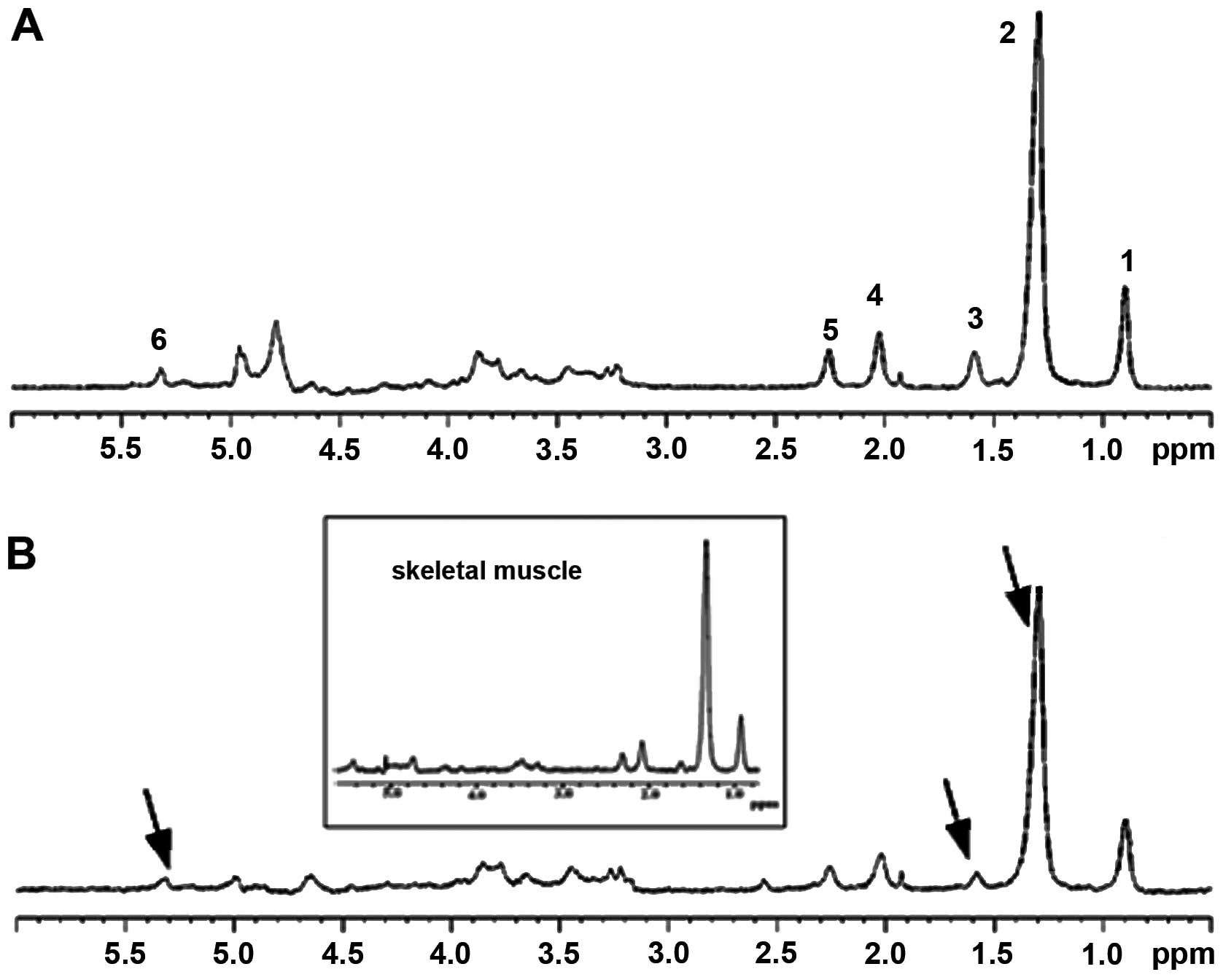
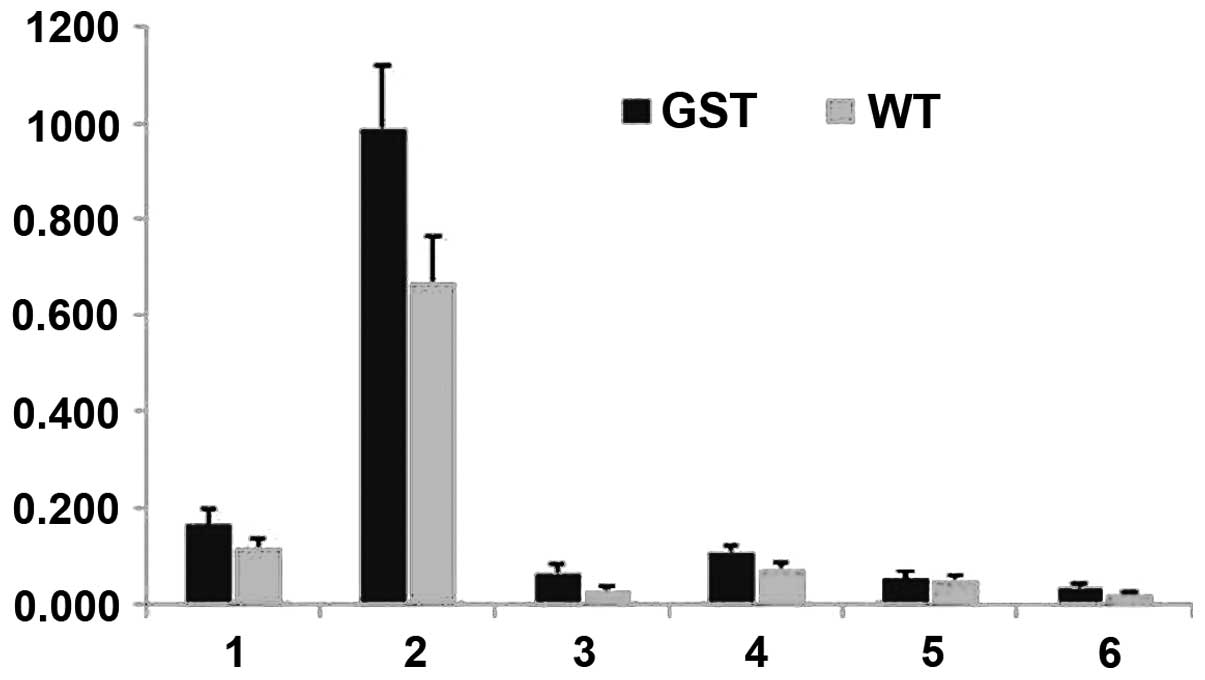
|
1
|
Weybright P, Millis K, Campbell N, Cory DG
and Singer S: Gradient, high-resolution, magic angle spinning
1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of intact
cells. Magn Reson Med. 39:337–345. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blankenberg FG, Storrs RW, Naumovski L,
Goralski T and Spielman D: Detection of apoptotic cell death by
proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Blood.
87:1951–1956. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng LL, Ma MJ, Becerra L, et al:
Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning
proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:6408–6413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng LL, Newell K, Mallory AE, Hyman BT
and Gonzalez RG: Quantification of neurons in Alzheimer and control
brains with ex vivo high resolution magic angle spinning proton
magnetic resonance spectroscopy and stereology. Magn Reson Imaging.
20:527–533. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Millis KK, Maas WE, Cory DG and Singer S:
Gradient, high-resolution, magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic
resonance spectroscopy of human adipocyte tissue. Magn Reson Med.
