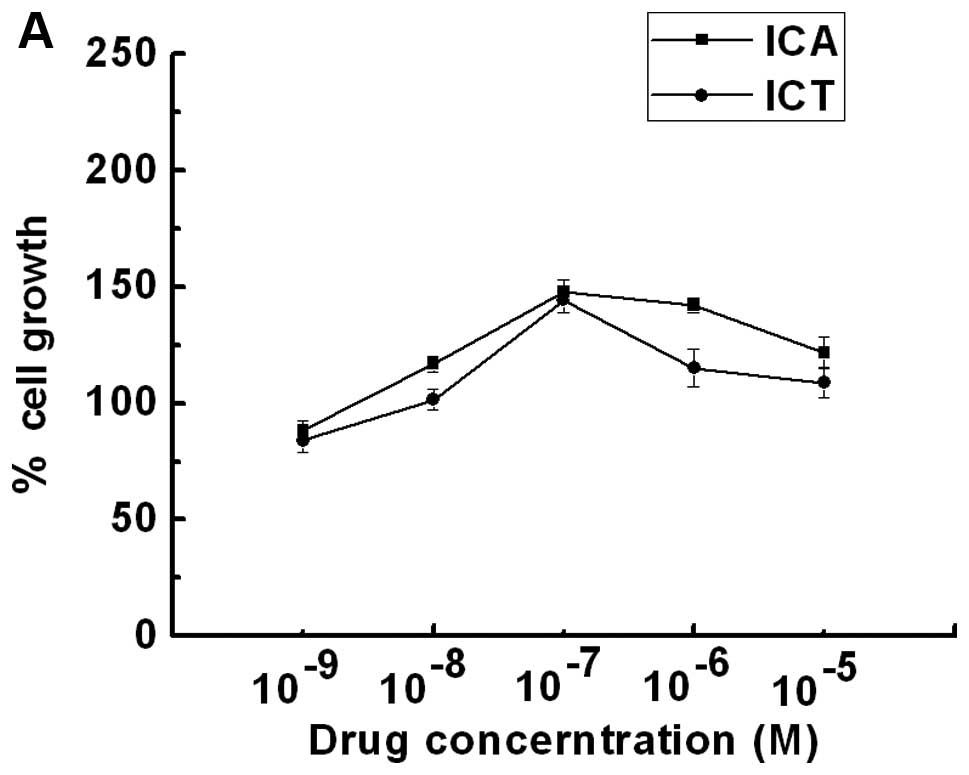
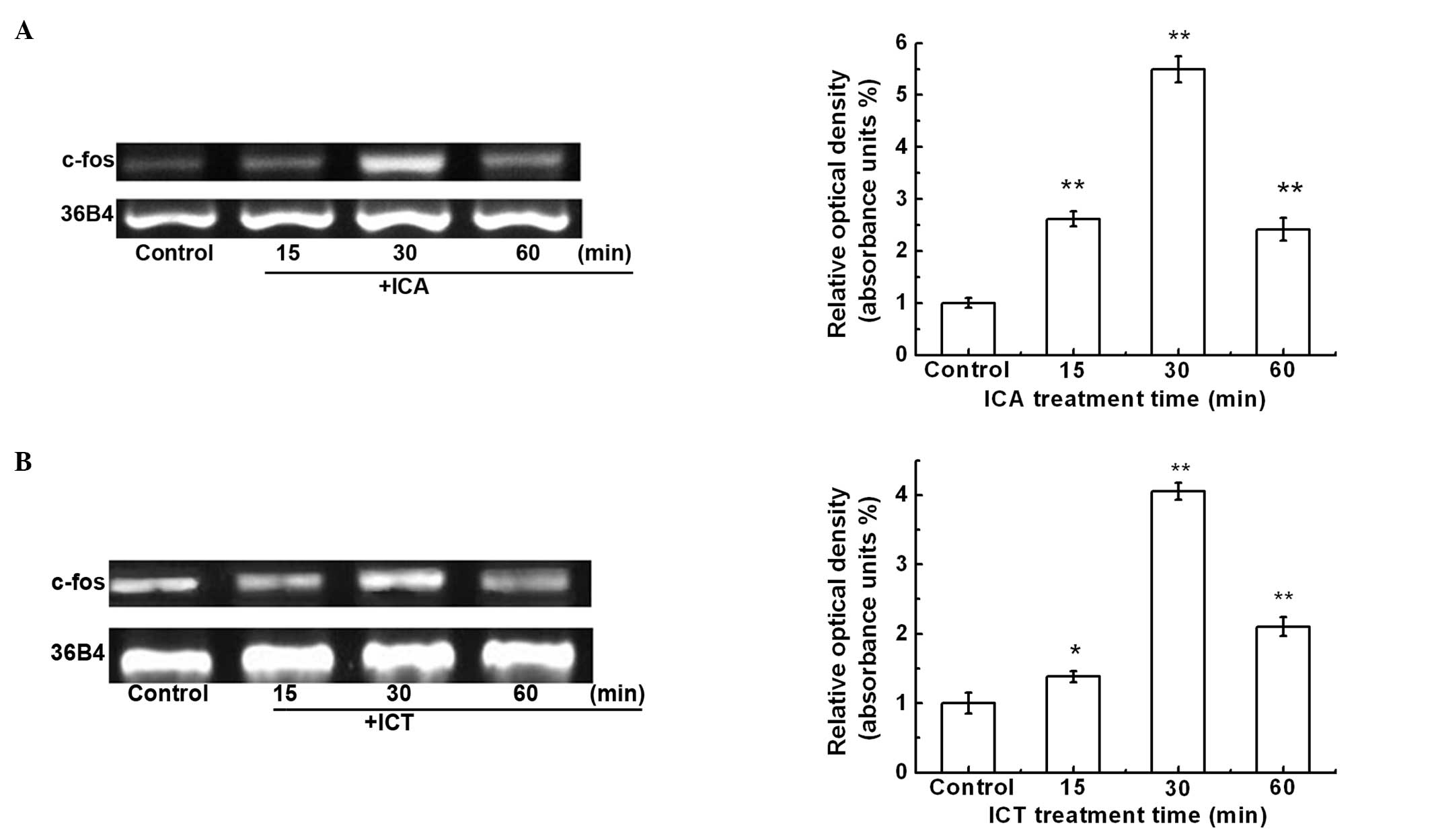
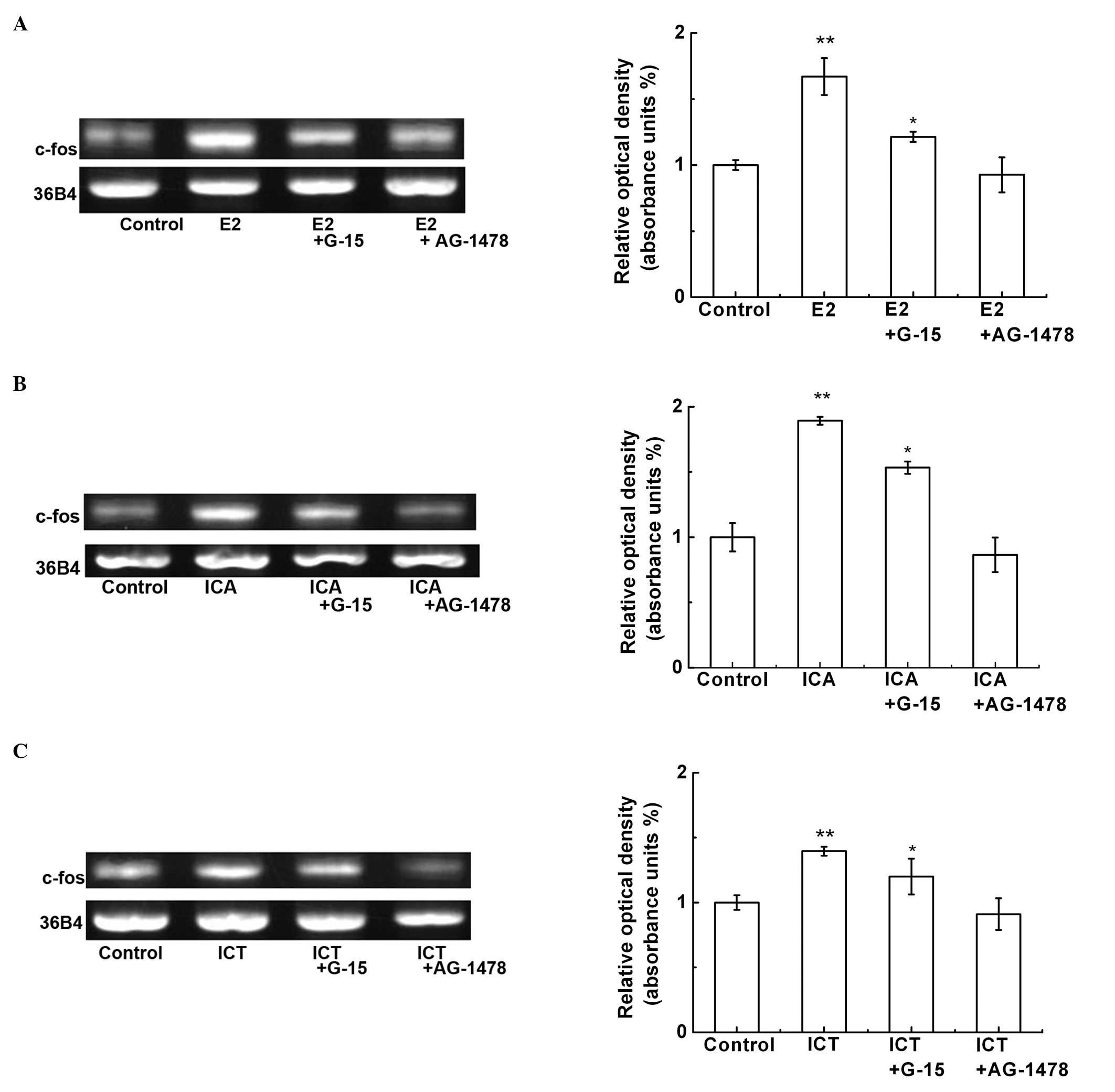
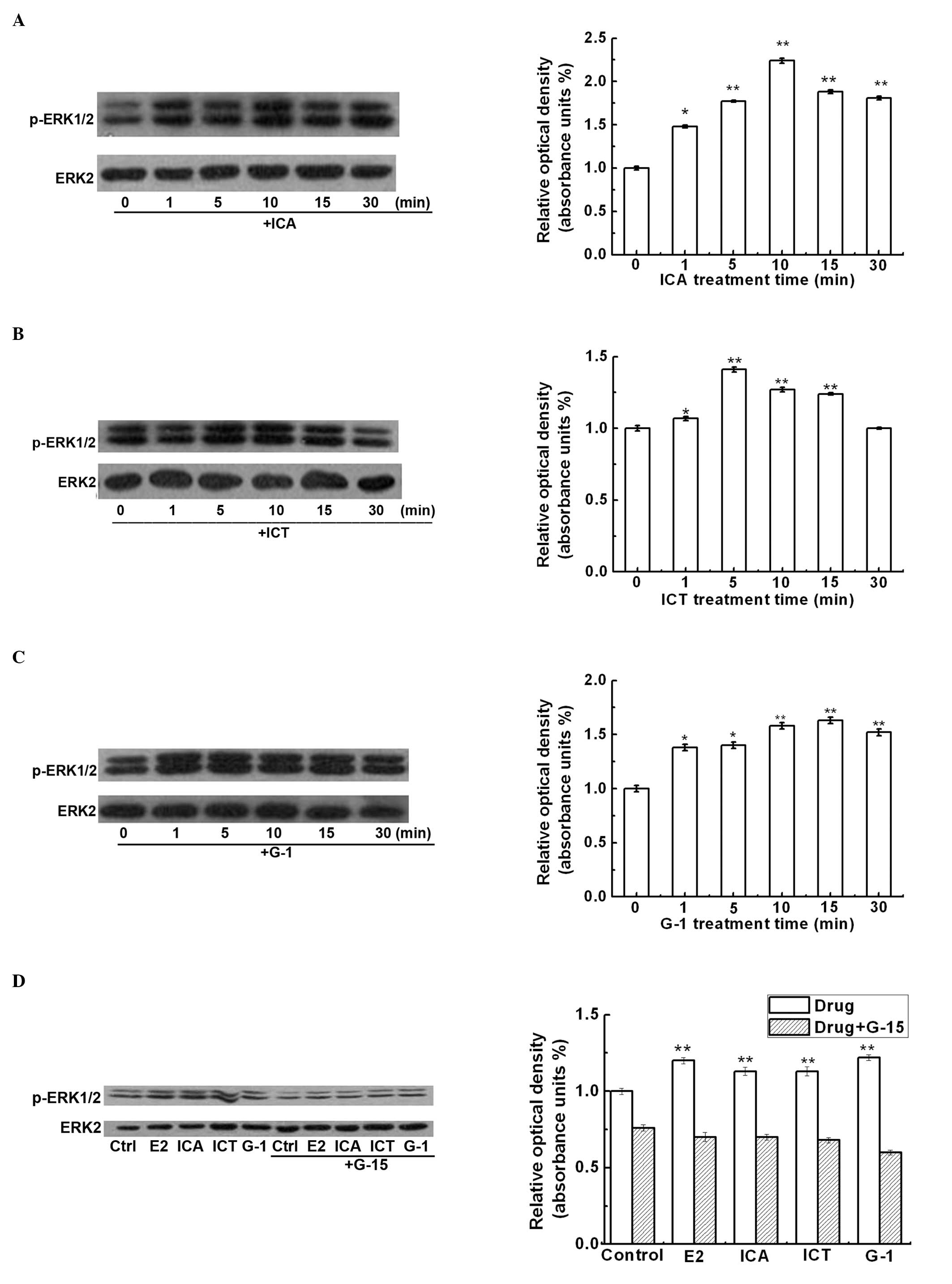
|
1
|
Owman C, Blay P, Nilsson C and Lolait SJ:
Cloning of human cDNA encoding a novel heptahelix receptor
expressed in Burkitt’s lymphoma and widely distributed in brain and
peripheral tissues. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 228:285–292.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M,
Nilsson S and Gustafsson JA: Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor
expressed in rat prostate and ovary. PNAS. 93:5925–5930. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carmeci C, Thompson DA, Ring HZ, Francke U
and Weigel RJ: Identification of a gene (GPR30) with homology to
the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily associated with estrogen
receptor expression in breast cancer. Genomics. 45:607–617. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bouskine A, Nebout M, Bruecker-Davis F,
Benahmed M and Fenichel P: Low doses of bisphenol A promote human
seminoma cell proliferation by activating PKA and PKG via a
membrane G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor. Environ Health Persp.
