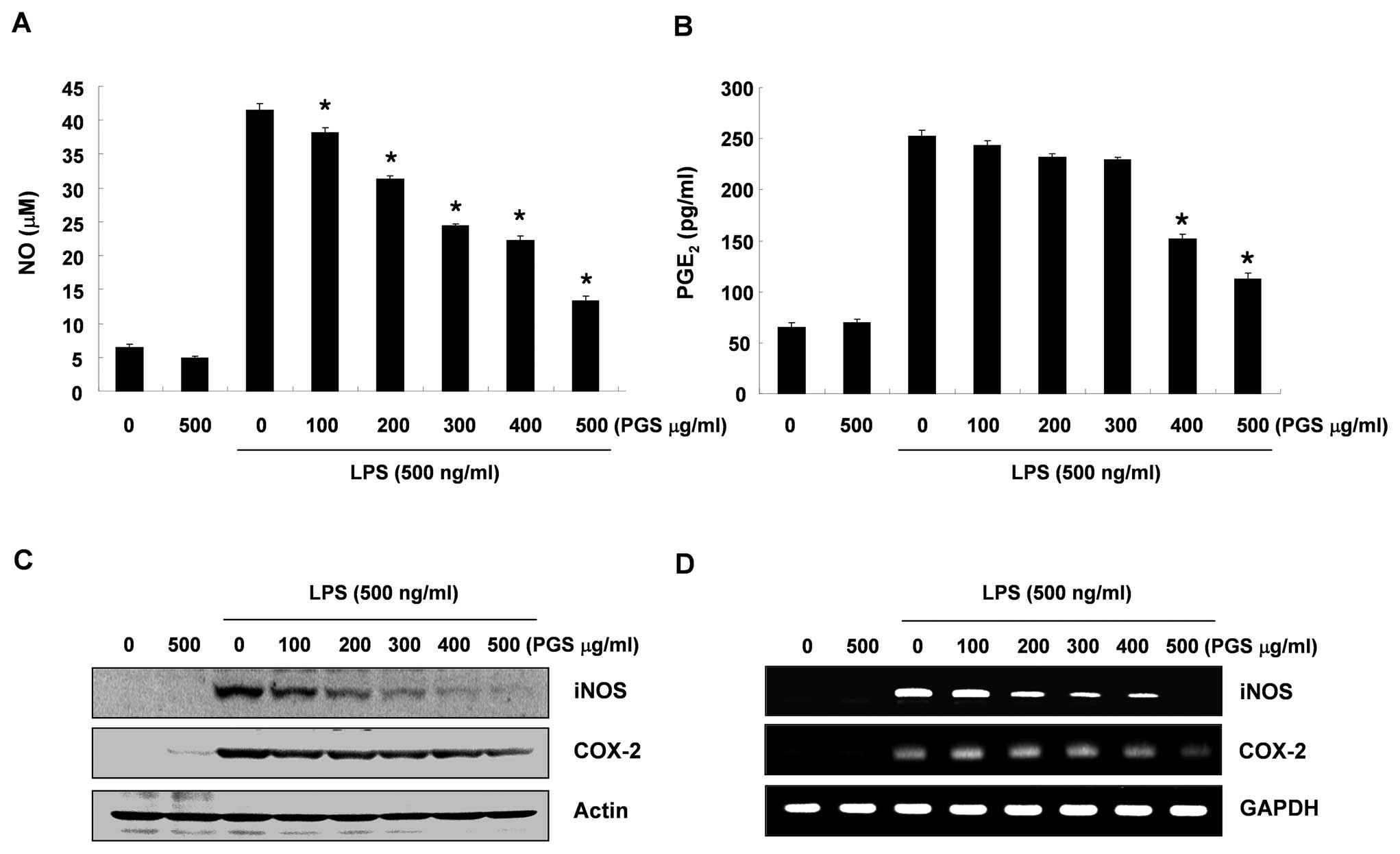
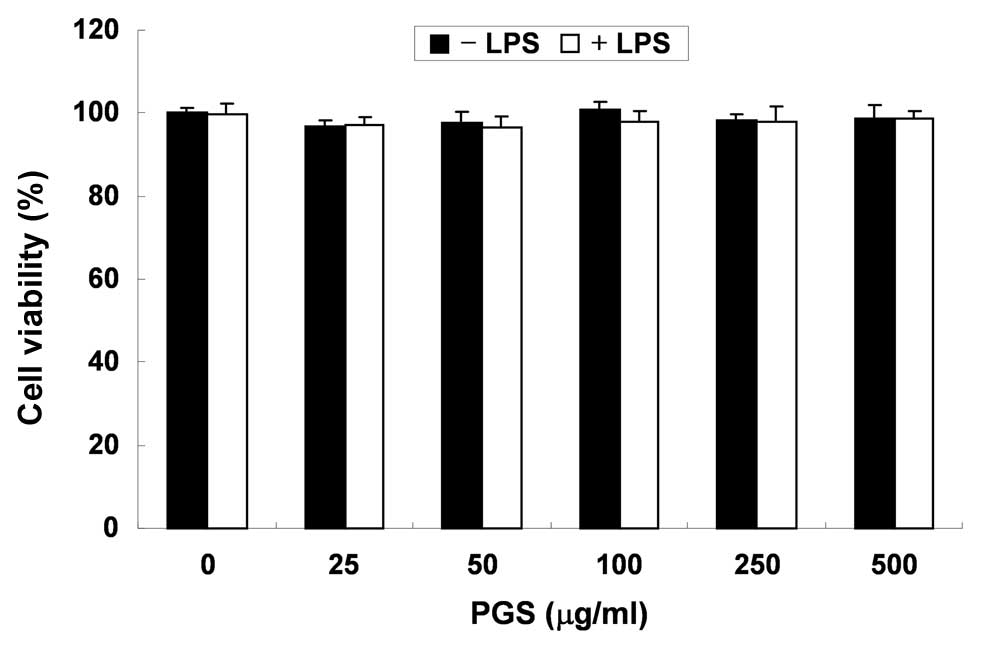
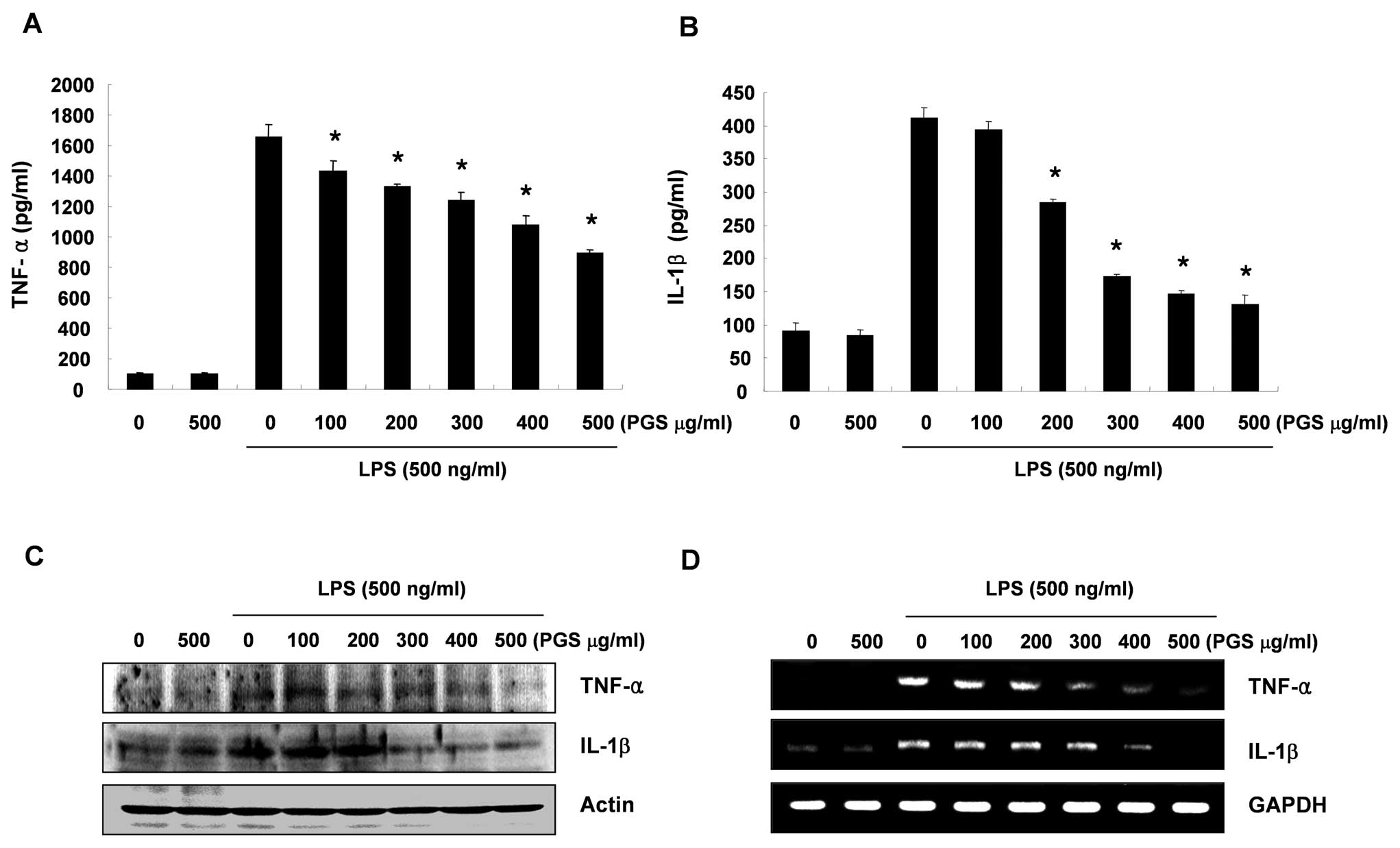
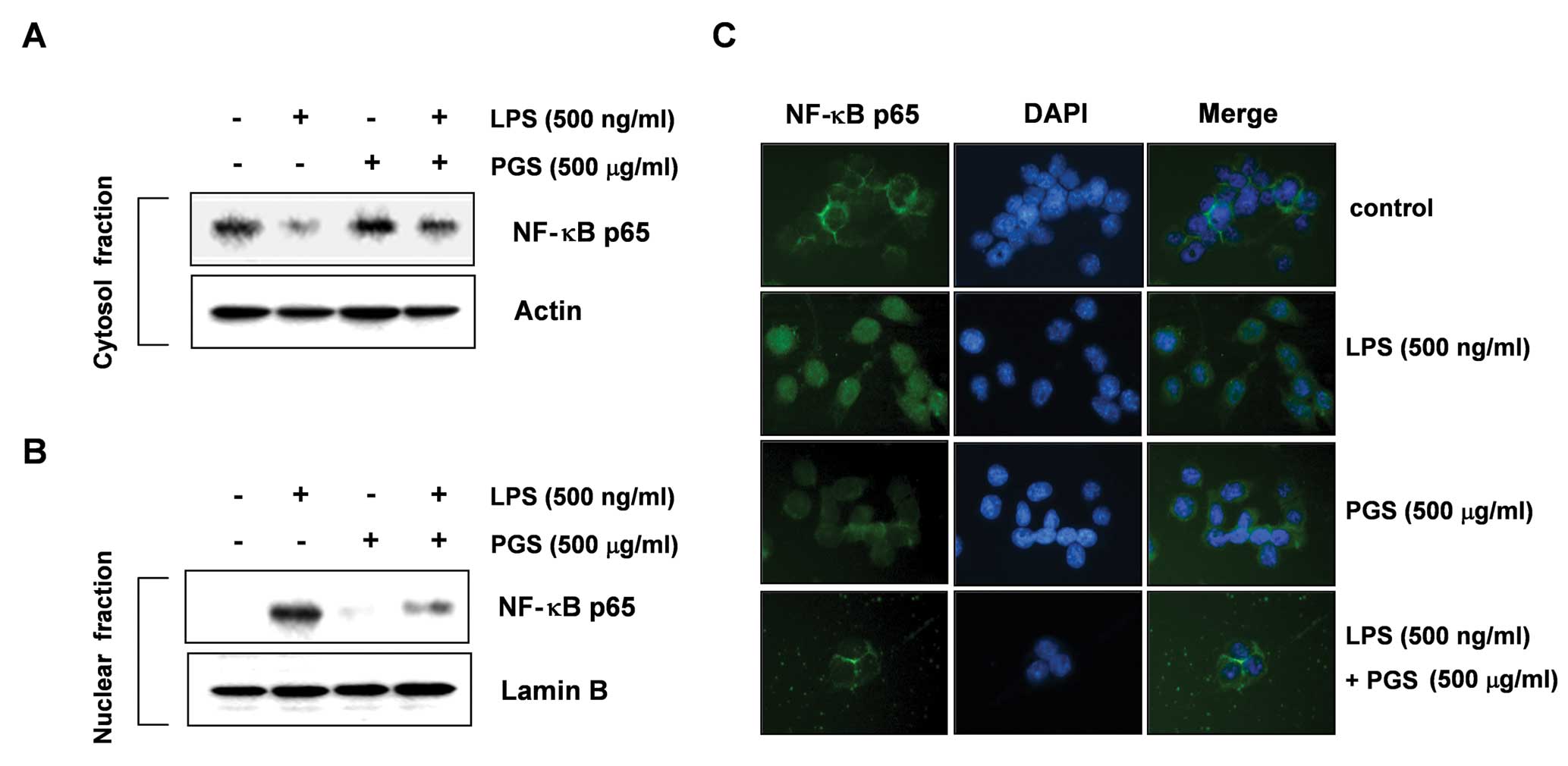
|
1
|
Knowles RG and Moncada S: Nitric oxide
synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 298:249–258. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Banion MK: Cyclooxygenase-2: molecular
biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology. Crit Rev Neurobiol.
13:45–82. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abrams J: Beneficial actions of nitrites
in cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 77:31C–37C. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hou YC, Janczuk A and Wang PG: Current
