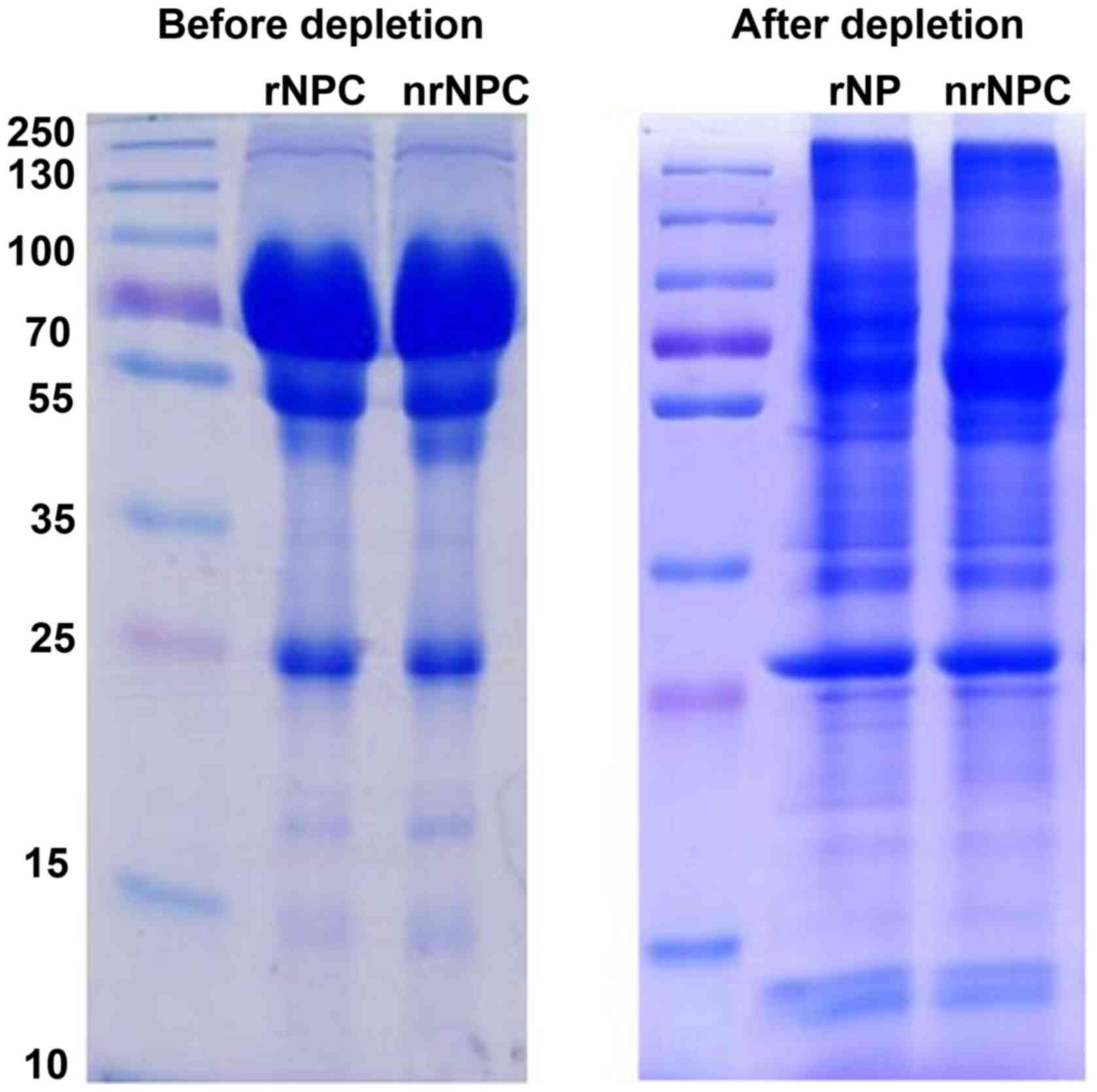
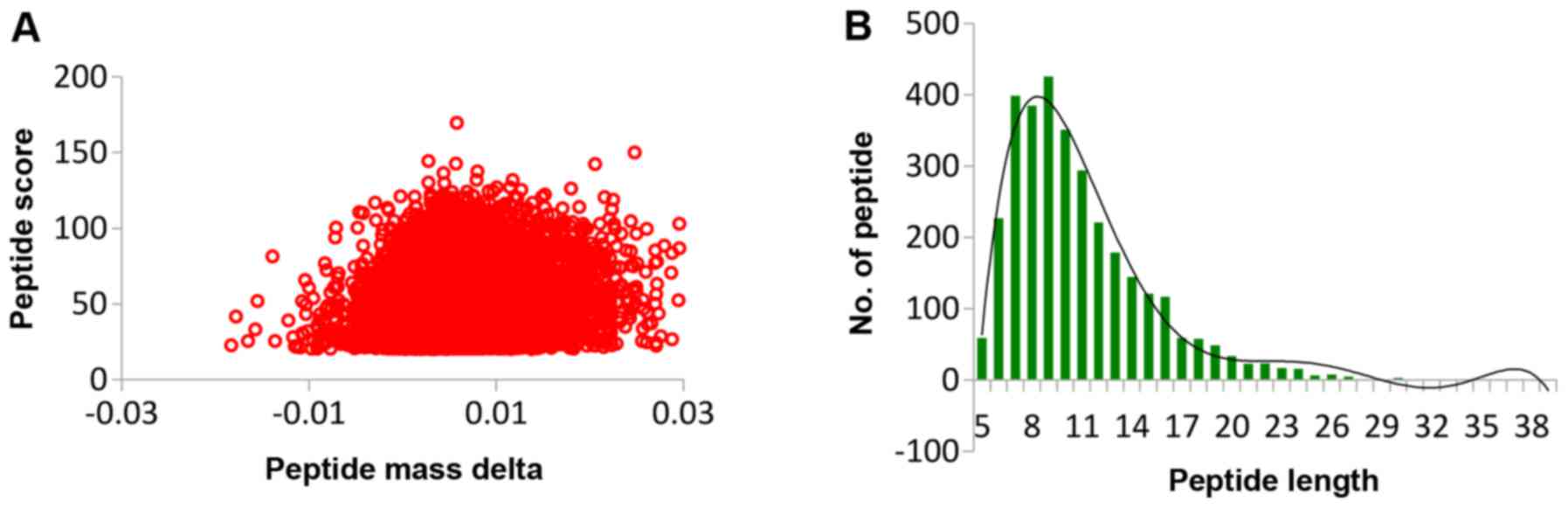
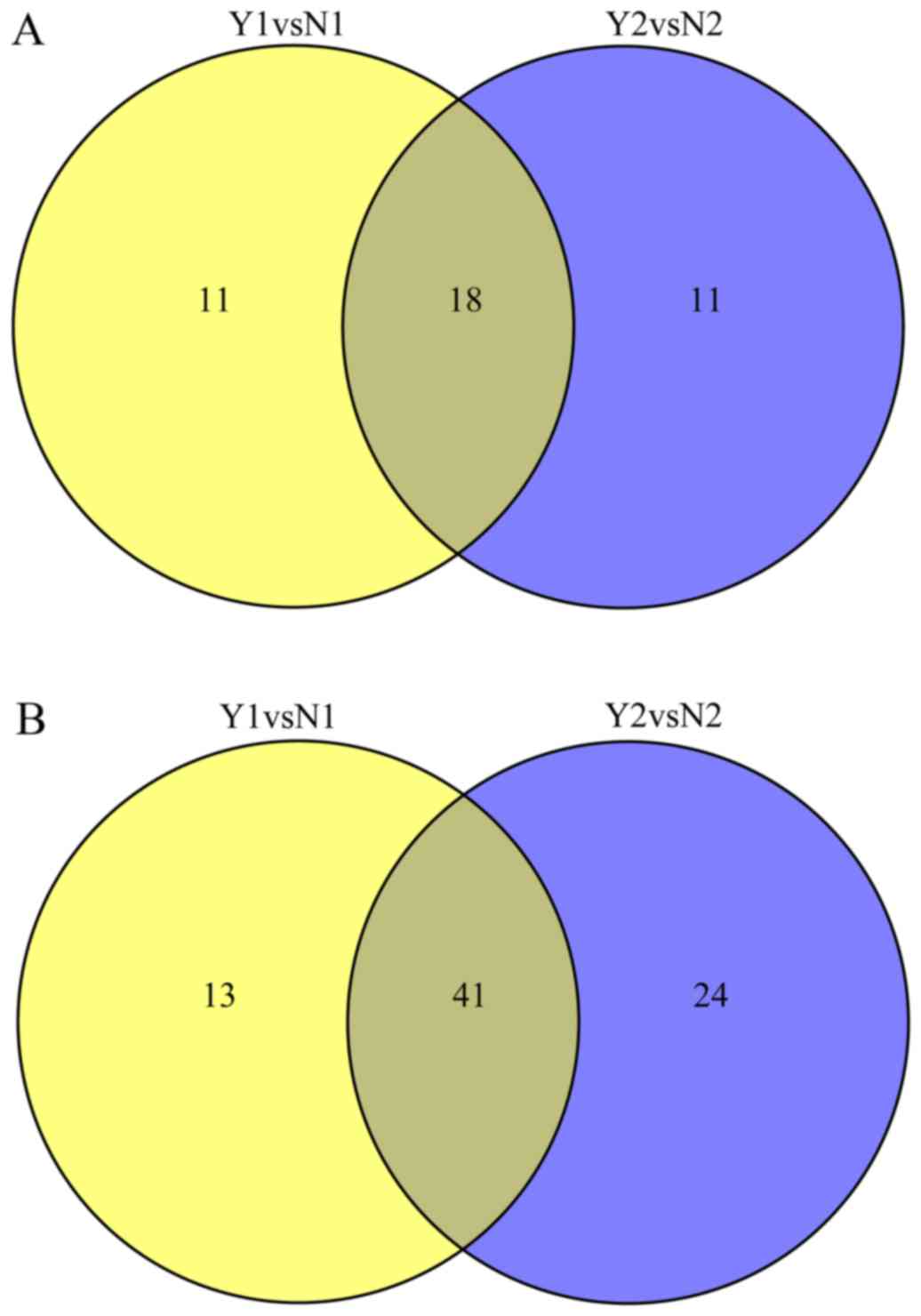
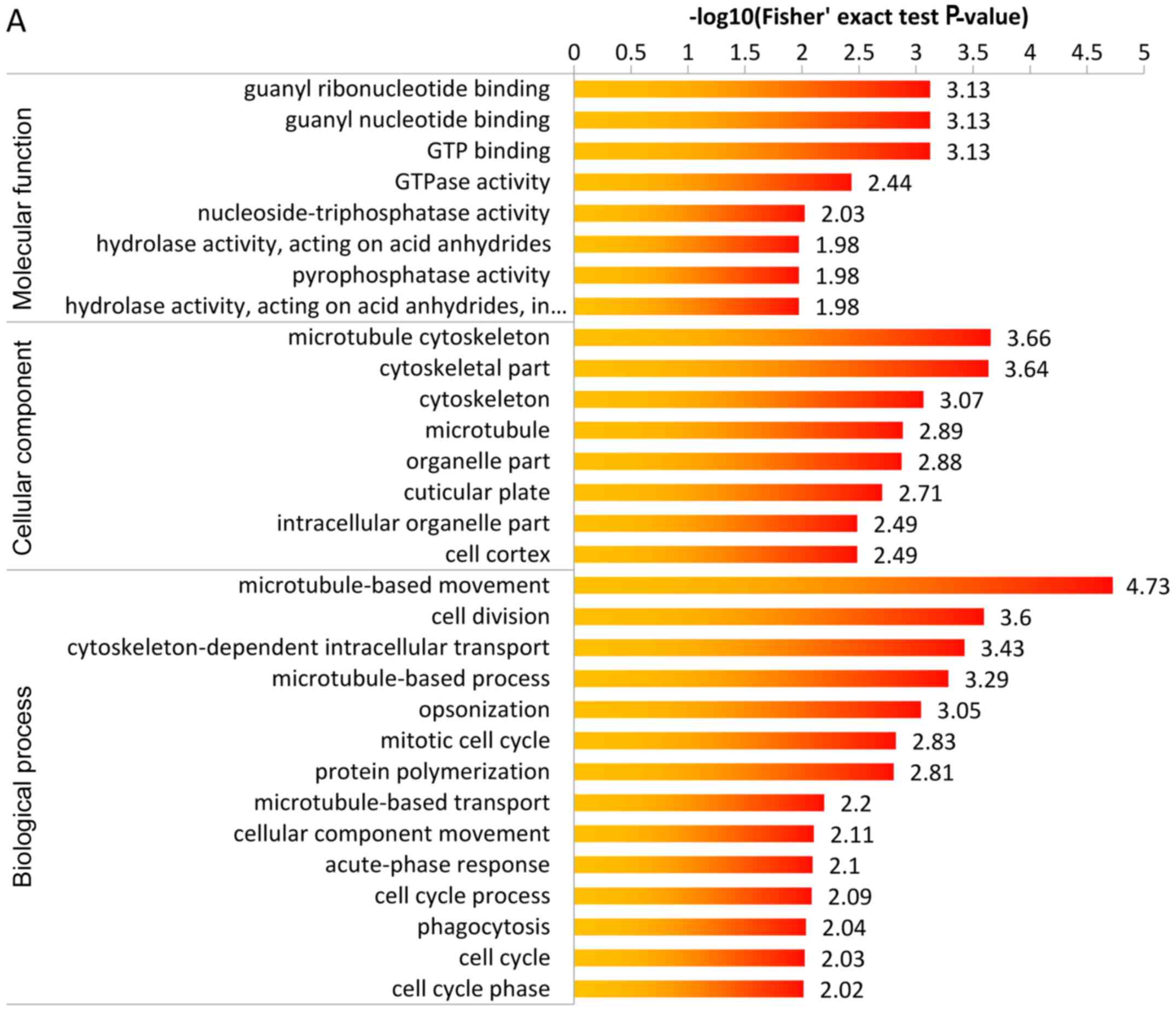
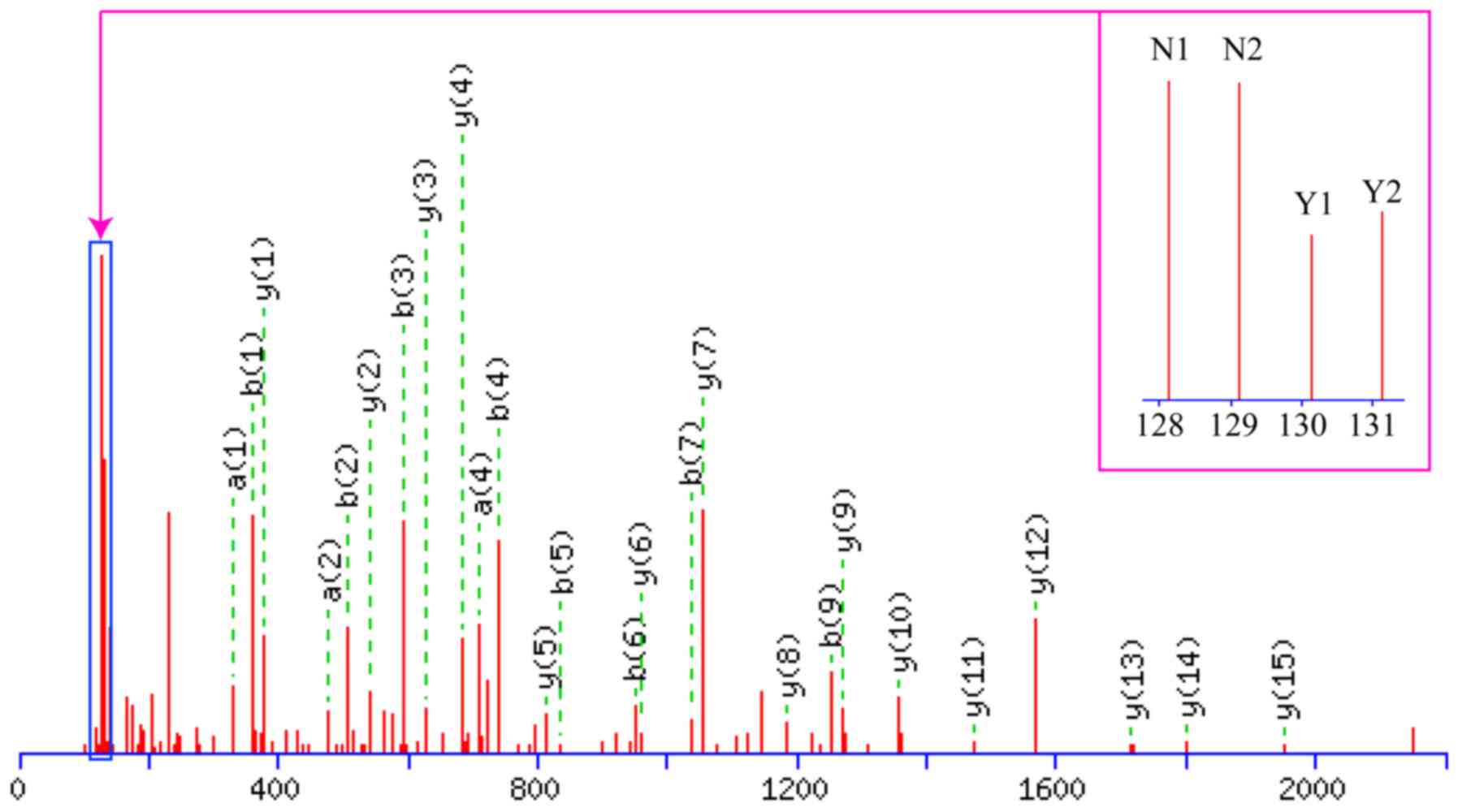
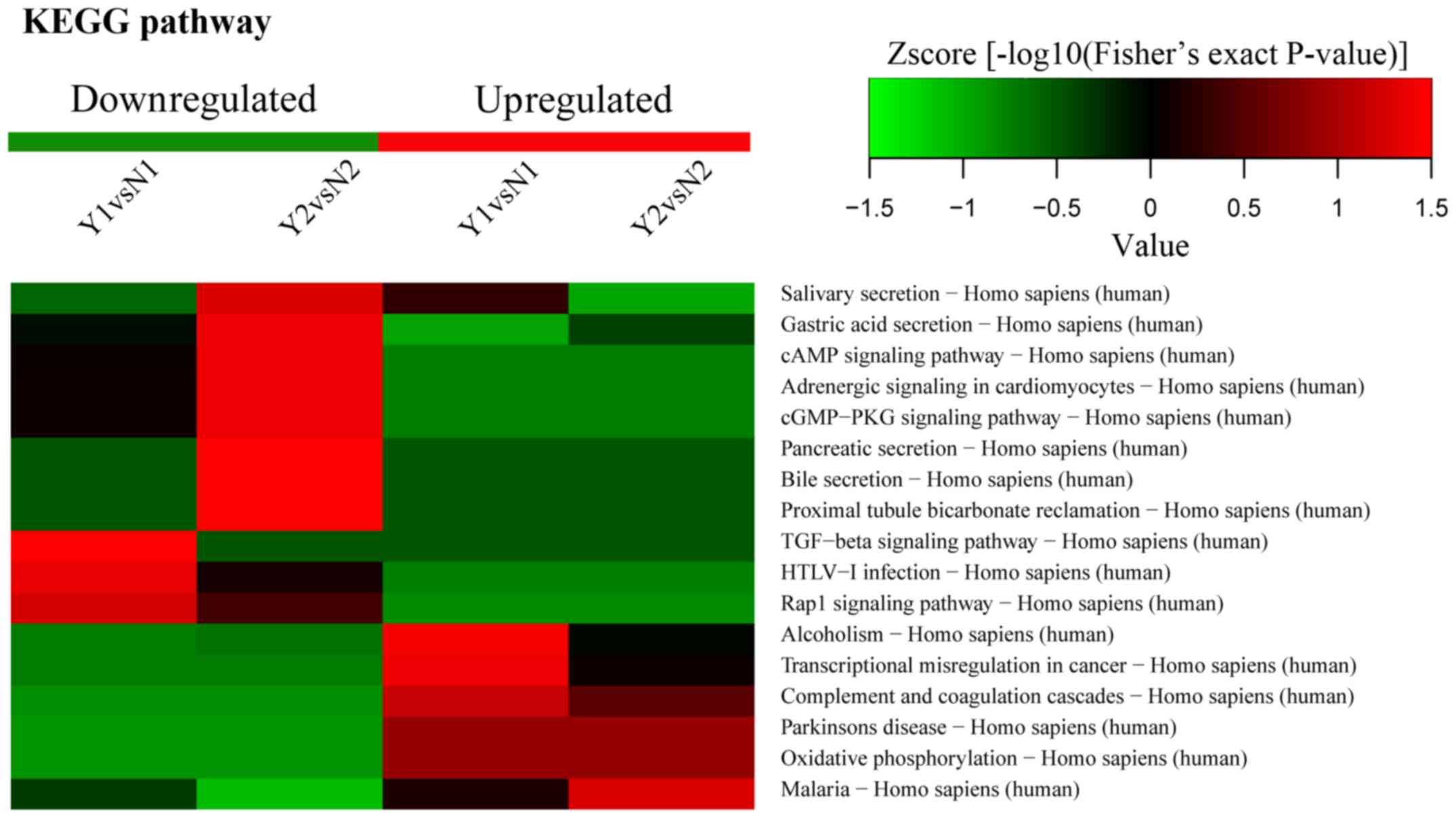
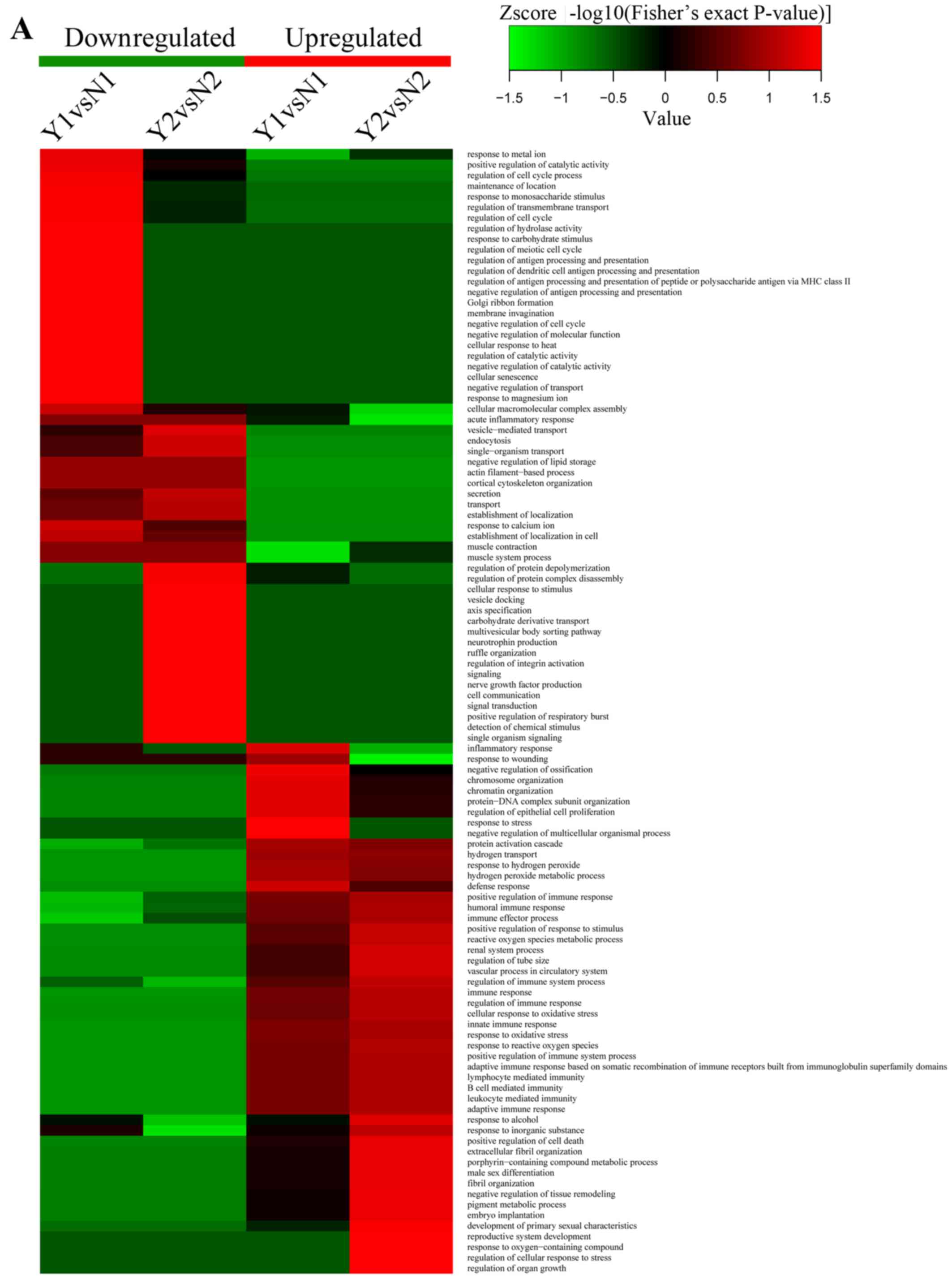
|
1
|
Chen ZT, Liang ZG and Zhu XD: A review:
Proteomics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
