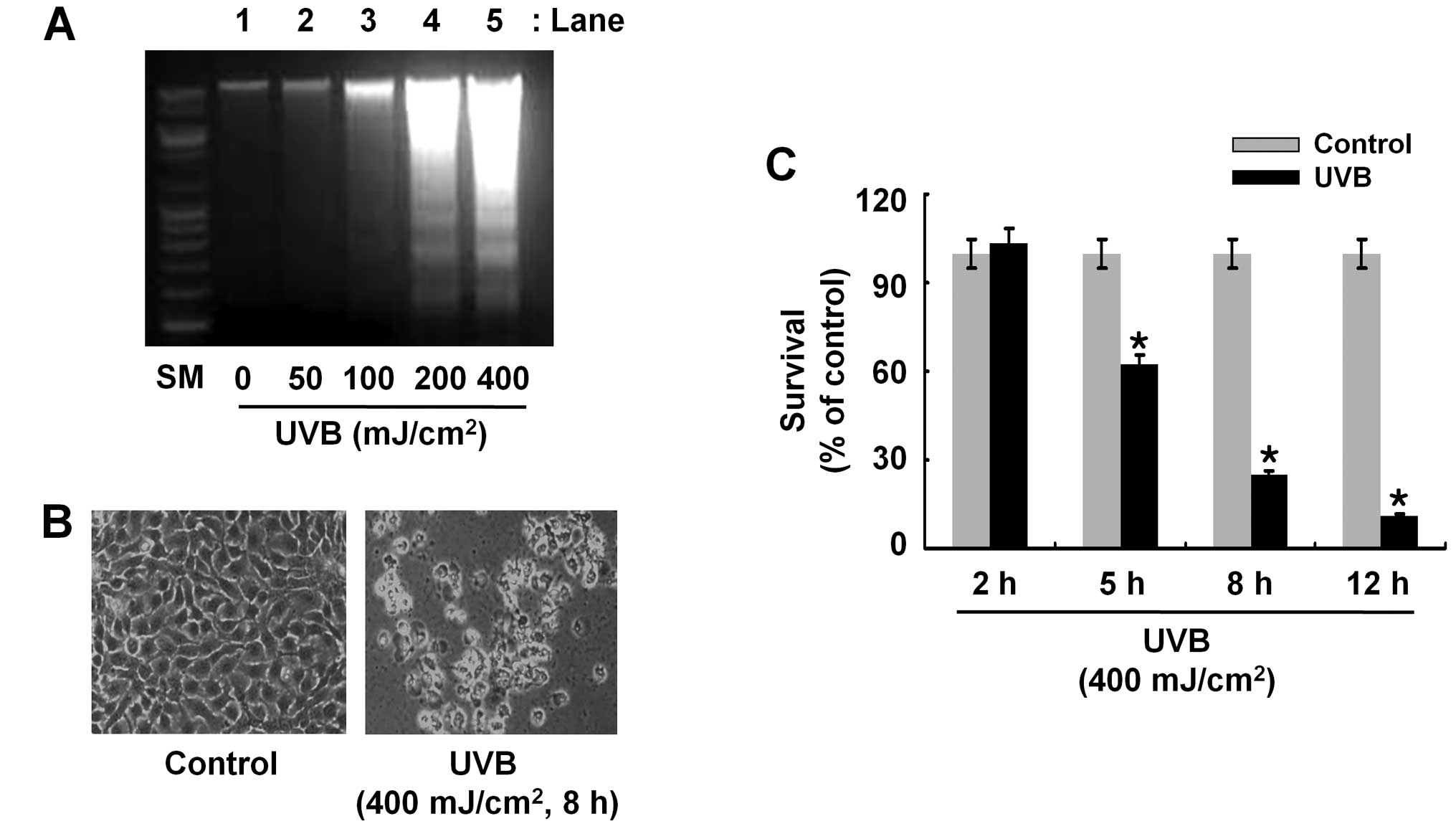
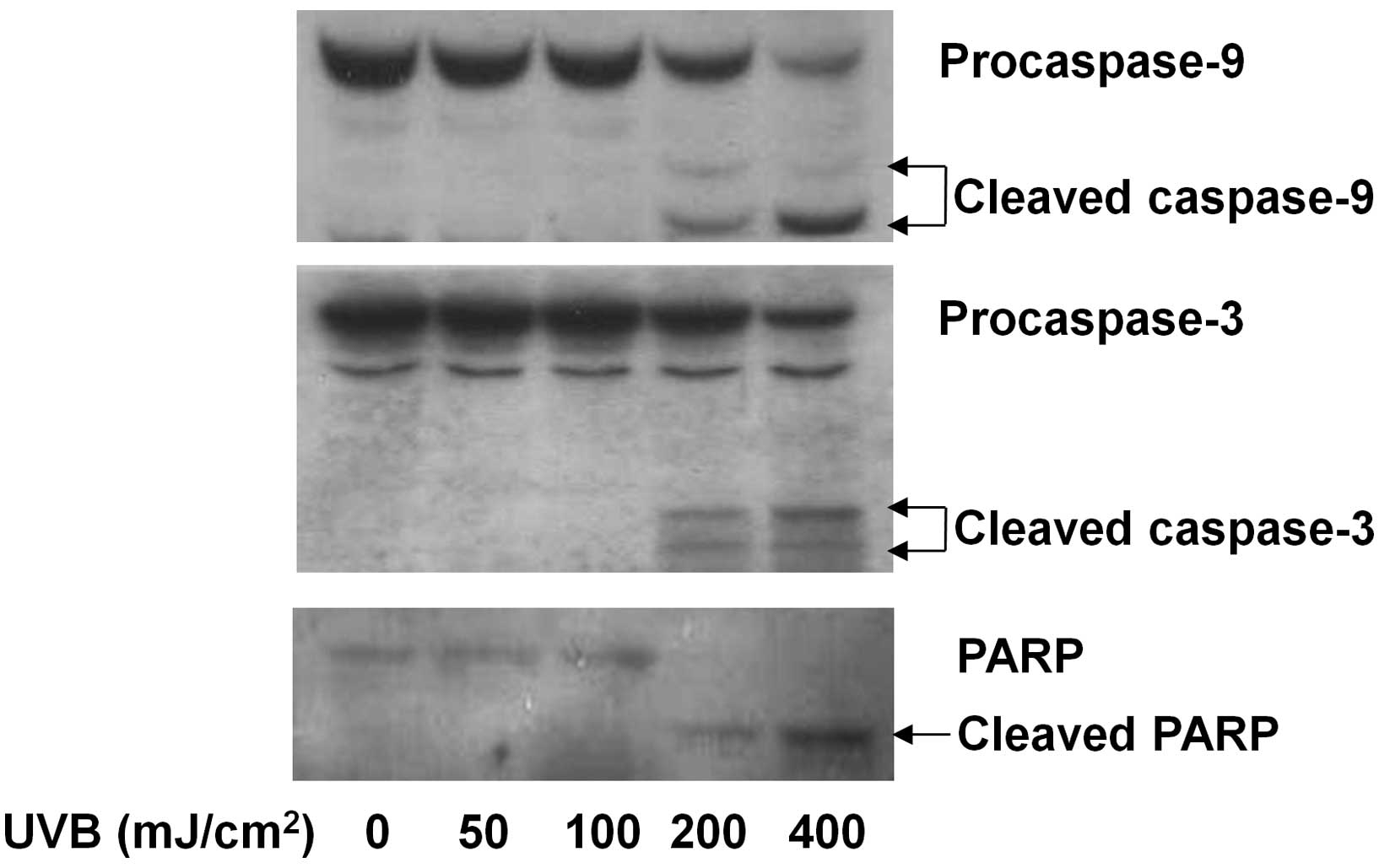
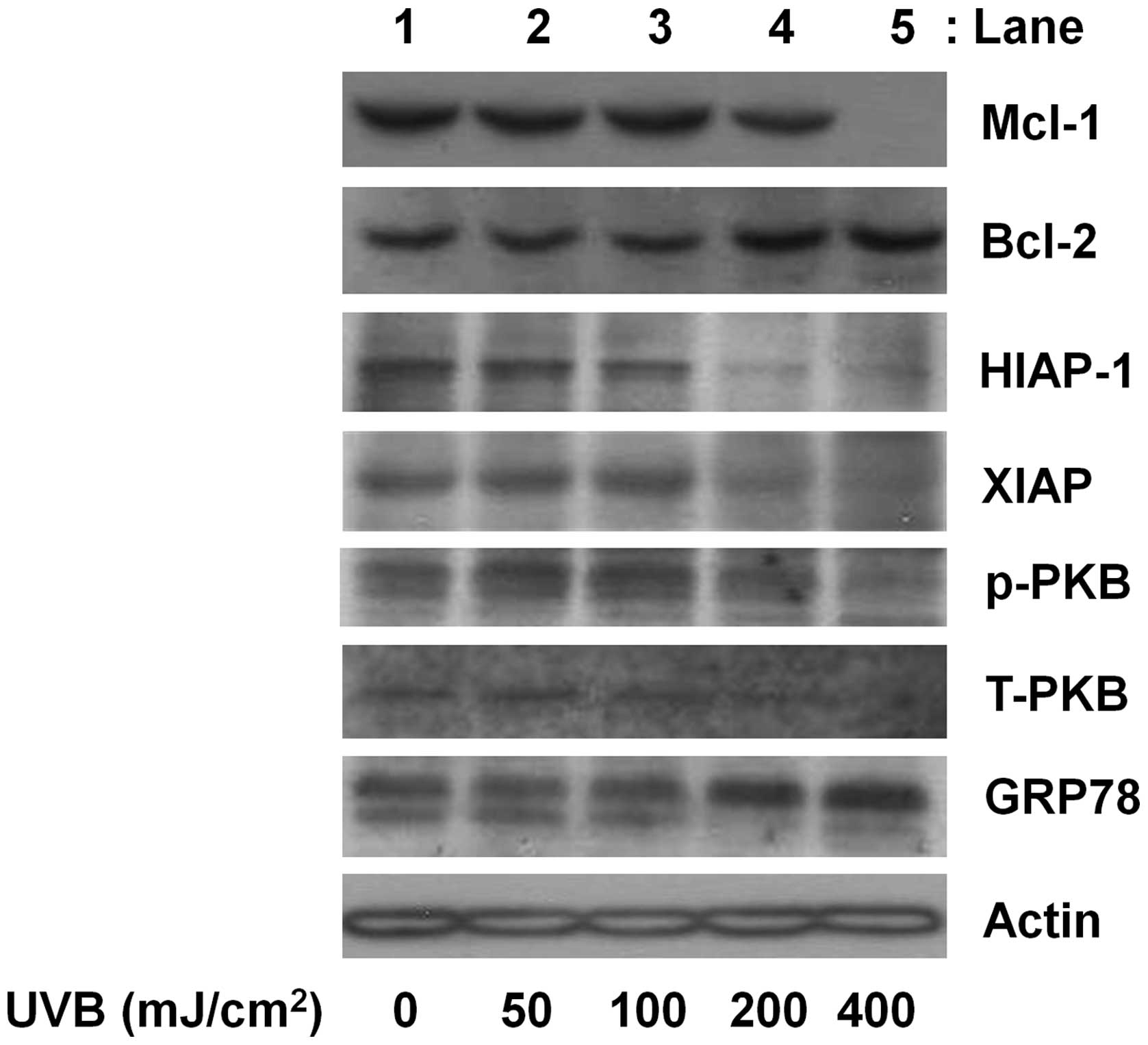
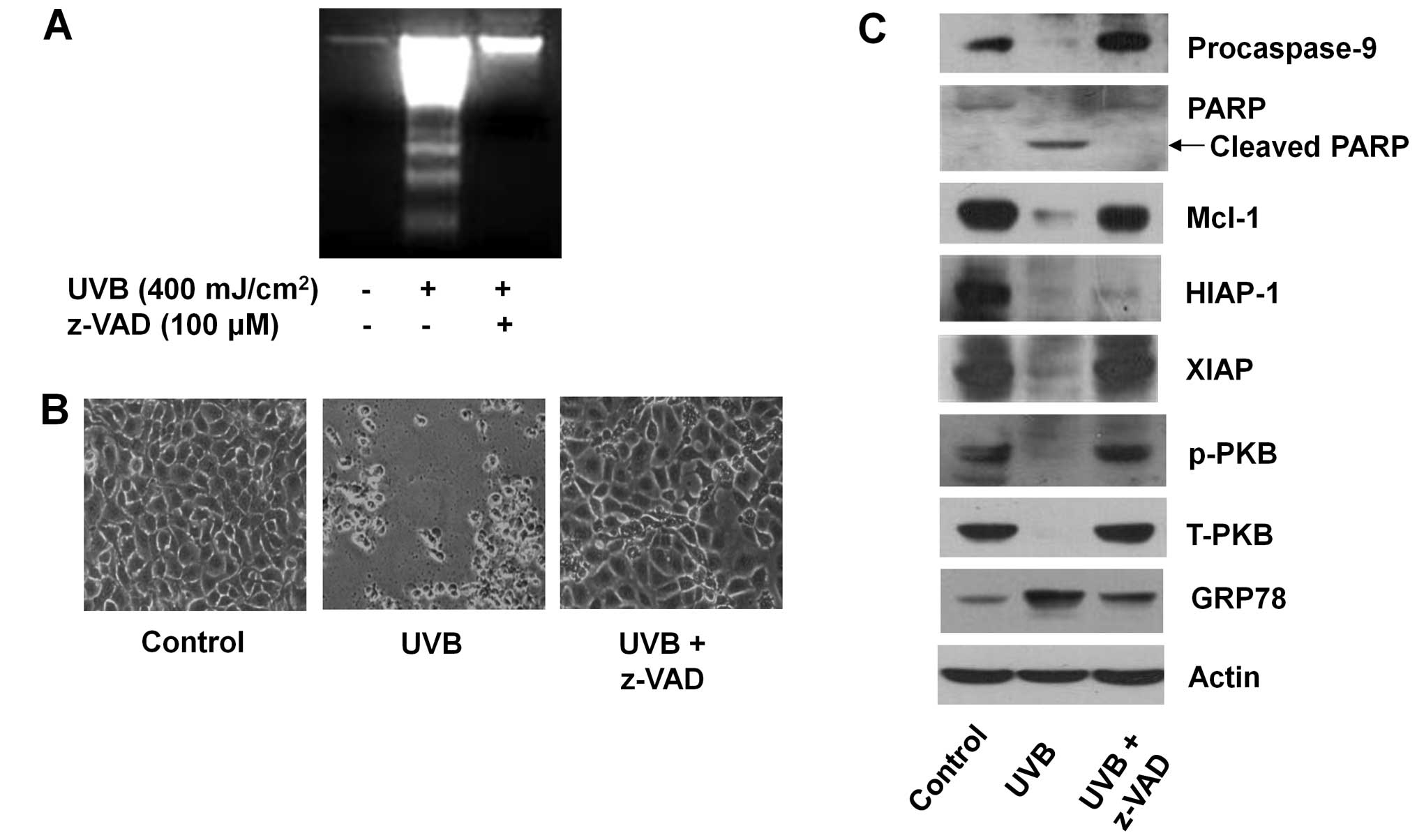
|
1
|
Shea CR and Parrish JA: Non-ionizing
radiation and the skin. Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular
Biology of the Skin. Goldsmith LA: 2. 2nd edition. Oxford
University Press; New York: pp. 910–927. 1991
|
|
2
|
Jin GH, Liu Y, Jin SZ, Liu XD and Liu SZ:
UVB induced oxidative stress in human keratinocytes and protective
effect of antioxidant agents. Radiat Environ Biophys. 46:61–68.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moniz LS and Stambolic V: Nek10 mediates
G2/M cell cycle arrest and MEK autoactivation in response to UV
irradiation. Mol Cell Biol. 31:30–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee KM, Lee KW, Jung SK, Lee EJ, Heo YS,
Bode AM, Lubet RA, Lee HJ and Dong Z: Kaempferol inhibits
UVB-induced COX-2 expression by suppressing Src kinase activity.
