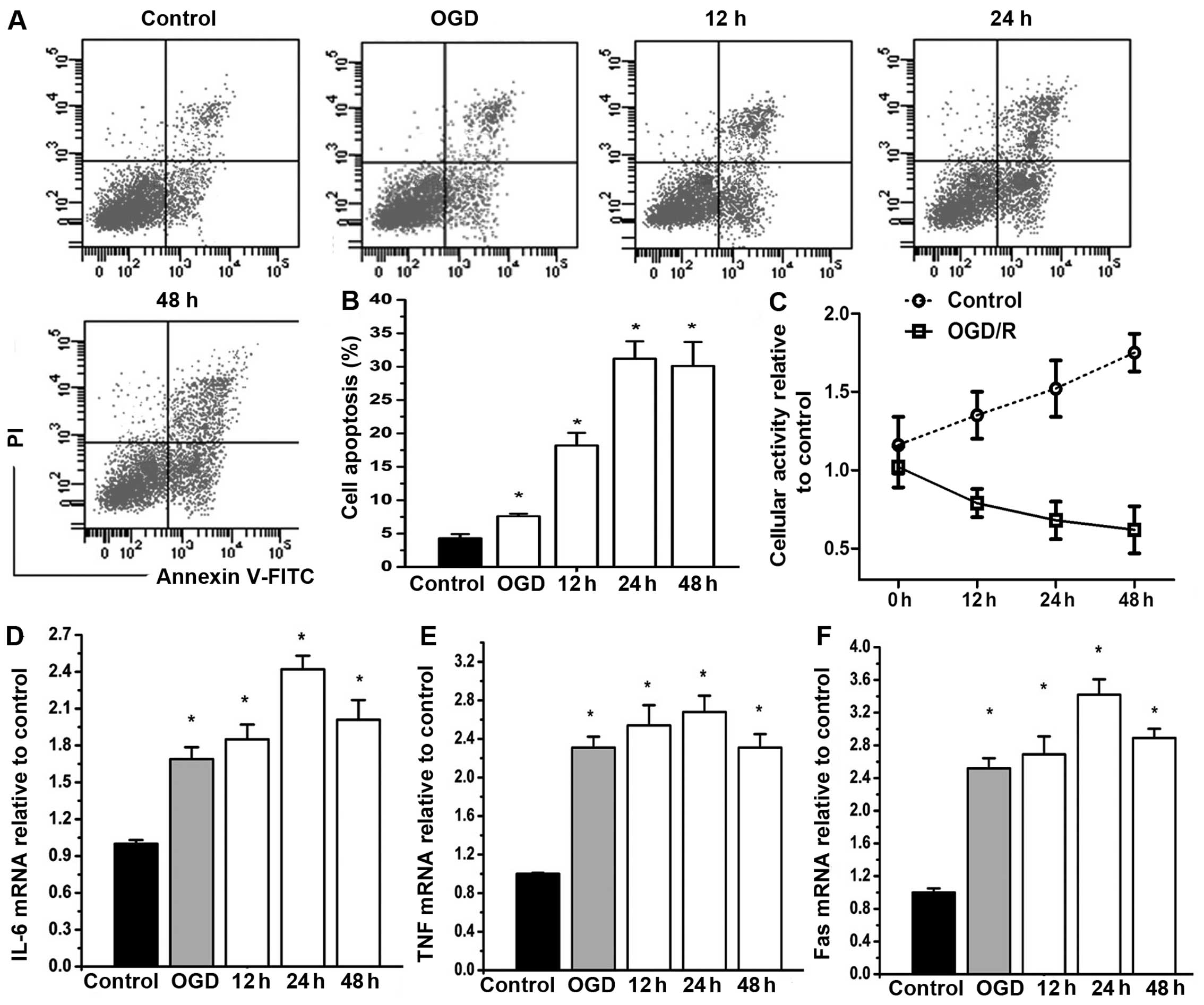
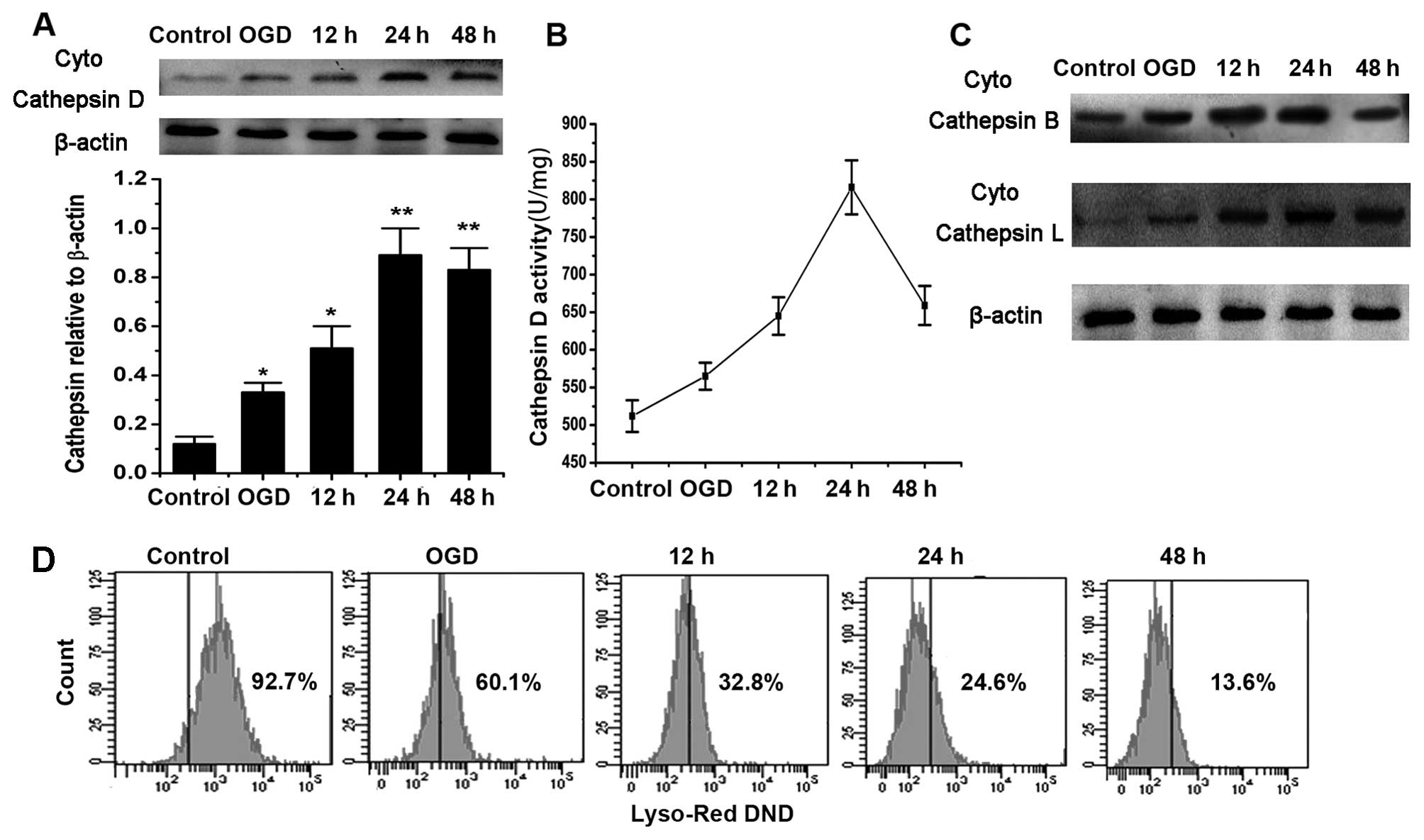
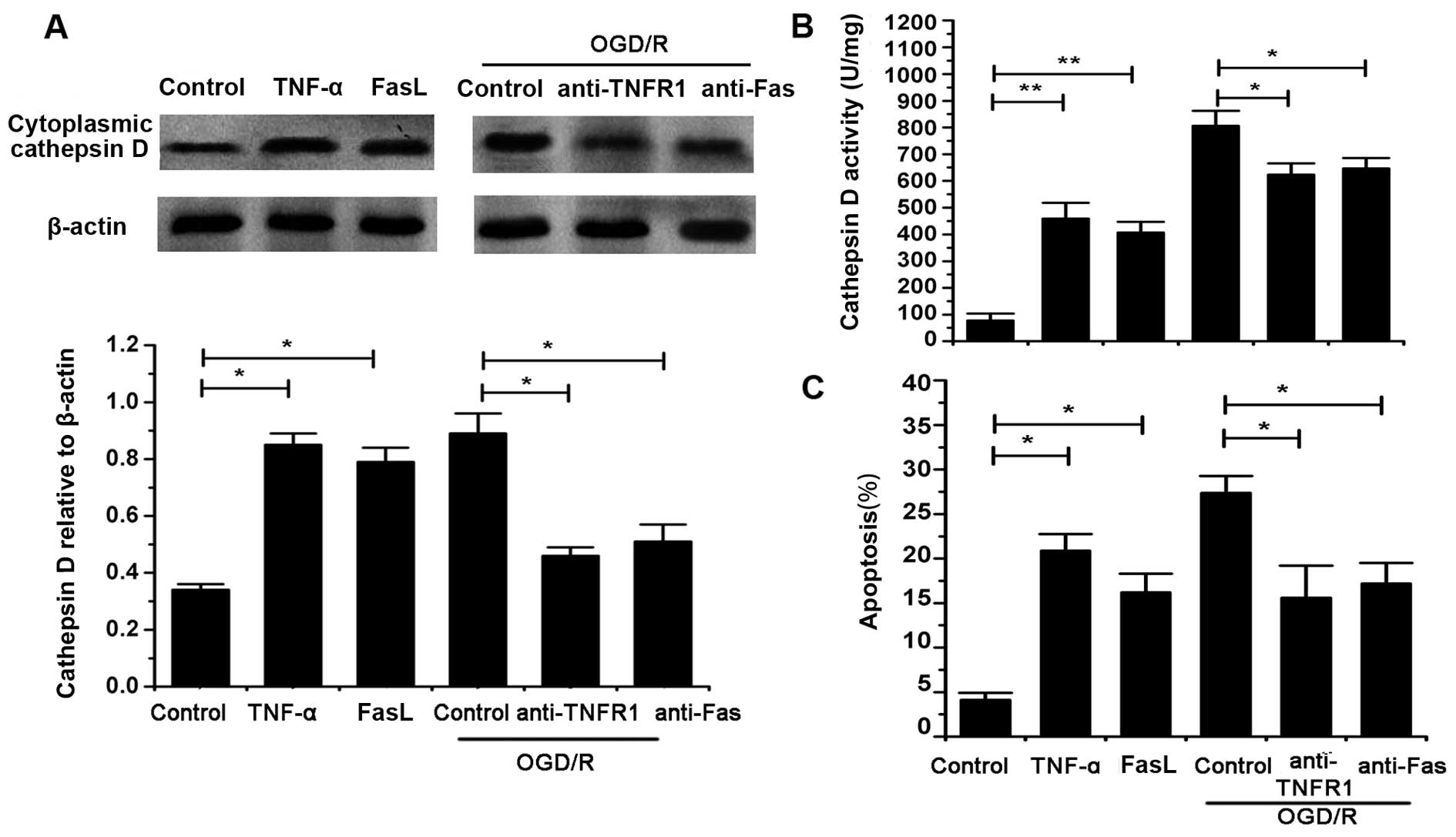
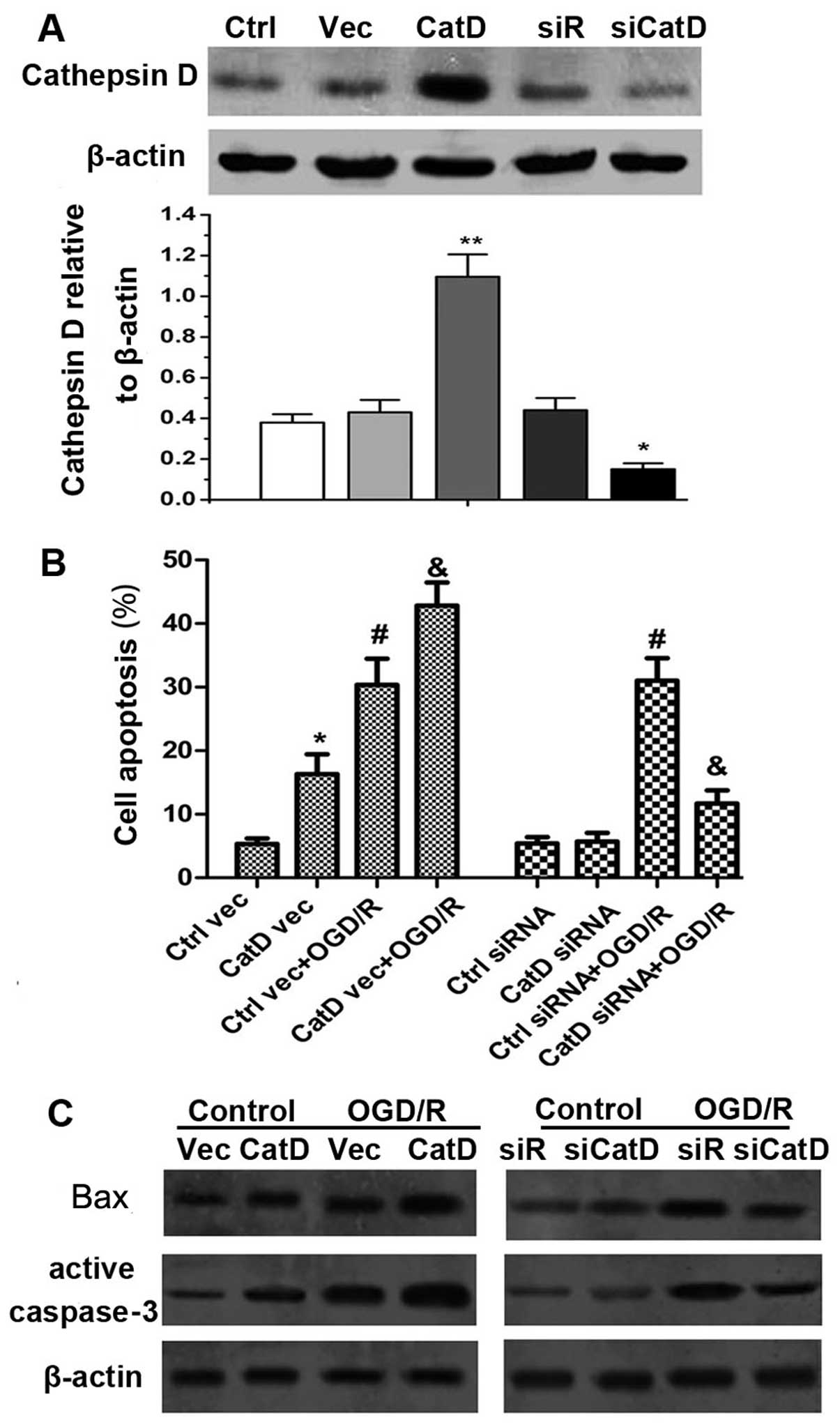
|
1
|
Tu Q, Cao H, Zhong W, Ding B and Tang X:
Atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Neural Regen
Res. 9:268–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo Y, He Q, Kuang G, Jiang Q and Yang J:
PPAR-alpha and PPAR-beta expression changes in the hippocampus of
rats undergoing global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion due to
PPAR-gamma status. Behav Brain Funct. 10:212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun BZ, Chen L, Wu Q, Wang HL, Wei XB,
