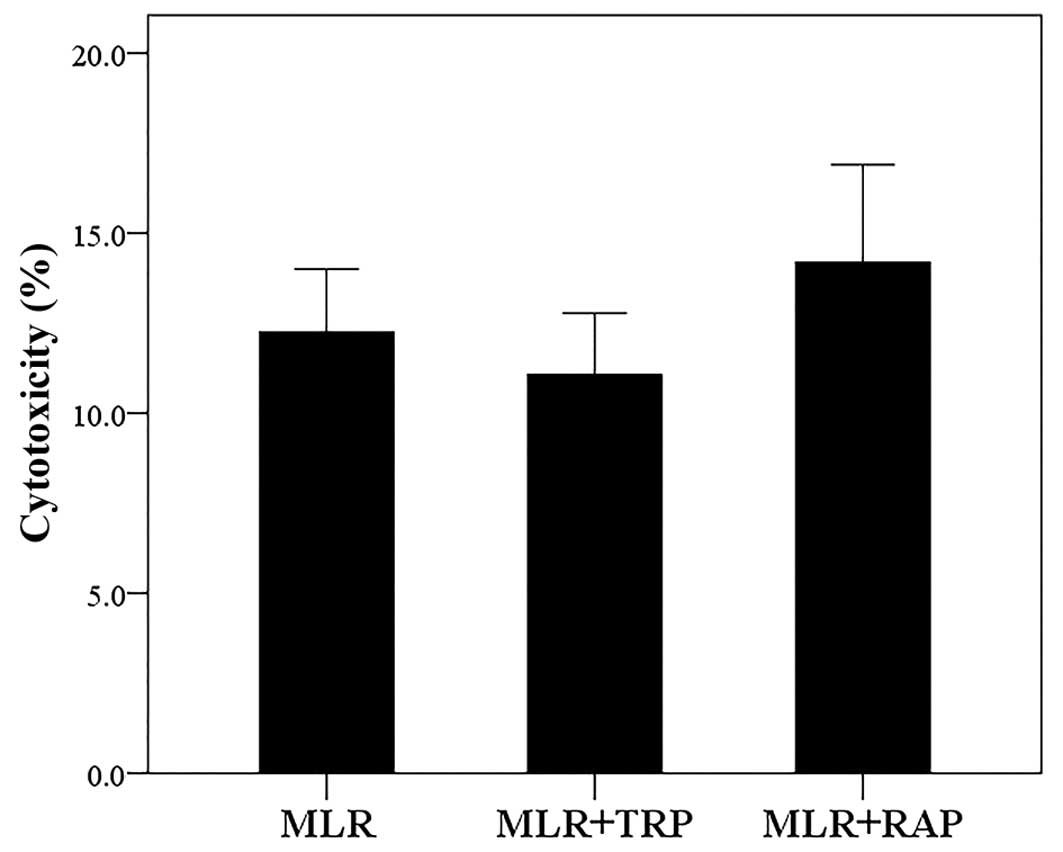
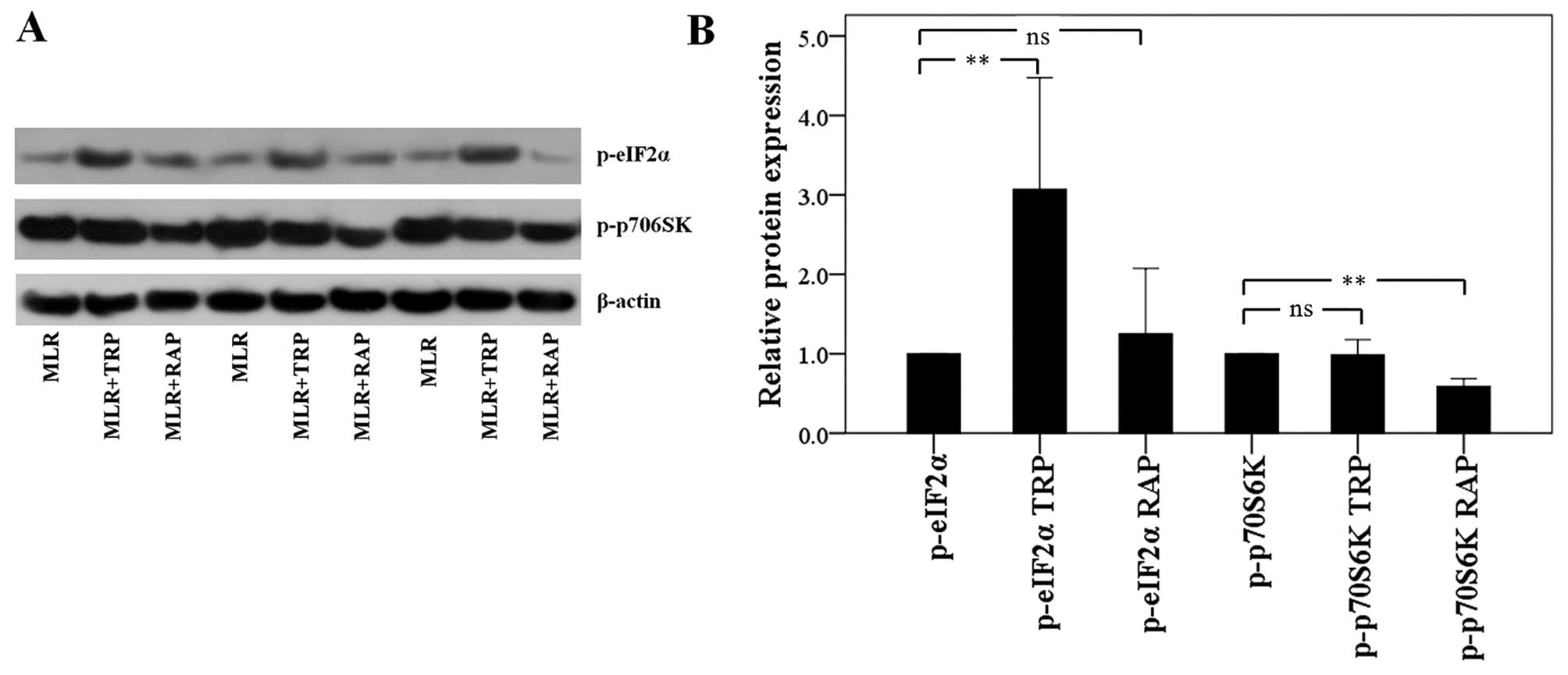
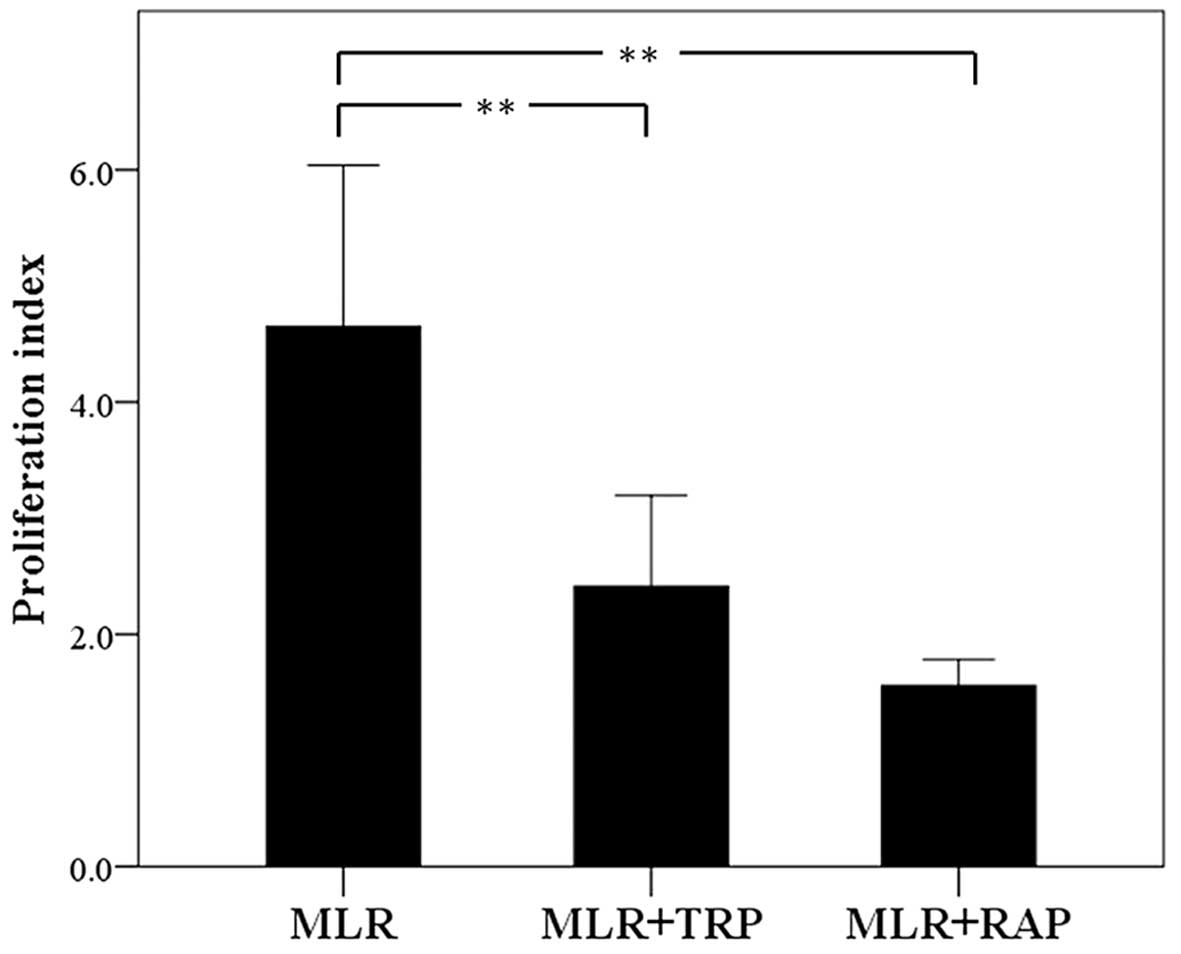
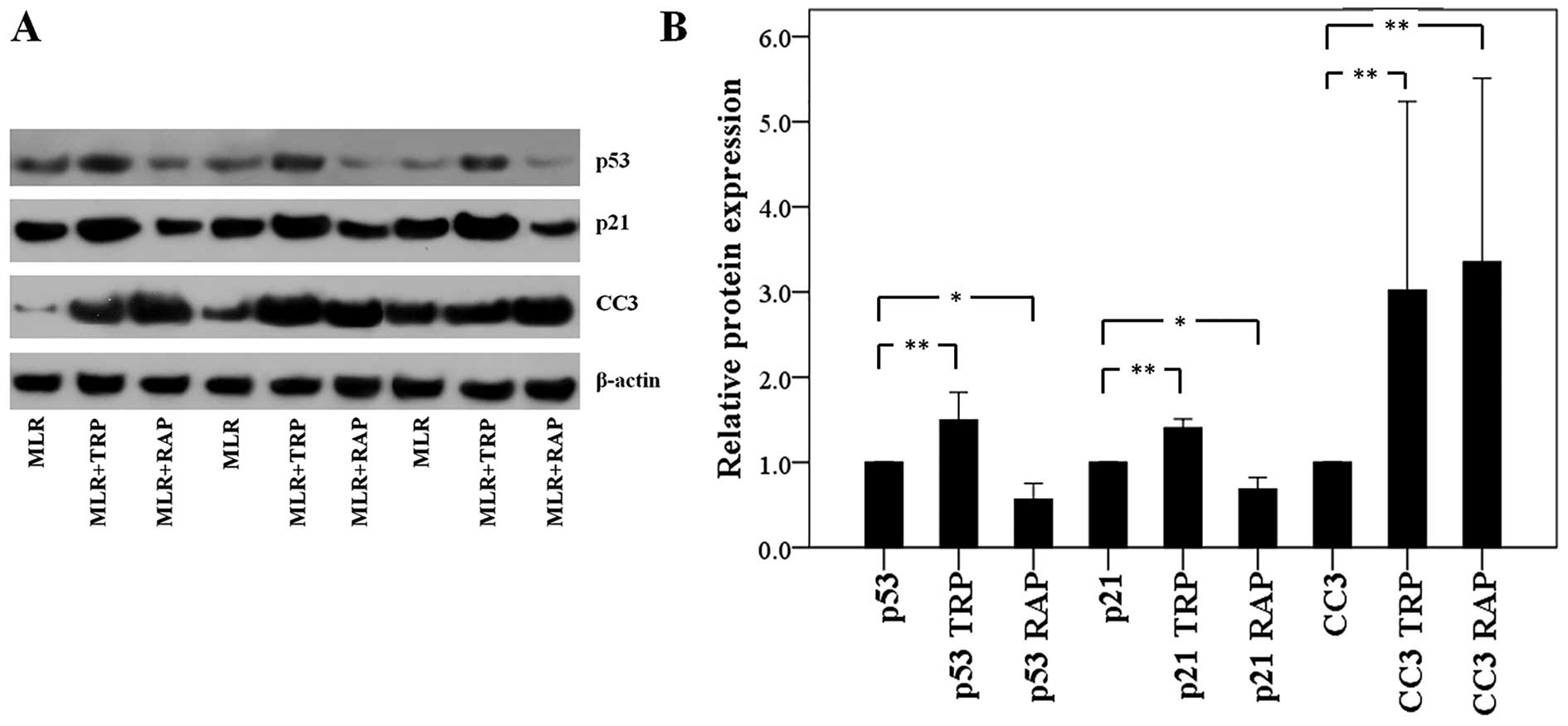
|
1
|
Bronte V and Zanovello P: Regulation of
immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:641–654. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mellor AL and Munn DH: IDO expression by
dendritic cells: Tolerance and tryptophan catabolism. Nat Rev
Immunol. 4:762–774. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong J, Qiu H, Garcia-Barrio M, Anderson J
and Hinnebusch AG: Uncharged tRNA activates GCN2 by displacing the
protein kinase moiety from a bipartite tRNA-binding domain. Mol
Cell. 6:269–279. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gallinetti J, Harputlugil E and Mitchell
JR: Amino acid sensing in dietary-restriction-mediated longevity:
Roles of signal-transducing kinases GCN2 and TOR. Biochem J.
449:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist
RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L and Sabatini DM: The Rag GTPases bind
raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science.
320:1496–1501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim E, Goraksha-Hicks P, Li L, Neufeld TP
and Guan KL: Regulation of TORC1 by Rag GTPases in nutrient
response. Nat Cell Biol. 10:935–945. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
depletes tryptophan, activates general control non-derepressible 2
kinase and down-regulates key enzymes involved in fatty acid
synthesis in primary human CD4+ T cells. Immunology.
146:292–300. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kilberg MS, Shan J and Su N:
ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid
limitation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 20:436–443. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Castilho BA, Shanmugam R, Silva RC, Ramesh
R, Himme BM and Sattlegger E: Keeping the eIF2 alpha kinase Gcn2 in
check. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:1948–1968. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
at a glance. J Cell Sci. 122:3589–3594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shihab F, Christians U, Smith L, Wellen JR
and Kaplan B: Focus on mTOR inhibitors and tacrolimus in renal
transplantation: Pharmacokinetics, exposure-response relationships,
and clinical outcomes. Transpl Immunol. 31:22–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Spanoulis A, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase increases p53 levels in alloreactive human T cells,
and both indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and p53 suppress glucose
uptake, glycolysis and proliferation. Int Immunol. 26:673–684.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Munn DH, Sharma MD, Baban B, Harding HP,
Zhang Y, Ron D and Mellor AL: GCN2 kinase in T cells mediates
proliferative arrest and anergy induction in response to
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunity. 22:633–642. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alexander AM, Crawford M, Bertera S,
Rudert WA, Takikawa O, Robbins PD and Trucco M: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase expression in transplanted NOD Islets prolongs
graft survival after adoptive transfer of diabetogenic splenocytes.
Diabetes. 51:356–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beutelspacher SC, Pillai R, Watson MP, Tan
PH, Tsang J, McClure MO, George AJ and Larkin DF: Function of
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in corneal allograft rejection and
prolongation of allograft survival by over-expression. Eur J
Immunol. 36:690–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Tredget EE, Ghaffari A, Lin X,
Kilani RT and Ghahary A: Local expression of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase protects engraftment of xenogeneic skin substitute.
J Invest Dermatol. 126:128–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I,
Conway SJ, Marshall B, Brown C and Mellor AL: Prevention of
allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science.
281:1191–1193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato T, Deiwick A, Raddatz G, Koyama K and
Schlitt HJ: Interactions of allogeneic human mononuclear cells in
the two-way mixed leucocyte culture (MLC): Influence of cell
numbers, subpopulations and cyclosporin. Clin Exp Immunol.
115:301–308. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lowe G and Tansley G: An investigation of
the mechanism of activation of tryptophan by tryptophanyl-tRNA
synthetase from beef pancreas. Eur J Biochem. 138:597–602. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pines M and Spector I: Halofuginone - the
multifaceted molecule. Molecules. 20:573–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chu TL, Guan Q, Nguan CY and Du C:
Halofuginone suppresses T cell proliferation by blocking proline
uptake and inducing cell apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol.
16:414–423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Forouzandeh F, Jalili RB, Germain M,
Duronio V and Ghahary A: Skin cells, but not T cells, are resistant
to indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase IDO) expressed by allogeneic
fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 16:379–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Habibi D, Jalili RB, Forouzandeh F, Ong CJ
and Ghahary A: High expression of IMPACT protein promotes
resistance to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-induced cell death. J
Cell Physiol. 225:196–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weichhart T, Costantino G, Poglitsch M,
Rosner M, Zeyda M, Stuhlmeier KM, Kolbe T, Stulnig TM, Hörl WH,
Hengstschläger M, et al: The TSC-mTOR signaling pathway regulates
the innate inflammatory response. Immunity. 29:565–577. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi SJ, You HS and Chung SY:
Rapamycin-induced cytotoxic signal transduction pathway. Transplant
Proc. 40:2737–2739. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brady CA and Attardi LD: p53 at a glance.