Biochem Pharmacol. 80:2042–2049. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sheikh MS, Antinore MJ, Huang Y and
Fornace AJ Jr: Ultraviolet-irradiation-induced apoptosis is
mediated via ligand independent activation of tumor necrosis factor
receptor 1. Oncogene. 17:2555–2563. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takahashi H, Honma M, Ishida-Yamamoto A,
Namikawa K, Miwa A, Okado H, Kiyama H and Iizuka H: In vitro and in
vivo transfer of bcl-2 gene into keratinocytes suppresses
UVB-induced apoptosis. Photochem Photobiol. 74:579–586. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kulms D and Schwarz T: Independent
contribution of three different pathways to ultraviolet-B-induced
apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 64:837–841. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang ES, Iwata K, Ikami K, Ham SA, Kim HJ,
Chang KC, Lee JH, Kim JH, Park SB, Kim JH, Yabe-Nishimura C and Seo
HG: Aldose reductase in keratinocytes attenuates cellular apoptosis
and senescence induced by UV radiation. Free Radic Biol Med.
50:680–688. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Larsson P, Andersson E, Johansson U,
Ollinger K and Rosdahl I: Ultraviolet A and B affect human
melanocytes and keratinocytes differently. A study of oxidative
alterations and apoptosis. Exp Dermatol. 14:117–123. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sitailo LA, Tibudan SS and Denning MF:
Activation of caspase-9 is required for UV-induced apoptosis of
human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 277:19346–19352. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Assefa Z, Garmyn M, Vantieghem A, Declercq
W, Vandenabeele P, Vandenheede JR and Agostinis P: Ultraviolet B
radiation-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes: cytosolic
activation of procaspase-8 and the role of Bcl-2. FEBS Lett.
540:125–132. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E, Zhong Q, Gao
W, Du F and Wang X: Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the
initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes
Dev. 17:1475–1486. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sitailo LA, Tibudan SS and Denning MF: The
protein kinase C delta catalytic fragment targets Mcl-1 for
degradation to trigger apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 281:29703–29710.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sitailo LA, Jerome-Morais A and Denning
MF: Mcl-1 functions as major epidermal survival protein required
for proper keratinocyte differentiation. J Invest Dermatol.
129:1351–1360. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chirico F, Fumelli C, Marconi A, Tinari A,
Straface E, Malorni W, Pellicciari R and Pincelli C:
Carboxyfullerenes localize within mitochondria and prevent the
UVB-induced intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Exp Dermatol. 16:429–436.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takasawa R and Tanuma S: Sustained release
of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria commits to undergo UVB-induced
apoptosis. Apoptosis. 8:291–299. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dallaglio K, Marconi A and Pincelli C:
Survivin: a dual player in healthy and diseased skin. J Invest
Dermatol. 132:18–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim W, Yang HJ, Youn H, Yun YJ, Seong KM
and Youn B: Myricetin inhibits Akt survival signaling and induces
Bad-mediated apoptosis in a low dose ultraviolet (UV)-B-irradiated
HaCaT human immortalized keratinocytes. J Radiat Res. 51:285–296.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ren SW, Li J, Wang W and Guan HS:
Protective effects of kappa-ca3000+CP against ultraviolet-induced
damage in HaCaT and MEF cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 101:22–30.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Denning MF, Wang Y, Tibudan S, Alkan S,
Nickoloff BJ and Qin JZ: Caspase activation and disruption of
mitochondrial membrane potential during UV radiation-induced
apoptosis of human keratinocytes requires activation of protein
kinase C. Cell Death Differ. 9:40–52. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen N, Ma Wy, Huang C and Dong Z:
Translocation of protein kinase C-epsilon and protein kinase
C-delta to membrane is required for ultraviolet B-induced
activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 274:15389–15394. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anand S, Chakrabarti E, Kawamura H, Taylor
CR and Maytin EV: Ultraviolet light (UVB and UVA) induces the
damage-responsive transcription factor CHOP/gadd153 in murine and
human epidermis: evidence for a mechanism specific to intact skin.
J Invest Dermatol. 125:323–333. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Borner C: The Bcl-2 protein family: sensor
and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol.