Xiang YX and Zhang XM: Suppression of inflammatory response by
flurbiprofen following focal cerebral ischemia involves the NF-κB
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:3087–3095. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Almeida AS, Queiroga CS, Sousa MF, Alves
PM and Vieira HL: Carbon monoxide modulates apoptosis by
reinforcing oxidative metabolism in astrocytes: role of Bcl-2. J
Biol Chem. 287:10761–10770. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hong S, Son MR, Yun K, Lee WT, Park KA and
Lee JE: Retroviral expression of human arginine decarboxylase
reduces oxidative stress injury in mouse cortical astrocytes. BMC
Neurosci. 15:992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun J, Zhu Y, Zhang L and Ma Y: Effects of
xuelian injection on cerebral TNF-α, IL-1β and MMP-9 in rats
experienced focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 7:2632–2638. 2014.
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Gao J, Shen Z,
Cheng Y, Shen Y, Wang RR, Wang X, Hu WW, et al: Cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal
injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy. 9:1321–1333. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J, Tan SH, Nicolas V, Bauvy C, Yang
ND, Zhang J, Xue Y, Codogno P and Shen HM: Activation of lysosomal
function in the course of autophagy via mTORC1 suppression and
autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Cell Res. 23:508–523. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qin AP, Zhang HL and Qin ZH: Mechanisms of
lysosomal proteases participating in cerebral ischemia-induced
neuronal death. Neurosci Bull. 24:117–123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin AP, Liu CF, Qin YY, Hong LZ, Xu M,
Yang L, Liu J, Qin ZH and Zhang HL: Autophagy was activated in
injured astrocytes and mildly decreased cell survival following
glucose and oxygen deprivation and focal cerebral ischemia.
