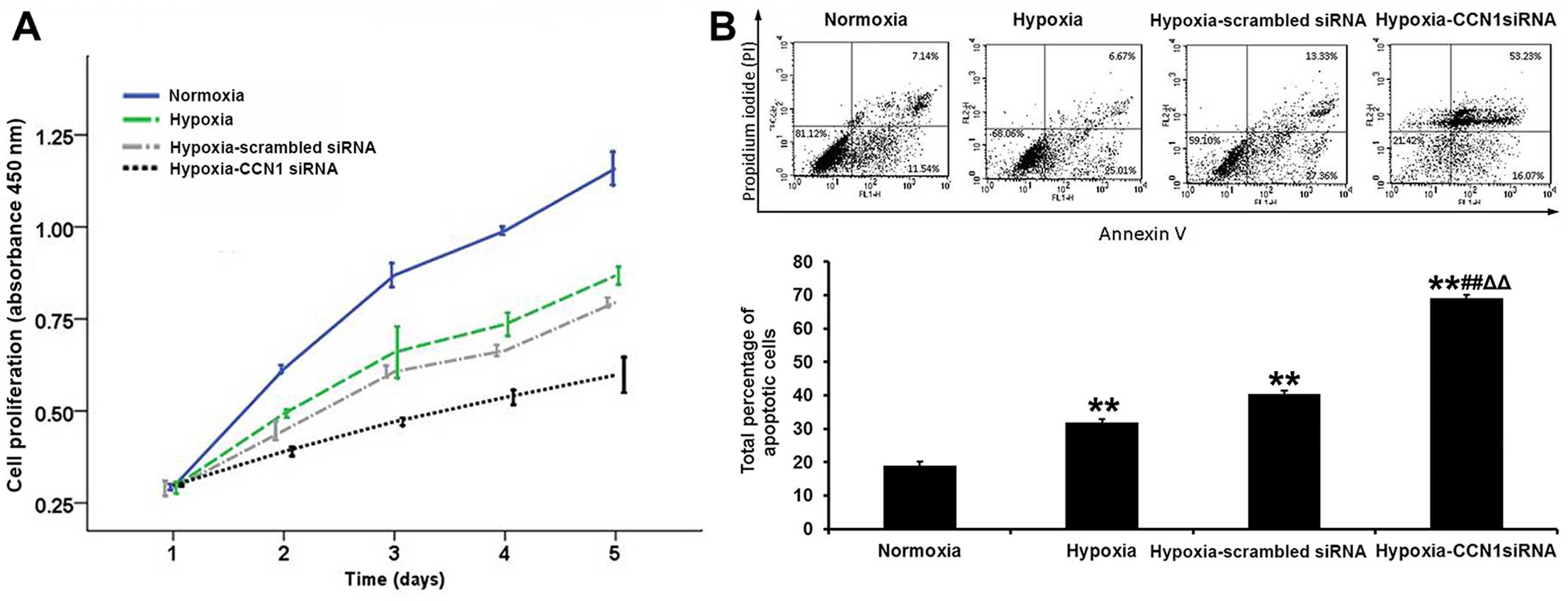
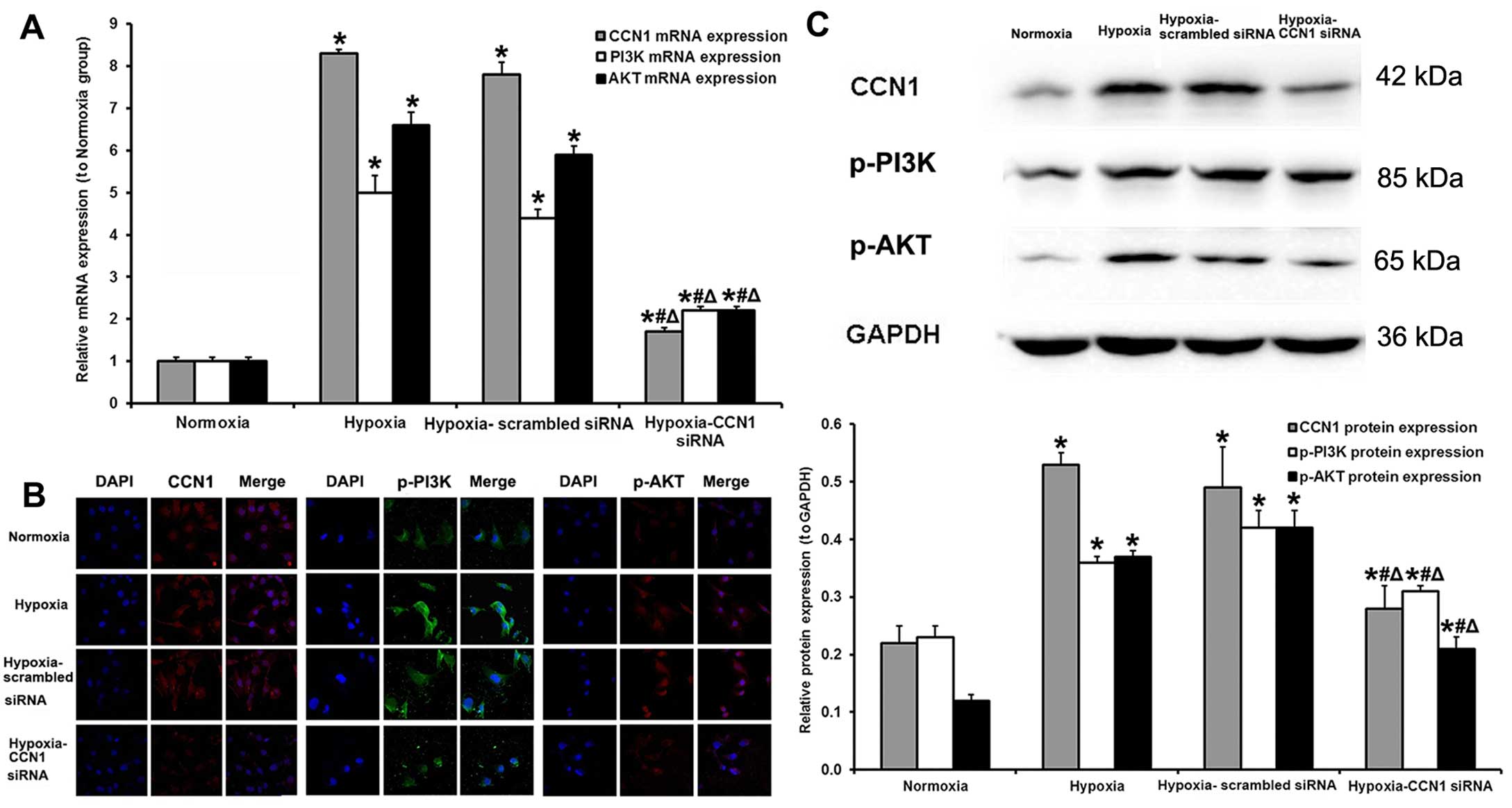
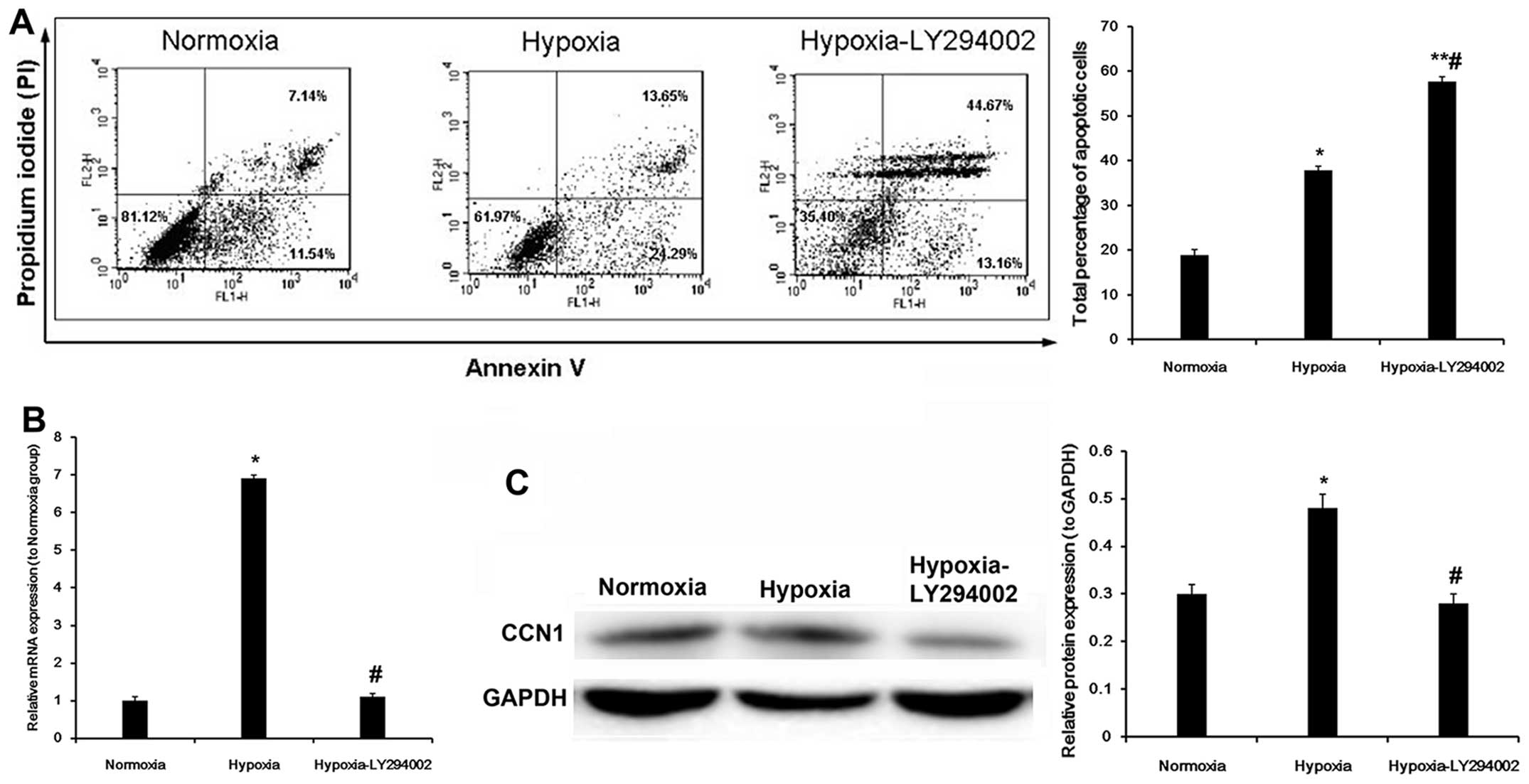
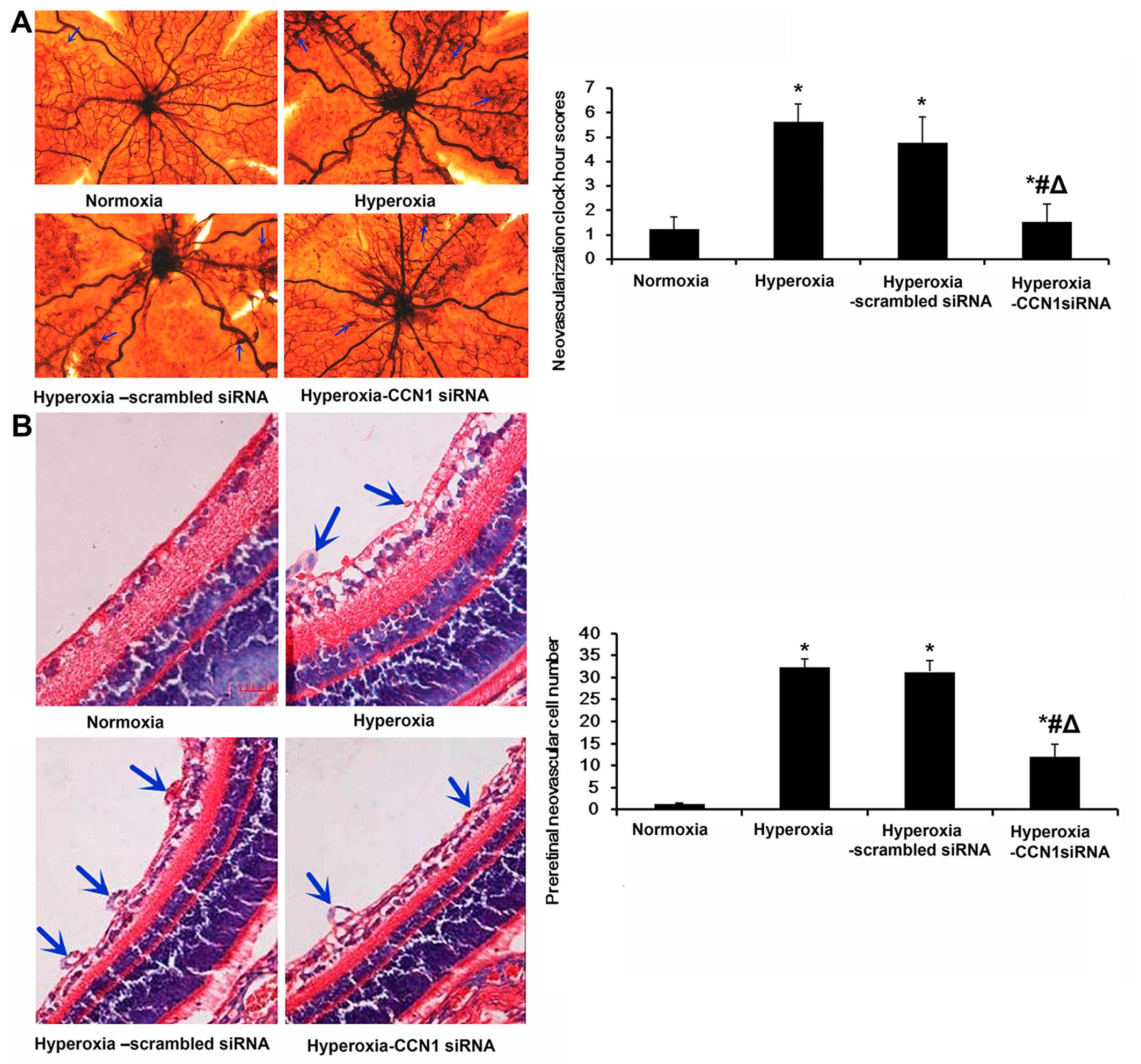
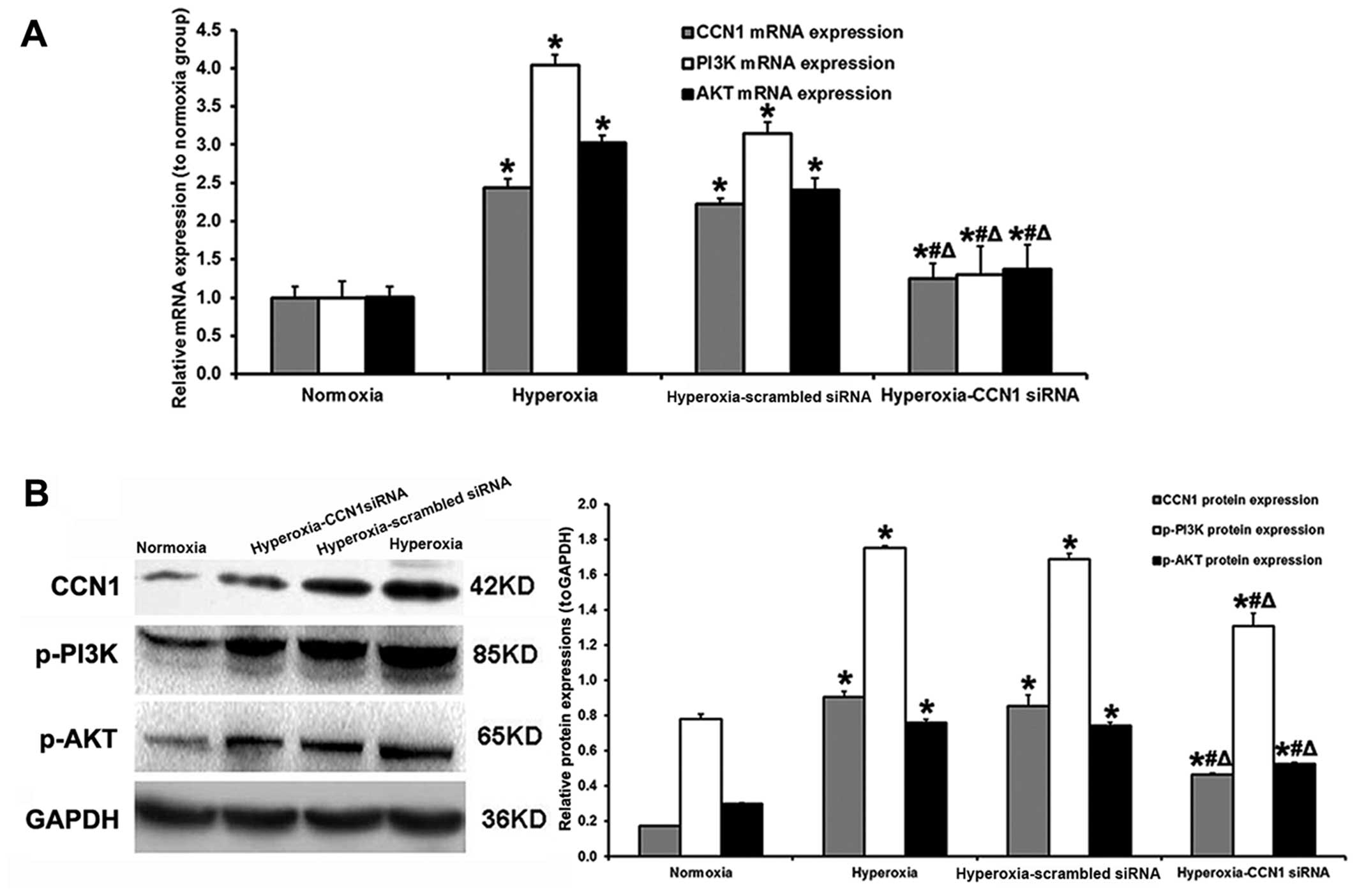
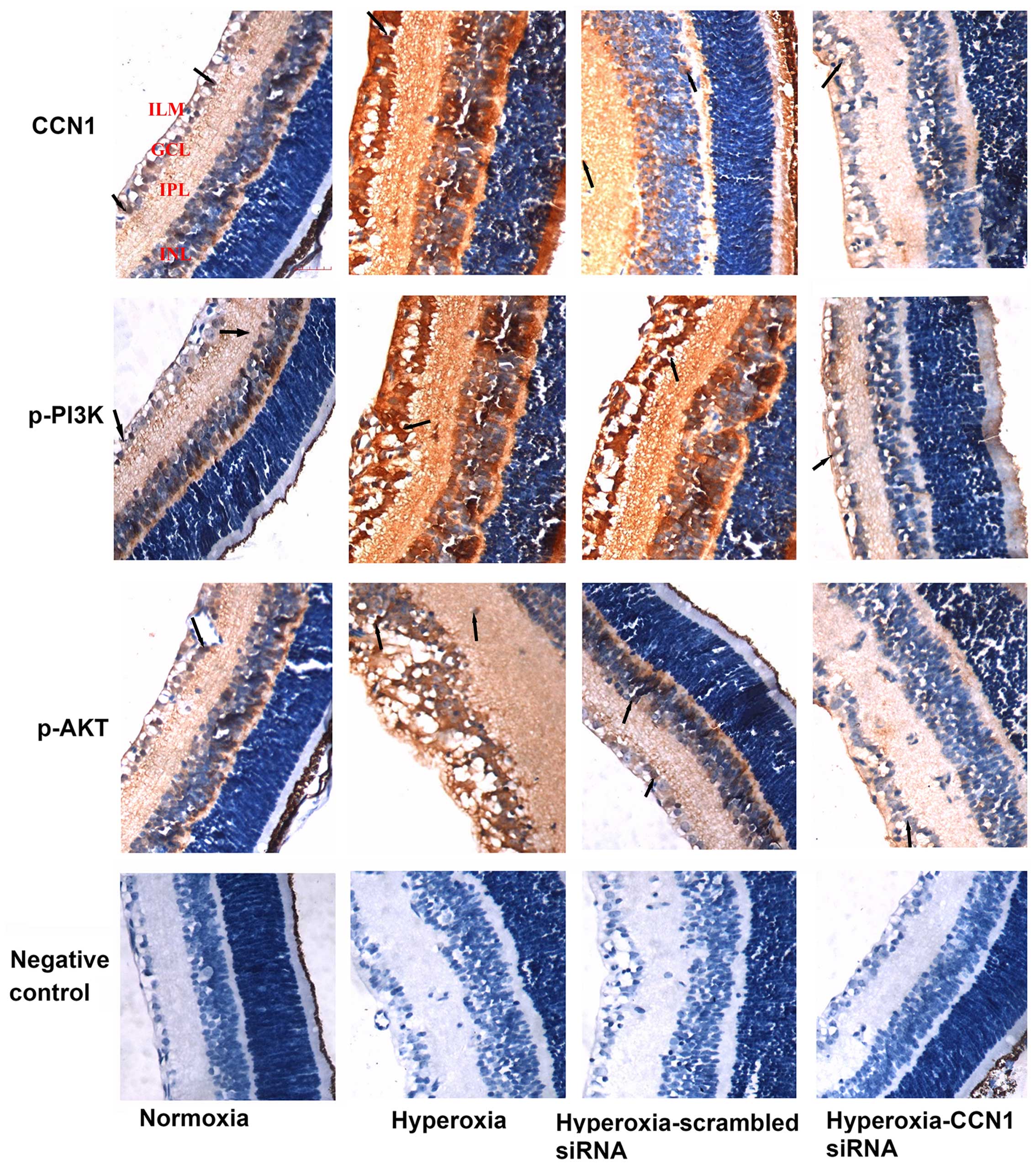
|
1
|
Li Z, He T, Du K, Xing YQ, Yan Y, Chen Z,
Zhang H and Shen Y: Overexpression of 15-lipoxygenase-1 in
oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy inhibits retinal
neovascularization via downregulation of vascular endothelial
growth factor-A expression. Mol Vis. 18:2847–2859. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Storto M, Cataudella T,
Ballini JP, Gatz R, Giorgio M, van den Bergh H, Plyte S and
Wagnières G: Angiogenesis inhibition by the maleimide-based small
molecule GNX-686. Microvasc Res. 83:105–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gergely K and Gerinec A: Retinopathy of
prematurity - epidemics, incidence, prevalence, blindness. Bratisl
Lek Listy. 111:514–517. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Wang F, Bai Y, Yu W, Han N, Huang L, Zhao
M, Zhou A, Zhao M and Li X: Anti-angiogenic effect of KH902 on
retinal neovascularization. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
251:2131–2139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hartnett ME and Penn JS: Mechanisms and
management of retinopathy of prematurity. N Engl J Med.
