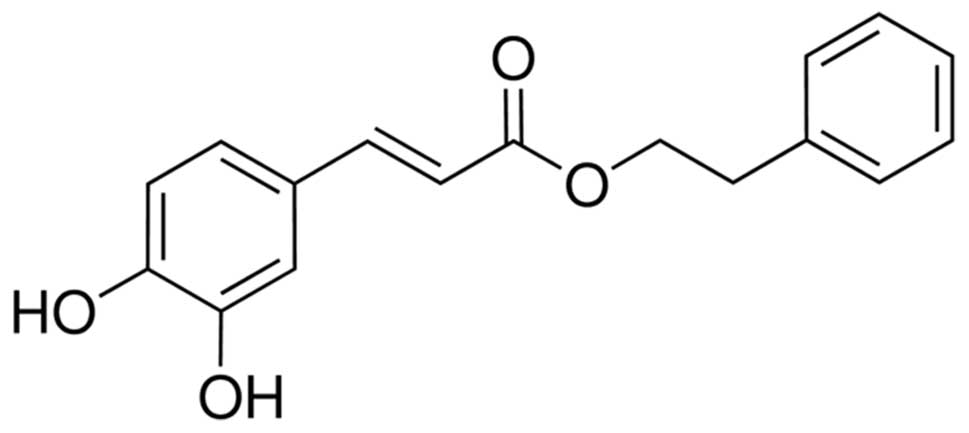
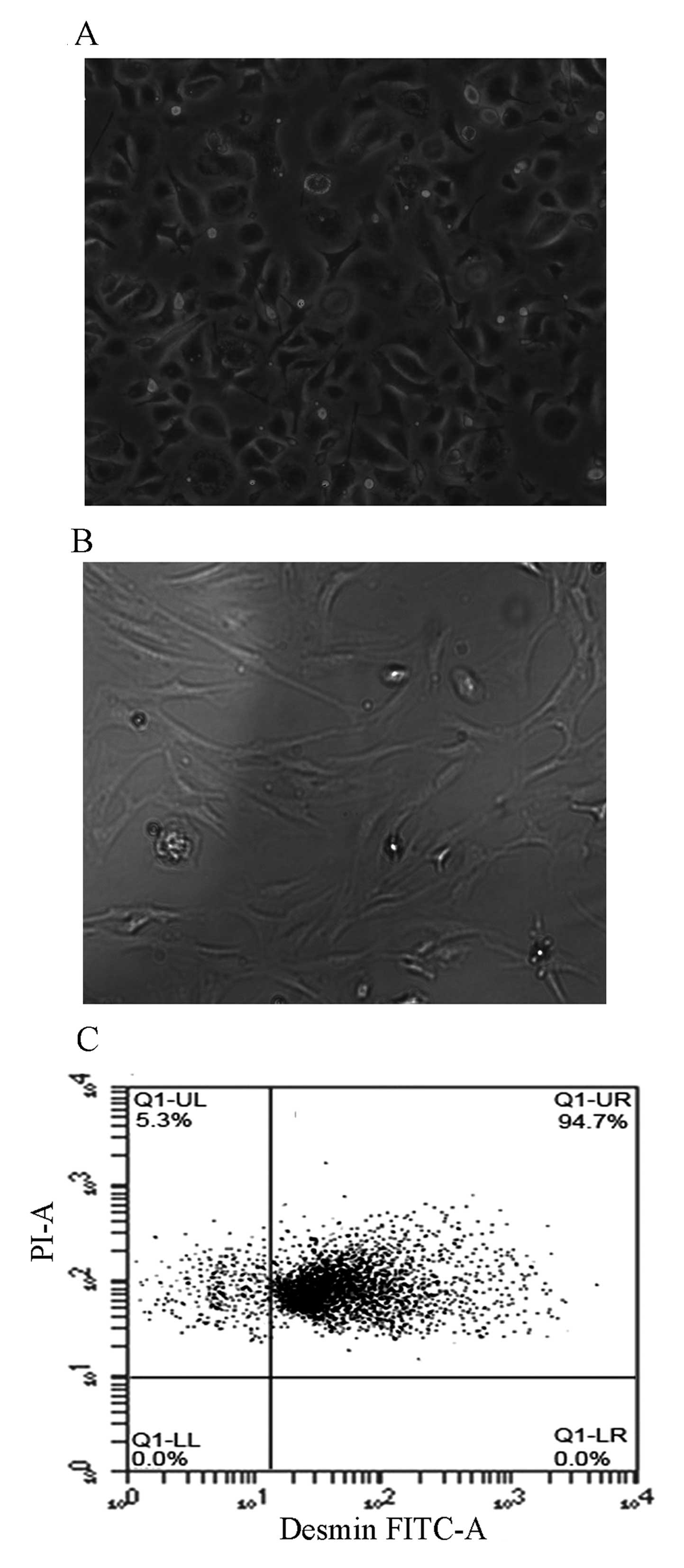
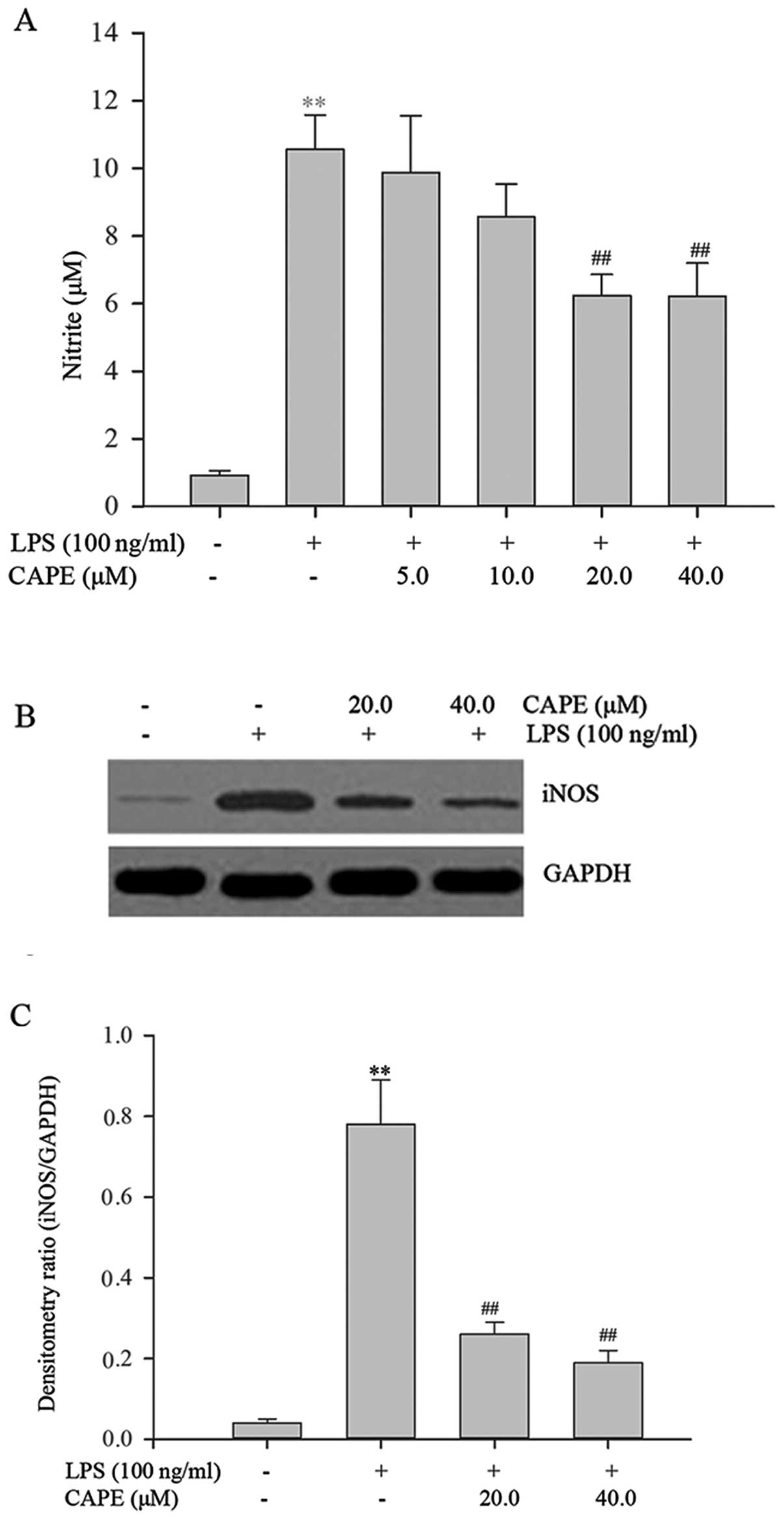
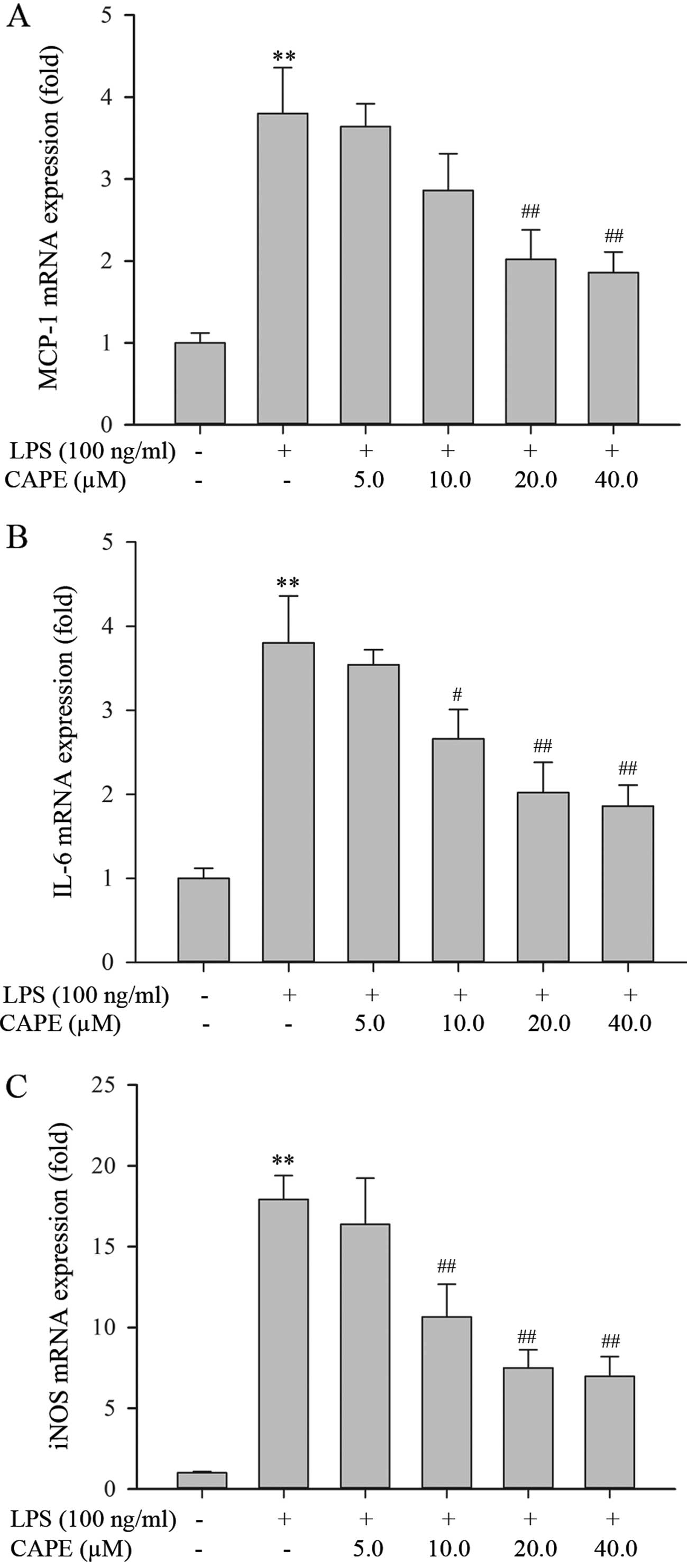
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Stellate cells: a moving
target in hepatic fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 40:1041–1043. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shaker ME, Ghani A, Shiha GE, Ibrahim TM
and Mehal WZ: Nilotinib induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death
of activated hepatic stellate cells via inhibition of histone
deacetylases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:1992–2003. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Priya S and Sudhakaran PR: Cell survival,
activation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells: modulation by
extracellular matrix proteins. Hepatol Res. 38:1221–1232.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tacke F and Weiskirchen R: Update on
hepatic stellate cells: pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel
isolation techniques. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:67–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Soares JB, Pimentel-Nunes P,
Roncon-Albuquerque R and Leite-Moreira A: The role of
lipopolysaccharide/toll-like receptor 4 signaling in chronic liver
diseases. Hepatol Int. 4:659–672. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, et
al: TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med.
