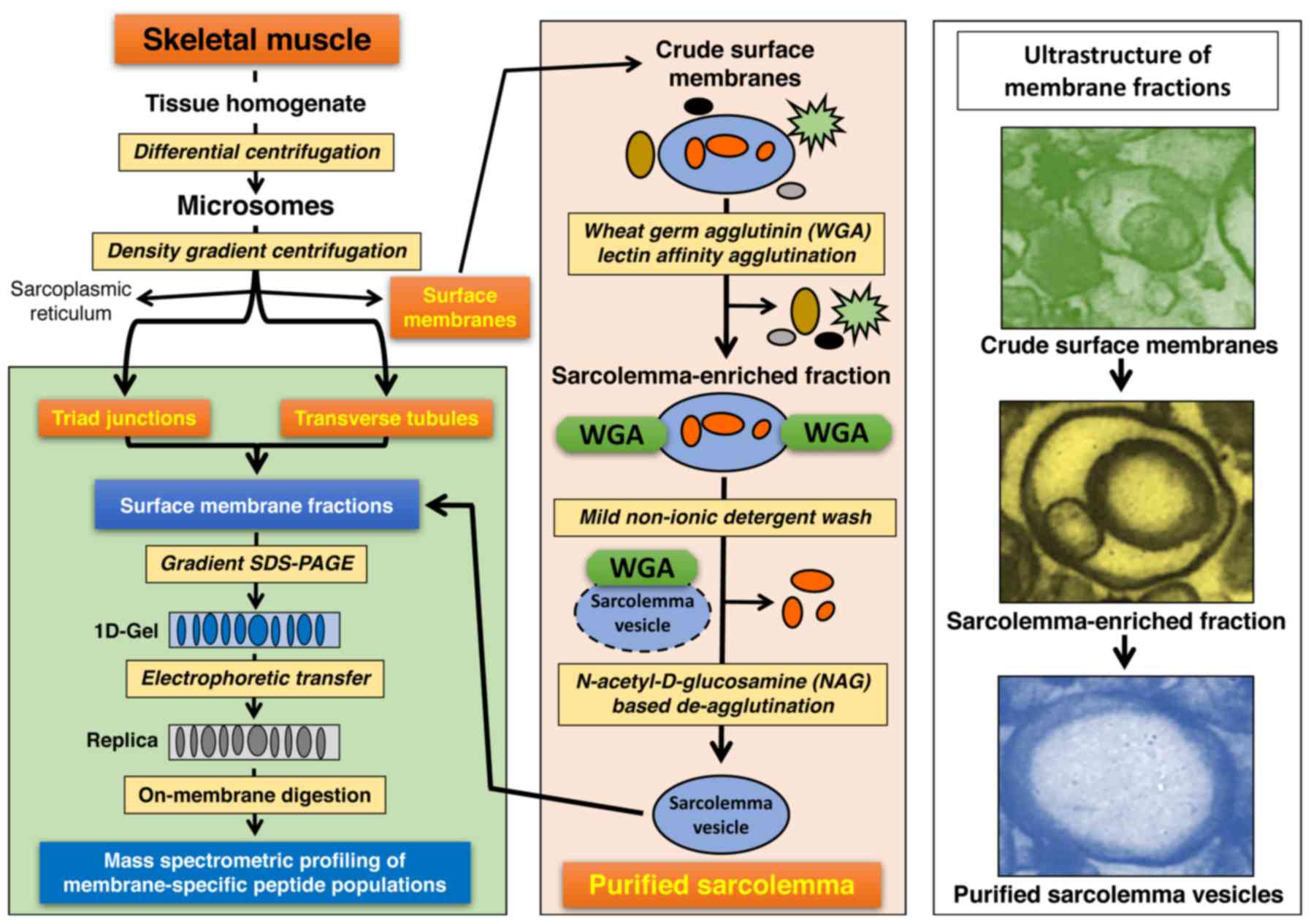
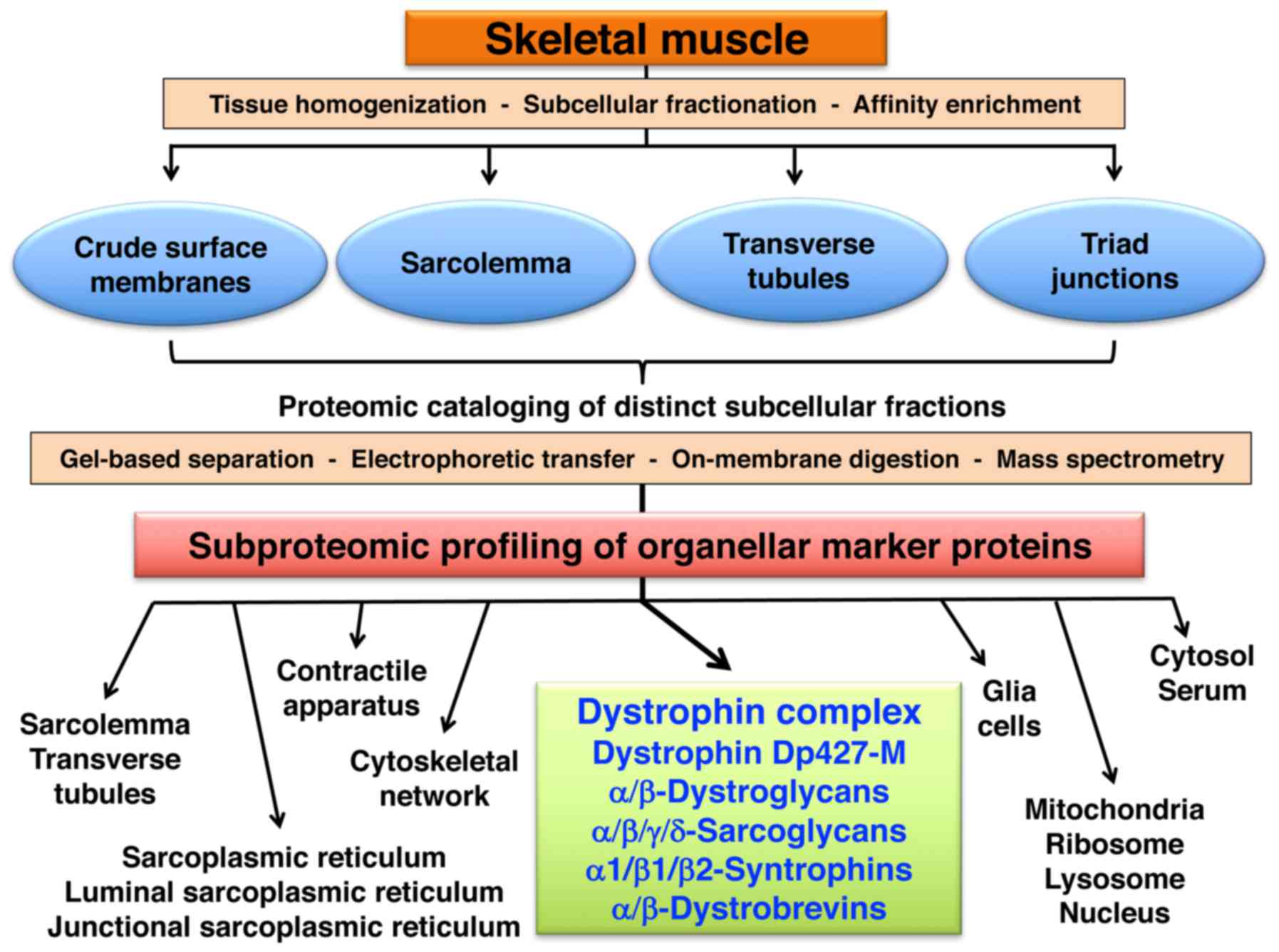
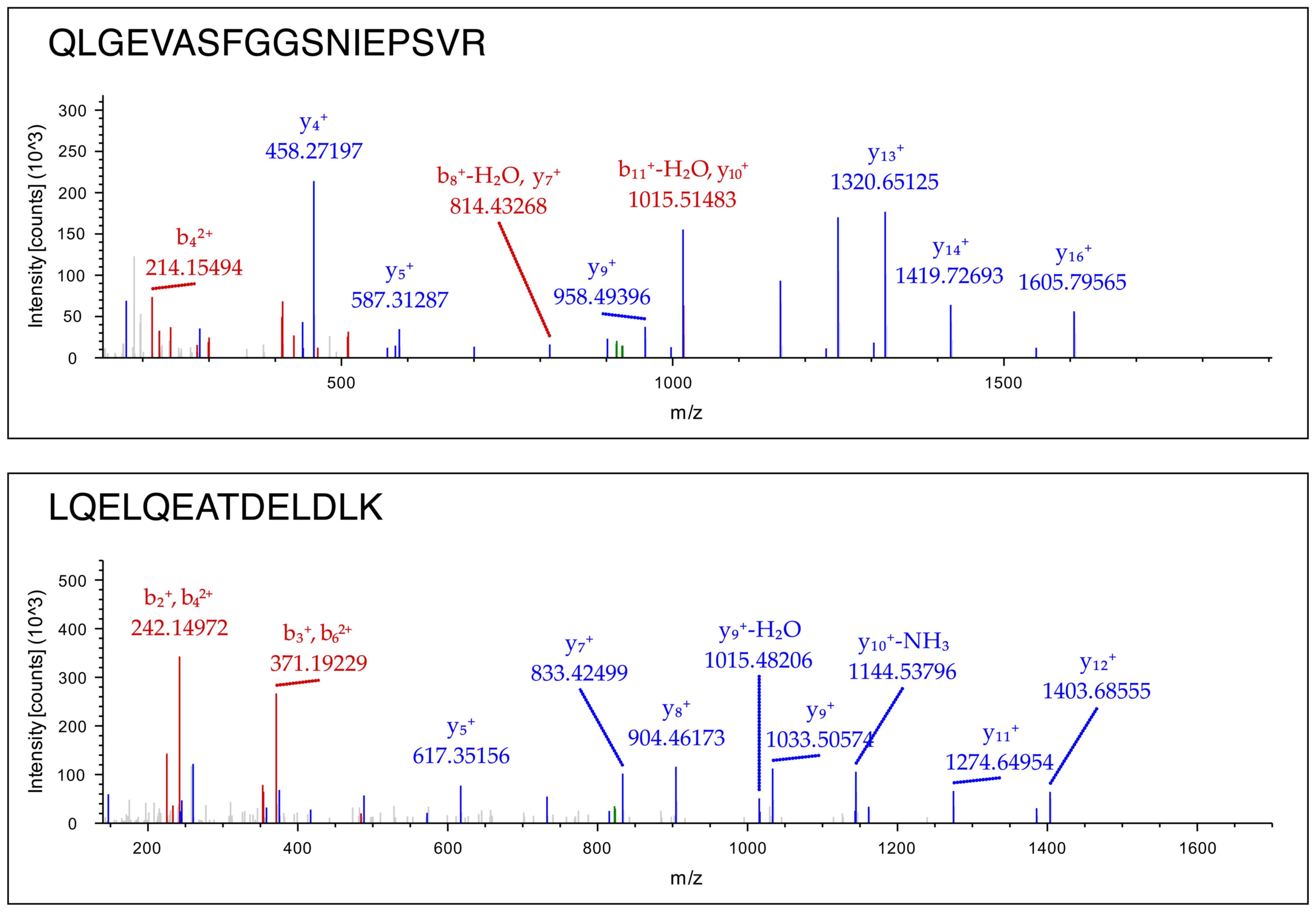
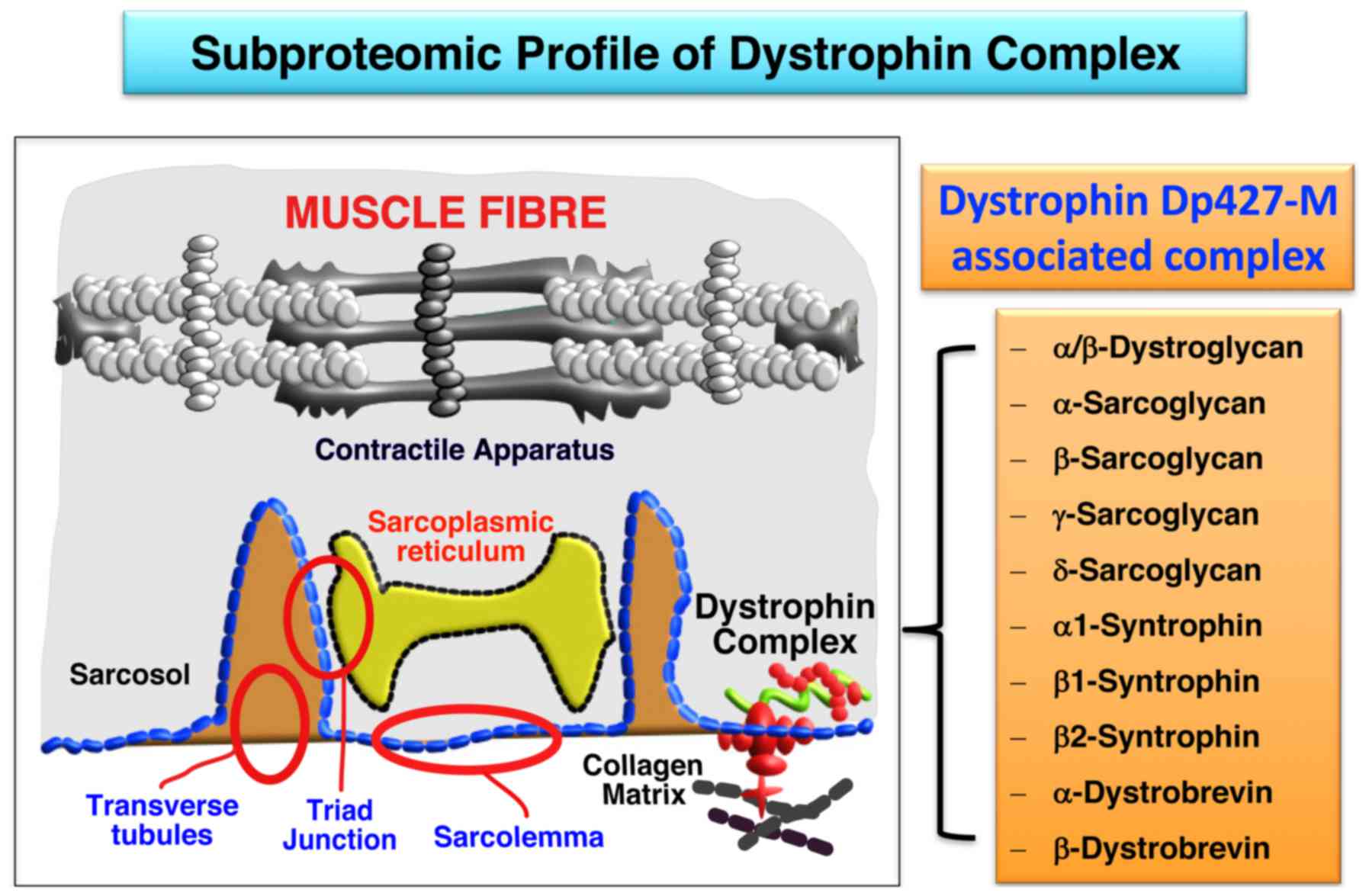
|
1
|
Cifani P and Kentsis A: Towards
comprehensive and quantitative proteomics for diagnosis and therapy
of human disease. Proteomics. 17:Jan;2017.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Angel TE, Aryal UK, Hengel SM, Baker ES,
Kelly RT, Robinson EW and Smith RD: Mass spectrometry-based
proteomics: Existing capabilities and future directions. Chem Soc
Rev. 41:3912–3928. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Riper SK, de Jong EP, Carlis JV and
Griffin TJ: Mass spectrometry-based proteomics: Basic principles
and emerging technologies and directions. Adv Exp Med Biol.