367:2515–2526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Phelps DL: Retinopathy of prematurity.
Pediatr Rev. 16:50–56. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
No authors listed. Cryotherapy for
Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group: Multicenter trial of
cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity. 3 1/2-year outcome -
structure and function. Arch Ophthalmol. 111:339–344. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xia XB, Xiong SQ, Song WT, Luo J, Wang YK
and Zhou RR: Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by siRNA
targeting VEGF(165). Mol Vis. 14:1965–1973. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan Y, He T, Shen Y, Chen X, Diao B, Li Z,
Liu Q and Xing YQ: Adenoviral 15-lipoxygenase-1 gene transfer
inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation of retinal microvascular
endothelial cells in vitro. Int J Ophthalmol. 5:562–569.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mintz-Hittner HA: Treatment of retinopathy
of prematurity with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors.
Early Hum Dev. 88:937–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Martínez-Castellanos MA, Schwartz S,
Hernández-Rojas ML, Kon-Jara VA, García-Aguirre G, Guerrero-Naranjo
JL, Chan RV and Quiroz-Mercado H: Long-term effect of
antiangiogenic therapy for retinopathy of prematurity up to 5 years
of follow-up. Retina. 33:329–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hanna M, Liu H, Amir J, Sun Y, Morris SW,
Siddiqui MA, Lau LF and Chaqour B: Mechanical regulation of the
proangiogenic factor CCN1/CYR61 gene requires the combined
activities of MRTF-A and CREB-binding protein histone
acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 284:23125–23136. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jun JI and Lau LF: Taking aim at the
extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:945–963. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brigstock DR: The connective tissue growth
factor/cysteine-rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family.
Endocr Rev. 20:189–206. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brigstock DR: The CCN family: a new
stimulus package. J Endocrinol. 178:169–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brigstock DR: Regulation of angiogenesis
and endothelial cell function by connective tissue growth factor
(CTGF) and cysteine-rich 61 (CYR61). Angiogenesis. 5:153–165. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yan L and Chaqour B: Cysteine-rich protein
61 (CCN1) and connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) at the
crosshairs of ocular neovascular and fibrovascular disease therapy.