Autophagy. 6:738–753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu M, Yang L, Rong JG, Ni Y, Gu WW, Luo Y,
Ishidoh K, Katunuma N, Li ZS and Zhang HL: Inhibition of cysteine
cathepsin B and L activation in astrocytes contributes to
neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia via blocking the
tBid-mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Glia. 62:855–880.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Windelborn JA and Lipton P: Lysosomal
release of cathepsins causes ischemic damage in the rat hippocampal
slice and depends on NMDA-mediated calcium influx, arachidonic acid
metabolism, and free radical production. J Neurochem. 106:56–69.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
García Samartino C, Delpino MV, Pott Godoy
C, Di Genaro MS, Pasquevich KA, Zwerdling A, Barrionuevo P, Mathieu
P, Cassataro J, Pitossi F, et al: Brucella abortus induces the
secretion of proinflammatory mediators from glial cells leading to
astrocyte apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 176:1323–1338. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li CY, Li X, Liu SF, Qu WS, Wang W and
Tian DS: Inhibition of mTOR pathway restrains astrocyte
proliferation, migration and production of inflammatory mediators
after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation. Neurochem Int.
83–84:9–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Česen MH, Pegan K, Špes A and Turk B:
Lysosomal pathways to cell death and their therapeutic
applications. Exp Cell Res. 318:1245–1251. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SJ, Park MH, Kim HJ and Koh JY:
Metallothionein-3 regulates lysosomal function in cultured
astrocytes under both normal and oxidative conditions. Glia.
58:1186–1196. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lipton P: Lysosomal membrane
permeabilization as a key player in brain ischemic cell death: a
'lysosomocentric' hypothesis for ischemic brain damage. Transl
Stroke Res. 4:672–684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamashima T and Oikawa S: The role of
lysosomal rupture in neuronal death. Prog Neurobiol. 89:343–358.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang ZB and Li ZG: Cathepsin B and
phospo-JNK in relation to ongoing apoptosis after transient focal
cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neurochem Res. 37:948–957. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haendeler J, Popp R, Goy C, Tischler V,
Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Cathepsin D and
H2O2 stimulate degradation of thioredoxin-1:
implication for endothelial cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
280:42945–42951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Conus S, Perozzo R, Reinheckel T, Peters
C, Scapozza L, Yousefi S and Simon HU: Caspase-8 is activated by
cathepsin D initiating neutrophil apoptosis during the resolution
of inflammation. J Exp Med. 205:685–698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beaujouin M and Liaudet-Coopman E:
Cathepsin D overexpressed by cancer cells can enhance
apoptosis-dependent chemo-sensitivity independently of its
catalytic activity. Hormonal Carcinogenesis V. Li JJ, Li S, Mohla
S, Rochefort H and Maudelonde T: 617. Springer; New York, NY: pp.
453–461. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Deiss LP, Galinka H, Berissi H, Cohen O
and Kimchi A: Cathepsin D protease mediates programmed cell death
induced by interferon-gamma, Fas/APO-1 and TNF-alpha. EMBO J.
15:3861–3870. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Heinrich M, Neumeyer J, Jakob M, Hallas C,
Tchikov V, Winoto-Morbach S, Wickel M, Schneider-Brachert W,
Trauzold A, Hethke A, et al: Cathepsin D links TNF-induced acid
sphingomyelinase to Bid-mediated caspase-9 and -3 activation. Cell
Death Differ. 11:550–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Repnik U and Turk B:
Lysosomal-mitochondrial cross-talk during cell death.
Mitochondrion. 10:662–669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terman A, Gustafsson B and Brunk UT: The
lysosomal-mitochondrial axis theory of postmitotic aging and cell
death. Chem Biol Interact. 163:29–37. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bidère N, Lorenzo HK, Carmona S, Laforge
M, Harper F, Dumont C and Senik A: Cathepsin D triggers Bax
activation, resulting in selective apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)
relocation in T lymphocytes entering the early commitment phase to
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 278:31401–31411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Zhou Y and Zhu K: Inhibition of
glioma cell lysosome exocytosis inhibits glioma invasion. PLoS One.
7:e459102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|