990:1–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Z, Wu S, Stenoien DL and Paša-Tolić
L: High-throughput proteomics. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto,
Calif). 7:427–454. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Allen DG, Whitehead NP and Froehner SC:
Absence of dystrophin disrupts skeletal muscle signaling: Roles of
Ca2+, reactive oxygen species, and nitric oxide in the
development of muscular dystrophy. Physiol Rev. 96:253–305. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Holland A, Murphy S, Dowling P and
Ohlendieck K: Pathoproteomic profiling of the skeletal muscle
matrisome in dystrophinopathy associated myofibrosis. Proteomics.
16:345–366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ohlendieck K and Swandulla D: Molecular
pathogenesis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy-related fibrosis.
Pathologe. 38:21–29. 2017.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murphy S and Ohlendieck K: The biochemical
and mass spectrometric profiling of the dystrophin complexome from
skeletal muscle. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 14:20–27. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fuller HR, Graham LC, Llavero Hurtado M
and Wishart TM: Understanding the molecular consequences of
inherited muscular dystrophies: Advancements through proteomic
experimentation. Expert Rev Proteomics. 13:659–671. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guiraud S, Aartsma-Rus A, Vieira NM,
Davies KE, van Ommen GJ and Kunkel LM: The pathogenesis and therapy
of muscular dystrophies. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 16:281–308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Doran P, Martin G, Dowling P, Jockusch H
and Ohlendieck K: Proteome analysis of the dystrophin-deficient MDX
diaphragm reveals a drastic increase in the heat shock protein
cvHSP. Proteomics. 6:4610–4621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rayavarapu S, Coley W, Cakir E, Jahnke V,
Takeda S, Aoki Y, Grodish-Dressman H, Jaiswal JK, Hoffman EP, Brown
KJ, et al: Identification of disease specific pathways using in
vivo SILAC proteomics in dystrophin deficient mdx mouse. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 12:1061–1073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Holland A, Henry M, Meleady P, Winkler CK,
Krautwald M, Brinkmeier H and Ohlendieck K: Comparative label-free
mass spectrometric analysis of mildly versus severely affected mdx
mouse skeletal muscles identifies Annexin, lamin, and Vimentin as
universal dystrophic markers. Molecules. 20:11317–11344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Holland A, Dowling P, Meleady P, Henry M,
Zweyer M, Mundegar RR, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Label-free
mass spectrometric analysis of the mdx-4cv diaphragm identifies the
matricellular protein periostin as a potential factor involved in
dystrophinopathy-related fibrosis. Proteomics. 15:2318–2331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Holland A, Carberry S and Ohlendieck K:
Proteomics of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex and
dystrophinopathy. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 14:680–697. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dowling P, Holland A and Ohlendieck K:
Mass spectrometry-based identification of muscle-associated and
muscle-derived proteomic biomarkers of dystrophinopathies. J
Neuromuscul Dis. 1:15–40. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murphy S, Dowling P and Ohlendieck K:
Comparative skeletal muscle proteomics using two-dimensional gel
electrophoresis. Proteomes. 4:272016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lewis C and Ohlendieck K: Mass
spectrometric identification of dystrophin isoform Dp427 by
on-membrane digestion of sarcolemma from skeletal muscle. Anal
Biochem. 404:197–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoon JH, Johnson E, Xu R, Martin LT,
Martin PT and Montanaro F: Comparative proteomic profiling of
dystroglycan-associated proteins in wild type, mdx, and Galgt2
transgenic mouse skeletal muscle. J Proteome Res. 11:4413–4424.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murphy S, Henry M, Meleady P, Zweyer M,
Mundegar RR, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Simultaneous
pathoproteomic evaluation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex
and secondary changes in the mdx-4cv mouse model of Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Biology (Basel). 4:397–423. 2015.