13:1324–1332. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan X, Lin Z, Chen F, et al: Human BAMBI
cooperates with Smad7 to inhibit transforming growth factor-beta
signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:30097–30104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trebicka J, Krag A, Gansweid S, et al:
Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-receptor levels in portal and
hepatic vein of patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis receiving
elective transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1218–1225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hanck C, Rossol S, Böcker U, Tokus M and
Singer MV: Presence of plasma endotoxin is correlated with tumour
necrosis factor receptor levels and disease activity in alcoholic
cirrhosis. Alcohol Alcohol. 33:606–608. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Q, Zou L, Jagavelu K, et al:
Intestinal decontamination inhibits TLR4 dependent
fibronectin-mediated cross-talk between stellate cells and
endothelial cells in liver fibrosis in mice. J Hepatol. 56:893–899.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai T, Lian LH, Wu YL, Wan Y and Nan JX:
Thymoquinone attenuates liver fibrosis via PI3K and TLR4 signaling
pathways in activated hepatic stellate cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
15:275–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pradere JP, Troeger JS, Dapito DH, Mencin
AA and Schwabe RF: Toll-like receptor 4 and hepatic fibrogenesis.
Semin Liver Dis. 30:232–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luedde T and Trautwein C: A molecular link
between inflammation and fibrogenesis: the bacterial microflora
influences hepatic fibrosis via toll-like receptor 4-dependent
modification of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in
hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 47:1089–1091. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Isayama F, Hines IN, Kremer M, et al: LPS
signaling enhances hepatic fibrogenesis caused by experimental
cholestasis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
290:G1318–G1328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lotfy M, Badra G, Burham W and Alenzi FQ:
Combined use of honey, bee propolis and myrrh in healing a deep,
infected wound in a patient with diabetes mellitus. Br J Biomed
Sci. 63:171–173. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ansorge S, Reinhold D and Lendeckel U:
Propolis and some of its constituents down-regulate DNA synthesis
and inflammatory cytokine production but induce TGF-beta1
production of human immune cells. Z Naturforsch C. 58:580–589.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wongmekiat O, Gomonchareonsiri S and
Thamprasert K: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects against
oxidative stress-related renal dysfunction in rats treated with
cyclosporin A. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 25:619–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oktar S, Yönden Z, Aydin M, Ilhan S, Alcin
E and Ozturk OH: Protective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester
on iron-induced liver damage in rats. J Physiol Biochem.
65:339–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Takasu S, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a
nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, on Helicobacter
pylori-induced gastritis in Mongolian gerbils. Int J Cancer.
125:1786–1795. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ozturk G, Ginis Z, Akyol S, Erden G, Gurel
A and Akyol O: The anticancer mechanism of caffeic acid phenethyl
ester (CAPE): review of melanomas, lung and prostate cancers. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 16:2064–2068. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee Y, Shin DH, Kim JH, et al: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester-mediated Nrf2 activation and IkappaB kinase
inhibition are involved in NFkappaB inhibitory effect: structural
analysis for NFkappaB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 643:21–28. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR Jr,
Grunberger D and Aggarwal BB: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a
potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear
transcription factor NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9090–9095. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abdel-Latif MM, Windle HJ, Homasany BS,
Sabra K and Kelleher D: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester modulates
Helicobacter pylori-induced nuclear factor-kappa B and
activator protein-1 expression in gastric epithelial cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 146:1139–1147. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ramm GA: Isolation and culture of rat
hepatic stellate cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:846–851. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weiskirchen R and Gressner AM: Isolation
and culture of hepatic stellate cells. Methods Mol Med. 117:99–113.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Robertson DA, Hughes GA and Lyles GA:
Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in cultured smooth
muscle cells from rat mesenteric lymphatic vessels.