trends in the development of nitric oxide donors. Curr Pharm Des.
5:417–441. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rock RB and Peterson PK: Microglia as a
pharmacological target in infectious and inflammatory diseases of
the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:117–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kaur C and Ling EA: Antioxidants and
neuroprotection in the adult and developing central nervous system.
Curr Med Chem. 15:3068–3080. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deng YY, Lu J, Ling EA and Kaur C: Role of
microglia in the process of inflammation in the hypoxic developing
brain. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 3:884–900. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perry VH and Gordon S: Macrophages and
microglia in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 92:273–274. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Napoli I and Neumann H: Microglial
clearance function in health and disease. Neuroscience.
158:1030–1038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eikelenboom P and van Gool WA:
Neuroinflammatory perspectives on the two faces of Alzheimer's
disease. J Neural Transm. 111:281–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Loane DJ and Byrnes KR: Role of microglia
in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics. 7:366–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu B and Hong JS: Role of microglia in
inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and
strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
304:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Germida JJ, Siciliano SD, Freitas JR and
Seib AM: Diversity of root-associated bacteria associated with
field-grown canola (Brassica napus L.) and wheat
(Triticum aestivum L.). FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 26:43–50. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee JY, Hwang WI and Lim ST: Antioxidant
and anticancer activities of organic extracts from Platycodon
grandiflorum A. De Candolle roots. J Ethnopharmacol.