|
|
21
|
Murphy S, Zweyer M, Mundegar RR, Henry M,
Meleady P, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Concurrent label-free mass
spectrometric analysis of dystrophin isoform Dp427 and the
myofibrosis marker collagen in crude extracts from mdx-4cv skeletal
muscles. Proteomes. 3:298–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Turk R, Hsiao JJ, Smits MM, Ng BH,
Pospisil TC, Jones KS, Campbell KP and Wright ME: Molecular
signatures of membrane protein complexes underlying muscular
dystrophy. Mol Cell Proteomics. 15:2169–2185. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bonilla E, Samitt CE, Miranda AF, Hays AP,
Salviati G, DiMauro S, Kunkel LM, Hoffman EP and Rowland LP:
Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Deficiency of dystrophin at the muscle
cell surface. Cell. 54:447–452. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoffman EP, Knudson CM, Campbell KP and
Kunkel LM: Subcellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of
skeletal muscle. Nature. 330:754–758. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Knudson CM, Hoffman EP, Kahl SD, Kunkel LM
and Campbell KP: Evidence for the association of dystrophin with
the transverse tubular system in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem.
263:8480–8484. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salviati G, Betto R, Ceoldo S, Biasia E,
Bonilla E, Miranda AF and Dimauro S: Cell fractionation studies
indicate that dystrophin is a protein of surface membranes of
skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 258:837–841. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohlendieck K, Ervasti JM, Snook JB and
Campbell KP: Dystrophin-glycoprotein complex is highly enriched in
isolated skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Cell Biol. 112:135–148.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohlendieck K and Campbell KP: Dystrophin
constitutes 5% of membrane cytoskeleton in skeletal muscle. FEBS
Lett. 283:230–234. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ohlendieck K and Campbell KP:
Dystrophin-associated proteins are greatly reduced in skeletal
muscle from mdx mice. J Cell Biol. 115:1685–1694. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ohlendieck K, Matsumura K, Ionasescu VV,
Towbin JA, Bosch EP, Weinstein SL, Sernett SW and Campbell KP:
Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Deficiency of dystrophin-associated
proteins in the sarcolemma. Neurology. 43:795–800. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dowling P, Lohan J and Ohlendieck K:
Comparative analysis of Dp427-deficient mdx tissues shows that the
milder dystrophic phenotype of extraocular and toe muscle fibres is
associated with a persistent expression of beta-dystroglycan. Eur J
Cell Biol. 82:222–230. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cluchague N, Moreau C, Rocher C, Pottier
S, Leray G, Cherel Y and Le Rumeur E: beta-Dystroglycan can be
revealed in microsomes from mdx mouse muscle by detergent
treatment. FEBS Lett. 572:216–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Daval S, Rocher C, Cherel Y and Le Rumeur
E: Several dystrophin-glycoprotein complex members are present in
crude surface membranes but they are sodium dodecyl sulphate
invisible in KCl-washed microsomes from mdx mouse muscle. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 15:134–152. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ohlendieck K: On-membrane digestion
technology for muscle proteomics. J Membr Sep Technol. 2:1–12.
2013.
|
|
35
|
Ohlendieck K: Organelle proteomics in
skeletal muscle biology. J Integr OMICS. 2:27–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zubrzycka-Gaarn EE, Bulman DE, Karpati G,
Burghes AH, Belfall B, Klamut HJ, Talbot J, Hodges RS, Ray PN and
Worton RG: The Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene product is
localized in sarcolemma of human skeletal muscle. Nature.
