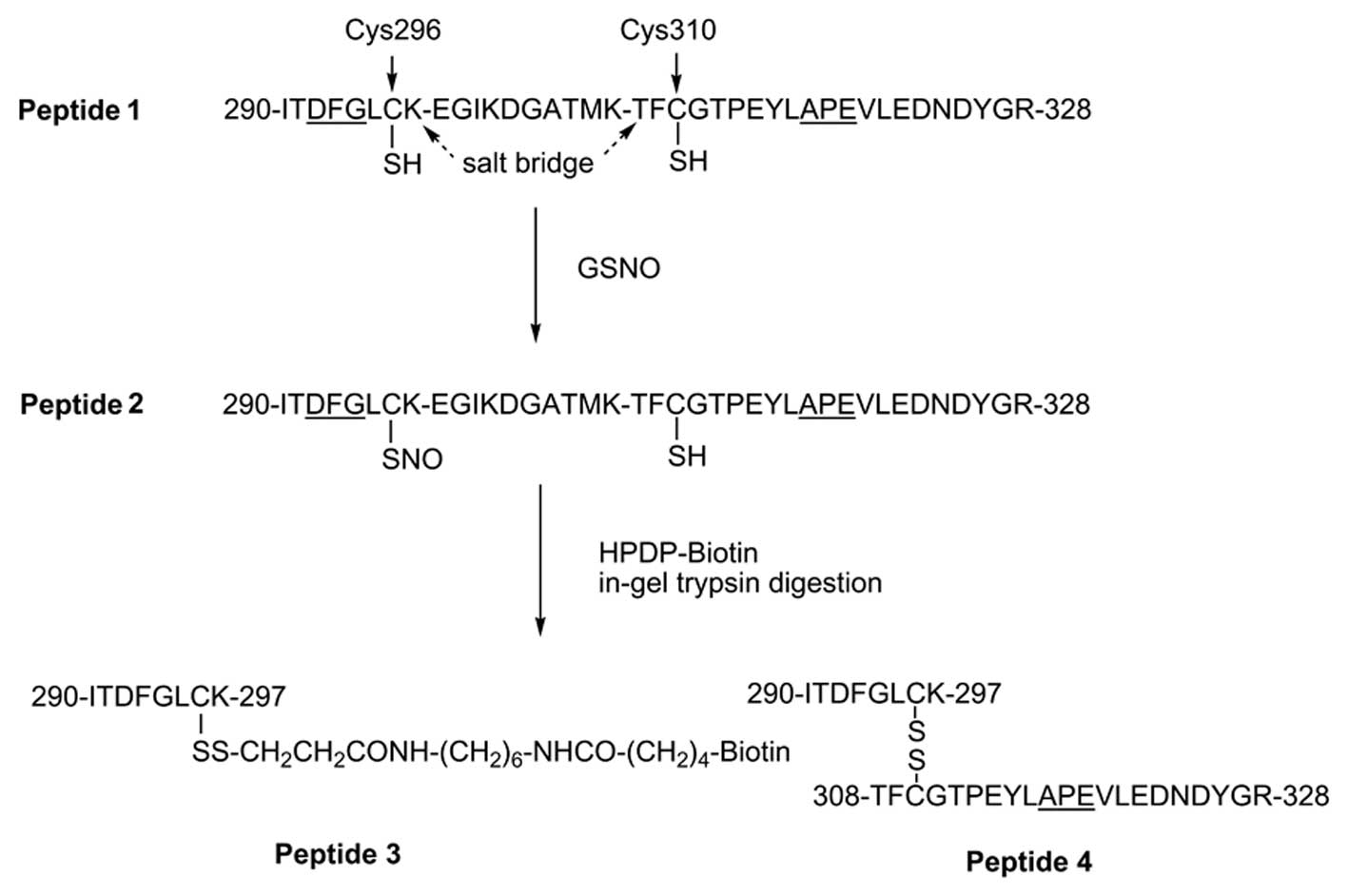
|
1
|
Biolo G, Fleming RY, Maggi SP, Nguye TT,
Herndon DN and Wolfe RR: Inverse regulation of protein turnover and
amino acid transport in skeletal muscle of hypercatabolic patients.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:3378–3384. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bruning JC, Winnay J, Cheatham B and Kahn
CR: Differential signaling by insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1)
and IRS-2 in IRS-1-deficient cells. Mol Cell Biol. 17:1513–1521.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carvalho E, Rondinone C and Smith U:
Insulin resistance in fat cells from obese Zucker rats - evidence
for an impaired activation and translocation of protein kinase B
and glucose transporter 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 206:7–16. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Araki E, Lipes MA, Patti ME, Bruning JC,
Haag B, Johnson RS and Kahn CR: Alternative pathway of insulin
signaling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene.