38:399–403. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Millis K, Weybright P, Campbell N, et al:
Classification of human liposarcoma and lipoma using ex vivo proton
NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 41:257–267. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barton SJ, Howe FA, Tomlins AM, et al:
Comparison of in vivo 1H MRS of human brain tumours with
1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of intact biopsy samples in
vitro. MAGMA. 8:121–128. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Griffin JL, Williams HJ, Sang E and
Nicholson JK: Abnormal lipid profile of dystrophic cardiac tissue
as demonstrated by one- and two-dimensional magic-angle spinning
(1)H NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 46:249–255. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tzika AA, Cheng LL, Goumnerova L, et al:
Biochemical characterization of pediatric brain tumors by using in
vivo and ex vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurosurg.
96:1023–1031. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tugnoli V, Schenetti L, Mucci A, et al:
Ex vivo HR-MAS MRS of human meningiomas: a comparison with
in vivo 1H MR spectra. Int J Mol Med. 18:859–869.
2006.
|
|
11
|
Astrakas LG, Goljer I, Yasuhara S, et al:
Proton NMR spectroscopy shows lipids accumulate in skeletal muscle
in response to burn trauma-induced apoptosis. FASEB J.
19:1431–1440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tzika AA, Astrakas LG, Cao H, et al:
Murine intramyocellular lipids quantified by NMR act as metabolic
biomarkers in burn trauma. Int J Mol Med. 21:825–832.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bollard ME, Garrod S, Holmes E, et al:
High-resolution (1)H and (1)H-(13)C magic angle spinning NMR
spectroscopy of rat liver. Magn Reson Med. 44:201–207. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szczepaniak LS, Babcock EE, Schick F, et
al: Measurement of intracellular triglyceride stores by H
spectroscopy: validation in vivo. Am J Physiol. 276:E977–E989.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Graaf M, Tack CJ, de Haan JH,
Klomp DW and Heerschap A: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy shows an
inverse correlation between intramyocellular lipid content in human
calf muscle and local glycogen synthesis rate. NMR Biomed.
23:133–141. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Jacob S, Machann J, Rett K, et al:
Association of increased intramyocellular lipid content with
insulin resistance in lean nondiabetic offspring of type 2 diabetic
subjects. Diabetes. 48:1113–1119. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Petersen KF, Befroy D, Dufour S, et al:
Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: possible role in insulin
resistance. Science. 300:1140–1142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feala JD, Coquin L, McCulloch AD and
Paternostro G: Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia
tolerance in Drosophila flight muscle: metabolomic and
computational systems analysis. Mol Syst Biol. 3:992007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pedersen KS, Kristensen TN, Loeschcke V,
et al: Metabolomic signatures of inbreeding at benign and stressful
temperatures in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics.
180:1233–1243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bharucha KN: The epicurean fly: using
Drosophila melanogaster to study metabolism. Pediatr Res.
65:132–137. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Null B, Liu CW, Hedehus M, Conolly S and
Davis RW: High-resolution, in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of
Drosophila at 18.8 Tesla. PLoS One. 3:e28172008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Righi V, Apidianakis Y, Rahme LG and Tzika
AA: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of live Drosophila
melanogaster using magic angle spinning. J Vis Exp.
38:17102010.
|
|
23
|
Baker KD and Thummel CS: Diabetic larvae
and obese flies-emerging studies of metabolism in
Drosophila. Cell Metab. 6:257–266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leopold P and Perrimon N:
Drosophila and the genetics of the internal milieu. Nature.
450:186–188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Singh SP, Coronella JA, Benes H, Cochrane
BJ and Zimniak P: Catalytic function of Drosophila
melanogaster glutathione S-transferase DmGSTS1–1 (GST-2) in
conjugation of lipid peroxidation end products. Eur J Biochem.
268:2912–2923. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meiboom S and Gill D: Modified spiin-echo
method for measuring nuclear relaxation time. Rev Sci Instrum.
29:688–691. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Levenberg K: A method for the solution of
certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q Appl Math.
2:164–168. 1944.
|
|
28
|
Marquardt D: An algorithm for
least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. SIAM J Appl Math.