333:466–469. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Watkins SC, Hoffman EP, Slayter HS and
Kunkel LM: Immunoelectron microscopic localization of dystrophin in
myofibres. Nature. 333:863–866. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cullen MJ, Walsh J, Nicholson LV and
Harris JB: Ultrastructural localization of dystrophin in human
muscle by using gold immunolabelling. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
240:197–210. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carpenter S, Karpati G, Zubrzycka-Gaarn E,
Bulman DE, Ray PN and Worton RG: Dystrophin is localized to the
plasma membrane of human skeletal muscle fibers by
electron-microscopic cytochemical study. Muscle Nerve. 13:376–380.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Staunton L, Jockusch H, Wiegand C,
Albrecht T and Ohlendieck K: Identification of secondary effects of
hyperexcit-ability by proteomic profiling of myotonic mouse muscle.
Mol Biosyst. 7:2480–2489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Murray BE and Ohlendieck K: Cross-linking
analysis of the ryanodine receptor and alpha1-dihydropyridine
receptor in rabbit skeletal muscle triads. Biochem J. 324:689–696.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rosemblatt M, Hidalgo C, Vergara C and
Ikemoto N: Immunological and biochemical properties of transverse
tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem.
56:8140–8148. 1981.
|
|
44
|
Sharp AH, Imagawa T, Leung AT and Campbell
KP: Identification and characterization of the
dihydropyridine-binding subunit of the skeletal muscle
dihydropyridine receptor. J Biol Chem. 262:12309–12315.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Muñoz P, Rosemblatt M, Testar X, Palacín M
and Zorzano A: Isola tion and characterization of distinct domains
of sarcolemma and T-tubules from rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J.
307:273–280. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Staunton L and Ohlendieck K: Mass
spectrometric characterization of the sarcoplasmic reticulum from
rabbit skeletal muscle by on-membrane digestion. Protein Pept Lett.
19:252–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ohlendieck K: Characterisation of the
dystrophin-related protein utrophin in highly purified skeletal
muscle sarcolemma vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1283:215–222.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vretblad P: Purification of lectins by
biospecific affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta.
434:169–176. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Luque-Garcia JL, Zhou G, Sun TT and
Neubert TA: Use of nitrocellulose membranes for protein
characterization by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 78:5102–5108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luque-Garcia JL, Zhou G, Spellman DS, Sun
TT and Neubert TA: Analysis of electroblotted proteins by mass
spectrometry: Protein identification after western blotting. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 7:308–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Luque-Garcia JL and Neubert TA:
On-membrane tryptic digestion of proteins for mass spectrometry
analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 536:331–341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havlis J, Olsen JV
and Mann M: In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric
characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc.
1:2856–2860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Murphy S, Dowling P, Zweyer M, Mundegar
RR, Henry M, Meleady P, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic
analysis of dystrophin deficiency and associated changes in the
aged mdx-4cv heart model of dystrophinopathy-related
cardiomyopathy. J Proteomics. 145:24–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu Y, Bouhenni RA, Dufresne CP, Semba RD
and Edward DP: Differential expression of vitreous proteins in
young and mature New Zealand white rabbits. PLoS One.
11:e01535602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ryan M, Butler-Browne G, Erzen I, Mouly V,
Thornell LE, Wernig A and Ohlendieck K: Persistent expression of
the alpha1S-dihydropyridine receptor in aged human skeletal muscle:
Implications for the excitation-contraction uncoupling hypothesis
of sarcopenia. Int J Mol Med. 11:425–434. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Glover L, Heffron JJ and Ohlendieck K:
Increased sensitivity of the ryanodine receptor to
halothane-induced oligomerization in malignant
hyperthermia-susceptible human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol
1985. 96:11–18. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Staunton L, Zweyer M, Swandulla D and
Ohlendieck K: Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of
middle-aged vs. aged vastus lateralis reveals increased levels of
carbonic anhydrase isoform 3 in senescent human skeletal muscle.
