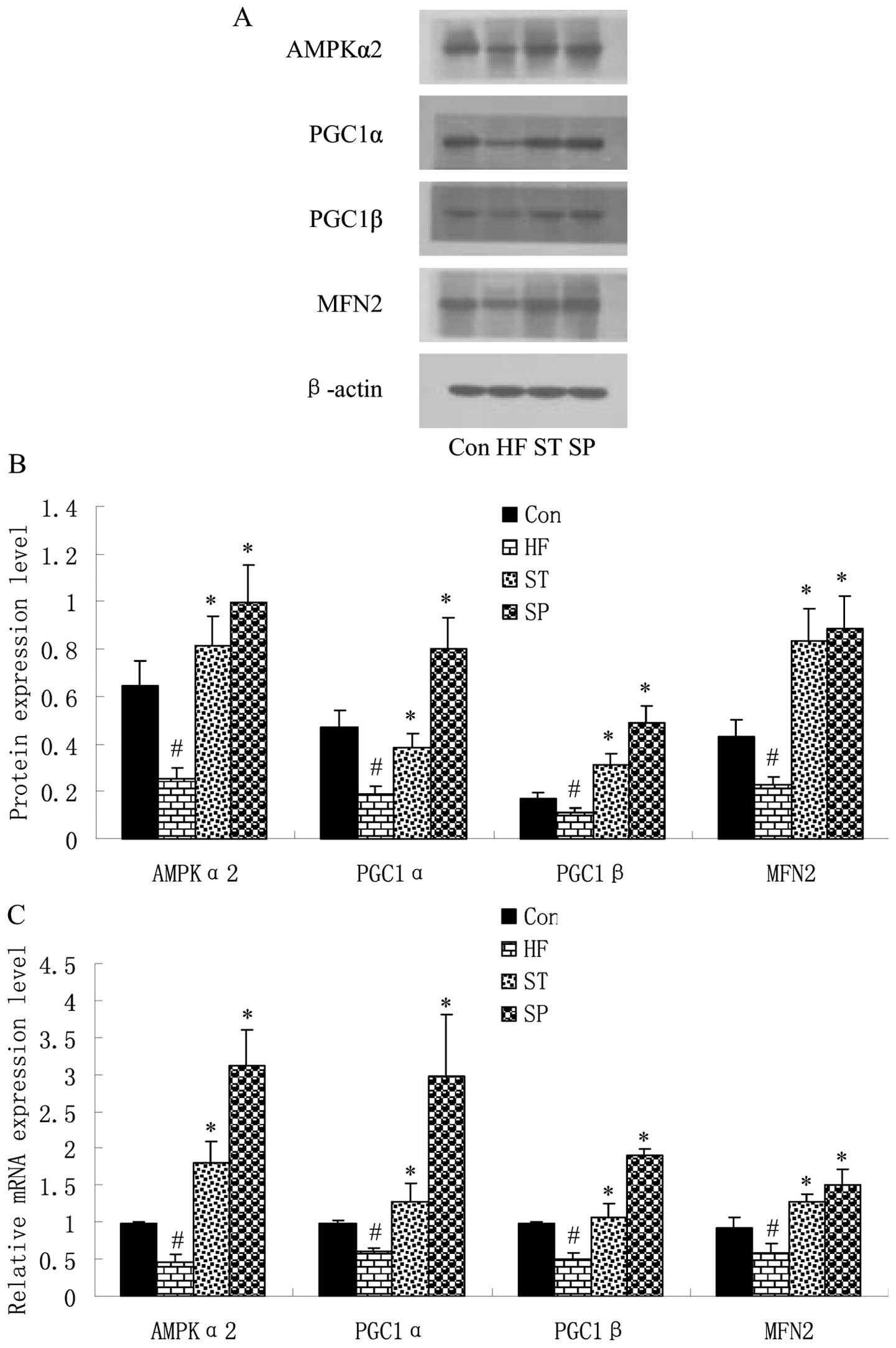
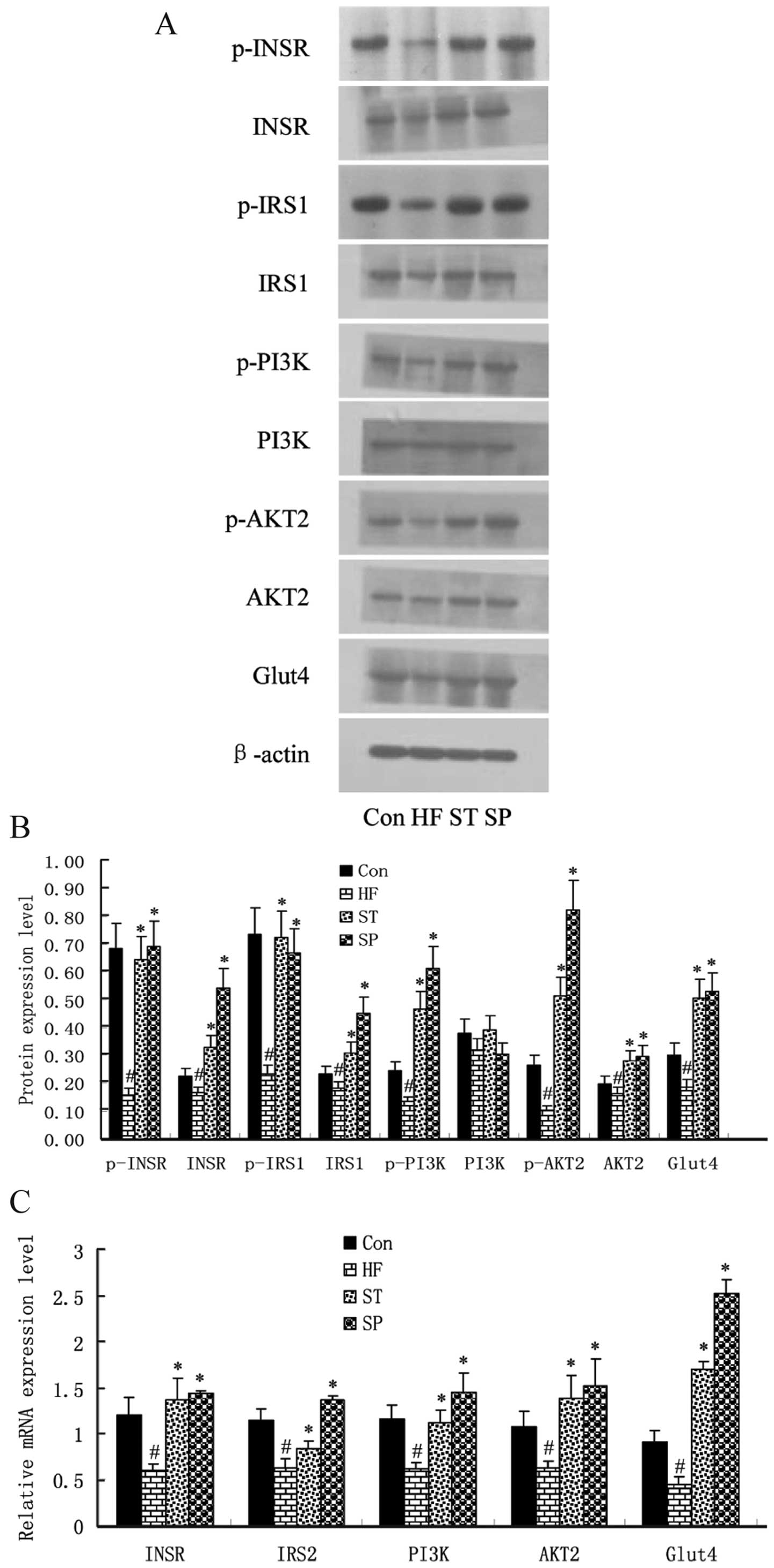
|
1
|
Karpe F, Dickmann JR and Frayn KN: Fatty
acids, obesity, and insulin resistance: time for a reevaluation.
