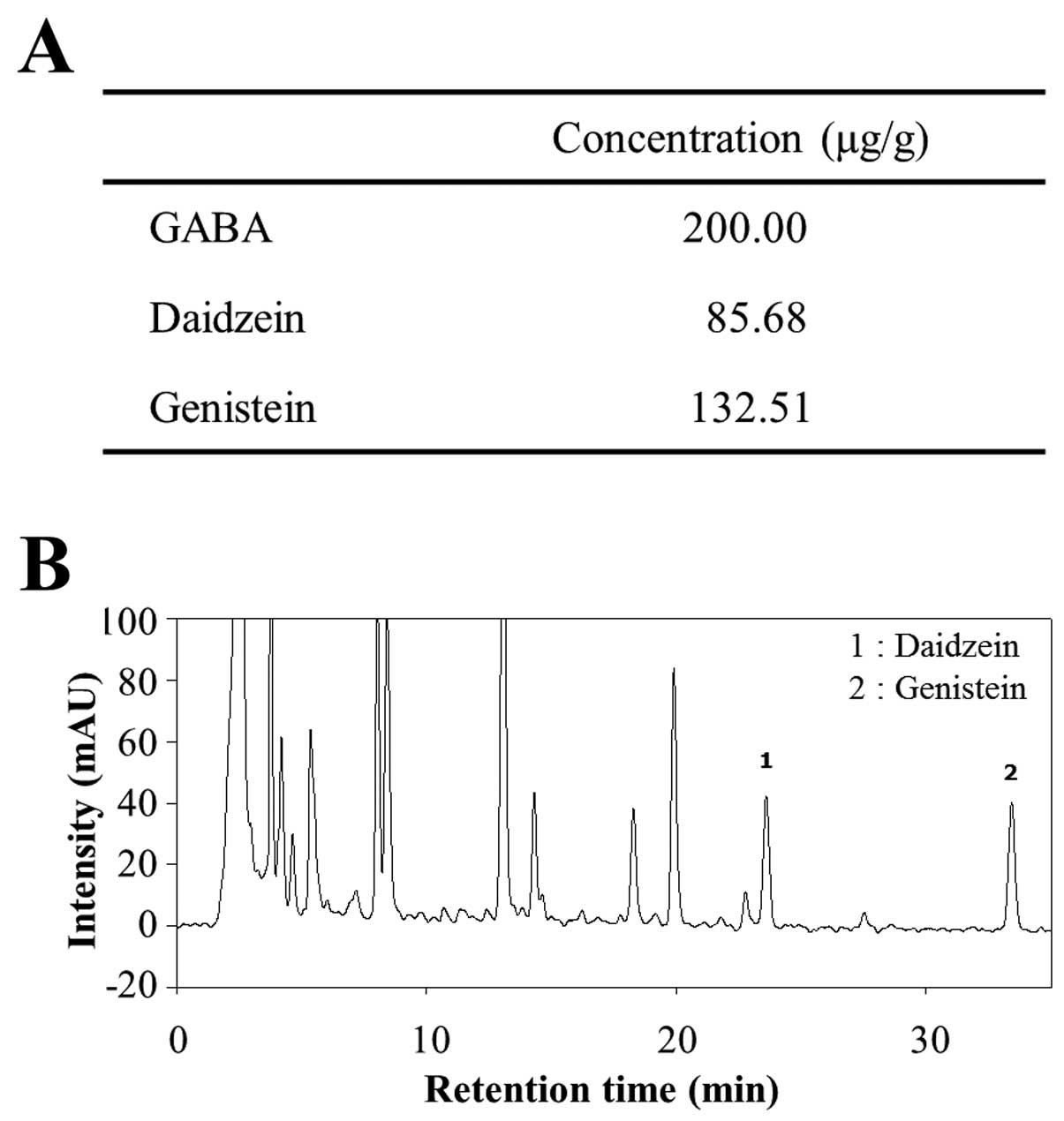
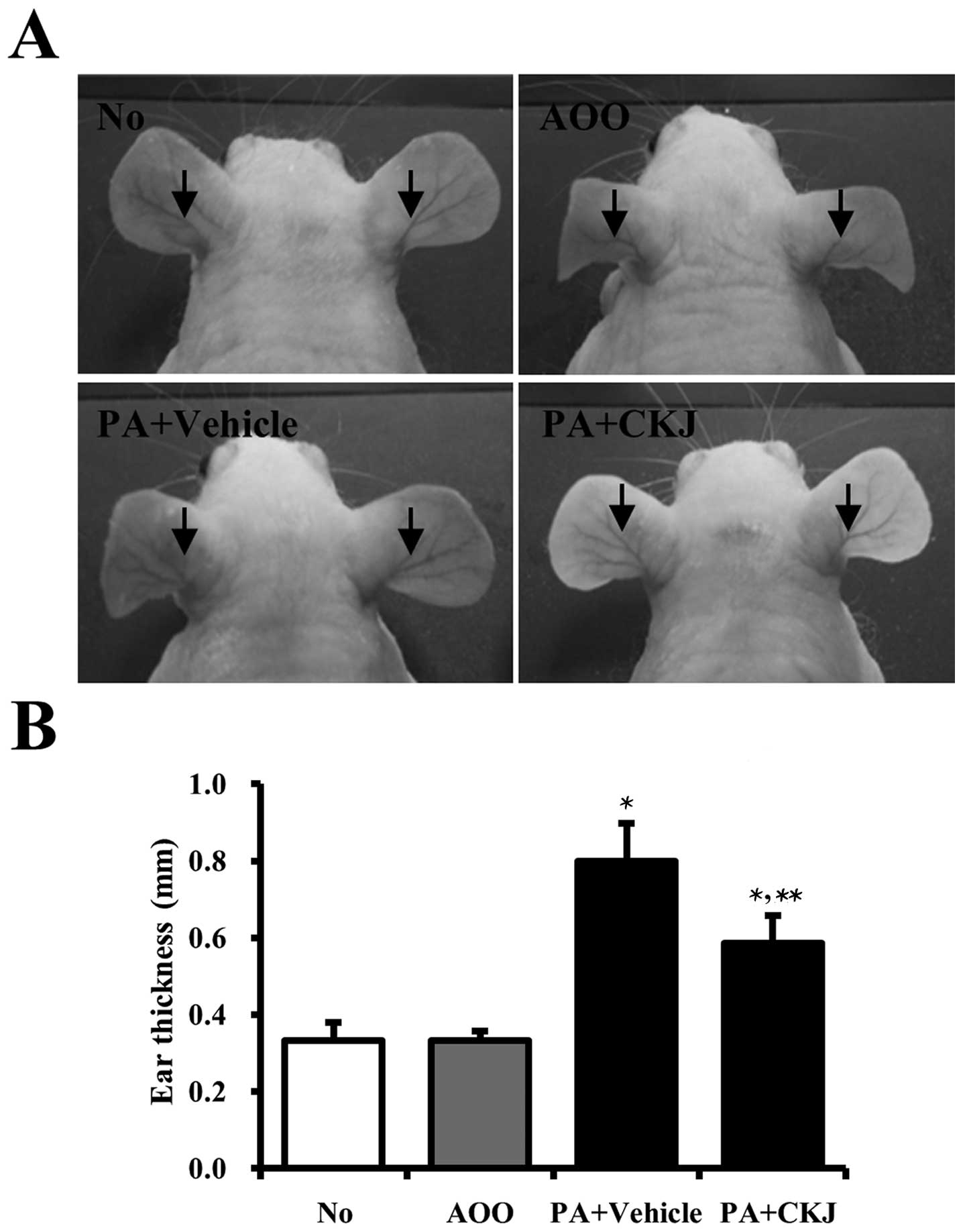
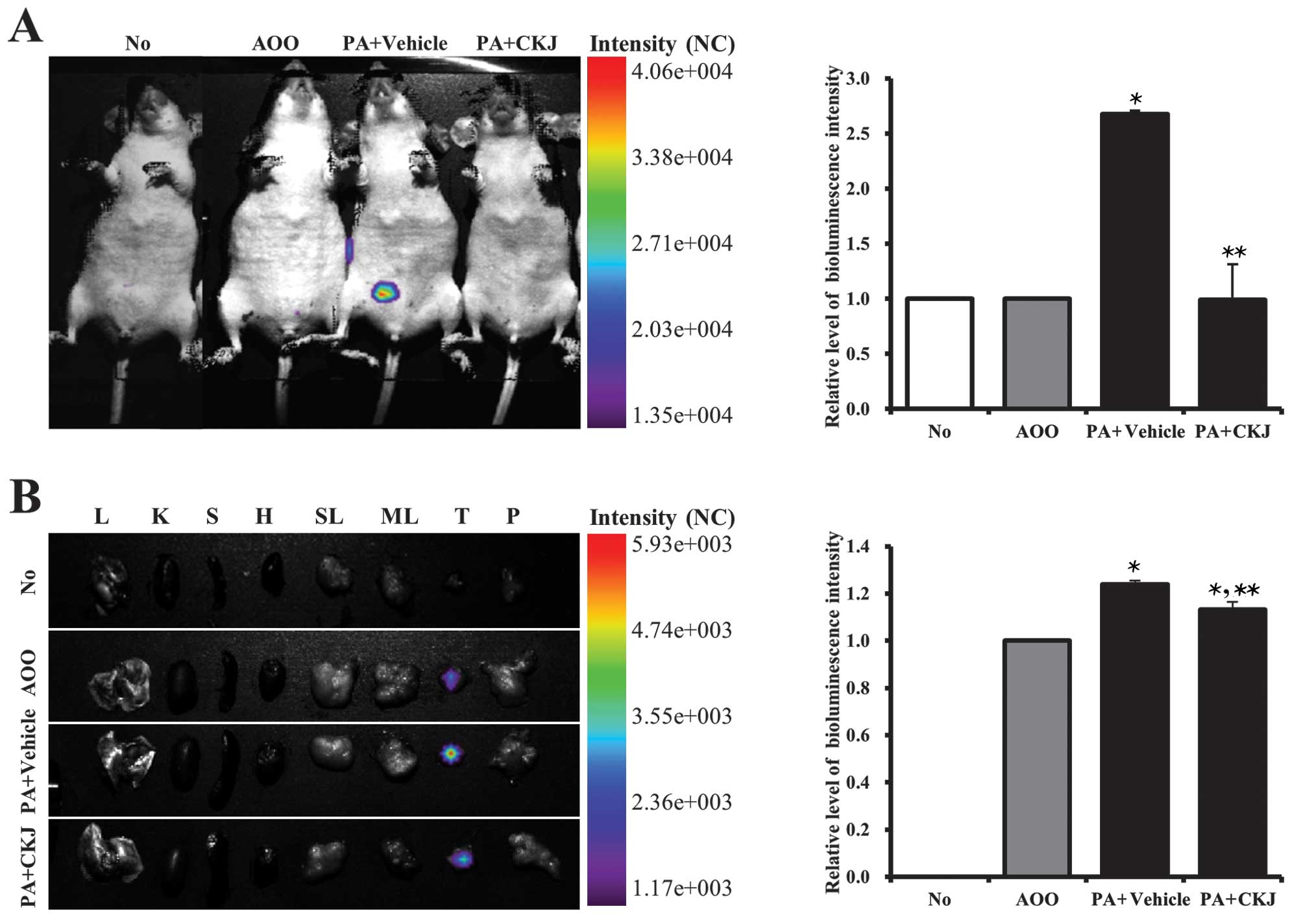
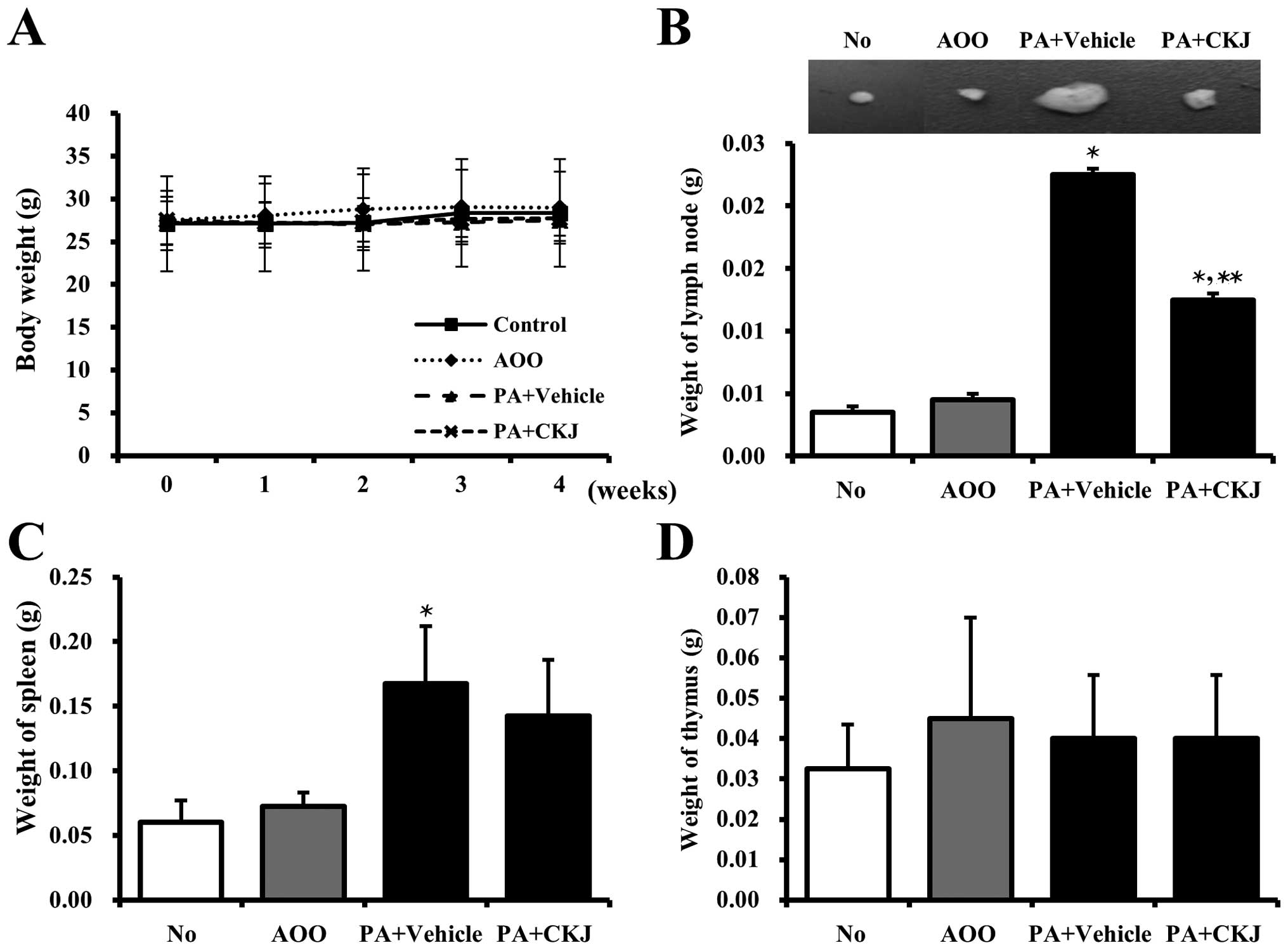
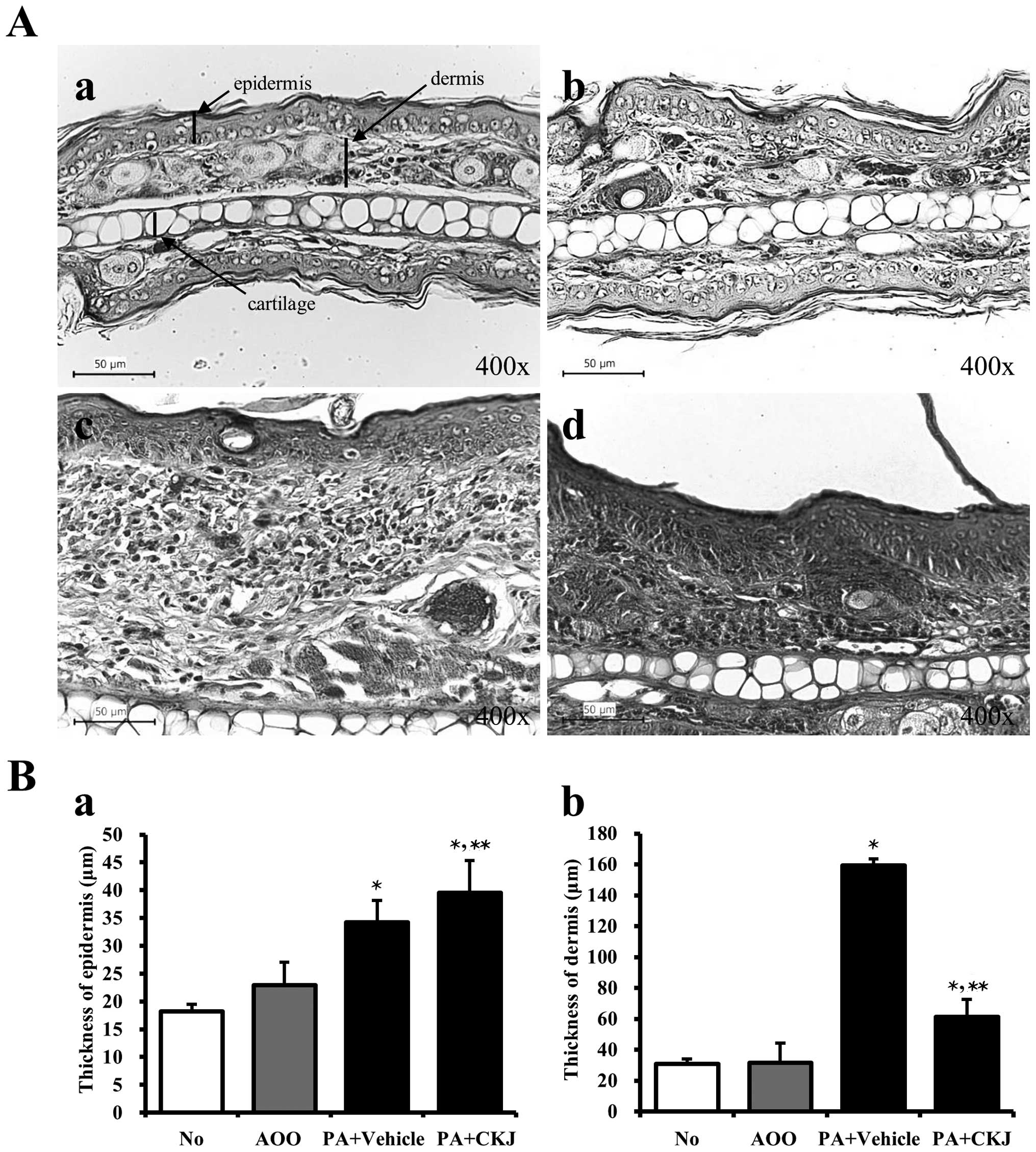
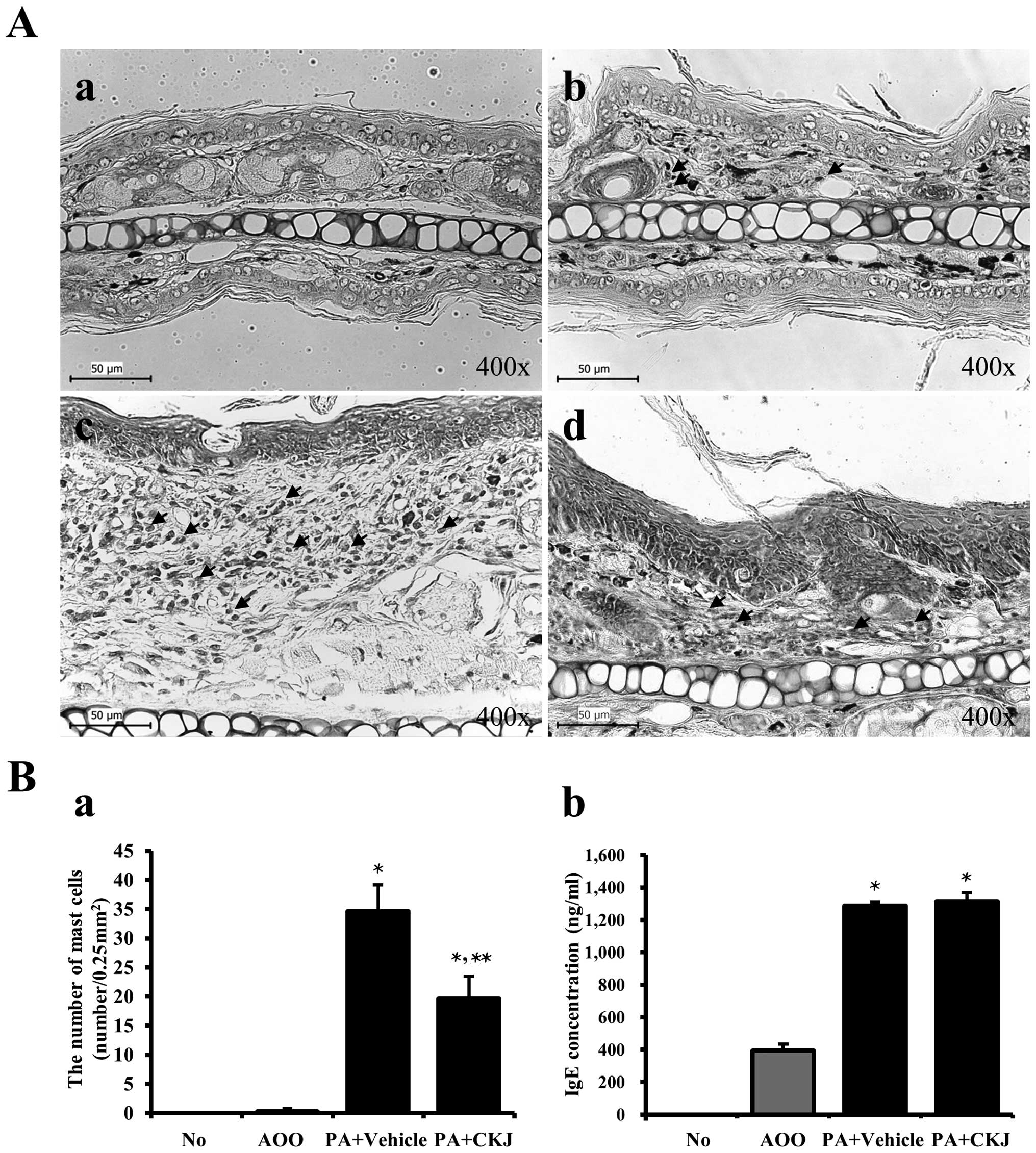