Nature. 372:186–190. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khoury W, Klausner JM, Ben-Abraham R and
Szold O: Glucose control by insulin for critically ill surgical
patients. J Trauma. 57:1132–1138. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carter EA, Burks D, Fischman AJ, White M
and Tompkins RG: Insulin resistance in thermally-injured rats is
associated with post-receptor alterations in skeletal muscle, liver
and adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med. 14:653–658. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johan Groeneveld AB, Beishuizen A and
Visser FC: Insulin: a wonder drug in the critically ill? Crit Care.
6:102–105. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ikezu T, Okamato T, Yonezawa K, Tompkins
RG and Martyn JA: Analysis of thermal injury-induced insulin
resistance in rodents. J Biol Chem. 272:25289–25295. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
White MF: Insulin signaling in health and
disease. Science. 302:1710–1711. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Carter EA, Ma BY, White M,
Fischman AF and Tompkins RG: Molecular mechanism(s) of burn-induced
insulin resistance in murine skeletal muscle: role of IRS
phosphorylation. Life Sci. 77:3068–3077. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ishiki M and Klip A: Minireview: recent
developments in the regulation of glucose transporter-4 traffic:
new signals, locations, and partners. Endocrinology. 146:5071–5078.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kaneki M, Shimizu N, Yamada D and Chang K:
Nitrosative stress and pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 9:1–11. 2007.
|
|
14
|
Song G, Quyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Neels JG and Olefsky JM: Cell signaling. A
new way to burn fat. Science. 312:1756–1758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tian R: Another role for celebrity: Akt
and insulin resistance. Circ Res. 96:139–140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lawlor MA and Alessi DR: PKB/Akt: a key
mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J
Cell Sci. 114:2903–2910. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Cron P, Thompson V, Good VM, Hess
D, Hemmings BA and Barford D: Molecular mechanism for the
regulation of protein kinase B/Akt by hydrophobic motif
phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 9:1227–1240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Cron P, Good VM, Thompson V,
Hemmings BA and Barford D: Crystal structure of an activated
Akt/protein kinase B ternary complex with GSK3-peptide and AMP-PNP.
Nat Struct Biol. 9:940–944. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang X, Begley M, Morgenstern KA, Gu Y,
Rose P, Zhao H and Zhu X: Crystal structure of an inactive Akt2
kinase domain. Structure. 11:21–30. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar CC and Madison V: Akt crystal
structure and Akt-specific inhibitors. Oncogene. 24:7493–7501.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fayard E, Tintignac LA, Baudry A and
Hemmings BA: Protein kinase B/Akt at a glance. J Cell Sci.
118:5675–5678. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ and Hemmings BA:
Advances in protein kinase B signaling: AKTion on multiple fronts.
Trends Biochem Sci. 29:233–242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brazil DP, Park J and Hemmings BA: PKB
binding proteins: getting in on the Akt. Cell. 111:293–303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang BX and Kim HY: Interdomain
conformational changes in Akt activation revealed by chemical
cross-linking and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics.
5:1045–1053. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sugita H, Kaneki M, Sugita M, Yasukawa T,
Yasuhara S and Martyn JA: Burn injury impairs insulin-stimulated
Akt/PKB activation in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 288:E585–E591. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carvalho-Filho MA, Ueno M, Hirabara SM,
Seabra AB, Carvalheira JB, de Oliveira MG, Velloso LA, Curi R and
Saad MJ: S-nitrosation of the insulin receptor, insulin receptor
substrate 1, and protein kinase B/Akt: novel mechanism of insulin
resistance. Diabetes. 54:959–967. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yasukawa T, Tokunaga E, Ota H, Sugita H,
Martyn JA and Kaneki M: S-Nitrosylation-dependent inactivation of
Akt/protein kinase B in insulin resistance. J Biol Chem.