Diabetes. 60:2441–2449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang ZL, Xia B, Shrestha U, et al:
Correlation between adiponectin polymorphisms and non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease with or without metabolic syndrome in Chinese
population. J Endocrinol Invest. 31:1086–1091. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chow L, From A and Seaquist E: Skeletal
muscle insulin resistance: the interplay of local lipid excess and
mitochondrial dysfunction. Metabolism. 59:70–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martins AR, Nachbar RT, Gorjao R, et al:
Mechanisms underlying skeletal muscle insulin resistance induced by
fatty acids: importance of the mitochondrial function. Lipids
Health Dis. 11:302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song GY, Ren LP, Chen SC, et al: Similar
changes in muscle lipid metabolism are induced by chronic
high-fructose feeding and high-fat feeding in C57BL/J6 mice. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 39:1011–1018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iellamo F, Caminiti G, Sposato B, et al:
Effect of high-intensity interval training versus moderate
continuous training on 24-h blood pressure profile and insulin
resistance in patients with chronic heart failure. Intern Emerg
Med. Jul 16–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Chowdhury KK, Legare DJ and Lautt WW:
Interaction of antioxidants and exercise on insulin sensitivity in
healthy and prediabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 91:570–577.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buettner R, Parhofer KG, Woenckhaus M, et
al: Defining high-fat-diet rat models: metabolic and molecular
effects of different fat types. J Mol Endocrinol. 36:485–501. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bray GA, Lovejoy JC, Smith SR, et al: The
influence of different fats and fatty acids on obesity, insulin
resistance and inflammation. J Nutr. 132:2488–2491. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McGarry JD: Banting lecture 2001:
dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 51:7–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gan KX, Wang C, Chen JH, Zhu CJ and Song
GY: Mitofusin-2 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin
resistance in liver of rats. World J Gastroenterol. 19:1572–1581.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song GY, Gao Y, Wang C, et al:
Rosiglitazone reduces fatty acid translocase and increases AMPK in
skeletal muscle in aged rats: a possible mechanism to prevent
high-fat-induced insulin resistance. Chin Med J (Engl).
123:2384–2391. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kong D, Song G, Wang C, et al:
Overexpression of mitofusin 2 improves translocation of glucose
transporter 4 in skeletal muscle of highfat dietfed rats through
AMP activated protein kinase signaling. Mol Med Rep. 8:205–210.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shulman GI: Cellular mechanisms of insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 106:171–176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu L, Zhang Y, Chen N, Shi X, Tsang B and
Yu YH: Upregulation of myocellular DGAT1 augments triglyceride
synthesis in skeletal muscle and protects against fat-induced
insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 117:1679–1689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schenk S and Horowitz JF: Acute exercise
increases triglyceride synthesis in skeletal muscle and prevents
fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest.
117:1690–1698. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang C, Han M, Zhao XM and Wen JK:
Kruppel-like factor 4 is required for the expression of vascular
smooth muscle cell differentiation marker genes induced by
all-trans retinoic acid. J Biochem. 144:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goodpaster BH, Krishnaswami S, Resnick H,
et al: Association between regional adipose tissue distribution and
both type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in elderly men
and women. Diabetes Care. 26:372–379. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perseghin G, Scifo P, De Cobelli F, et al:
Intramyocellular triglyceride content is a determinant of in vivo
insulin resistance in humans: a 1H-13C nuclear magnetic resonance
spectroscopy assessment in offspring of type 2 diabetic parents.
Diabetes. 48:1600–1606. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Virkamaki A, Korsheninnikova E,
Seppala-Lindroos A, et al: Intramyocellular lipid is associated
with resistance to in vivo insulin actions on glucose uptake,
antilipolysis, and early insulin signaling pathways in human
skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 50:2337–2343. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Oppert JM, Nadeau A, Tremblay A, Despres
JP, Theriault G and Bouchard C: Negative energy balance with
exercise in identical twins: plasma glucose and insulin responses.