117:1053–1058. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filardo EJ: Epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) transactivation by estrogen via the
G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR30: a novel signaling pathway with
potential significance for breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem.
80:231–238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Revankar CM: A transmembrane intracellular
estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science.
307:1625–1630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pearce ST and Jordan VC: The biological
role of estrogen receptors α and β in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 50:3–22. 2004.
|
|
8
|
Prossnitz ER, Sklar LA, Oprea TI and
Arterburn JB: GPR30: a novel therapeutic target in estrogen-related
disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:116–123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma H, He X, Yang Y, Li M, Hao D and Jia Z:
The genus Epimedium: An ethnopharmacological and phytochemical
review. J Ethnopharmacol. 134:519–541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang X, Zhu D and Lou Y: A novel
anticancer agent, icaritin, induced cell growth inhibition, G1
arrest and mitochondrial transmembrane potential drop in human
prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 564:26–36. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chung BH, Kim JD, Kim CK, Kim JH, Won MH,
Lee HS, et al: Icariin stimulates angiogenesis by activating the
MEK/ERK- and PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent signal pathways in human
endothelial cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 376:404–408. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, Zhang X, Li KF, Li DX, Xiao YM,
Fan YJ, et al: Icariin promotes extracellular matrix synthesis and
gene expression of chondrocytes in vitro. Phytother Res.
26:1385–1392. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ming LG, Chen KM and Xian CJ: Functions
and action mechanisms of flavonoids genistein and icariin in
regulating bone remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 228:513–521. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang ZQ and Lou YJ:
Proliferation-stimulating effects of icaritin and desmethylicaritin
in MCF-7 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 504:147–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu Y, Yan H, Hu S and Zhang J: Study on
the estrogen-like effects of Epimedium extractive. J Xi’an Jiao
tong Univ (Med Sci). 30:373–376. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Guo Y, Zhang X, Meng J and Wang ZY: An
anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits
growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:114–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye HY and Lou YJ: Estrogenic effects of
two derivatives of icariin on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.
Phytomedicine. 12:735–741. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Levin ER: Bidirectional signaling between
the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol
Endocrinol. 17:309–317. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Razandi M: Proximal events in signaling by
plasma membrane estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem. 278:2701–2712.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fujiwara S, Terai Y, Kawaguchi H, Takai M,
Yoo S, Tanaka Y, et al: GPR30 regulates the EGFR-Akt cascade and
predicts lower survival in patients with ovarian cancer. J Ovarian
Res. 5:352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Bland KI and
Frackelton AR Jr: Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2
requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs
via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
through release of HB-EGF. Mol Endocrinol. 14:1649–1660. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Du GQ, Zhou L, Chen XY, Wan XP and He YY:
The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates the proliferative and
invasive effects induced by hydroxytamoxifen in endometrial cancer
cells. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 420:343–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Albanito L, Madeo A, Lappano R, Vivacqua
A, Rago V, Carpino A, et al: G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30)
mediates gene expression changes and growth response to 17
beta-estradiol and selective GPR30 ligand G-1 in ovarian cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 67:1859–1866. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vivacqua A, Bonofiglio D, Albanito L,
Madeo A, Rago V, Carpino A, et al: 17beta-estradiol, genistein, and
4-hydroxytamoxifen induce the proliferation of thyroid cancer cells
through the G protein-coupled receptor GPR30. Mol Pharmacol.
70:1414–1423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maggiolini M: The G protein-coupled
receptor GPR30 mediates c-fos up-regulation by 17-estradiol and
phytoestrogens in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
279:27008–27016. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma H, Lu Z, Sun Y, Peng T, Shuai Z, Ma Y,
et al: Selection of donor nuclei in somatic cell-mediated gene
transfer using a co-transfection method. J Reprod Develop.
53:95–104. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang K, Lee SB, Jung SH, Cha KH, Park WD,
Sohn YC, et al: Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor α,
exerts its estrogenic effects via an ERK-dependent pathway. Mol
Cells. 27:351–357. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|