Int J Mol Med. 30:723–733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chartier A, Klein P, Pierson S, Barbezier
N, Gidaro T, Casas F, Carberry S, Dowling P, Maynadier L, Bellec M,
et al: Mitochondrial dysfunction reveals the role of mRNA poly(A)
tail regulation in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy pathogenesis.
PLoS Genet. 11:e10050922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Drissi R, Dubois ML and Boisvert FM:
Proteomics methods for subcellular proteome analysis. FEBS J.
280:5626–5634. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Breckels LM, Gatto L, Christoforou A,
Groen AJ, Lilley KS and Trotter MW: The effect of organelle
discovery upon sub-cellular protein localisation. J Proteomics.
88:129–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mueller SJ, Hoernstein SN and Reski R:
Approaches to characterize organelle, compartment, or structure
purity. Methods Mol Biol. 1511:13–28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Larance M and Lamond AI: Multidimensional
proteomics for cell biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:269–280.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lefort N, Yi Z, Bowen B, Glancy B, De
Filippis EA, Mapes R, Hwang H, Flynn CR, Willis WT, Civitarese A,
et al: Proteome profile of functional mitochondria from human
skeletal muscle using one-dimensional gel electrophoresis and
HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. J Proteomics. 72:1046–1060. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lombardi A, Silvestri E, Cioffi F, Senese
R, Lanni A, Goglia F, de Lange P and Moreno M: Defining the
transcriptomic and proteomic profiles of rat ageing skeletal muscle
by the use of a cDNA array, 2D- and Blue native-PAGE approach. J
Proteomics. 72:708–721. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ferreira R, Vitorino R, Alves RM, Appell
HJ, Powers SK, Duarte JA and Amado F: Subsarcolemmal and
intermyofibrillar mitochondria proteome differences disclose
functional specializations in skeletal muscle. Proteomics.
10:3142–3154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu Z, Du X, Deng J, Gu M, Hu H, Gui M,
Yin CC and Chang Z: The interactions between mitochondria and
sarcoplasmic reticulum and the proteome characterization of
mitochondrion-associated membrane from rabbit skeletal muscle.
Proteomics. 15:2701–2704. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu Z, Du X, Yin C and Chang Z: Shotgun
proteomic analysis of sarcoplasmic reticulum preparations from
rabbit skeletal muscle. Proteomics. 13:2335–2338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Vitorino R, Ferreira R, Neuparth M, Guedes
S, Williams J, Tomer KB, Domingues PM, Appell HJ, Duarte JA and
Amado M: Subcellular proteomics of mice gastrocnemius and soleus
muscles. Anal Biochem. 366:156–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Toigo M, Donohoe S, Sperrazzo G, Jarrold
B, Wang F, Hinkle R, Dolan E, Isfort RJ and Aebersold R: ICAT-MS-MS
time course analysis of atrophying mouse skeletal muscle cytosolic
subproteome. Mol Biosyst. 1:229–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Maughan DW, Henkin JA and Vigoreaux JO:
Concentrations of glycolytic enzymes and other cytosolic proteins
in the diffusible fraction of a vertebrate muscle proteome. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 4:1541–1549. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ohlendieck K: Proteomics of skeletal
muscle glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:2089–2101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gannon J, Doran P, Kirwan A and Ohlendieck
K: Drastic increase of myosin light chain MLC-2 in senescent
skeletal muscle indicates fast-to-slow fibre transition in
sarcopenia of old age. Eur J Cell Biol. 88:685–700. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Holland A and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic
profiling of the contractile apparatus from skeletal muscle. Expert
Rev Proteomics. 10:239–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ohlendieck K: Towards an understanding of
the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: Linkage between the
extracellular matrix and the membrane cytoskeleton in muscle
fibers. Eur J Cell Biol. 69:1–10. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Murray BE, Froemming GR, Maguire PB and
Ohlendieck K: Excitation-contraction-relaxation cycle: Role of
Ca2+-regulatory membrane proteins in normal, stimulated
and pathological skeletal muscle (Review). Int J Mol Med.
1:677–687. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|