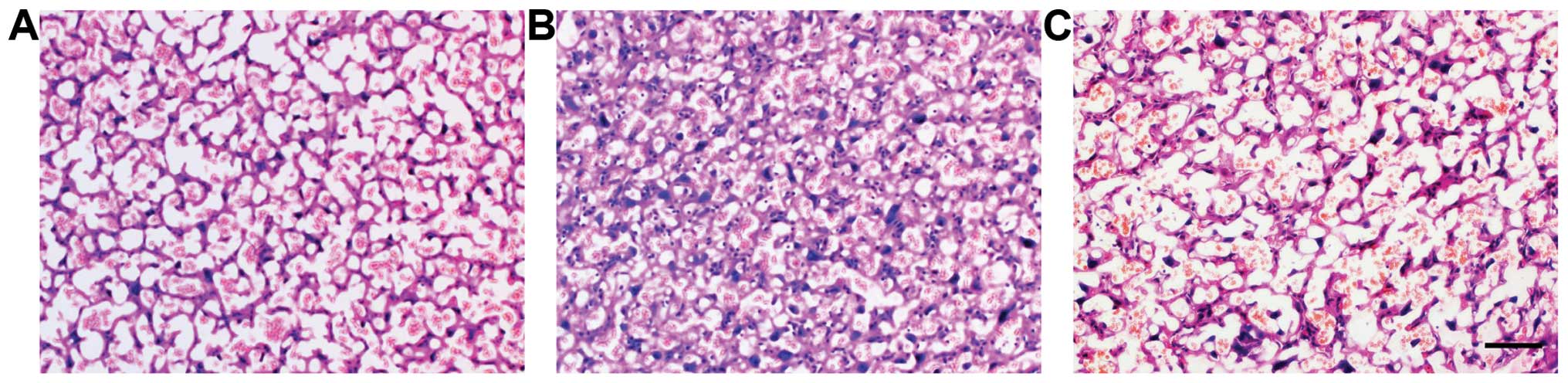
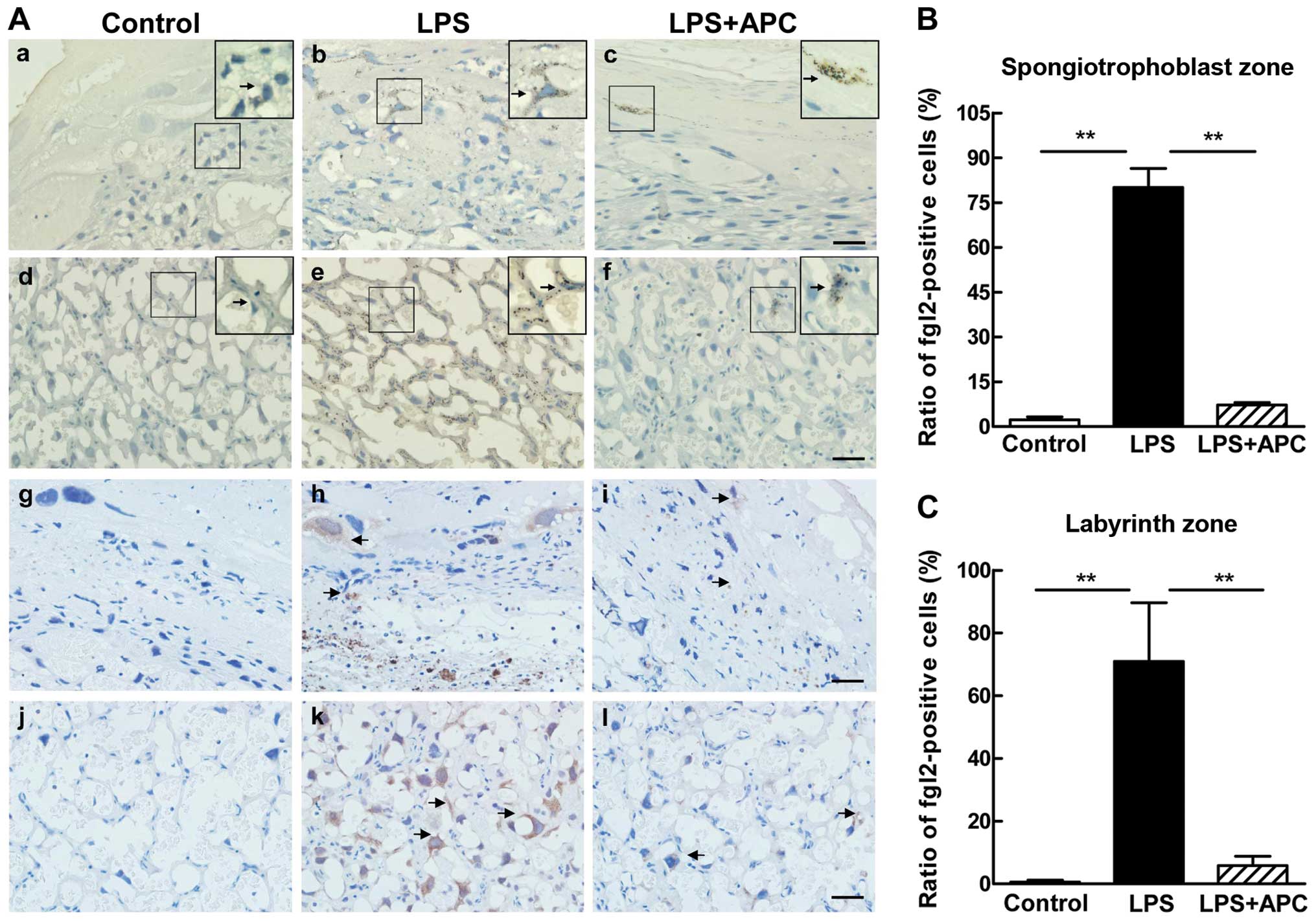
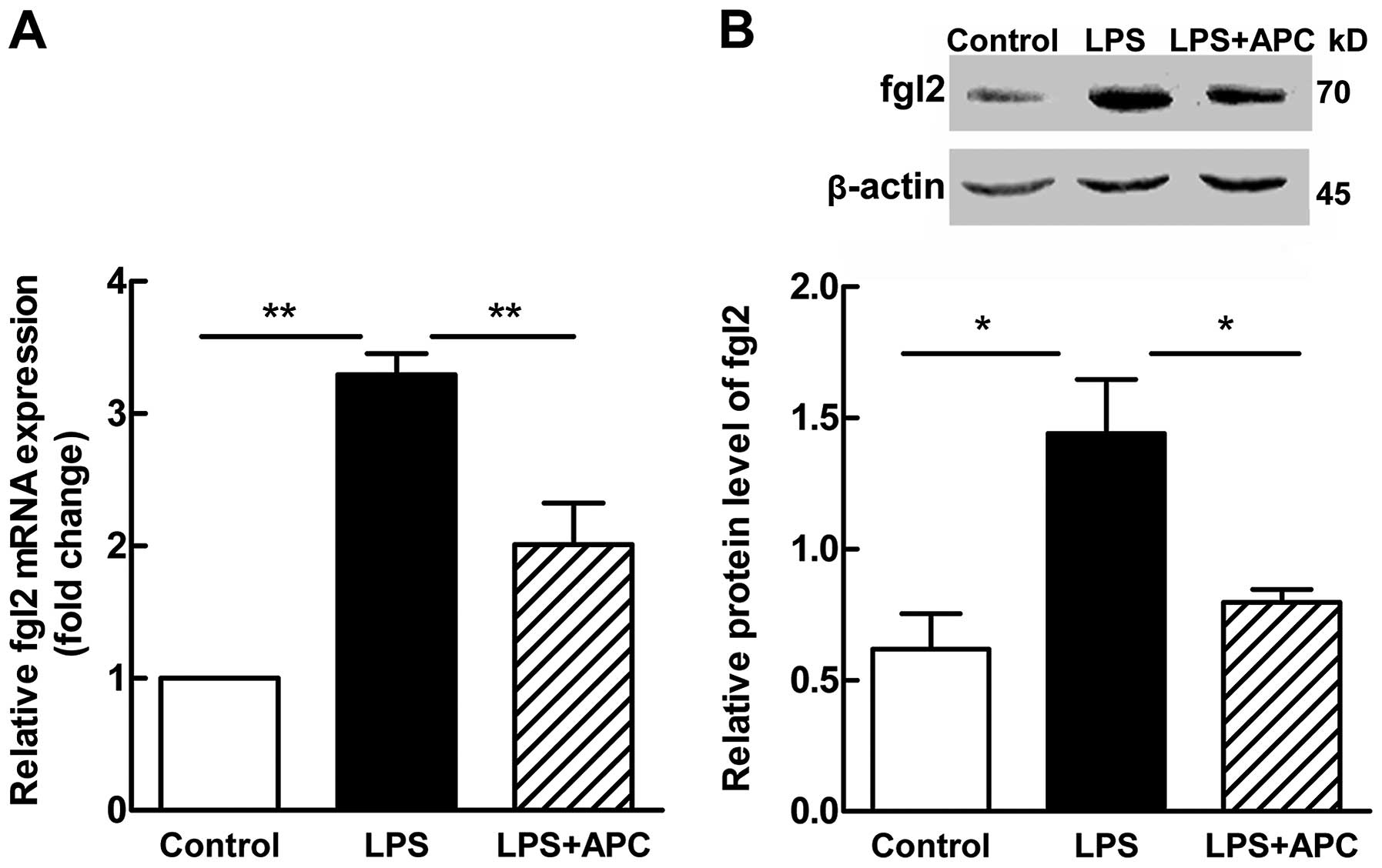
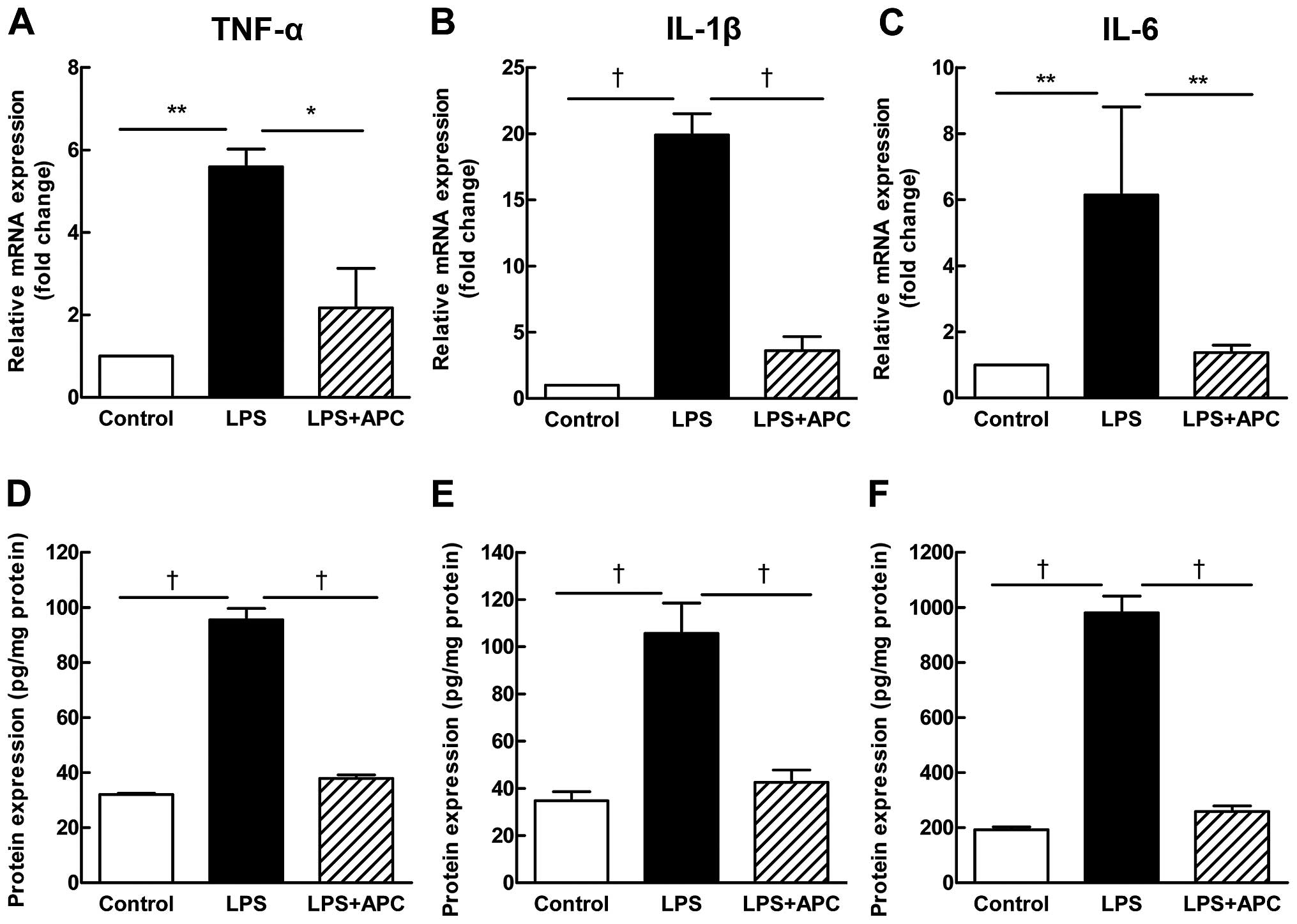
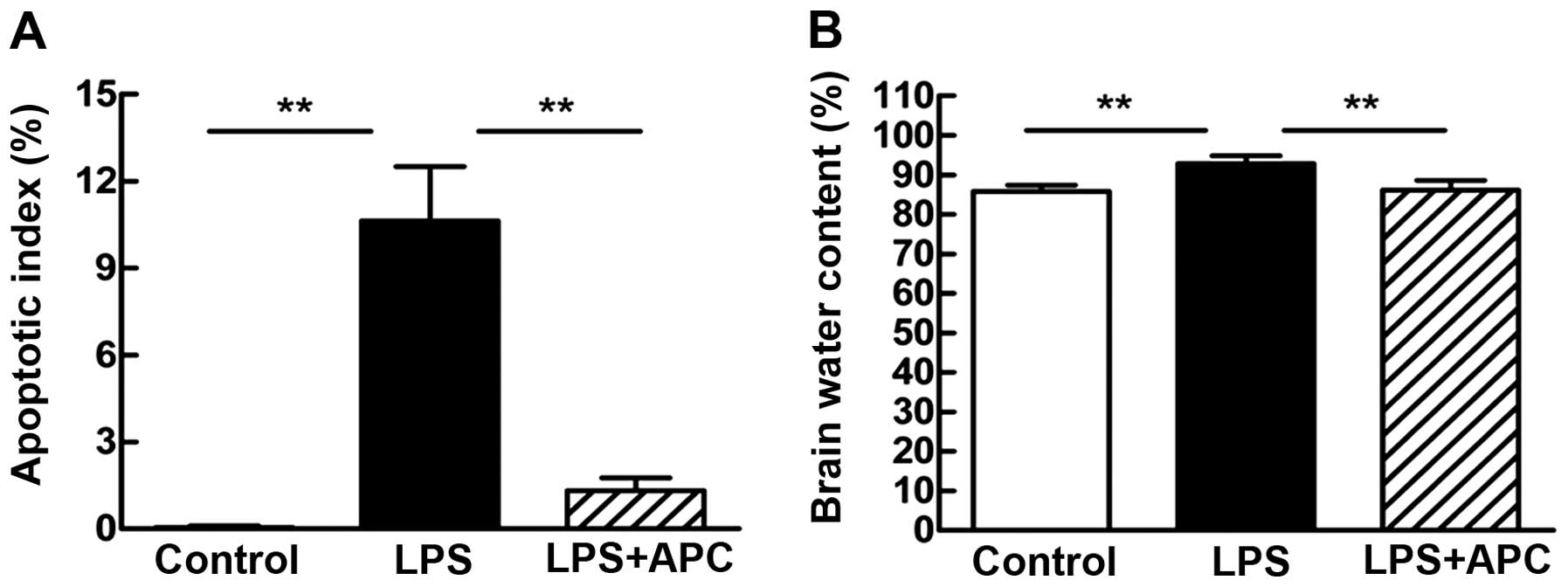
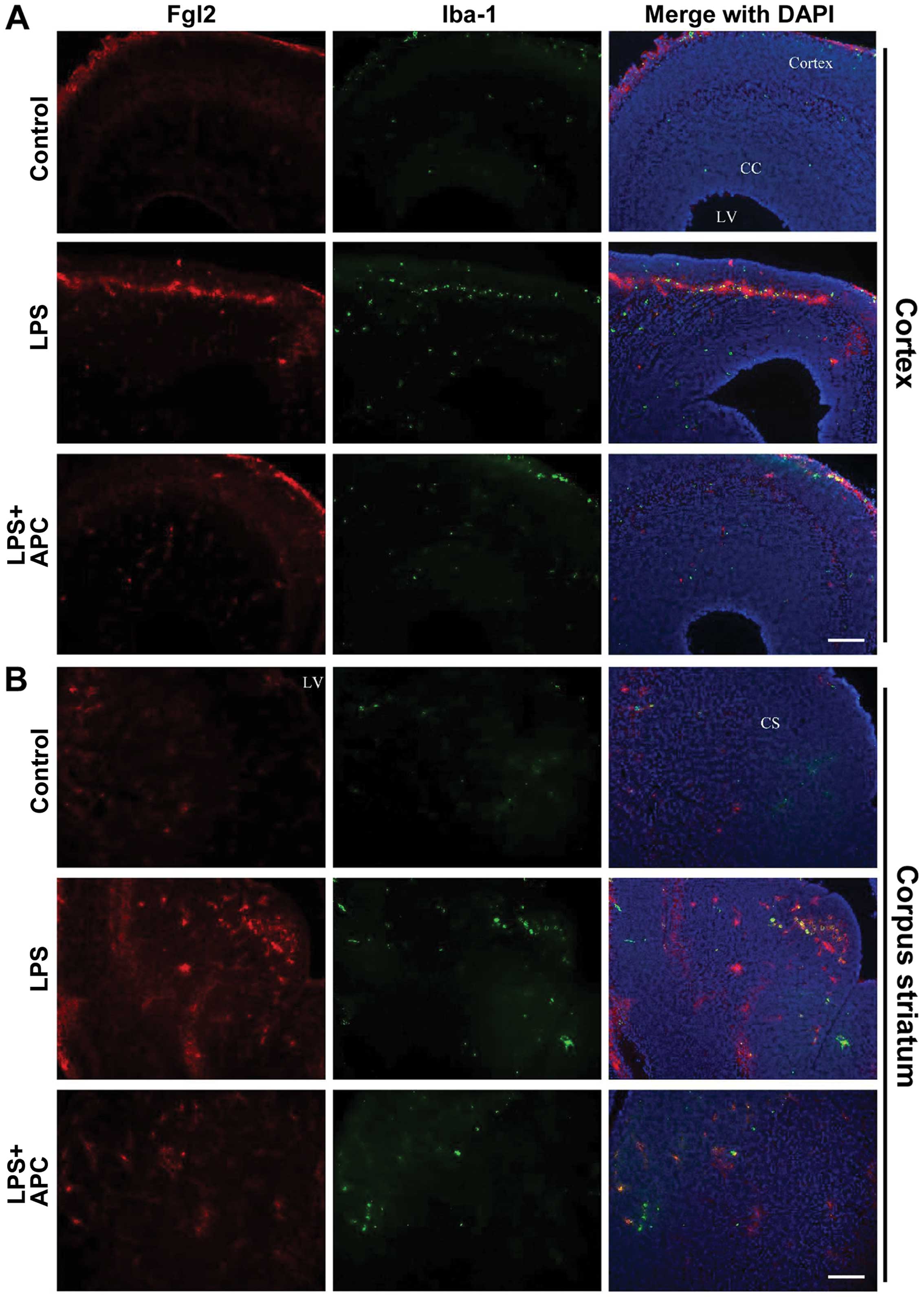
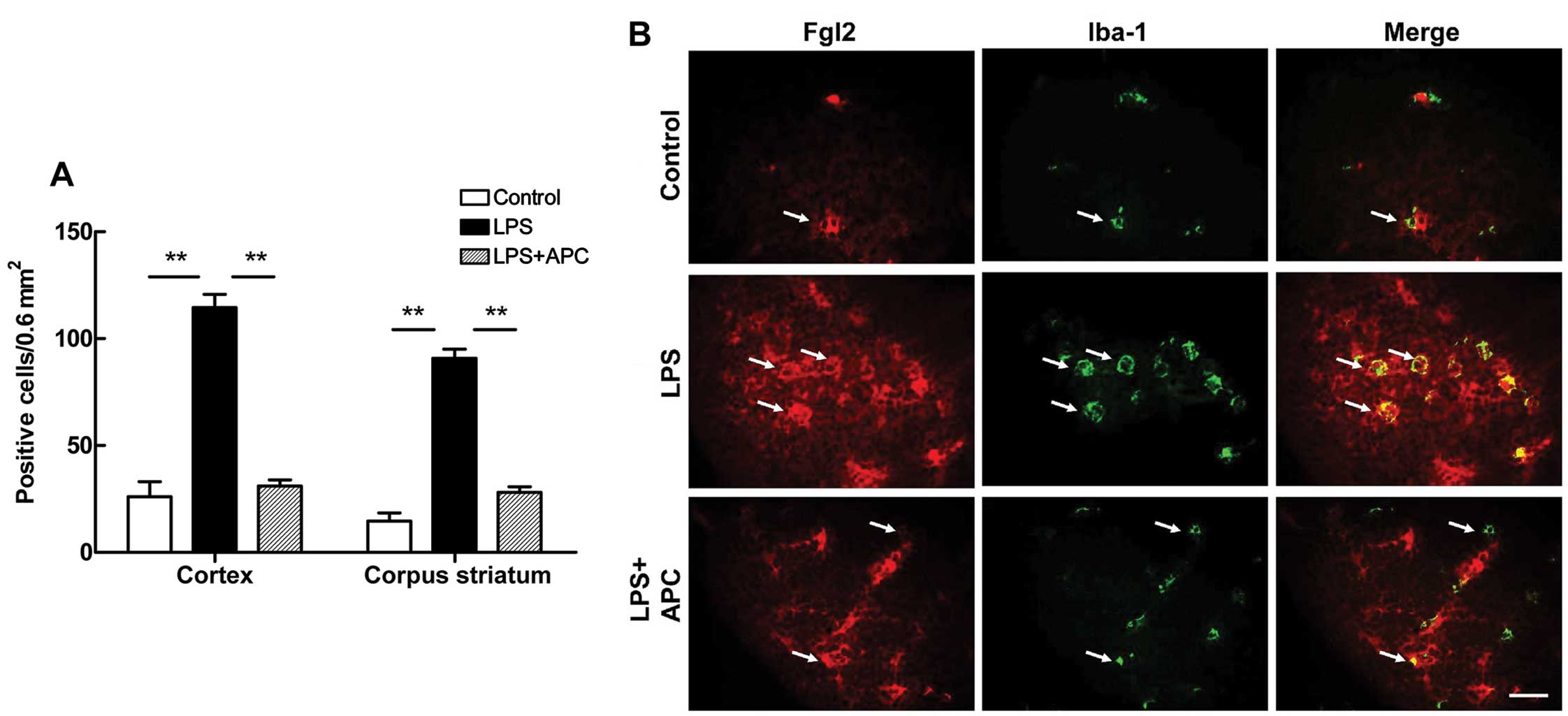
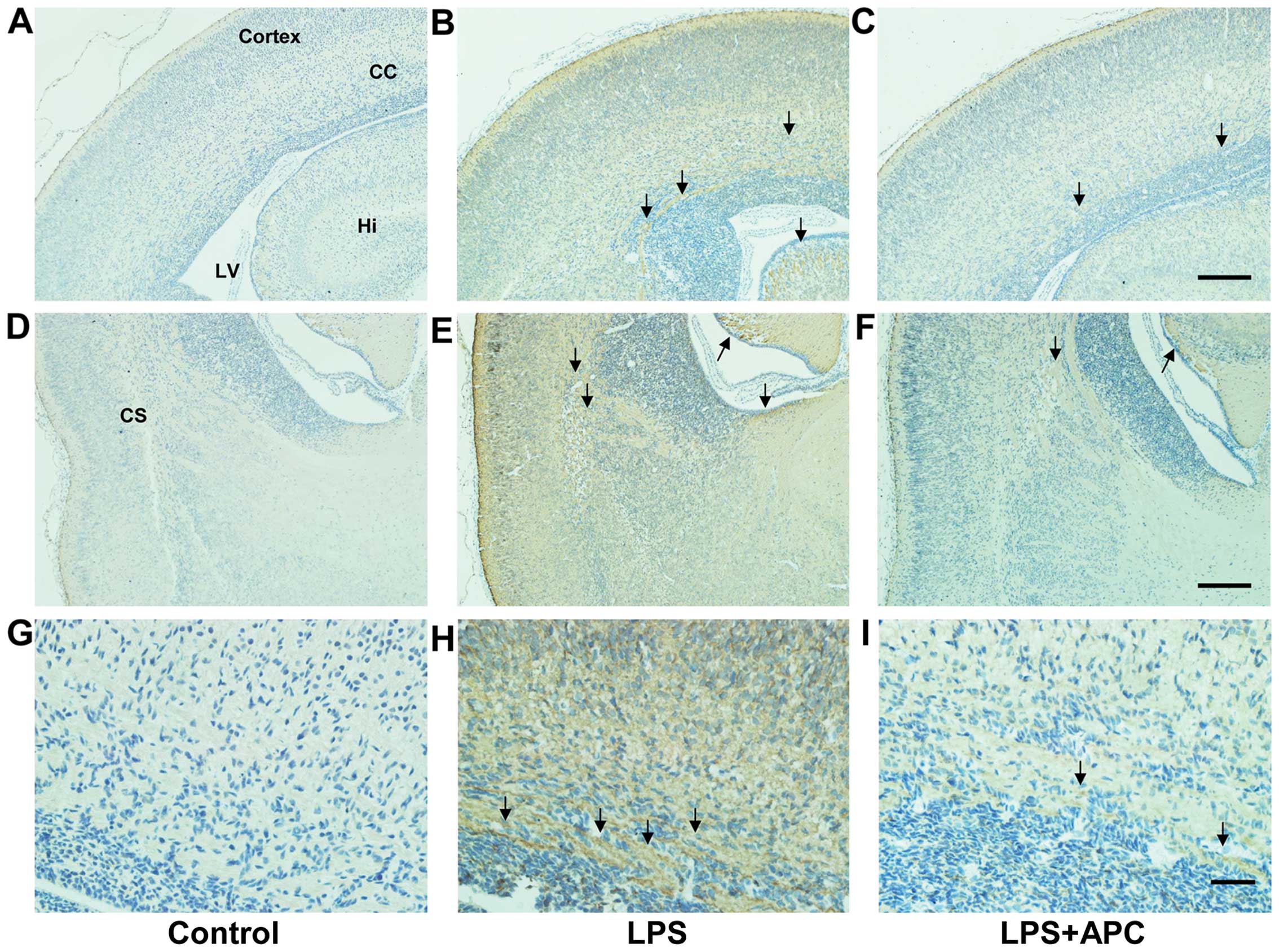
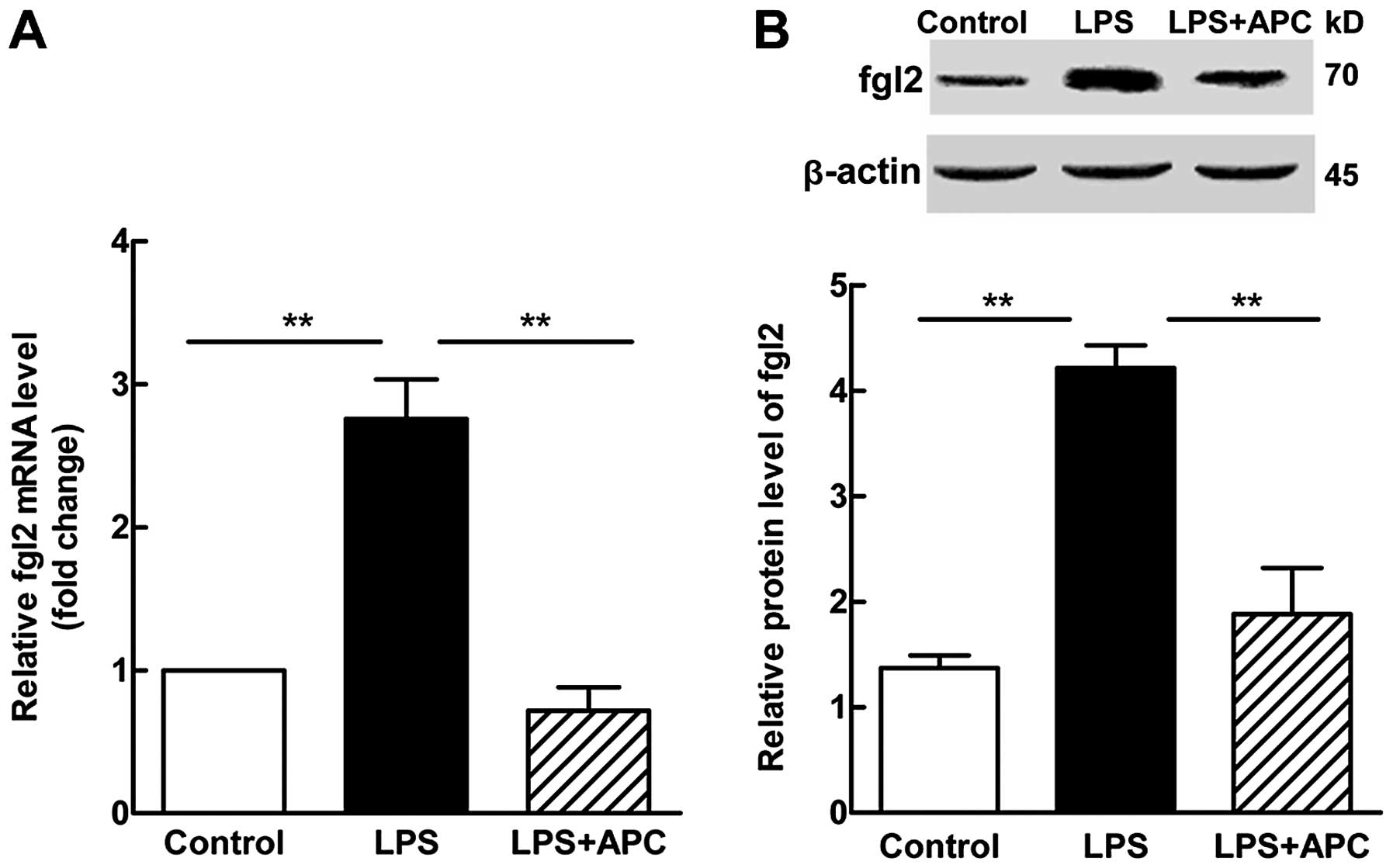
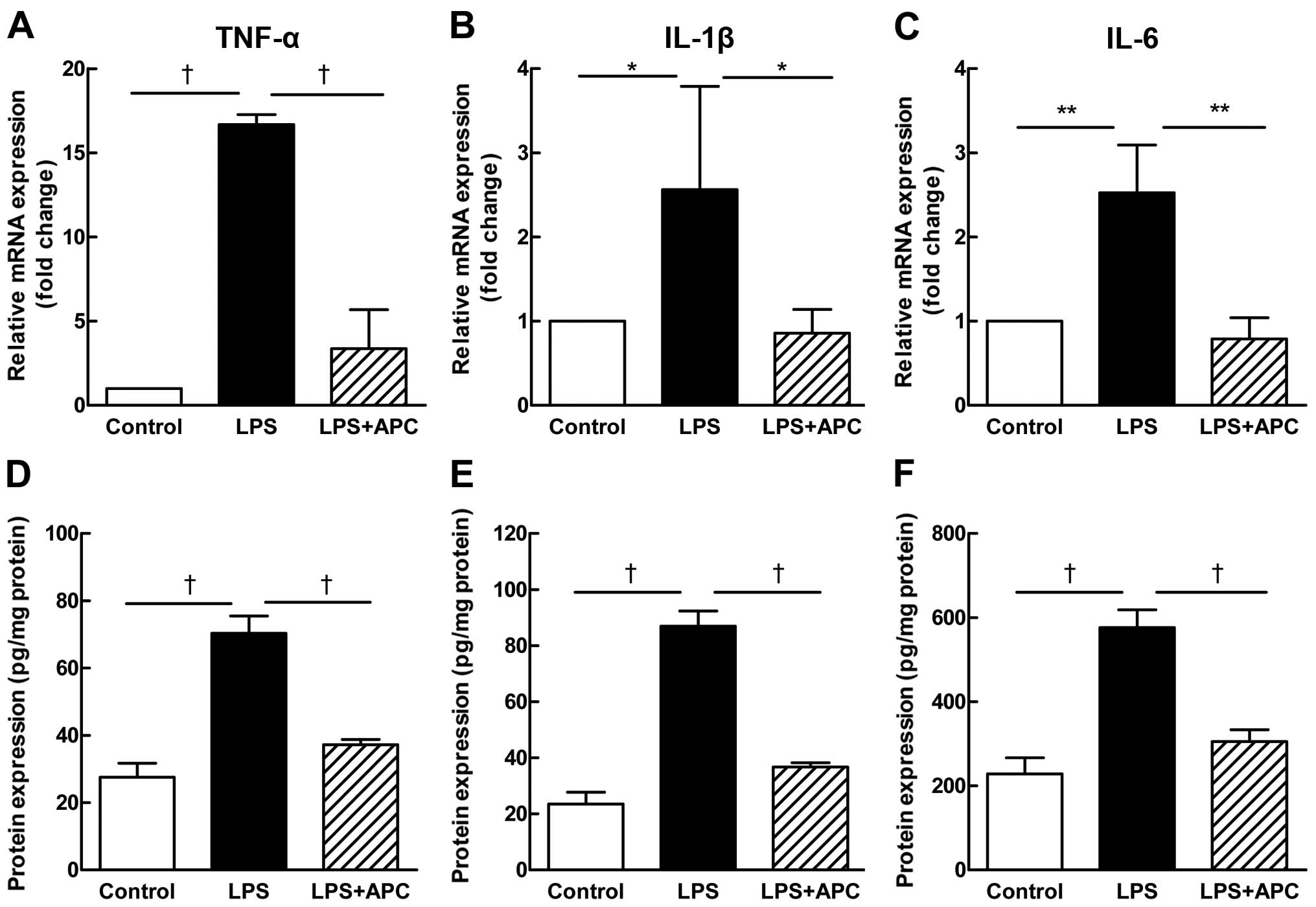
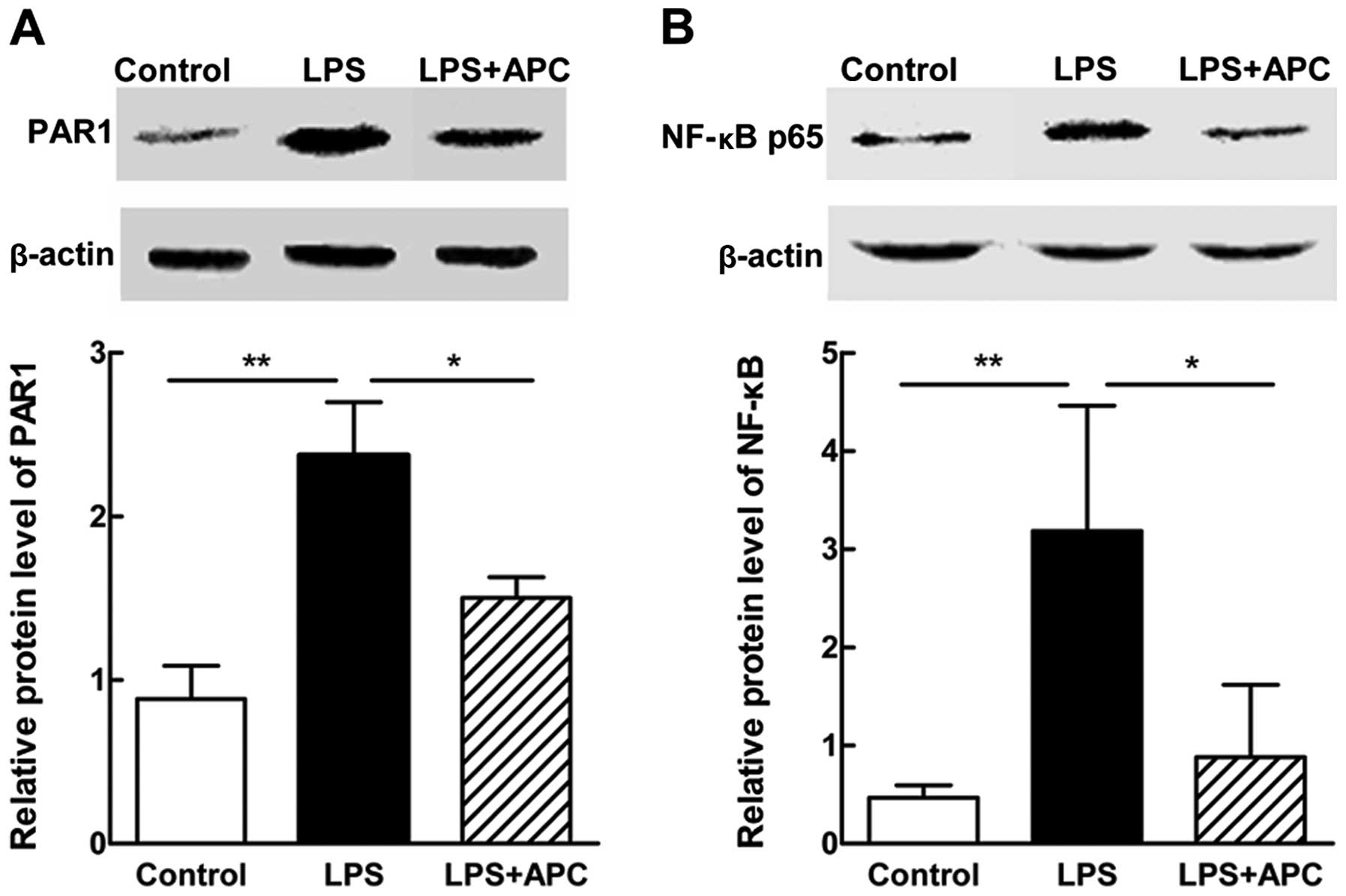
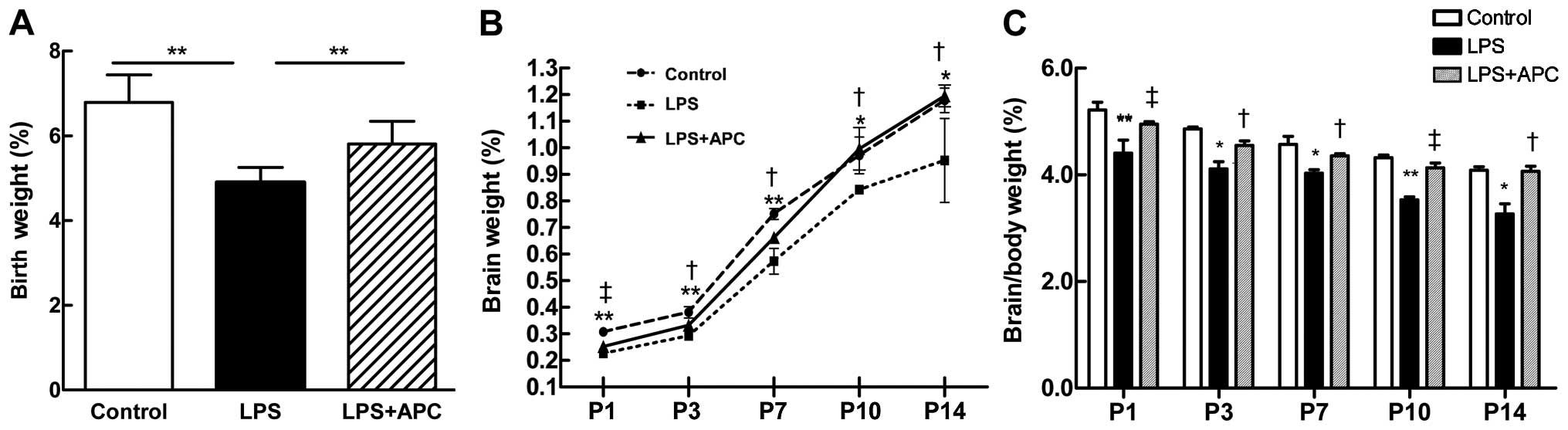