93:409–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ishii H, Tori K, Tozyo T and Yoshimura Y:
Structures of polygalacin-D and -D2, platycodin-D and -D2, and
their monoacetates, saponins isolated from Platycodon
grandiflorum A. DC., determined by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic
resonance spectroscopy. Chem Pharm Bull. 26:674–677. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fu WW, Shimizu N, Dou DQ, Takeda T, Fu R,
Pei YH and Chen YJ: Five new triterpenoid saponins from the roots
of Platycodon grandiflorum. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
54:557–560. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YP, Lee EB, Kim SY, Li D, Ban HS, Lim
SS, Shin KH and Ohuchi K: Inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production
by platycodin D isolated from the root of Platycodon
grandiflorum. Planta Med. 67:362–364. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang C, Schuller Levis GB, Lee EB, Levis
WR, Lee DW, Kim BS, Park SY and Park E: Platycodin D and D3
isolated from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum modulate
the production of nitric oxide and secretion of TNF-alpha in
activated RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1039–1049.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoon YD, Kang JS, Han SB, Park SK, Lee HS,
Kang JS and Kim HM: Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases
and AP-1 by polysaccharide isolated from the radix of Platycodon
grandiflorum in RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
4:1477–1487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ahn KS, Noh EJ, Zhao HL, Jung SH, Kang SS
and Kim YS: Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and
cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via
suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells.
Life Sci. 76:2315–2328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chung JW, Noh EJ, Zhao HL, Sim JS, Ha YW,
Shin EM, Lee EB, Cheong CS and Kim YS: Anti-inflammatory activity
of prosapogenin methyl ester of platycodin D via nuclear
factor-kappaB pathway inhibition. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:2114–2120.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jang MH, Kim CJ, Kim EH, Kim MG, Leem KH
and Kim J: Effects of Platycodon grandiflorum on
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of prostaglandin E2,
nitric oxide, and interleukin-8 in mouse microglial BV2 cells. J
Med Food. 9:169–174. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Bae DS, Kim YH, Pan CH, Nho CW, Samdan J,
Yansan J and Lee JK: Protopine reduces the inflammatory activity of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages. BMB Rep.
45:108–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC,
Schottelius AJ, Baldwin AS Jr and Mayo MW: Akt suppresses apoptosis
by stimulating the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65
subunit of NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol. 20:1626–1638. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei J and Feng J: Signaling pathways
associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm
Allergy Drug Discov. 4:105–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fiebich BL, Lieb K, Kammerer N and Hüll M:
Synergistic inhibitory effect of ascorbic acid and acetylsalicylic
acid on prostaglandin E2 release in primary rat microglia. J
Neurochem. 86:173–178. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liang X, Wu L, Wang Q, Hand T, Bilak M,
McCullough L and Andreasson K: Function of COX-2 and prostaglandins
in neurological disease. J Mol Neurosci. 33:94–99. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Scher JU and Pillinger MH: The
anti-inflammatory effects of prostaglandins. J Investig Med.
57:703–708. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Levi G, Minghetti L and Aloisi F:
Regulation of prostanoid synthesis in microglial cells and effects
of prostaglandin E2 on microglial functions. Biochimie. 80:899–904.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giovannini MG, Scali C, Prosperi C,
Bellucci A, Pepeu G and Casamenti G: Experimental brain
inflammation and neurode-generation as model of Alzheimer's
disease: protective effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 16:31–40. 2003.