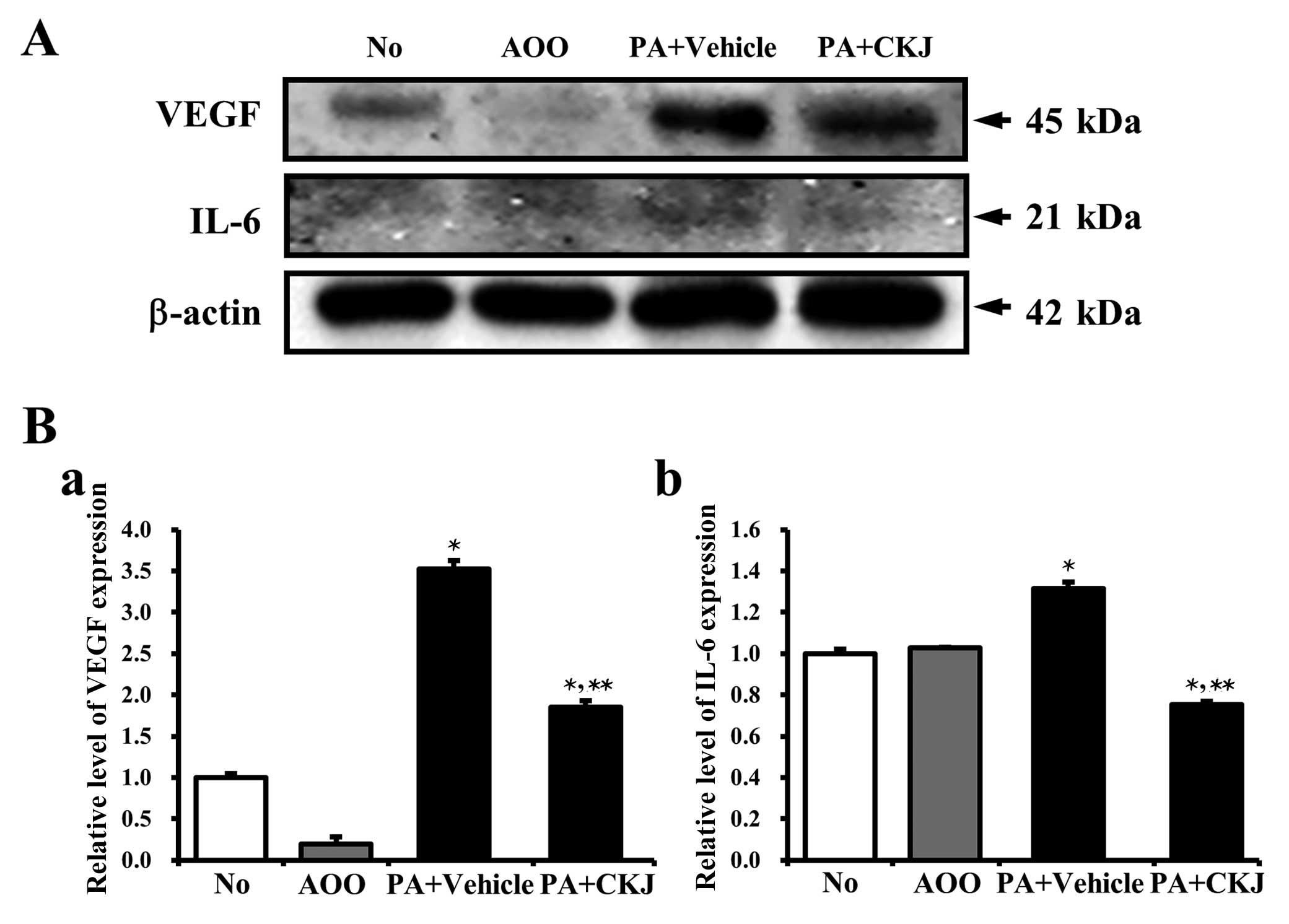
|
1
|
Hanifin JM and Rajka G: Diagnostic
features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh).
92:44–47. 1980.
|
|
2
|
Leung DY and Bieber T: Atopic dermatitis.
Lancet. 361:151–160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kay AB: Overview of ‘allergy and allergic
diseases: with a view to the future’. Br Med Bull. 56:843–864.
2000.
|
|
4
|
Kay AB: Allergy and allergic diseases.
First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 344:30–37. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jin H, He R, Oyoshi M and Geha RS: Animal
models of atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 129:31–40. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Spergel JM and Paller AS: Atopic
dermatitis and the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 112(Suppl
6): S118–S127. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turner KJ, Stewart GA, Sharp AH and Czarny
D: Standardization of allergen extracts by inhibition of RAST, skin
test, and chemical composition. Clin Allergy. 10:441–450. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johansson SG: ImmunoCAP specific IgE test:
an objective tool for research and routine allergy diagnosis.
Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 4:273–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petersen AB, Gudmann P, Milvang-Grønager
P, Mørkeberg R, Bøgestrand S, Linneberg A and Johansen N:
Performance evaluation of a specific IgE assay developed for the
ADVIA centaur immunoassay system. Clin Biochem. 37:882–892. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bae CJ, Lee JW, Bae HS, Shim SB, Jee SW,
Lee SH, Lee CK, Hong JT and Hwang DY: Detection of allergenic
compounds using an IL-4/luciferase/CNS-1 transgenic mice model.
Toxicol Sci. 120:349–359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kwak MH, Kim JE, Hwang IS, Lee YJ, An BS,
Hong JT, Lee SH and Hwang DY: Quantitative evaluation of
therapeutic effect of Liriope platyphylla on phthalic
anhydride-induced atopic dermatitis in IL-4/Luc/CNS-1 Tg mice. J
Ethnopharmacol. 148:880–889. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JJ, Lee DS and Kim HB: Fermentation
patterns of chungkookjang and Kanjang by Bacillus
licheniformis B1. Korean J Microbiol. 35:296–301. 1999.
|
|
13
|
Nakajima N, Nozaki N, Ishihara K, Ishikawa
A and Tsuji H: Analysis of isoflavone content in tempeh, a
fermented soybean, and preparation of a new isoflavone-enriched
tempeh. J Biosci Bioeng. 100:685–687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kwon DY, Jang JS, Lee JE, Kim YS, Shin DH
and Park S: The isoflavonoid aglycone-rich fractions of
Chungkookjang, fermented unsalted soybean, enhance insulin
signaling and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
activity in vitro. Biofactors. 26:245–258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Su CL, Wu CJ, Chen FN, Wang BJ, Shen SR
and Won SJ: Supernatant of bacterial fermented soybean induces
apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep 3B cells via
activation of caspase-8 and mitochondria. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:303–314. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim MH, Kim SY, Ko JM, Jeong DY and Kim
YS: Biological activities of cheonggukjang prepared with several
soybean cultivars. Food Sci Biotechnol. 21:475–483. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kwon EY, Jung KO, Moon SH and Park KY:
Studies on enhancing chemopreventive effect of
chungkookjangs-antimutagenic activity of chungkookjangs prepared
with the different varieties of soybean and starter. J Korean Assoc
Cancer Prev. 7:200–209. 2002.
|
|
18
|
Choi J, Kwon SH, Park KY, Yu BP, Kim ND,
Jung JH and Chung HY: The anti-inflammatory action of fermented
soybean products in kidney of high-fat-fed rats. J Med Food.
14:232–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jalin AMA, Lee CK, Lee CY, Kang AR, Park
CM, Cha J, Kim JH, Lee SW, Song YS, Lee JT and Kang SG:
Thrombolytic activity of cheonggukjang kinase in recovery from
brain damage in a rat cerebral embolic stroke model. Neural Regen
Res. 5:1875–1882. 2010.
|
|
20
|
Ko JA, Koo SY and Park HJ: Effects of
alginate microencapsulation on the fibrinolytic activity of
fermented soybean paste (cheonggukjang) extract. Food Chem.
111:921–924. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Matsuda A, Tanaka A, Pan W, Okamoto N,
Oida K, Kingyo N, Amagai Y, Xia Y, Jang H, Nishikawa S, Kajiwara N,
Ahn G, Ohmori K and Matsuda H: Supplementation of the fermented soy
product ImmuBalance™ effectively reduces itching behavior of atopic
NC/Tnd mice. J Dermatol Sci. 67:130–139. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Jang SN, Kim KL, Yun MY and Kang SM: The
effect of γ-PGA on NC/Nga mice, a mouse model for mite
antigen-induced atopic dermatitis. Korean J Microbiol Biotechnol.
38:53–63. 2010.(In Korean).
|
|
23
|
Choi YH, Lim H, Heo MY, Kwon DY and Kim
HP: Anti-inflammatory activity of the ethanol extract of
chungkukjang, Korean fermented bean: 5-lipoxygenase inhibition. J
Med Food. 11:539–543. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang IS, Kim JE, Lee YJ, Kwak MH, Lee HG,
Kim HS, Lee HS and Hwang DY: Growth sensitivity in the epiphyseal
growth plate, liver and muscle of SD rats is significantly enhanced
by treatment with a fermented soybean product (cheonggukjang)
through stimulation of growth hormone secretion. Mol Med Rep.
9:166–172. 2014.
|
|
25
|
Lee YJ, Kim JE, Kwak MH, Go J, Son HJ, Kim
DS and Hwang DY: In vitro and in vivo study of effects of fermented
soybean product (chungkookjang) on NGF secretion ability and NGF
receptor signaling pathway. Lab Anim Res. 29:113–126. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang G and Brown AW: The rapid
determination of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Phytochemistry.