J Cell Commun Signal. 7:253–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi J, Lin A, Shrier E, Lau LF, Grant MB
and Chaqour B: Degradome products of the matricellular protein CCN1
as modulators of pathological angiogenesis in the retina. J Biol
Chem. 288:23075–23089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CC and Lau LF: Functions and
mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 41:771–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, Li Y, Xu JF,
Zhu J, Zhao W, Chu DK and Wiedemann P: Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK
in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in
laser-induced rat choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 50:1873–1879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
You JJ, Yang CH, Yang CM and Chen MS:
Cyr61 induces the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
via the integrin ανβ3, FAK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB pathways in retinal
vascular endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 26:133–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sasore T, Reynolds AL and Kennedy BN:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in ocular neovascularization.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 801:805–811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo H, Lv Y, Tian T, Hu TH, Wang WJ, Sui
X, Jiang L, Ruan ZP and Nan KJ: Downregulation of p57 accelerates
the growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1897–1904. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han Z, Yang Q, Liu B, Wu J, Li Y, Yang C
and Jiang Y: MicroRNA-622 functions as a tumor suppressor by
targeting K-Ras and enhancing the anticarcinogenic effect of
resveratrol. Carcinogenesis. 33:131–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aubry JP, Blaecke A, Lecoanet-Henchoz S,
Jeannin P, Herbault N, Caron G, Moine V and Bonnefoy JY: Annexin V
used for measuring apoptosis in the early events of cellular
cytotoxicity. Cytometry. 37:197–204. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H and
Reutelingsperger C: A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric
detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells
using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 184:39–51.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk
SK, D'Amato R, Sullivan R and D'Amore PA: Oxygen-induced
retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 35:101–111.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Masuda I, Matsuo T, Yasuda T and Matsuo N:
Gene transfer with liposomes to the intraocular tissues by
different routes of administration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
37:1914–1920. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
You JJ, Yang CH, Chen MS and Yang CM:
Cysteine-rich 61, a member of the CCN family, as a factor involved
in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3447–3455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Guan Y, Zhang S, Zhu C,
Xu GT and Wang L: Suppression of retinal neovascularization by the
iNOS inhibitor aminoguanidine in mice of oxygen-induced
retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 247:919–927. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hasan A, Pokeza N, Shaw L, Lee HS, Lazzaro
D, Chintala H, Rosenbaum D, Grant MB and Chaqour B: The
matricellular protein cysteine-rich protein 61 (CCN1/Cyr61)
enhances physiological adaptation of retinal vessels and reduces
pathological neovascularization associated with ischemic
retinopathy. J Biol Chem. 286:9542–9554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lambert V, Lecomte J, Hansen S, Blacher S,
Gonzalez ML, Struman I, Sounni NE, Rozet E, de Tullio P, Foidart
JM, et al: Laser-induced choroidal neovascularization model to
study age-related macular degeneration in mice. Nat Protoc.
8:2197–2211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ecoiffier T, Yuen D and Chen L:
Differential distribution of blood and lymphatic vessels in the
murine cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:2436–2440. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Barnett JM, McCollum GW, Fowler JA, Duan
JJ, Kay JD, Liu RQ, Bingaman DP and Penn JS: Pharmacologic and
genetic manipulation of MMP-2 and -9 affects retinal
neovascularization in rodent models of OIR. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 48:907–915. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park K, Chen Y, Hu Y, Mayo AS, Kompella
UB, Longeras R and Ma JX: Nanoparticle-mediated expression of an
angiogenic inhibitor ameliorates ischemia-induced retinal
neovascularization and diabetes-induced retinal vascular leakage.
Diabetes. 58:1902–1913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Smith LE: Pathogenesis of retinopathy of
prematurity. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 91:26–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grote K, Salguero G, Ballmaier M, Dangers
M, Drexler H and Schieffer B: The angiogenic factor CCN1 promotes
adhesion and migration of circulating CD34+ progenitor cells:
potential role in angiogenesis and endothelial regeneration. Blood.
110:877–885. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Leu SJ, Lam SC and Lau LF: Pro-angiogenic
activities of CYR61 (CCN1) mediated through integrins alphavbeta3
and alpha6beta1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 277:46248–46255. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kireeva ML, Latinkić BV, Kolesnikova TV,
Chen CC, Yang GP, Abler AS and Lau LF: Cyr61 and Fisp12 are both
ECM-associated signaling molecules: Activities, metabolism, and
localization during development. Exp Cell Res. 233:63–77. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kireeva ML, Mo FE, Yang GP and Lau LF:
Cyr61, a product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene,
promotes cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion. Mol Cell
Biol. 16:1326–1334. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang X, Yu W and Dong F: Cysteine-rich 61
(CYR61) is up-regulated in proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 250:661–668. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Meyuhas R, Pikarsky E, Tavor E, Klar A,
Abramovitch R, Hochman J, Lago TG and Honigman A: A Key role for
cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein in hypoxia-mediated
activation of the angiogenesis factor CCN1 (CYR61) in Tumor cells.