|
|
31
|
MacMicking J, Xie QW and Nathan C: Nitric
oxide and macrophage function. Ann Rev Immunol. 15:323–330. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitchell JA, Larkin S and Williams TJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2: regulation and relevance in inflammation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 50:1535–1542. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mulrennan SA and Redington AE: Nitric
oxide synthase inhibition: therapeutic potential in asthma. Treat
Respir Med. 3:79–88. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cau SB, Carneiro FS and Tostes RC:
Differential modulation of nitric oxide synthases in aging:
therapeutic opportunities. Front Physiol. 3:2182012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iadecola C and Ross ME: Molecular
pathology of cerebral ischemia: delayed gene expression and
strategies for neuroprotection. Ann NY Acad Sci. 835:203–217. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
del Zoppo G, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM,
Iadecola C, Wang X and Feuerstein GZ: Inflammation and stroke:
putative role for cytokines, adhesion molecules and iNOS in brain
response to ischemia. Brain Pathol. 10:95–112. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Boka G, Anglade P, Wallach D, Javoy-Agid
F, Agid Y and Hirsch EC: Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor
necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci
Lett. 172:151–154. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hunot S, Dugas N, Faucheux B, Hartmann A,
Tardieu M, Debré P, Agid Y, Dugas B and Hirsch EC:
FcepsilonRII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson's disease and induces,
in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha in glial cells. J Neurosci. 19:3440–3447.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De Nardin E: The role of inflammatory and
immunological mediators in periodontitis and cardiovascular
disease. Ann Periodontol. 6:30–40. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Viscido A, Aratari A, Maccioni F, Signore
A and Caprilli R: Inflammatory bowel diseases: clinical update of
practical guidelines. Nucl Med Commun. 26:649–655. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sawada M, Kondo N, Suzumura A and
Marunouchi T: Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by
microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 491:394–397. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Owens T: Identification of new therapeutic
targets for prevention of CNS inflammation. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 6:203–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rothwell N, Allan S and Toulmond S: The
role of interleukin 1 in acute neurodegeneration and stroke:
pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. J Clin Invest.
100:2648–2652. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Suzumura A, Takeuchi H, Zhang G, Kuno R
and Mizuno T: Roles of glia-derived cytokines on neuronal
degeneration and regeneration. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1088:219–229. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee JY, Jhun BS, Oh YT, Lee JH, Choe W,
Baik HH, Ha J, Yoon KS, Kim SS and Kang I: Activation of adenosine
A3 receptor suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha
production through inhibition of PI3-kinase/Akt and NF-kappaB
activation in murine BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 396:1–6.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mankan AK, Lawless MW, Gray SG, Kelleher D
and McManus R: NF-kappaB regulation: the nuclear response. J Cell
Mol Med. 13:631–643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee JW, Lee MS, Kim TH, Lee HJ, Hong SS,
Noh YH, Hwang BY, Ro JS and Hong JT: Inhibitory effect of
inflexinol on nitric oxide generation and iNOS expression via
inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Mediators Inflamm.
2007:931482007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee YH, Jeon SH, Kim SH, Kim C, Lee SJ,
Koh D, Lim Y, Ha K and Shin SY: A new synthetic chalcone
derivative, 2-hydroxy-3′,5,5′-trimethoxychalcone (DK-139),
suppresses the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response
through inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway in BV2 microglial
cells. Exp Mol Med. 44:369–377. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moon DO, Choi YH, Kim ND, Park YM and Kim
GY: Anti-inflammatory effects of beta-lapachone in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:506–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Garrington TP and Johnson GL: Organization
and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 11:211–218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ashwell JD: The many paths to p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in the immune system.
Nat Rev Immunol. 6:532–540. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cuenda A, Rouse J, Doza YN, Meier R, Cohen
P, Gallagher TF, Young PR and Lee JC: SB 203580 is a specific
inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular
stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 364:229–233. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Barone FC, Irving EA, Ray AM, Lee JC,
Kassis S, Kumar S, Badger AM, Legos JJ, Erhardt JA, Ohlstein EH,
Hunter AJ, Harrison DC, Philpott K, Smith BR, Adams JL and Parsons
AA: Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase provides
neuroprotection in cerebral focal ischemia. Med Res Rev.
21:129–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|