Am J Physiol. 272:E248–E254. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Corcoran MP, Lamon-Fava S and Fielding RA:
Skeletal muscle lipid deposition and insulin resistance: effect of
dietary fatty acids and exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:662–677.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Samuel VT, Petersen KF and Shulman GI:
Lipid-induced insulin resistance: unravelling the mechanism.
Lancet. 375:2267–2277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Campbell SE, Tandon NN, Woldegiorgis G,
Luiken JJ, Glatz JF and Bonen A: A novel function for fatty acid
translocase (FAT)/CD36: involvement in long chain fatty acid
transfer into the mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 279:36235–36241. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sebastian D, Herrero L, Serra D, Asins G
and Hegardt FG: CPT I overexpression protects L6E9 muscle cells
from fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 292:E677–E686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smathers RL and Petersen DR: The human
fatty acid-binding protein family: evolutionary divergences and
functions. Hum Genomics. 5:170–191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Storch J and Thumser AE: Tissue-specific
functions in the fatty acid-binding protein family. J Biol Chem.
285:32679–32683. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kusudo T, Kontani Y, Kataoka N, Ando F,
Shimokata H and Yamashita H: Fatty acid-binding protein 3
stimulates glucose uptake by facilitating AS160 phosphorylation in
mouse muscle cells. Genes Cells. 16:681–691. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruderman NB, Carling D, Prentki M and
Cacicedo JM: AMPK, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome.
J Clin Invest. 123:2764–2772. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao S, Li B, Yi X, et al: Effects of
exercise on AMPK signaling and downstream components to PI3K in rat
with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 7:e517092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Velkov T: Interactions between human liver
fatty acid binding protein and peroxisome proliferator activated
receptor selective drugs. PPAR Res. 2013:9384012013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kramer DK, Al-Khalili L, Guigas B, Leng Y,
Garcia-Roves PM and Krook A: Role of AMP kinase and PPARdelta in
the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in human skeletal
muscle. J Biol Chem. 282:19313–19320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liesa M, Palacin M and Zorzano A:
Mitochondrial dynamics in mammalian health and disease. Physiol
Rev. 89:799–845. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sebastian D, Hernandez-Alvarez MI, Segales
J, et al: Mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) links mitochondrial and endoplasmic
reticulum function with insulin signaling and is essential for
normal glucose homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:5523–5528.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zorzano A, Liesa M and Palacin M:
Mitochondrial dynamics as a bridge between mitochondrial
dysfunction and insulin resistance. Arch Physiol Biochem. 115:1–12.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hernandez-Alvarez MI, Thabit H, Burns N,
et al: Subjects with early-onset type 2 diabetes show defective
activation of the skeletal muscle PGC-1{alpha}/Mitofusin-2
regulatory pathway in response to physical activity. Diabetes Care.
33:645–651. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zorzano A, Hernandez-Alvarez MI, Palacin M
and Mingrone G: Alterations in the mitochondrial regulatory
pathways constituted by the nuclear co-factors PGC-1alpha or
PGC-1beta and mitofusin 2 in skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetes.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1797:1028–1033. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Akimoto T, Pohnert SC, Li P, et al:
Exercise stimulates Pgc-1alpha transcription in skeletal muscle
through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem.
280:19587–19593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wright DC, Geiger PC, Han DH, Jones TE and
Holloszy JO: Calcium induces increases in peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha and
mitochondrial biogenesis by a pathway leading to p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem.
282:18793–18799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Egan B, Carson BP, Garcia-Roves PM, et al:
Exercise intensity-dependent regulation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1 mRNA abundance is
associated with differential activation of upstream signalling
kinases in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 588:1779–1790. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Previs SF, Withers DJ, Ren JM, White MF
and Shulman GI: Contrasting effects of IRS-1 versus IRS-2 gene
disruption on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 275:38990–38994. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Osorio-Fuentealba C, Contreras-Ferrat AE,
Altamirano F, et al: Electrical stimuli release ATP to increase
GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake via PI3Kgamma-Akt-AS160 in
skeletal muscle cells. Diabetes. 62:1519–1526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|