J Cell Sci. 123:2527–2532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Metcalfe SM, Canman CE, Milner J, Morris
RE, Goldman S and Kastan MB: Rapamycin and p53 act on different
pathways to induce G1 arrest in mammalian cells. Oncogene.
15:1635–1642. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Miyake N, Chikumi H, Takata M, Nakamoto M,
Igishi T and Shimizu E: Rapamycin induces p53-independent apoptosis
through the mitochondrial pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 28:848–854. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN and
Forsthuber TG: T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in
autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 74:5–17. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fallarino F, Grohmann U, You S, McGrath
BC, Cavener DR, Vacca C, Orabona C, Bianchi R, Belladonna ML, Volpi
C, et al: The combined effects of tryptophan starvation and
tryptophan catabolites down-regulate T cell receptor zeta-chain and
induce a regulatory phenotype in naive T cells. J Immunol.
176:6752–6761. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ito H, Ando T, Ando K, Ishikawa T, Saito
K, Moriwaki H and Seishima M: Induction of hepatitis B virus
surface antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be
up-regulated by the inhibition of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase
activity. Immunology. 142:614–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mezrich JD, Fechner JH, Zhang X, Johnson
BP, Burlingham WJ and Bradfield CA: An interaction between
kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate
regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 185:3190–3198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Delgoffe GM, Kole TP, Zheng Y, Zarek PE,
Matthews KL, Xiao B, Worley PF, Kozma SC and Powell JD: The mTOR
kinase differentially regulates effector and regulatory T cell
lineage commitment. Immunity. 30:832–844. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pollizzi KN and Powell JD: Regulation of T
cells by mTOR: The known knowns and the known unknowns. Trends
Immunol. 36:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Lee K, Gudapati P, Dragovic S, Spencer C,
Joyce S, Killeen N, Magnuson MA and Boothby M: Mammalian target of
rapamycin protein complex 2 regulates differentiation of Th1 and
Th2 cell subsets via distinct signaling pathways. Immunity.
32:743–753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Delgoffe GM, Pollizzi KN, Waickman AT,
Heikamp E, Meyers DJ, Horton MR, Xiao B, Worley PF and Powell JD:
The kinase mTOR regulates the differentiation of helper T cells
through the selective activation of signaling by mTORC1 and mTORC2.
Nat Immunol. 12:295–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen
JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, Markhard AL and Sabatini DM: Prolonged
rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell.
22:159–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Askar M: T helper subsets and regulatory T
cells: Rethinking the paradigm in the clinical context of solid
organ transplantation. Int J Immunogenet. 41:185–194. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pan F, Barbi J and Pardoll DM:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: A link between metabolism and T cell
differentiation and a potential therapeutic target. Oncoimmunology.
1:510–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dang EV, Barbi J, Yang HY, Jinasena D, Yu
H, Zheng Y, Bordman Z, Fu J, Kim Y, Yen HR, et al: Control of
T(H)17/T(reg) balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
146:772–784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM,
Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ and Abraham RT: Regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the
mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 22:7004–7014. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sutton TA, Wilkinson J, Mang HE, Knipe NL,
Plotkin Z, Hosein M, Zak K, Wittenborn J and Dagher PC: p53
regulates renal expression of HIF-1{alpha} and pVHL under
physiological conditions and after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F1666–F1677. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nieminen AL, Qanungo S, Schneider EA,
Jiang BH and Agani FH: Mdm2 and HIF-1alpha interaction in tumor
cells during hypoxia. J Cell Physiol. 204:364–369. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kaluz S, Kaluzová M and Stanbridge EJ:
Does inhibition of degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)
alpha always lead to activation of HIF? Lessons learnt from the
effect of proteasomal inhibition on HIF activity. J Cell Biochem.
104:536–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Schmid T, Zhou J, Köhl R and Brüne B: p300
relieves p53-evoked transcriptional repression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 (HIF-1). Biochem J. 380:289–295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
François M, Romieu-Mourez R, Li M and
Galipeau J: Human MSC suppression correlates with cytokine
induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and bystander M2
macrophage differentiation. Mol Ther. 20:187–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mercalli A, Calavita I, Dugnani E, Citro
A, Cantarelli E, Nano R, Melzi R, Maffi P, Secchi A, Sordi V, et
al: Rapamycin unbalances the polarization of human macrophages to
M1. Immunology. 140:179–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|