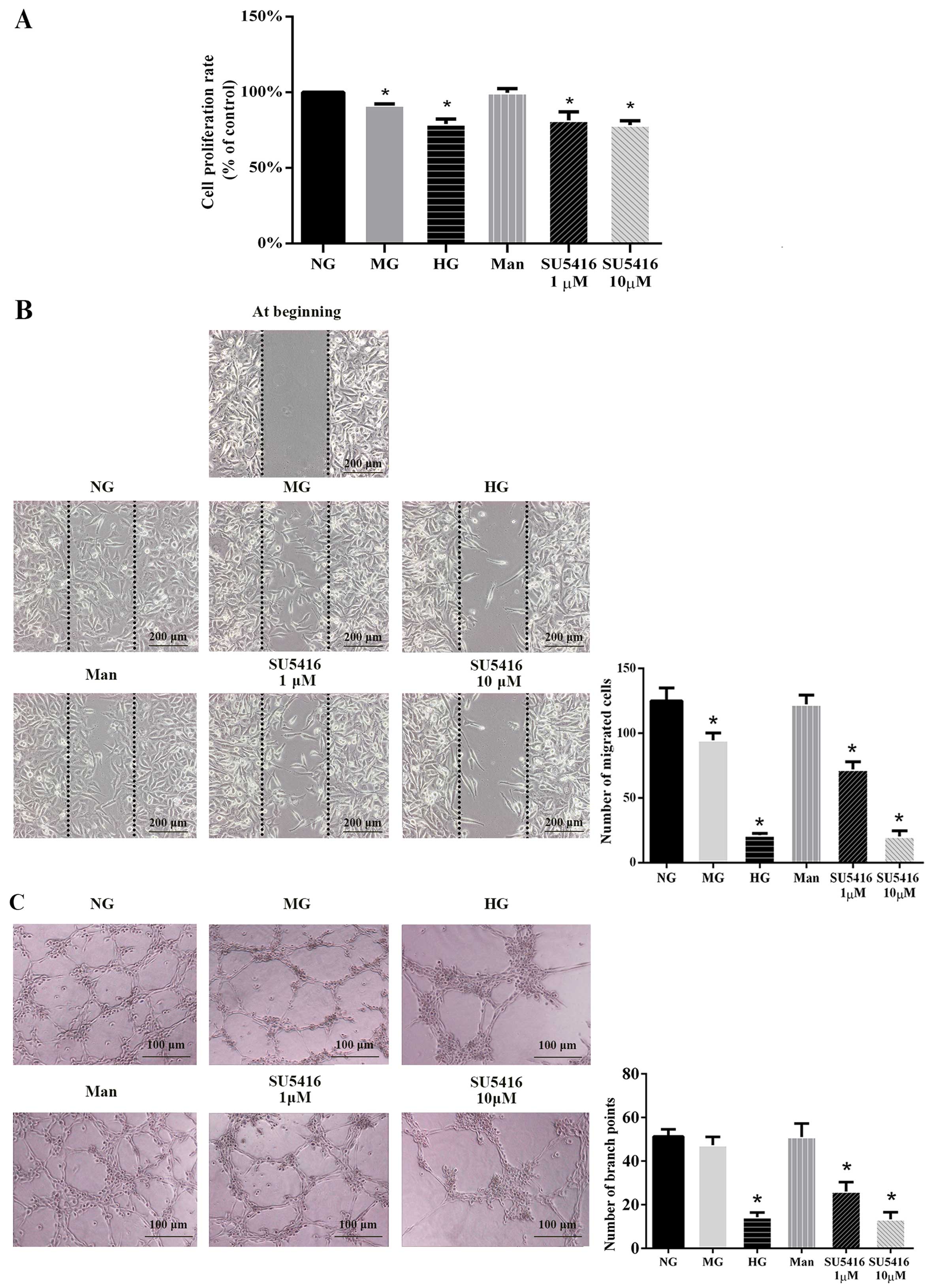
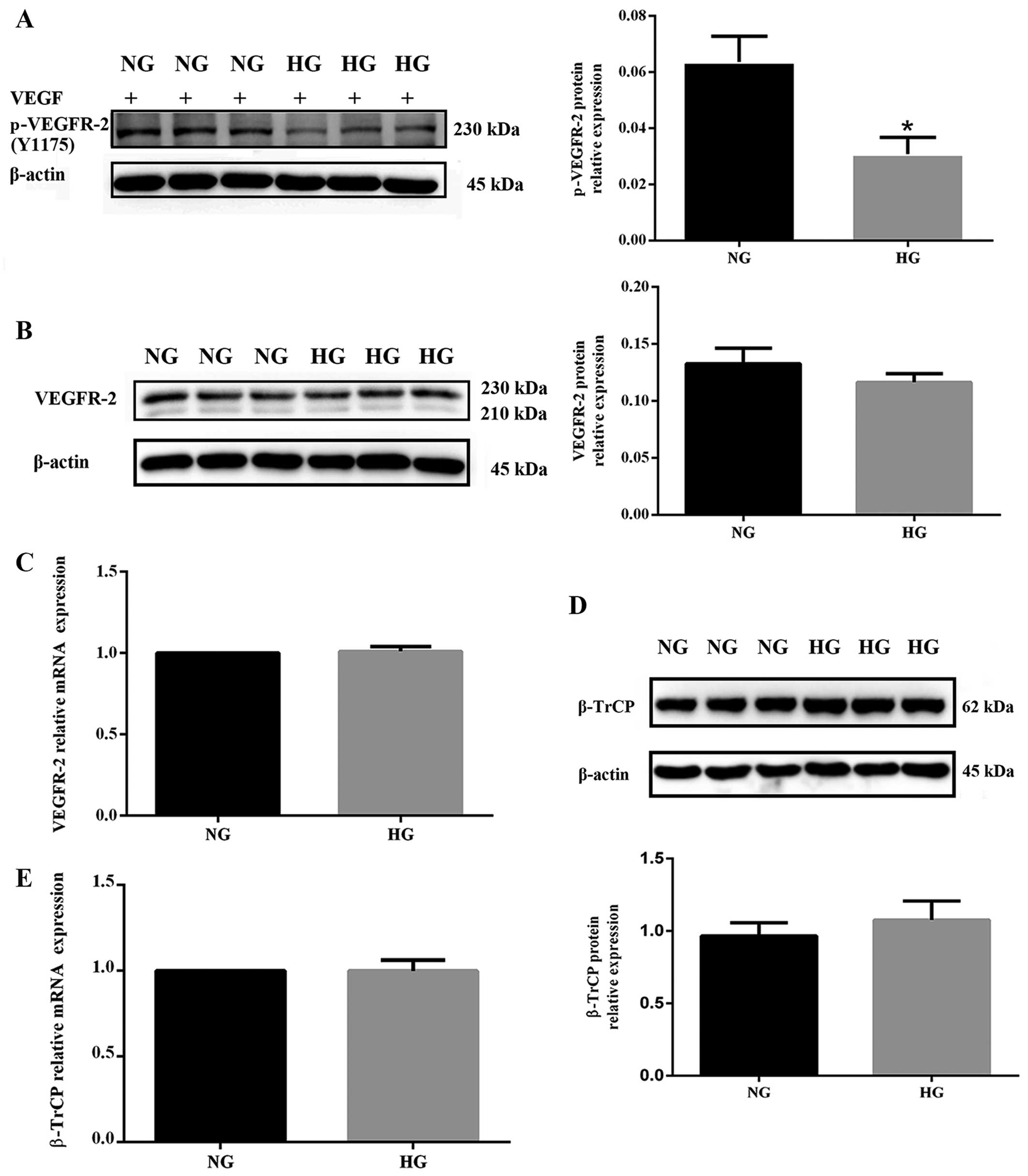
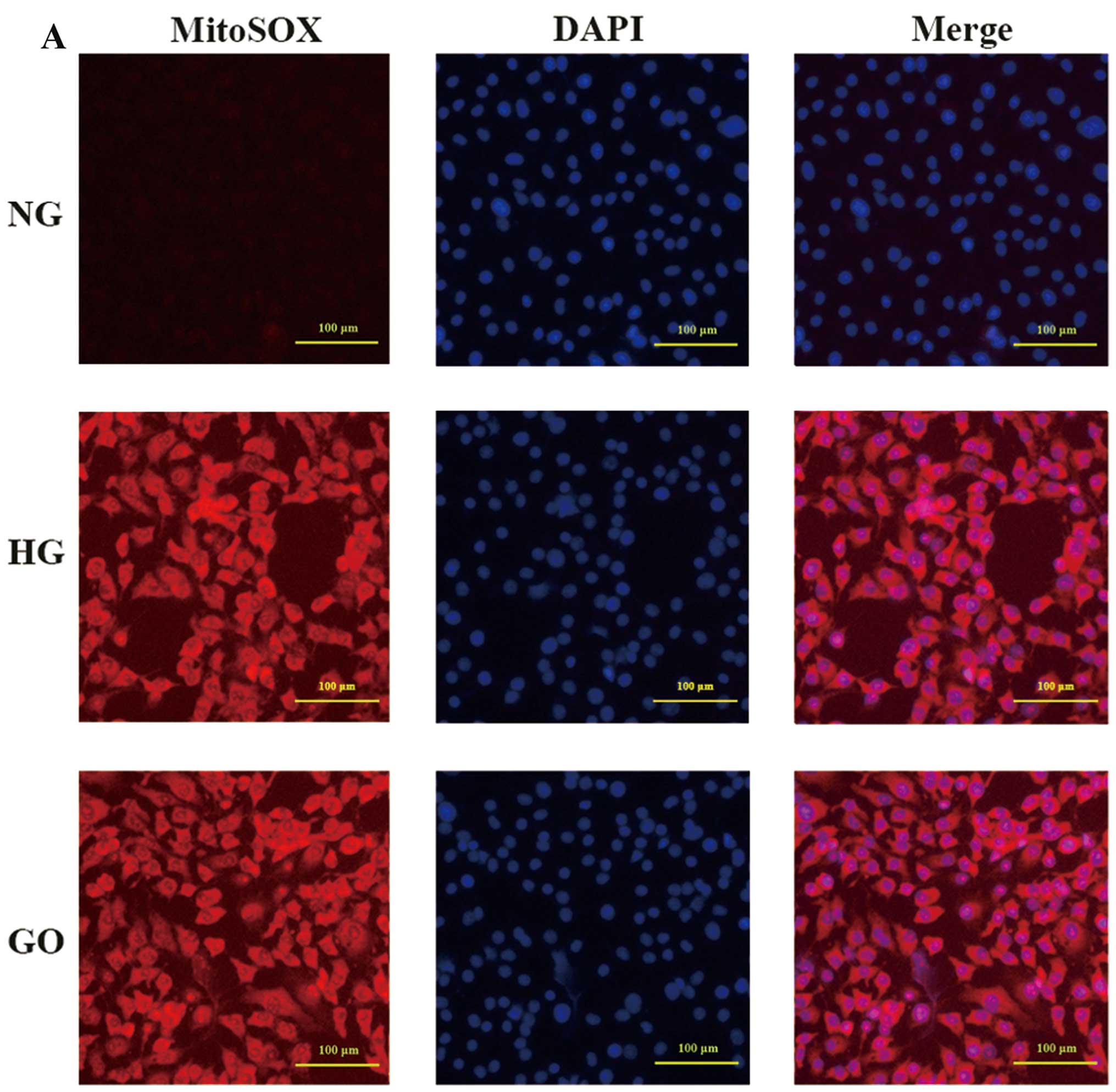
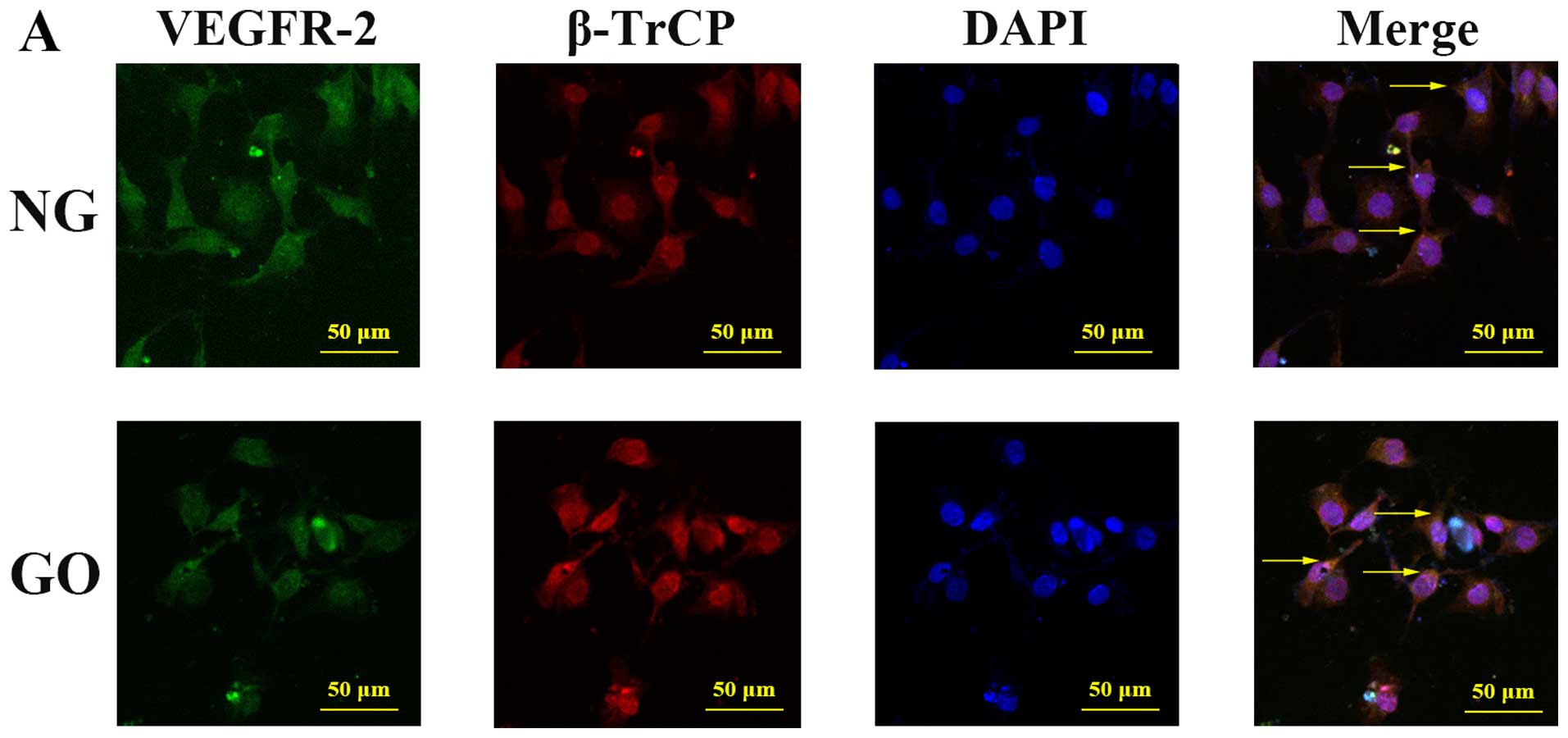
|
1
|
Waltenberger J: VEGF resistance as a
molecular basis to explain the angiogenesis paradox in diabetes
mellitus. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:1167–1170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schiekofer S, Galasso G, Sato K, Kraus BJ
and Walsh K: Impaired revascularization in a mouse model of type 2
diabetes is associated with dysregulation of a complex
angiogenic-regulatory network. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:1603–1609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shibuya M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and its receptor system: physiological functions in
angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J Biochem.