11:431–441. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Swanson MG, Zektzer AS, Tabatabai ZL, et
al: Quantitative analysis of prostate metabolites using
1H HR-MAS spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 55:1257–1264.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Righi V, Apidianakis Y, Psychogios N,
Rahme LG, Tompkins RG and Tzika AA: In vivo high-resolution magic
angle spinning proton NMR spectroscopy of Drosophila
melanogaster flies as a model system to investigate
mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila mutants. Intl Soc
Mag Reson Med. 1460:192011.
|
|
31
|
Garofalo RS: Genetic analysis of insulin
signaling in Drosophila. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
13:156–162. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abmayr SM, Zhuang S and Geisbrecht ER:
Myoblast fusion in Drosophila. Methods Mol Biol. 475:75–97.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Richardson B, Beckett K and Baylies M:
Visualizing new dimensions in Drosophila myoblast fusion.
Bioessays. 30:423–431. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rochlin K, Yu S, Roy S and Baylies MK:
Myoblast fusion: when it takes more to make one. Dev Biol.
341:66–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Partridge L and Tower J: Yeast, a feast:
The fruit fly Drosophila as a model organism for research
into aging. The Molecular Biology of Aging. Guarente L and
Partridge L: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; pp. 267–308.
2008
|
|
37
|
Marsh JL and Thompson LM:
Drosophila in the study of neurodegenerative disease.
Neuron. 52:169–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ramsden S, Cheung YY and Seroude L:
Functional analysis of the Drosophila immune response during
aging. Aging Cell. 7:225–236. 2008.
|
|
39
|
Zerofsky M, Harel E, Silverman N and Tatar
M: Aging of the innate immune response in Drosophila
melanogaster. Aging Cell. 4:103–108. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ocorr K, Akasaka T and Bodmer R:
Age-related cardiac disease model of Drosophila. Mech Ageing
Dev. 128:112–116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smith JM, Bozcuk AN and Tebbutt S: Protein
turnover in adult Drosophila. J Insect Physiol. 16:601–613.
1970. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Webster GC, Beachell VT and Webster SL:
Differential decrease in protein synthesis by microsomes from aging
Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Gerontol. 15:495–497. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gartner LP: Aging and the visceral
musculature of the adult fruitfly: an ultrastructural
investigation. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 96:48–55. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miller MS, Lekkas P, Braddock JM, et al:
Aging enhances indirect flight muscle fiber performance yet
decreases flight ability in Drosophila. Biophys J.
95:2391–2401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Takahashi A, Philpott DE and Miquel J:
Electron microscope studies on aging Drosophila
melanogaster. 3 Flight muscle. J Gerontol. 25:222–228. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zheng J, Edelman SW, Tharmarajah G, Walker
DW, Pletcher SD and Seroude L: Differential patterns of apoptosis
in response to aging in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:12083–12088. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ferguson M, Mockett RJ, Shen Y, Orr WC and
Sohal RS: Age-associated decline in mitochondrial respiration and
electron transport in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J.