44:1007–1009. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim JE, Lee YK, Nam SH, Choi SI, Goo JS,
Jang MJ, Lee HS, Son HJ, Lee CY and Hwang DY: The symptoms of
atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice were significantly relieved by the
water extract of Liriope platyphylla. Lab Anim Res.
26:377–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Stahlmann R, Wegner M, Riecke K, Kruse M
and Platzek T: Sensitising potential of four textile dyes and some
of their metabolites in a modified local lymph node assay.
Toxicology. 219:113–123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bae CJ, Shim SB, Jee SW, Lee SH, Kim MR,
Lee JW, Lee CK and Hwang DY: IL-6, VEGF, KC and RANTES are a major
cause of a high irritant dermatitis to phthalic anhydride in
C57BL/6 inbred mice. Allergol Int. 59:389–397. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prussin C and Metcalfe DD: 4. IgE, mast
cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
111(Suppl 2): S486–S494. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Spergel JM, Mizoguchi E, Brewer JP, Martin
TR, Bhan AK and Geha RS: Epicutaneous sensitization with protein
antigen induces localized allergic dermatitis and
hyperresponsiveness to methacholine after single exposure to
aerosolized antigen in mice. J Clin Invest. 101:1614–1622. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kimura M, Tsuruta S and Yoshida T:
Correlation of house dust mite-specific lymphocyte proliferation
with IL-5 production, eosinophilia, and the severity of symptoms in
infants with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 101:84–89.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S,
Feingold KR, Leung DY, Holleran W, Uchida Y and Elias PM:
Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple
features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and
biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone
challenges. J Invest Dermatol. 128:79–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Laouini D, Kawamoto S, Yalcindag A, Bryce
P, Mizoguchi E, Oettgen H and Geha RS: Epicutaneous sensitization
with superantigen induces allergic skin inflammation. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 112:981–987. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan LS, Robinson N and Xu L: Expression
of interleukin-4 in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in a
pruritic inflammatory skin disease: an experimental animal model to
study atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 117:977–983. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dillon SR, Sprecher C, Hammond A, et al:
Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces
dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol. 5:752–760. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, et al:
Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic
inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 3:673–680.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim E, Lee JE, Namkung JH, Park JH, Kim S,
Shin ES, Cho EY and Yang JM: Association of the single-nucleotide
polymorphism and haplotype of the interleukin 18 gene with atopic
dermatitis in Koreans. Clin Exp Allergy. 37:865–871. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weih F, Warr G, Yang H and Bravo R:
Multifocal defects in immune responses in RelB-deficient mice. J
Immunol. 158:5211–5218. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsukuba T, Okamoto K, Okamoto Y, Yanagawa
M, Kohmura K, Yasuda Y, Uchi H, Nakahara T, Furue M, Nakayama K,
Kadowaki T, Yamamoto K and Nakayama KI: Association of cathepsin E
deficiency with development of atopic dermatitis. J Biochem.
134:893–902. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Watanabe O, Natori K, Tamari M, Shiomoto
Y, Kubo S and Nakamura Y: Significantly elevated expression of PF4
(platelet factor 4) and eotaxin in the NOA mouse, a model for
atopic dermatitis. J Hum Genet. 44:173–176. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hikita I, Yoshioka T, Mizoguchi T,
Tsukahara K, Tsuru K, Nagai H, Hirasawa T, Tsuruta Y, Suzuki R,
Ichihashi M and Horikawa T: Characterization of dermatitis arising
spontaneously in DS-Nh mice maintained under conventional
conditions: another possible model for atopic dermatitis. J
Dermatol Sci. 30:142–153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim JE, Hwang IS, Goo JS, Nam SH, Choi SI,
Lee HR, Lee YJ, Kim YH, Park SJ, Kim NS, Choi YH and Hwang DY:
LP9M80-H isolated from Liriope platyphylla could help
alleviate diabetic symptoms via the regulation of glucose and lipid
concentration. J Life Sci. 22:634–641. 2012.
|
|
44
|
Kawakami T, Ando T, Kimura M, Wilson BS
and Kawakami Y: Mast cells in atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Immunol.
21:666–678. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Galli SJ: Mast cells and basophils. Curr
Opin Hematol. 7:32–39. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gao XK, Nakamura N, Fuseda K, Tanaka H,
Inagaki N and Nagai H: Establishment of allergic dermatitis in
NC/Nga mice as a model for severe atopic dermatitis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 27:1376–1381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dearman RJ, Skinner RA, Humphreys NE and
Kimber I: Methods for the identification of chemical respiratory
allergens in rodents: comparisons of cytokine profiling with
induced changes in serum IgE. J Appl Toxicol. 23:199–207. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|