|
1
|
Deng W: Neurobiology of injury to the
developing brain. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:328–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Volpe JJ: Brain injury in premature
infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental
disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 8:110–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Favrais G, van de Looij Y, Fleiss B, et
al: Systemic inflammation disrupts the developmental program of
white matter. Ann Neurol. 70:550–565. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuypers E, Ophelders D, Jellema RK,
Kunzmann S, Gavilanes AW and Kramer BW: White matter injury
following fetal inflammatory response syndrome induced by
chorioamnionitis and fetal sepsis: lessons from experimental ovine
models. Early Hum Dev. 88:931–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leclerc J, Pu Q, Corseaux D, Haddad E,
Decoene C, Bordet R, Six I, Jude B and Vallet B: A single endotoxin
injection in the rabbit causes prolonged blood vessel dysfunction
and a procoagulant state. Crit Care Med. 28:3672–3678. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cai Z, Pan ZL, Pang Y, Evans OB and Rhodes
PG: Cytokine induction in fetal rat brains and brain injury in
neonatal rats after maternal lipopolysaccharide administration.
Pediatr Res. 47:64–72. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoon BH, Jun JK, Romero R, Park KH, Gomez
R, Choi JH and Kim IO: Amniotic fluid inflammatory cytokines
(interleukin-6, interleukin-1(beta), and tumor necrosis
factor-(alpha)), neonatal brain white matter lesions, and cerebral
palsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 177:19–26. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee J, Chan SL and Mattson MP: Adverse
effect of a presenilin-1 mutation in microglia results in enhanced
nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokine responses to immune
challenge in the brain. Neuromolecular Med. 2:29–45. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao Q, Li P, Lu J, Dheen ST, Kaur C and
Ling EA: Nuclear factor NF-κB/p65 responds to changes in the Notch
signaling pathway in murine BV-2 cells and in amoeboid microglia in
postnatal rats treated with the γ-secretase complex blocker DAPT. J
Neurosci Res. 88:2701–2714. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Levy GA, Liu M, Ding J, Yuwaraj S,
Leibowitz J, Marsden PA, Ning Q, Kovalinka A and Phillips MJ:
Molecular and functional ana1ysis of the human prothrombinase gene
(hfgl2) and its role in viral hepatitis. Am J Pathol.
156:1217–1225. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chan CW, Chan MW, Liu M, Fung L, Cole EH,
Leibowitz JL, Marsden PA, Clark DA and Levy GA: Kinetic analysis of
a unique direct prothrombinase, fgl2, and identification of a
serine residue critical for the prothrombinase activity. J Immunol.