Mol Cancer Res. 6:1397–1409. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Leask A: CCN1: A novel target for
pancreatic cancer. J Cell Commun Signal. 5:123–124. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Perbal B: CCN proteins: multifunctional
signalling regulators. Lancet. 363:62–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Su BC and Mo FE: CCN1 enables Fas
ligand-induced apoptosis in cardiomyoblast H9c2 cells by disrupting
caspase inhibitor XIAP. Cell Signal. 26:1326–1334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gerszten RE, Friedrich EB, Matsui T, Hung
RR, Li L, Force T and Rosenzweig A: Role of phosphoinositide
3-kinase in monocyte recruitment under flow conditions. J Biol
Chem. 276:26846–26851. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zheng ZZ and Liu ZX: Activation of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Akt pathway mediates
CD151-induced endothelial cell proliferation and cell migration.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:340–348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Quan Y, Wang N, Chen Q, Xu J, Cheng W, Di
M, Xia W and Gao WQ: SIRT3 inhibits prostate cancer by
destabilizing oncoprotein c-MYC through regulation of the
PI3K/Aktpathway. Oncotarget. 6:26494–26507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Long QZ, Zhou M, Liu XG, Du YF, Fan JH, Li
X and He DL: Interaction of CCN1 with αvβ3 integrin induces
P-glycoprotein and confers vinblastine resistance in renal cell
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 24:810–817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin BR, Chang CC, Chen LR, Wu MH, Wang MY,
Kuo IH, Chu CY, Chang KJ, Lee PH, Chen WJ, et al: Cysteine-rich 61
(CCN1) enhances chemotactic migration, transendothelial cell
migration, and intravasation by concomitantly up-regulating
chemokine receptor 1 and 2. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1111–1123. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin MT, Kuo IH, Chang CC, Chu CY, Chen HY,
Lin BR, Sureshbabu M, Shih HJ and Kuo ML: Involvement of
hypoxia-inducing factor-1alpha-dependent plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 up-regulation in Cyr61/CCN1-induced gastric cancer cell
invasion. J Biol Chem. 283:15807–15815. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hanrahan F, Humphries P and Campbell M:
RNAi-mediated barrier modulation: synergies of the brain and eye.
Ther Deliv. 1:587–594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Roy S, Nasser S, Yee M, Graves DT and Roy
S: A long-term siRNA strategy regulates fibronectin overexpression
and improves vascular lesions in retinas of diabetic rats. Mol Vis.
17:3166–3174. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kuwabara K, Ogawa S, Matsumoto M, Koga S,
Clauss M, Pinsky DJ, Lyn P, Leavy J, Witte L and Joseph-Silverstein
J: Hypoxia-mediated induction of acidic/basic fibroblast growth
factor and platelet-derived growth factor in mononuclear phagocytes
stimulates growth of hypoxic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:4606–4610. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kunz M, Hartmann A, Flory E, Toksoy A,
Koczan D, Thiesen HJ, Mukaida N, Neumann M, Rapp UR, Bröcker EB and
Gillitzer R: Anoxia-induced up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human
malignant melanoma. A potential mechanism for high tumor
aggressiveness. Am J Pathol. 155:753–763. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yamashita K, Discher DJ, Hu J, Bishopric
NH and Webster KA: Molecular regulation of the endothelin-1 gene by
hypoxia. Contributions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1, activator
protein-1, GATA-2, AND p300/CBP. J Biol Chem. 276:12645–12653.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Woo KJ, Lee TJ, Park JW and Kwon TK:
Desferrioxamine, an iron chelator, enhances HIF-1alpha accumulation
via cyclooxy-genase-2 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 343:8–14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
You JJ, Yang CM, Chen MS and Yang CH:
Regulation of Cyr61/CCN1 expression by hypoxia through cooperation
of c-Jun/AP-1 and HIF-1α in retinal vascular endothelial cells. Exp
Eye Res. 91:825–836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chaqour B and Goppelt-Struebe M:
Mechanical regulation of the Cyr61/CCN1 and CTGF/CCN2 proteins.
FEBS J. 273:3639–3649. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee HY, Chung JW, Youn SW, Kim JY, Park
KW, Koo BK, Oh BH, Park YB, Chaqour B, Walsh K and Kim HS: Forkhead
transcription factor FOXO3a is a negative regulator of angiogenic
immediate early gene CYR61, leading to inhibition of vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Circ
Res. 100:372–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen CC, Chen N and Lau LF: The angiogenic
factors Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor induce adhesive
signaling in primary human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
276:10443–10452. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Murphy LO, MacKeigan JP and Blenis J: A
network of immediate early gene products propagates subtle
differences in mitogen-activated protein kinase signal amplitude
and duration. Mol Cell Biol. 24:144–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Mo FE, Muntean AG, Chen CC, Stolz DB,
Watkins SC and Lau LF: CYR61 (CCN1) is essential for placental
development and vascular integrity. Mol Cell Biol. 22:8709–8720.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chaqour B: Molecular control of vascular
development by the matricellular proteins CCN1 (Cyr61) and CCN2
(CTGF). Trends Dev Biol. 7:59–72. 2013.
|