280:7511–7518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carter EA, Derojas-Walker T, Tamir S,
Tannenbaum SR, Yu YM and Tompkins RG: Nitric oxide production is
intensely and persistently increased in tissue by thermal injury.
Biochem J. 304:201–204. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Auguin D, Barthe P, Auge-Senegas MT, Stern
MH, Noguchi M and Roumestand C: Solution structure and backbone
dynamics of the Pleckstrin homology domain of the human protein
kinase B (PKB/Akt). Interaction with inositol phosphates. J Biomol
NMR. 28:137–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murata H, Ihara Y, Nakamura H, Yodoi J,
Sumikawa K and Kondo T: Glotaredoxin exerts an antiapoptotic effect
by regulating the redox state of Akt. J Biol Chem. 278:50226–50233.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu XM, Lu MY, Fischman AJ and Tompkins RG:
A new approach for sequencing human IRS1 phosphotyrosine-containing
peptides using CapLC-Q-TOF(micro). J Mass Spectrom. 40:599–607.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu XM, Lu M, Tompkins RG and Fischman AJ:
Site-specific detection of S-nitrosylated PKBa/Akt1 from rat soleus
muscle using CapLC-Q-TOF(micro) mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom.
40:1140–1148. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris
CD, Tempst P and Snyder SH: Protein S-nitrosylation: a
physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol.
3:193–197. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jaffrey SR and Snyder SH: The biotin
switch method for detection of S-nitrosylated proteins. Science
STKE. 86:1–9. 2001.
|
|
36
|
Greco TM, Hodara R, Parastatidis I,
Heijnen HFG, Dennehy MK, Liebler DC and Ischiropoulos H:
Identification of S-nitrosylation motifs by site-specific mapping
of the S-nitrosocysteine proteome in human vascular smooth muscle
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7420–7425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hao G, Derakhshan B, Shi L, Campagne F and
Gross SS: SNOSID, a proteomic method for identification of cysteine
S-nitrosylation sites in complex protein mixtures. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:1012–1017. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kuncewicz T, Sheta EA, Goldknopf IL and
Kone BC: Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylated proteins in mesangial
cell. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2:156–163. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martinez-Ruiz A and Lamas S: Detection and
proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in endothelial
cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 423:192–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gan HT and Chen JDZ: Roles of nitric oxide
and prostaglandins in pathogenesis of delayed colonic transit after
burn injury in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
288:R1316–R1324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Torres SH, De Sanctis JB, de L Briceno M,
Hernandez N and Finol HJ: Inflammation and nitric oxide production
in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic patients. J Endocrinol.
181:419–427. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benhar M, Forrester MT and Stamler JS:
Nitrosative stress in the ER: a new role for S-nitrosylation in
neurodegenerative diseases. ACS Chem Biol. 1:355–358. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tannenbaum SR and White FM: Regulation and
specificity of S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation. ACS Chem Biol.
1:615–618. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hogg N: The biochemistry and physiology of
S-nitrosothiols. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 42:585–600. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Arnelle DR and Stamler JS: NO+,
NO•, and NO− donation by S-nitrosothiols:
implications for regulation of physiological functions by
S-nitrosylation and acceleration of disulfide formation. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 318:279–285. 1995.
|
|
46
|
Carvalho-Filho MA, Ueno M, Carvalheira JB,
Velloso LA and Saad MJ: Targeted disruption of iNOS prevents
LPS-induced S-nitrosation of IRbeta/IRS-1 and Akt and insulin
resistance in muscle of mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
291:E476–E482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu WI, Voegtli WC, Sturgis HL, Dizon FP,
Vigers GP and Brandhuber BJ: Crystal structure of human AKT1 with
an allosteric inhibitor reveals a new mode of kinase inhibition.
PLos One. 5:e129132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kloet DE and Burgering BM: The PKB/FOXO
switch in aging and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1926–1937.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|