168:5170–5177. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Phillippe M, Diamond AK, Sweet LM,
Oppenheimer KH and Bradley DF: Expression of coagulation-related
protein genes during LPS-induced preterm delivery in the pregnant
mouse. Reprod Sci. 18:1071–1079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Melnyk MC, Shalev I, Zhang J, et al: The
prothrombinase activity of FGL2 contributes to the pathogenesis of
experimental arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 40:269–278. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ning Q, Sun Y, Han M, et al: Role of
fibrinogen-like protein 2 prothrombinase/fibroleukin in
experimental and human allograft rejection. J Immunol.
174:7403–7411. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu G, Sun Y, Foerster K, Manuel J, Molina
H, Levy GA, Gorczynski RM and Clark DA: LPS-induced murine
abortions require C5 but not C3, and are prevented by upregulating
expression of the CD200 tolerance signaling molecule. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 60:135–140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu M, Mendicino M, Ning Q, et al:
Cytokine-induced hepatic apoptosis is dependent on
FGL2/fibroleukin: the role of Sp1/Sp3 and STAT1/PU.1 composite cis
elements. J Immunol. 176:7028–7038. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zlokovic BV and Griffin JH: Cytoprotective
protein C pathways and implications for stroke and neurological
disorders. Trends Neurosci. 34:198–209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deane R, LaRue B, Sagare AP, Castellino
FJ, Zhong Z and Zlokovic BV: Endothelial protein C
receptor-assisted transport of activated protein C across the mouse
blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:25–33. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li B, Yu D and Xu Z: Activated protein C
inhibits amyloid β production via promoting expression of ADAM-10.
Brain Res. 1545:35–44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Chow N, Rajput PS, Griffin
JH, Lyden PD and Zlokovic BV: Activated protein C analog protects
from ischemic stroke and extends the therapeutic window of
tissue-type plasminogen activator in aged female mice and
hypertensive rats. Stroke. 44:3529–3536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yesilirmak DC, Kumral A, Tugyan K, Cilaker
S, Baskin H, Yilmaz O, Duman N and Ozkan H: Effects of activated
protein C on neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Brain Res.
1210:56–62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yesilirmak DC, Kumral A, Baskin H, et al:
Activated protein C reduces endotoxin-induced white matter injury
in the developing rat brain. Brain Res. 1164:14–23. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Olivier P, Fontaine RH, Loron G, et al:
Melatonin promotes oligodendroglial maturation of injured white
matter in neonatal rats. PLoS One. 4:e71282009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bell MJ, Hallenbeck JM and Gallo V:
Determining the fetal inflammatory response in an experimental
model of intrauterine inflammation in rats. Pediatr Res.
56:541–546. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zaretsky MV, Alexander JM, Byrd W and
Bawdon RE: Transfer of inflammatory cytokines across the placenta.
Obstet Gynecol. 103:546–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia P, Wang J, Wang L, et al: TNF-α
upregulates fgl2 expression in rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Microcirculation. 20:524–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Clark DA, Ding JW, Yu G, Levy GA and
Gorczynski RM: Fgl2 prothrombinase expression in mouse trophoblast
and decidua triggers abortion but may be countered by OX-2. Mol Hum
Reprod. 7:185–194. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leviton A and Dammann O: Coagulation,
inflammation, and the risk of neonatal white matter damage. Pediatr
Res. 55:541–545. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rezaie AR: Regulation of the protein C
anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Curr Med Chem.
17:2059–2069. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bell MJ and Hallenbeck JM: Effects of
intrauterine inflammation on developing rat brain. J Neurosci Res.
70:570–579. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
French HM, Reid M, Mamontov P, Simmons RA
and Grinspan JB: Oxidative stress disrupts oligodendrocyte
maturation. J Neurosci Res. 87:3076–3087. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brehmer F, Bendix I, Prager S, et al:
Interaction of inflammation and hyperoxia in a rat model of
neonatal white matter damage. PLoS One. 7:e490232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karperien A, Ahammer H and Jelinek HF:
Quantitating the subtleties of microglial morphology with fractal
analysis. Front Cell Neurosci. 7:32013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Verney C, Pogledic I, Biran V,
Adle-Biassette H, Fallet-Bianco C and Gressens P: Microglial
reaction in axonal crossroads is a hallmark of noncystic
periventricular white matter injury in very preterm infants. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 71:251–264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suo Z, Wu M, Ameenuddin S, Anderson HE and
Zoloty JE: Participation of protease-activated receptor-1 in
thrombin-induced microglial activation. J Neurochem. 80:655–666.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan TM, Sun Y, Zhan CY and Yu HM:
Intrauterine infection/inflammation and perinatal brain damage:
role of glial cells and Toll-like receptor signaling. J
Neuroimmunol. 229:16–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gabre J, Chabasse C, Cao C, Mukhopadhyay
S, Siefert S, Bi Y, Netzel-Arnett S, Sarkar R and Zhang L:
Activated protein C accelerates venous thrombus resolution through
heme oxygenase-1 induction. J Thromb Haemost. 12:93–102. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Puig F, Fuster G, Adda M, Blanch L and
Farre R: Barrier-protective effects of activated protein C in human
alveolar epithelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e569652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ishii S, Mochizuki T, Nagao T, Kudo S,
Fujita A, Taniguchi K, Kondo S and Kiyoki M: Pharmacokinetics of
human activated protein C. 2nd communication: tissue distribution
study of a lyophilized purified human activated protein C after
single or repeated intravenous administration in male mice and
placental transfer and milk passage study after intravenous
administration in pregnant and lactating mice.
Arzneimittelforschung. 45:644–656. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Crawley JT and Efthymiou M: Cytoprotective
effect of activated protein C: specificity of PAR-1 signaling. J
Thromb Haemost. 6:951–953. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Riewald M, Petrovan RJ, Donner A, Mueller
BM and Ruf W: Activation of endothelial cell protease activated
receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science. 296:1880–1882. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cao C, Gao Y, Li Y, Antalis TM, Castellino
FJ and Zhang L: The efficacy of activated protein C in murine
endotoxemia is dependent on integrin CD11b. J Clin Invest.
120:1971–1980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mosnier LO, Yang XV and Griffin JH:
Activated protein C mutant with minimal anticoagulant activity,
normal cytoprotective activity, and preservation of thrombin
activatable fibrinolysis inhibitordependent cytoprotective
functions. J Biol Chem. 282:33022–33033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|