153:13–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shibuya M: VEGFR and type-V RTK activation
and signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0090922013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koch S and Claesson-Welsh L: Signal
transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0065022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shibuya M and Claesson-Welsh L: Signal
transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 312:549–560. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Warren CM, Ziyad S, Briot A, Der A and
Iruela-Arispe ML: A ligand-independent VEGFR2 signaling pathway
limits angiogenic responses in diabetes. Sci Signal. 7:ra12014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen YS and Qiu XB: Ubiquitin at the
crossroad of cell death and survival. Chin J Cancer. 32:640–647.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shaik S, Nucera C, Inuzuka H, Gao D,
Garnaas M, Frechette G, Harris L, Wan L, Fukushima H, Husain A, et
al: SCF(β-TRCP) suppresses angiogenesis and thyroid cancer cell
migration by promoting ubiquitination and destruction of VEGF
receptor 2. J Exp Med. 209:1289–1307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei S, Lin LF, Yang CC, Wang YC, Chang GD,
Chen H and Chen CS: Thiazolidinediones modulate the expression of
beta-catenin and other cell-cycle regulatory proteins by targeting
the F-box proteins of Skp1-Cul1-F-box protein E3 ubiquitin ligase
independently of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Mol Pharmacol. 72:725–733. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei S, Yang HC, Chuang HC, Yang J, Kulp
SK, Lu PJ, Lai MD and Chen CS: A novel mechanism by which
thiazolidinediones facilitate the proteasomal degradation of cyclin
D1 in cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:26759–26770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cardozo T and Pagano M: The SCF ubiquitin
ligase: insights into a molecular machine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:739–751. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Liu J and Gao T: beta-TrCP-mediated
ubiquitination and degradation of PHLPP1 are negatively regulated
by Akt. Mol Cell Biol. 29:6192–6205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of beta-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bischof M, Abdollahi A, Gong P, Stoffregen
C, Lipson KE, Debus JU, Weber KJ and Huber PE: Triple combination
of irradiation, chemotherapy (pemetrexed), and VEGFR inhibition
(SU5416) in human endothelial and tumor cells. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 60:1220–1232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang BR, Hong SJ, Lee SM, Cong WH, Wan JB,
Zhang ZR, Zhang QW, Zhang Y, Wang YT and Lin ZX: Pro-angiogenic
activity of notoginsenoside R1 in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells in vitro and in a chemical-induced blood vessel loss model of
zebrafish in vivo. Chin J Integr Med. Dec 22–2014.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cukiernik M, Hileeto D, Evans T, Mukherjee
S, Downey D and Chakrabarti S: Vascular endothelial growth factor
in diabetes induced early retinal abnormalities. Diabetes Res Clin
Pract. 65:197–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ettenson DS and Gotlieb AI: Centrosomes,
microtubules, and microfilaments in the reendothelialization and
remodeling of double-sided in vitro wounds. Lab Invest. 66:722–733.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pollman MJ, Naumovski L and Gibbons GH:
Endothelial cell apoptosis in capillary network remodeling. J Cell
Physiol. 178:359–370. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–1070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi SE, Jang HJ, Kang Y, Jung JG, Han SJ,
Kim HJ, Kim DJ and Lee KW: Atherosclerosis induced by a high-fat
diet is alleviated by lithium chloride via reduction of VCAM
expression in ApoE-deficient mice. Vascul Pharmacol. 53:264–272.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kobayashi T, Matsumoto T and Kamata K: The
PI3-K/Akt pathway: roles related to alterations in vasomotor
responses in diabetic models. J Smooth Muscle Res. 41:283–302.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nikoulina SE, Ciaraldi TP, Mudaliar S,
Mohideen P, Carter L and Henry RR: Potential role of glycogen
synthase kinase-3 in skeletal muscle insulin resistance of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 49:263–271. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eldar-Finkelman H and Krebs EG:
Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by glycogen
synthase kinase 3 impairs insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:9660–9664. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coghlan MP, Culbert AA, Cross DA, Corcoran
SL, Yates JW, Pearce NJ, Rausch OL, Murphy GJ, Carter PS, Roxbee
Cox L, et al: Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen
synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene
transcription. Chem Biol. 7:793–803. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mora A, Sabio G, Risco AM, Cuenda A,
Alonso JC, Soler G and Centeno F: Lithium blocks the PKB and GSK3
dephosphorylation induced by ceramide through protein
phosphatase-2A. Cell Signal. 14:557–562. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Klein PS and Melton DA: A molecular
mechanism for the effect of lithium on development. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:8455–8459. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rossetti L: Normalization of insulin
sensitivity with lithium in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 38:648–652.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dejana E: The role of wnt signaling in
physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Circ Res. 107:943–952.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi W, Yang C, Dai Z, Che D, Feng J, Mao Y,
Cheng R, Wang Z, He X, Zhou T, et al: High levels of pigment
epithelium-derived factor in diabetes impair wound healing through
suppression of Wnt signaling. Diabetes. 64:1407–1419. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hou Q, Lei M, Hu K and Wang M: The effects
of high glucose levels on reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis
and involved signaling in human vascular endothelial cells.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 15:140–146. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Meyer RD, Srinivasan S, Singh AJ, Mahoney
JE, Gharahassanlou KR and Rahimi N: PEST motif serine and tyrosine
phosphorylation controls vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 stability and downregulation. Mol Cell Biol.
31:2010–2025. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|