Microcirculation. 11:503–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cikos S, Bukovska A and Koppel J: Relative
quantification of mRNA: comparison of methods currently used for
real-time PCR data analysis. BMC Mol Biol. 8:1132007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simone RE, Russo M, Catalano A, et al:
Lycopene inhibits NF-κB-mediated IL-8 expression and changes redox
and PPARγ signalling in cigarette smoke-stimulated macrophages.
PLoS One. 6:e196522011.
|
|
30
|
Bhoopathi P, Chetty C, Kunigal S, Vanamala
SK, Rao JS and Lakka SS: Blockade of tumor growth due to matrix
metalloproteinase-9 inhibition is mediated by sequential activation
of beta1-integrin, ERK, and NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 283:1545–1552.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Zheng HW, Chen H, et al: Hepatitis B
virus particles preferably induce Kupffer cells to produce
TGF-beta1 over pro-inflammatory cytokines. Dig Liver Dis.
44:328–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schnabl B, Brandl K, Fink M, et al: A
TLR4/MD2 fusion protein inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammatory
signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
375:210–214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Frasinariu OE, Ceccarelli S, Alisi A,
Moraru E and Nobili V: Gut-liver axis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: an input for novel therapies. Dig Liver Dis.
45:543–551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gäbele E, Dostert K, Hofmann C, et al: DSS
induced colitis increases portal LPS levels and enhances hepatic
inflammation and fibrogenesis in experimental NASH. J Hepatol.
55:1391–1399. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo J and Friedman SL: Toll-like receptor
4 signaling in liver injury and hepatic fibrogenesis. Fibrogenesis
Tissue Repair. 3:212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guo J, Loke J, Zheng F, et al: Functional
linkage of cirrhosis-predictive single nucleotide polymorphisms of
Toll-like receptor 4 to hepatic stellate cell responses.
Hepatology. 49:960–968. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brun P, Castagliuolo I, Pinzani M, Palu G
and Martines D: Exposure to bacterial cell wall products triggers
an inflammatory phenotype in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 289:G571–G578. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Gwak GY, et al: CCR1
and CCR5 promote hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:1858–1870. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Seki E, de Minicis S, Inokuchi S, et al:
CCR2 promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 50:185–197.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Borrelli F, Izzo AA, Di Carlo G, et al:
Effect of a propolis extract and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on
formation of aberrant crypt foci and tumors in the rat colon.
Fitoterapia. 73(Suppl 1): S38–S43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Juman S, Yasui N, Ikeda K, et al: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in hypertrophic adipocytes through
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull.
35:1941–1946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kawelke N, Vasel M, Sens C, Au A, Dooley S
and Nakchbandi IA: Fibronectin protects from excessive liver
fibrosis by modulating the availability of and responsiveness of
stellate cells to active TGF-beta. PLoS One. 6:e281812011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Novotny NM, Markel TA, Crisostomo PR and
Meldrum DR: Differential IL-6 and VEGF secretion in adult and
neonatal mesenchymal stem cells: role of NFkB. Cytokine.
43:215–219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Rangan GK, Goodwin B, Tay YC and
Harris DC: Lipopolysaccharide-induced MCP-1 gene expression in rat
tubular epithelial cells is nuclear factor-kappaB dependent. Kidney
Int. 57:2011–2022. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Karin M and Delhase M: The I kappa B
kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory
signalling. Semin Immunol. 12:85–98. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ribeiro PS, Cortez-Pinto H, Solá S, et al:
Hepatocyte apoptosis, expression of death receptors, and activation
of NF-kappaB in the liver of nonalcoholic and alcoholic
steatohepatitis patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1708–1717. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|