16:15497–15530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei YS, Zheng YH, Liang WB, Zhang JZ, Yang
ZH, Lv ML, Jia J and Zhang L: Identification of serum biomarkers
for nasopharyngeal carcinoma by proteomic analysis. Cancer.
112:544–551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Du C, Ying H, Zhou J, Hu C and Zhang Y:
Experience with combination of docetaxel, cisplatin plus
5-fluorouracil chemotherapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy
for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin
Oncol. 18:464–471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tao YL, Li Y, Gao J, Liu ZG, Tu ZW, Li G,
Xu BQ, Niu DL, Jiang CB and Yi W: Identifying FGA peptides as
nasopharyngeal carcinoma-associated biomarkers by magnetic beads. J
Cell Biochem. 113:2268–2278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhong Yu LJ: Diagnostic progress of
recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clinical Imaging Technology.
24:1633–1674. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Sahu A, Nandakumar N, Sawant S and Krishna
CM: Recurrence prediction in oral cancers: A serum Raman
spectroscopy study. Analyst. 140:2294–2301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholson BD, Shinkins B, Pathiraja I,
Roberts NW, James TJ, Mallett S, Perera R, Primrose JN and Mant D:
Blood CEA levels for detecting recurrent colorectal cancer.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12:CD0111342015.
|
|
8
|
Li GP, Wang H, Lai YK, Chen SC, Lin MC, Lu
G, Zhang JF, He XG, Qian CN and Kung HF: Proteomic profiling
between CNE-2 and its strongly metastatic subclone S-18 and
functional characterization of HSP27 in metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proteomics. 11:2911–2920. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao Z, Li G, Chen Y, Li M, Peng F, Li C,
Li F, Yu Y, Ouyang Y, Xiao Z and Chen Z: Quantitative proteomic
analysis of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded nasopharyngeal
carcinoma using iTRAQ labeling, two-dimensional liquid
chromatography, and tandem mass spectrometry. J Histochem Cytochem.
58:517–527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seriramalu R, Pang WW, Jayapalan JJ,
Mohamed E, Abdul-Rahman PS, Bustam AZ, Khoo AS and Hashim OH:
Application of champedak mannose-binding lectin in the
glycoproteomic profiling of serum samples unmasks reduced
expression of alpha-2 macroglobulin and complement factor B in
patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Electrophoresis.