390:501–511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Girardot F, Lasbleiz C, Monnier V and
Tricoire H: Specific age-related signatures in Drosophila
body parts transcriptome. BMC Genomics. 7:692006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Magwere T, Goodall S, Skepper J, Mair W,
Brand MD and Partridge L: The effect of dietary restriction on
mitochondrial protein density and flight muscle mitochondrial
morphology in Drosophila. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
61:36–47. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sohal RS, Sohal BH and Orr WC:
Mitochondrial superoxide and hydrogen peroxide generation, protein
oxidative damage, and longevity in different species of flies. Free
Radic Biol Med. 19:499–504. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Goddeeris MM, Cook-Wiens E, Horton WJ, et
al: Delayed behavioural aging and altered mortality in
Drosophila beta integrin mutants. Aging Cell. 2:257–264.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Miller BM, Zhang S, Suggs JA, et al: An
alternative domain near the nucleotide-binding site of
Drosophila muscle myosin affects ATPase kinetics. J Mol
Biol. 353:14–25. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kronert WA, Dambacher CM, Knowles AF,
Swank DM and Bernstein SI: Alternative relay domains of
Drosophila melanogaster myosin differentially affect ATPase
activity, in vitro motility, myofibril structure and muscle
function. J Mol Biol. 379:443–456. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kronert WA, Melkani GC, Melkani A and
Bernstein SI: Mutating the converter-relay interface of
Drosophila myosin perturbs ATPase activity, actin motility,
myofibril stability and flight ability. J Mol Biol. 398:625–632.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Das N, Levine RL, Orr WC and Sohal RS:
Selectivity of protein oxidative damage during aging in
Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J. 360:209–216. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Toroser D, Orr WC and Sohal RS:
Carbonylation of mitochondrial proteins in Drosophila
melanogaster during aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
363:418–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wheeler JC, Bieschke ET and Tower J:
Muscle-specific expression of Drosophila hsp70 in response
to aging and oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
92:10408–10412. 1995.
|
|
58
|
Zhan M, Yamaza H, Sun Y, Sinclair J, Li H
and Zou S: Temporal and spatial transcriptional profiles of aging
in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 17:1236–1243. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Singh SP, Niemczyk M, Saini D, Awasthi YC,
Zimniak L and Zimniak P: Role of the electrophilic lipid
peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal in the development and
maintenance of obesity in mice. Biochemistry. 47:3900–3911. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Weis J, Johansson L, Ortiz-Nieto F and
Ahlstrom H: Assessment of lipids in skeletal muscle by LCModel and
AMARES. J Magn Reson Imaging. 30:1124–1129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang L, Salibi N, Wu Y, Schweitzer ME and
Regatte RR: Relaxation times of skeletal muscle metabolites at 7T.
J Magn Reson Imaging. 29:1457–1464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen JH, Sambol EB, Decarolis P, et al:
High-resolution MAS NMR spectroscopy detection of the spin
magnetization exchange by cross-relaxation and chemical exchange in
intact cell lines and human tissue specimens. Magn Reson Med.
55:1246–1256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Boesch C, Slotboom J, Hoppeler H and Kreis
R: In vivo determination of intra-myocellular lipids in human
muscle by means of localized 1H-MR-spectroscopy. Magn
Reson Med. 37:484–493. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vermathen P, Kreis R and Boesch C:
Distribution of intramyocellular lipids in human calf muscles as
determined by MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med. 51:253–262.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Havel RJ, Carlson LA, Ekelund LG and
Holmgren A: Turnover rate and oxidation of different free fatty
acids in man during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 19:613–618.
1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mehring M: High Resolution NMR in Solids.
Springer-Verlag; New York: 1982
|
|
67
|
Garroway AN: Magic-angle sample spinning
of liquids. J Magn Reson. 49:168–171. 1982.
|
|
68
|
Barbara TM: Cylindrical demagnetization
fields and microprobe design in high resolution NMR. J Magn Reson
A. 109:2651994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Chen JH, Enloe BM, Xiao Y, Cory DG and
Singer S: Isotropic susceptibility shift under MAS: the origin of
the split water resonances in 1H MAS NMR spectra of cell
suspensions. Magn Reson Med. 50:515–521. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chu SC, Xu Y, Balschi JA and Springer CS
Jr: Bulk magnetic susceptibility shifts in NMR studies of
compartmentalized samples: use of paramagnetic reagents. Magn Reson
Med. 13:239–262. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kayar SR, Hoppeler H, Howald H, Claassen H
and Oberholzer F: Acute effects of endurance exercise on
mitochondrial distribution and skeletal muscle morphology. Eur J
Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 54:578–584. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Canavoso LE, Jouni ZE, Karnas KJ,
Pennington JE and Wells MA: Fat metabolism in insects. Annu Rev
Nutr. 21:23–46. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Gilby AR: Lipids and their metabolism in
insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 10:141–160. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Fast PG: A comparative study of the
phospholipids and fatty acids of some insect lipids. Science.