39:615–647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deveraux QL and Reed JC: IAP family
proteins - suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13:239–252. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Svobodová A, Zdarilová A and Vostálová J:
Lonicera caerulea and Vaccinium myrtillus fruit
polyphenols protect HaCaT keratinocytes against UVB-induced
phototoxic stress and DNA damage. J Dermatol Sci. 56:196–204.
2009.
|
|
27
|
Won YK, Ong CN and Shen HM: Parthenolide
sensitizes ultraviolet (UV)-B-induced apoptosis via protein kinase
C-dependent pathways. Carcinogenesis. 26:2149–2156. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Allen RT, Hunter WJ III and Agrawal DK:
Morphological and biochemical characterization and analysis of
apoptosis. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 37:215–228. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cohen GM: Caspases: the executioners of
apoptosis. Biochem J. 326:1–16. 1997.
|
|
30
|
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S,
Poirier GG and Earnshaw WC: Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 371:346–347.
1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Casciola-Rosen L, Nicholson DW, Chong T,
Rowan KR, Thornberry NA, Miller DK and Rosen A: Apopain/CPP32
cleaves proteins that are essential for cellular repair: a
fundamental principle of apoptotic death. J Exp Med. 183:1957–1964.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aragane Y, Kulms D, Metze D, Wilkes G,
Poppelmann B, Luger TA and Schwarz T: Ultraviolet light induces
apoptosis via direct activation of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) independently
of its ligand CD95L. J Cell Biol. 140:171–182. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Daher A, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM and
Rosenthal DS: Apoptosis induced by ultraviolet B in
HPV-immortalized human keratinocytes requires caspase-9 and is
death receptor independent. Exp Dermatol. 15:23–34. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS and
Reed JC: X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death
proteases. Nature. 388:300–304. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shiozaki EN, Chai J, Rigotti DJ, Riedl SJ,
Li P, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Fairman R and Shi Y: Mechanism of
XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol Cell. 11:519–527. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wan YS, Wang ZQ, Shao Y, Voorhees JJ and
Fisher GJ: Ultraviolet irradiation activates PI3-kinase/AKT
survival pathway via EGF receptors in human skin in vivo.
Int J Oncol. 18:461–466. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Claerhout S, Van Laethem A, Agostinis P
and Garmyn M: Pathways involved in sunburn cell formation:
deregulation in skin cancer. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 5:199–207.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deacon EM, Pongracz J, Griffiths G and
Lord JM: Isoenzymes of protein kinase C: differential involvement
in apoptosis and pathogenesis. Mol Pathol. 50:124–131. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brodie C and Blumberg PM: Regulation of
cell apoptosis by protein kinase C delta. Apoptosis. 8:19–27. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang C and Kazanietz MG: Divergence and
complexities in DAG signaling: looking beyond PKC. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:602–608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Berra E, Municio MM, Sanz L, Frutos S,
Diaz-Meco MT and Moscat J: Positioning atypical protein kinase C
isoforms in the UV-induced apoptotic signaling cascade. Mol Cell
Biol. 17:4346–4354. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Denning MF, Wang Y, Nickoloff BJ and
Wrone-Smith T: Protein kinase C-delta is activated by
caspase-dependent proteolysis during ultraviolet radiation-induced
apoptosis of human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 273:29995–30002.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Frutos S, Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT:
Cleavage of zetaPKC but not lambda/iotaPKC by caspase-3 during
UV-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 274:10765–10770. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee AS: The glucose-regulated proteins:
stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci.
26:504–510. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ma Y, Brewer JW, Diehl JA and Hendershot
LM: Two distinct stress signaling pathways converge upon the CHOP
promoter during the mammalian unfolded protein response. J Mol
Biol. 318:1351–1365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
De Haro C, Méndez R and Santoyo J: The
eIF-2 alpha kinases and the control of protein synthesis. FASEB J.
10:1378–1387. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Haze K, Yoshida H, Yanagi H, Yura T and
Mori K: Mammalian transcription factor ATF6 is synthesized as a
transmembrane protein and activated by proteolysis in response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Biol Cell. 10:3787–3799. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mera K, Kawahara K, Tada K, Kawai K,
Hashiguchi T, Maruyama I and Kanekura T: ER signaling is activated
to protect human HaCaT keratinocytes from ER stress induced by
environmental doses of UVB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
397:350–354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|