31:2388–2395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang CE, Tan T, Li C, Chen ZC, Ruan L,
Wang HH, Su T, Zhang PF and Xiao ZQ: Identification of Galectin-1
as a novel biomarker in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by proteomic
analysis. Oncol Rep. 24:495–500. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho WC, Yip TT, Yip C, Yip V, Thulasiraman
V, Ngan RK, Yip TT, Lau WH, Au JS and Law SC: Identification of
serum amyloid A protein as a potentially useful biomarker to
monitor relapse of nasopharyngeal cancer by serum proteomic
profiling. Clin Cancer Res. 10:43–52. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang X, Dai W, Kwong DL, Szeto CY, Wong
EH, Ng WT, Lee AW, Ngan RK, Yau CC and Tung SY: Epigenetic markers
for non-invasive early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
methylation-sensitive high resolution melting. Int J Cancer.
136:127–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
White NM, Masui O, Desouza LV, Krakovska
O, Metias S, Romaschin AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace K, Lee J, et
al: Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential diagnostic
markers and pathways involved in pathogenesis of renal cell
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:506–518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tian X, Sun D, Zhao S, Xiong H and Fang J:
Screening of potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets
against colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 8:1691–1699.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan LR, Wang DX, Liu H, Zhang XX, Zhao H,
Hua L, Xu P and Li YS: A pro-atherogenic HDL profile in coronary
heart disease patients: an iTRAQ labelling-based proteomic
approach. PloS One. 9:e983682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sandberg A, Branca RM, Lehtiö J and
Forshed J: Quantitative accuracy in mass spectrometry based
proteomics of complex samples: The impact of labeling and precursor
interference. J Proteomics. 96:133–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Janvilisri T: Omics-based identification
of biomarkers for naso-pharyngeal carcinoma. Dis Markers.
2015:7621282015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Luftig M: Heavy LIFting: Tumor promotion
and radioresistance in NPC. J Clin Invest. 123:4999–5001. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uenishi K, Criss WE and Kakiuchi S:
Calcium-activatable phosphodiesterase and calcium-dependent
modulator protein in transplantable hepatoma tissues. J Biochem.
87:601–607. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei JW, Morris HP and Hickie RA: Positive
correlation between calmodulin content and hepatoma growth rates.
Cancer Res. 42:2571–2574. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Colomer J, Agell N, Engel P and Bachs O:
Expression of calmodulin and calmodulin binding proteins in
lymphoblastoid cells. J Cell Physiol. 159:542–550. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Colomer J, Agell N, Engel P, Alberola-Ila
J and Bachs O: Calmodulin expression during proliferative
activation of human T lymphocytes. Cell calclum. 14:609–618. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Berchtold MW and Villalobo A: The many
faces of calmodulin in cell proliferation, programmed cell death,
autophagy, and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:398–435. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu GX, Sheng HF and Wu S: A study on the
levels of calmodulin and DNA in human lung cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 73:889–901. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schuller HM, Correa E, Orloff M and Reznik
GK: Successful chemotherapy of experimental neuroendocrine lung
tumors in hamsters with an antagonist of
Ca2+/calmodulin. Cancer Res. 50:1645–1649.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lönn U and Lönn S: Increased growth
inhibition and DNA lesions in human colon adenocarcinoma cells
treated with methotrexate or 5-fluorodeoxyuridine followed by
calmodulin inhibitor. Cancer Res. 48:3319–3323. 1988.
|
|
28
|
Hait WN, Gesmonde J and Cheng E: Effects
of KS-501, KS-502 and their enantiomers on calmodulin-sensitive
enzyme activity and cellular proliferation. Biochem Pharmacol.
50:69–74. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan K, Yong S, Xu F, Zhou T, McDonald JM
and Chen Y: Calmodulin antagonists promote TRA-8 therapy of
resistant pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 6:25308–25319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mukhopadhyay D and Akbarali HI: Depletion
of [Ca2+]i inhibits hypoxia-induced vascular
permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 229:733–738. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Salnikow K, Kluz T, Costa M, Piquemal D,
Demidenko ZN, Xie K and Blagosklonny MV: The regulation of hypoxic
genes by calcium involves c-Jun/AP-1, which cooperates with
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in response to hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
22:1734–1741. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jung HJ, Kim JH, Shim JS and Kwon HJ: A
novel Ca2+/calmodulin antagonist HBC inhibits
angiogenesis and downregulates hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol
Chem. 285:25867–25874. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|