155:1680–1681. 1967.
|
|
75
|
Stanley-Samuelson DW, Jurenka RA, Cripps
C, Blomquist GJ and deRenobales M: Fatty acids in insects:
composition, metabolism, and biological significance. Arch Insect
Biochem Physiol. 9:1–33. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Horne I, Haritos VS and Oakeshott JG:
Comparative and functional genomics of lipases in holometabolous
insects. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 39:547–567. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Patel RT, Soulages JL, Hariharasundaram B
and Arrese EL: Activation of the lipid droplet controls the rate of
lipolysis of triglycerides in the insect fat body. J Biol Chem.
280:22624–22631. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bharucha KN, Tarr P and Zipursky SL: A
glucagon-like endocrine pathway in Drosophila modulates both
lipid and carbohydrate homeostasis. J Exp Biol. 211:3103–3110.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Righi V, Apidianakis Y, Mintzopoulos D,
Astrakas L, Rahme LG and Tzika AA: In vivo high-resolution
magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopy of
Drosophila melanogaster at 14.1 T shows trauma in aging and
in innate immune-deficiency is linked to reduced insulin signaling.
Int J Mol Med. 26:175–184. 2010.
|
|
80
|
Machann J, Thamer C, Schnoedt B, et al:
Age and gender related effects on adipose tissue compartments of
subjects with increased risk for type 2 diabetes: a whole body
MRI/MRS study. MAGMA. 18:128–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Nakagawa Y, Hattori M, Harada K, Shirase
R, Bando M and Okano G: Age-related changes in intramyocellular
lipid in humans by in vivo H-MR spectroscopy. Gerontology.
53:218–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Muller MJ and Herndon DN: The challenge of
burns. Lancet. 343:216–220. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ikezu T, Okamoto T, Yonezawa K, Tompkins
RG and Martyn JA: Analysis of thermal injury-induced insulin
resistance in rodents. Implication of postreceptor mechanisms. J
Biol Chem. 272:25289–25295. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sinha R, Dufour S, Petersen KF, et al:
Assessment of skeletal muscle triglyceride content by (1)H nuclear
magnetic resonance spectroscopy in lean and obese adolescents:
relationships to insulin sensitivity, total body fat, and central
adiposity. Diabetes. 51:1022–1027. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Hesselink MK,
Schrauwen P and Kooi ME: Intramyocellular lipid content in human
skeletal muscle. Obesity (Silver Spring). 14:357–367. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Consitt LA, Bell JA and Houmard JA:
Intramuscular lipid metabolism, insulin action, and obesity. IUBMB
Life. 61:47–55. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Johnson AB, Argyraki M, Thow JC, Cooper
BG, Fulcher G and Taylor R: Effect of increased free fatty acid
supply on glucose metabolism and skeletal muscle glycogen synthase
activity in normal man. Clin Sci (Lond). 82:219–226.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Clancy DJ, Gems D, Harshman LG, et al:
Extension of life-span by loss of CHICO, a Drosophila
insulin receptor substrate protein. Science. 292:104–106. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bohni R, Riesgo-Escovar J, Oldham S, et
al: Autonomous control of cell and organ size by CHICO, a
Drosophila homolog of vertebrate IRS1–4. Cell. 97:865–875.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Paumen MB, Ishida Y, Muramatsu M, Yamamoto
M and Honjo T: Inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I
augments sphingolipid synthesis and palmitate-induced apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 272:3324–3329. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ruddock MW, Stein A, Landaker E, et al:
Saturated fatty acids inhibit hepatic insulin action by modulating
insulin receptor expression and post-receptor signalling. J
Biochem. 144:599–607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fernandez-Real JM and Pickup JC: Innate
immunity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 19:10–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|